Arts & Entertainment
Henry Gerber: Ahead of his time
Celebrating LGBT History Month
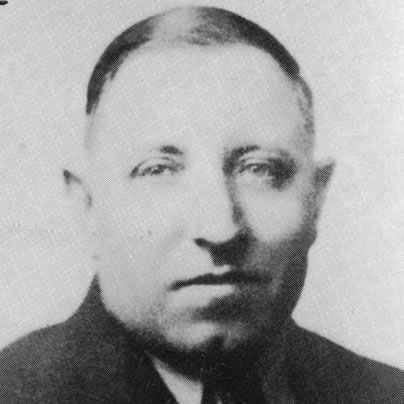
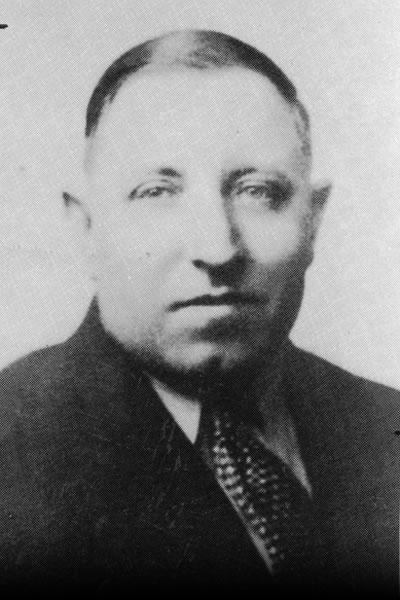


Henry Gerber started a gay rights group in Chicago in 1924.
By ST. SUKIE DE LA CROIX
WINDY CITY TIMES
On May 15, 1871, the German Criminal Code was revised to include Paragraph 175, a law making sexual acts between males illegal. The first challenge to the law came in 1897 when Dr. Magnus Hirschfeld founded the gay organization Wissenschaftlich-humanitäres Komitee (Scientific-Humanitarian Committee). Its first action was to draft a petition against Paragraph 175 with 6,000 signatures of prominent people in the arts, politics and the medical profession; it failed to have any effect.
One American inspired by the work of Hirschfeld was Henry Gerber, who in 1924 was granted an official charter by the state of Illinois for the Society for Human Rights, the first gay-rights organization in the United States, which he ran from his home on Crilly Court in Chicago.
Gerber was born Josef Henry Dittmar on June 29, 1892, in Passau, Bavaria, Germany. On Oct. 27, 1913, Gerber (still called Dittmar at the time) arrived at New York’s Ellis Island on the SS George Washington and then traveled west to Chicago, where he worked briefly for Montgomery Ward’s mail-order house. His first known address in the United States was 507 Stone St., Joliet, Ill., from where he enlisted in the Army on Jan. 26, 1914. In his military documents, he described himself as 5-foot-7 and one-half, 180 pounds, with blue eyes and brown hair. He changed his name to Gerber afterward — though he was still using the name Joseph Henry Dittmar on his June 5, 1917, draft registration card, which described him as 5-foot-8, slender, with blue eyes and blond hair. On it, he mentioned prior military service but now claimed exemption on grounds of conscientious objection to war.
On April 6, 1917, the United States declared war on Germany, and the newspapers became filled with lurid tales of German spies. As a result, the United States opened internment camps; 50,000 unnaturalized aliens of German birth were now “alien enemies,” and 8,000 were detained using presidential arrest warrants. Gerber was “offered internment,” which he accepted, as it guaranteed three meals a day. After the war, he re-enlisted in the Army on Oct. 2, 1919, at Jefferson Barracks, near Lemay, Mo., a training and recruitment center for soldiers being sent to fight in Europe, or, in Gerber’s case, to join a regiment of the American Forces in Germany, where he was part of a company engaged in publishing the daily AMAROC News for troops.
It was while serving in Koblenz that Gerber found Hirschfeld’s Scientific-Humanitarian Committee. He wrote later: “In Coblenz on the Rhine, I had subscribed to German homophile magazines and made several trips to Berlin, which was then not occupied by American forces. I had always bitterly felt the injustice with which my own American society accused the homosexual of ‘immoral acts.’
“What could be done about it, I thought. Unlike Germany, where the homosexual was partially organized and where sex legislation was uniform for the whole country, the United States was in a condition of chaos and misunderstanding concerning its sex laws, and no one was trying to unravel the tangle and bring relief to the abused.”
Gerber returned to Chicago, took up residence at 1710 N. Crilly Ct. and began work for the Post Office Department. In the spring of 1924, he formed SHR with a handful of friends. Gerber’s strategy was to network and gain support from other “sex reform” leaders, including Margaret Sanger, the American birth-control advocate, but nobody seemed interested. Undeterred, he decided to go it alone. Through a lawyer, SHR applied for and received a charter from the state of Illinois on Dec. 10, 1924. It is thought the group never had more than 10 members. Gerber elected himself secretary; president was the Rev. John T. Graves, “a preacher who preached brotherly love to small groups of Negroes”; vice president was Al Meininger, an “indigent laundry queen”; and treasurer was Ralph Ellsworth Booher, whose job with a railroad was threatened when his homosexuality became known. Throughout the rest of his life, Gerber lamented that SHR failed to attract “men of good reputation.” In Germany, the homophile movement included enlightened politicians, doctors and scientists, as well as those in the arts, but in the United States nobody was willing to stick a neck out for homosexuals.
Gerber produced two issues of the SHR newsletter Friendship and Freedom, of which no known copies exist, although in “Paris Gay 1925” (1981), a French book co-written by Gilles Barbedette and Michel Carassou, is reprinted a review of Friendship and Freedom, written by Clarens and published in the magazine L’amitié in 1925. (See this author’s “Chicago Whispers: A History of LGBT Chicago Before Stonewall” for translation.)
The SHR was short-lived. In July 1925, the group was raided and the headline in the Chicago Examiner read “Strange Sex Cult Exposed.” Even though the case was thrown out of court, Gerber was suspended from the post office.
After the demise of SHR, Gerber became despondent about homosexuals. He later wrote, “I have absolutely no confidence in the Dorian crowd, mostly a bunch of selfish, uncultured, ignorant egoists who have nothing for the ideal side of life.” Gerber re-enlisted in the Army, serving another 17 years; in 1945, he retired with an honorable discharge and a $100-a-month pension. As late as 1942, his primary World War II draft registration was still under the name Joseph H. Dittmar, though the records also contain a cross-reference from the name Henry Gerber; by then, “Gerber” appears to have been how he was known to the military.
Gerber spent his twilight years in the U.S. Soldiers’ and Airmen’s Home in Washington, D.C., where he died from pneumonia on Dec. 31, 1972, age 80.
Gerber was posthumously inducted into the Chicago Gay and Lesbian Hall of Fame in 1992 and the Henry Gerber House, located at 1710 N. Crilly Ct., was designated a Chicago Landmark on June 1, 2001.
The above article is an abbreviated version of the chapter “Henry Gerber and the German Sex Reformers” in St. Sukie de la Croix’s book “Chicago Whispers: A History of LGBT Chicago Before Stonewall,” published in 2012 by the University of Wisconsin Press.
a&e features
Eastern Shore chef named James Beard Finalist
Harley Peet creates inventive food in an inclusive space
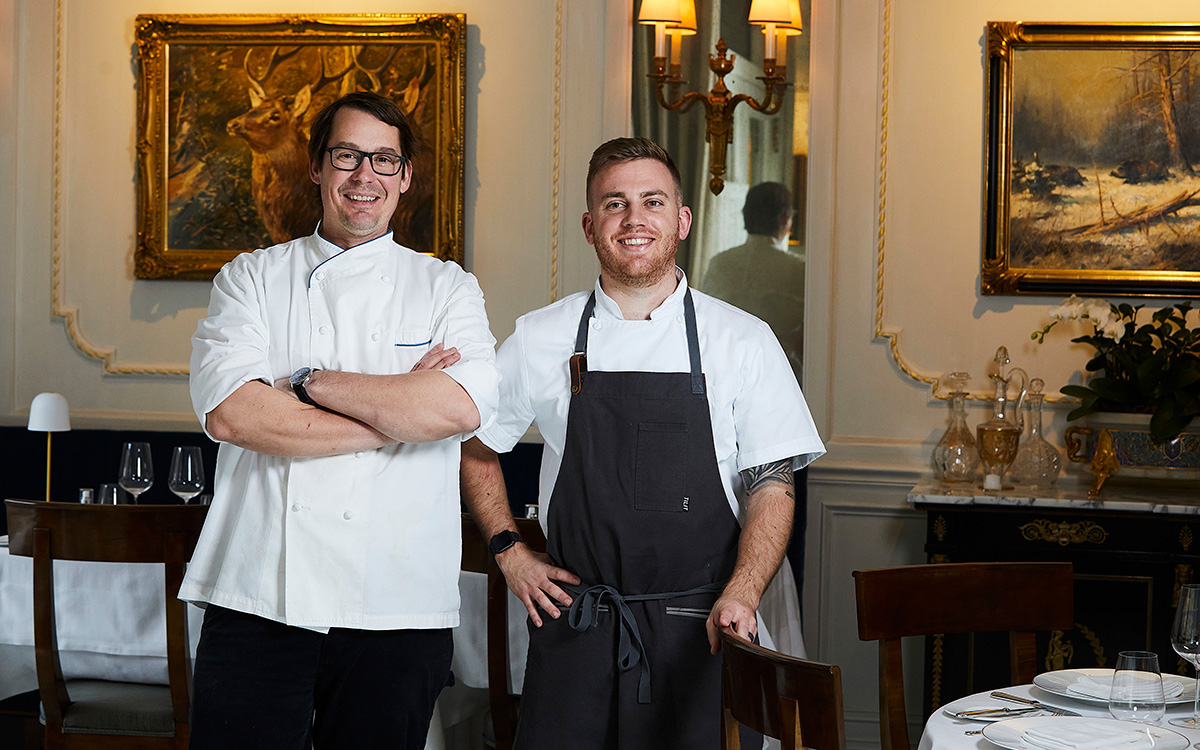

In a small Eastern Shore town filled with boutiques, galleries, and the occasional cry of waterfowl from the Chesapeake, Chef Harley Peet is most at home. In his Viennese-inflected, Maryland-sourced fine-dining destination Bas Rouge, Peet draws from his Northern Michigan upbringing, Culinary Institute of America education, and identity as a gay man, for inspiration.
And recently, Peet was named a James Beard Finalist for Best Chef: Mid-Atlantic – the first “Best Chef: Mid-Atlantic” finalist representing the Eastern Shore.
Peet, after graduation from the Culinary Institute of America, took a position as sous chef at Tilghman Island Inn, not far from Bas Rouge. Falling in love with the Eastern Shore, he continued his passion for racing sailboats, boating, gardening, and fishing, and living his somewhat pastoral life as he opened Bas Rouge in 2016 as head chef, a restaurant part of the Bluepoint Hospitality group, which runs more than a dozen concepts in and around Easton, Md.
Coming from a rural area and being gay, Peet knew he had his work cut out for him. He was always aware that the service and hospitality industry “can be down and dirty and rough.”
Now as a leader in the kitchen, he aims to “set a good example, and treat people how I want to be treated. I also want to make sure if you’re at our establishment, I’m the first to stand up and say something.”
The Bas Rouge cuisine, he says, is Contemporary European. “I’m inspired by old-world techniques of countries like Austria, Germany, and France, but I love putting a new spin on classic dishes and finding innovative ways to incorporate the bounty of local Chesapeake ingredients.”
His proudest dish: the humble-yet-elevated Wiener Schnitzel. “It is authentic to what one would expect to find in Vienna, down to the Lingonberries.” From his in-house bakery, Peet dries and grinds the housemade Kaiser-Semmel bread to use as the breadcrumbs.
Peet works to support the LGBTQ community inside and outside of the kitchen. “I love that our Bluepoint Hospitality team has created welcoming spaces where our patrons feel comfortable dining at each of our establishments. Our staff have a genuine respect for one another and work together free of judgment.”
Representing Bluepoint, Peet has participated in events like Chefs for Equality with the Human Rights Campaign, advocating for LGBTQ rights.
At Bas Rouge, Peet brings together his passion for inclusion steeped in a sustainability ethic. He sees environmental stewardship as a way of life. Peet and his husband have lived and worked on their own organic farm for several years. Through research in Europe, he learned about international marine sourcing. Witnessing the impacts of overfishing, Peet considers his own role in promoting eco-friendly practices at Bas Rouge. To that end, he ensures responsible sourcing commitments through his purveyors, relationships that have helped create significant change in how people dine in Easton.
“I have built great relationships in the community and there’s nothing better than one of our long-standing purveyors stopping in with a cooler of fresh fish from the Chesapeake Bay. This goes especially for catching and plating the invasive blue catfish species, which helps control the species’ threat to the local ecosystem.
Through his kitchen exploits, Peet expressed a unique connection to another gay icon in a rural fine-dining restaurant: Patrick O’Connell, of three Michelin starred Inn at Little Washington. In fact, Peet’s husband helped design some of O’Connell’s kitchen spaces. They’ve both been able to navigate treacherous restaurant-industry waters, and have come out triumphant and celebrated. Of O’Connell, Peet says that he “sees [his restaurants] as canvas, all artistry, he sees this as every night is a show.” But at the same time, his “judgment-free space makes him a role model.”
Being in Easton itself is not without challenges. Sourcing is a challenge, having to either fly or ship in ingredients, whereas urban restaurants have the benefit of trucking, he says. The small town “is romantic and charming,” but logistics are difficult – one of the reasons that Peet ensures his team is diverse, building in different viewpoints, and also “making things a hell of a lot more fun.”
Reflecting on challenges and finding (and creating) space on the Eastern Shore, Peet confirmed how important it was to surround himself with people who set a good example, and “if you don’t like the way something is going, fuck them and move on.”

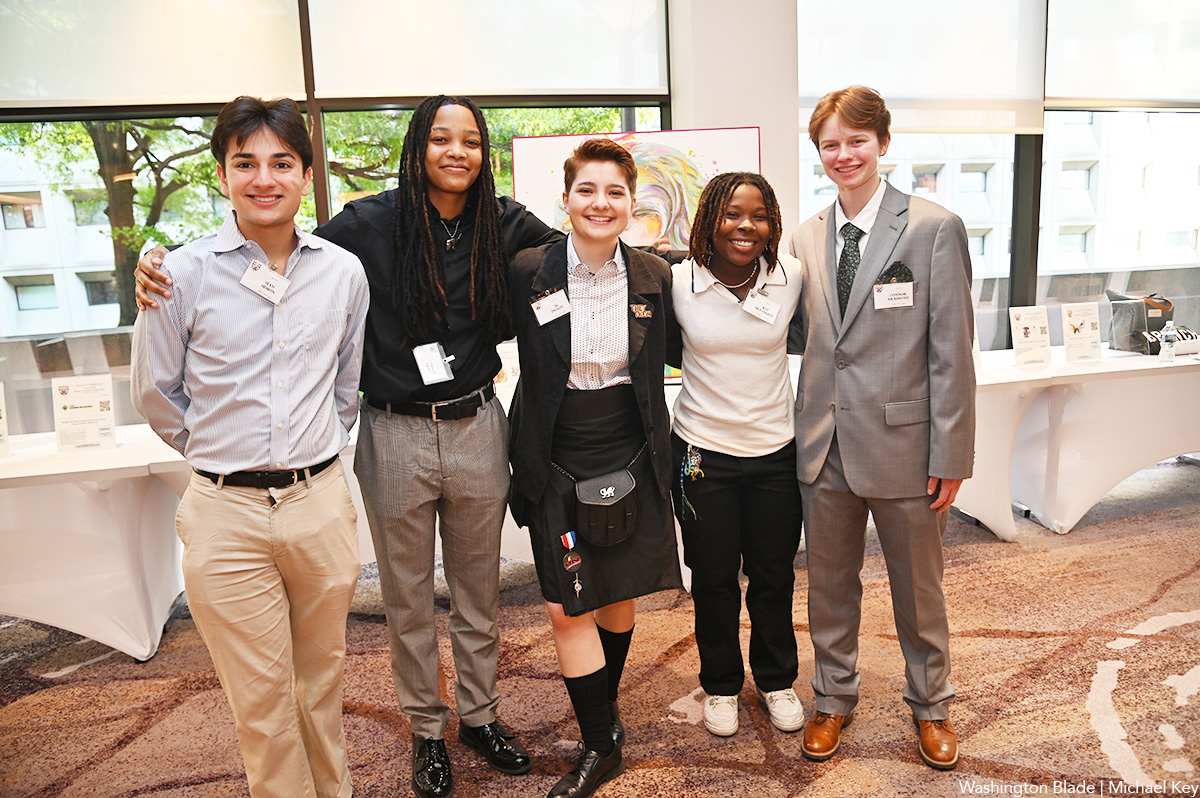
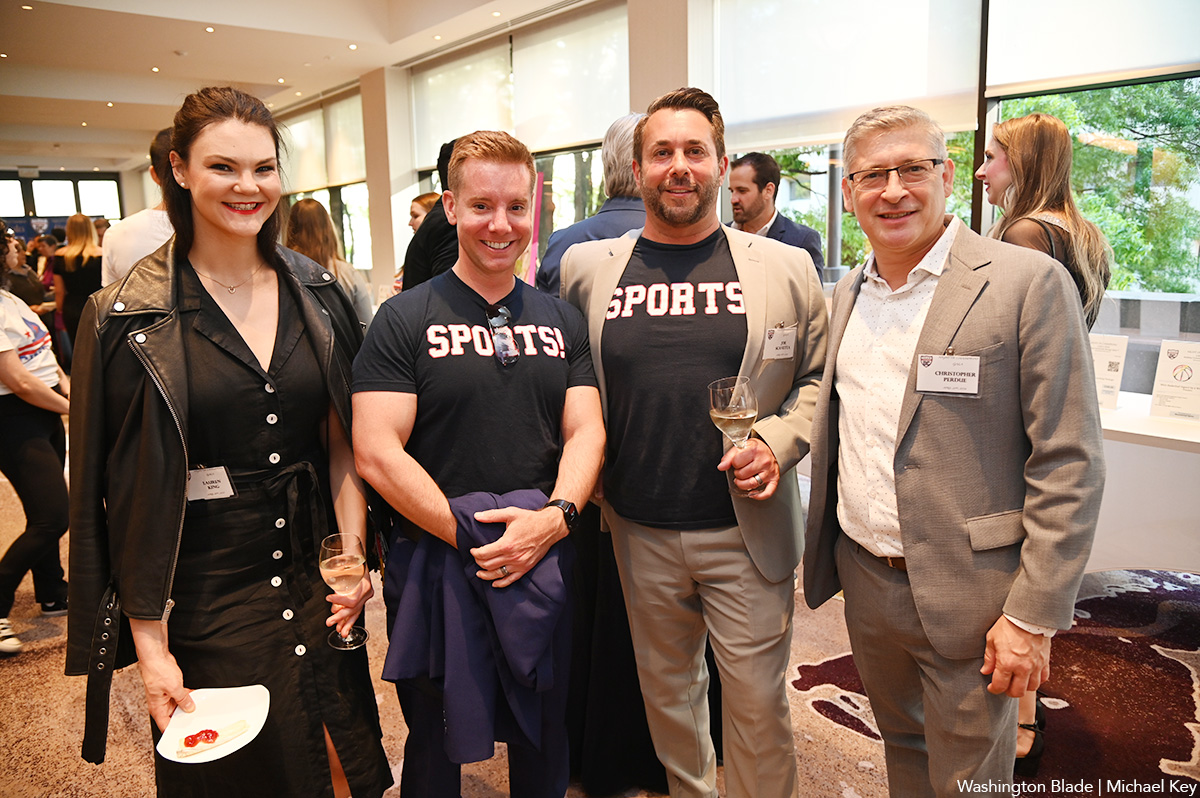
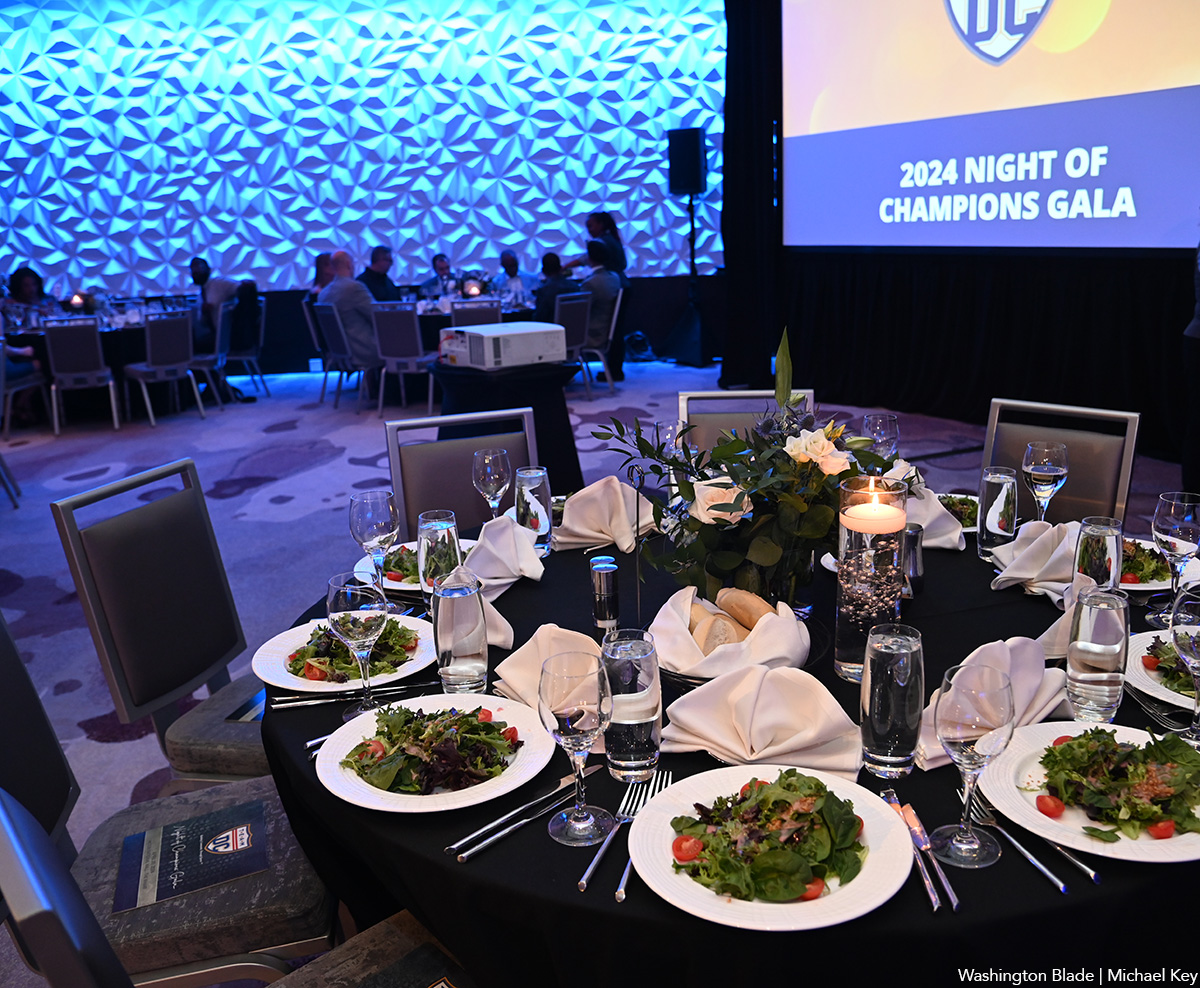
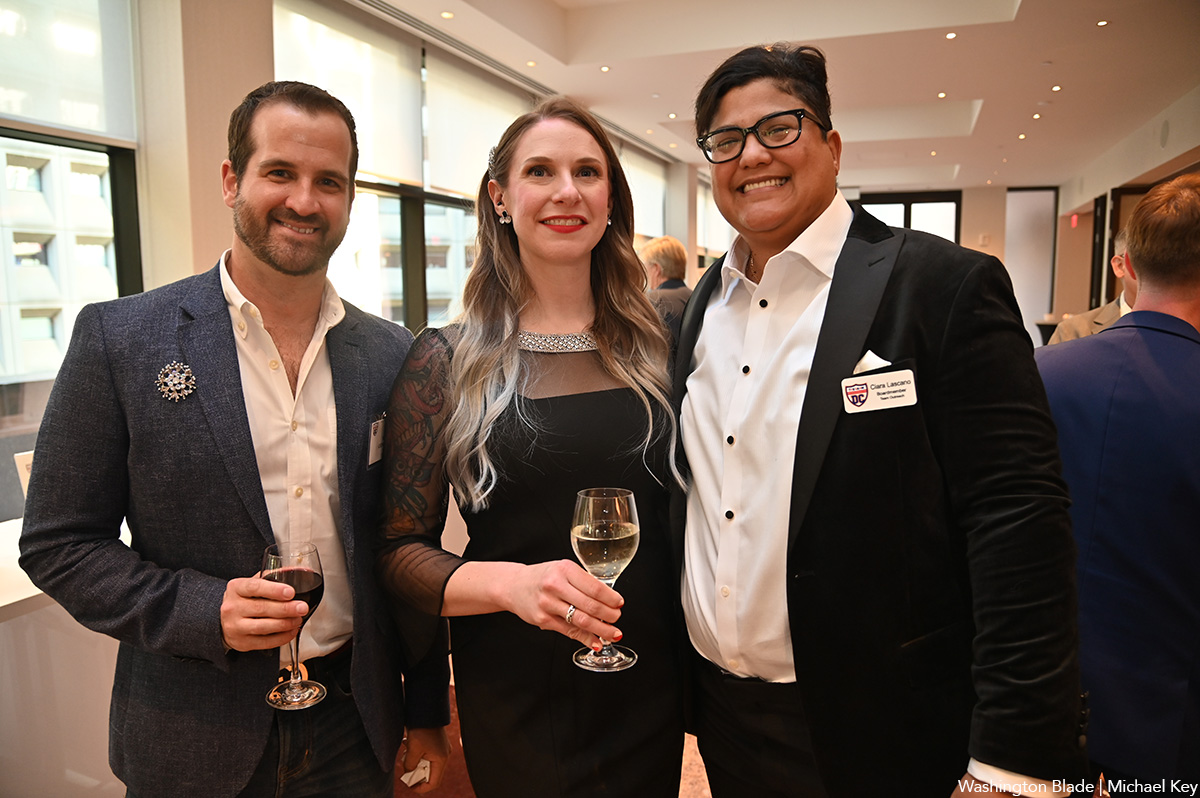
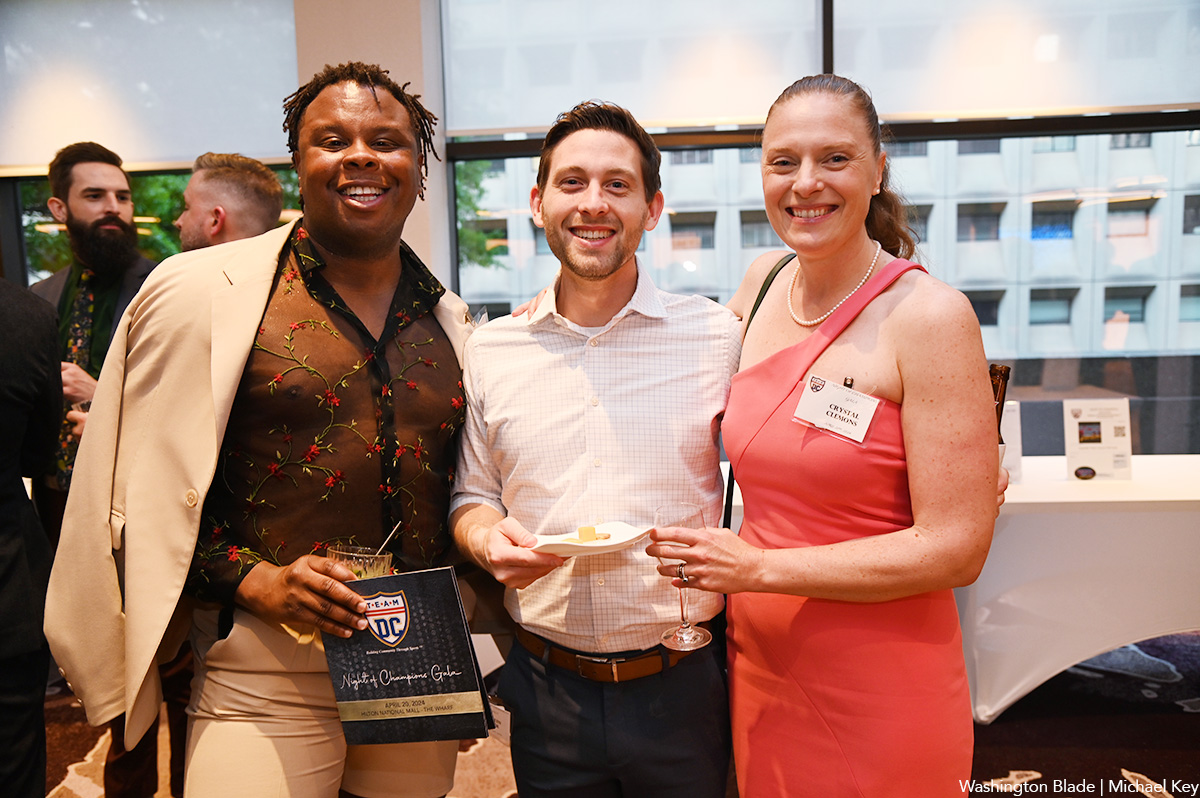
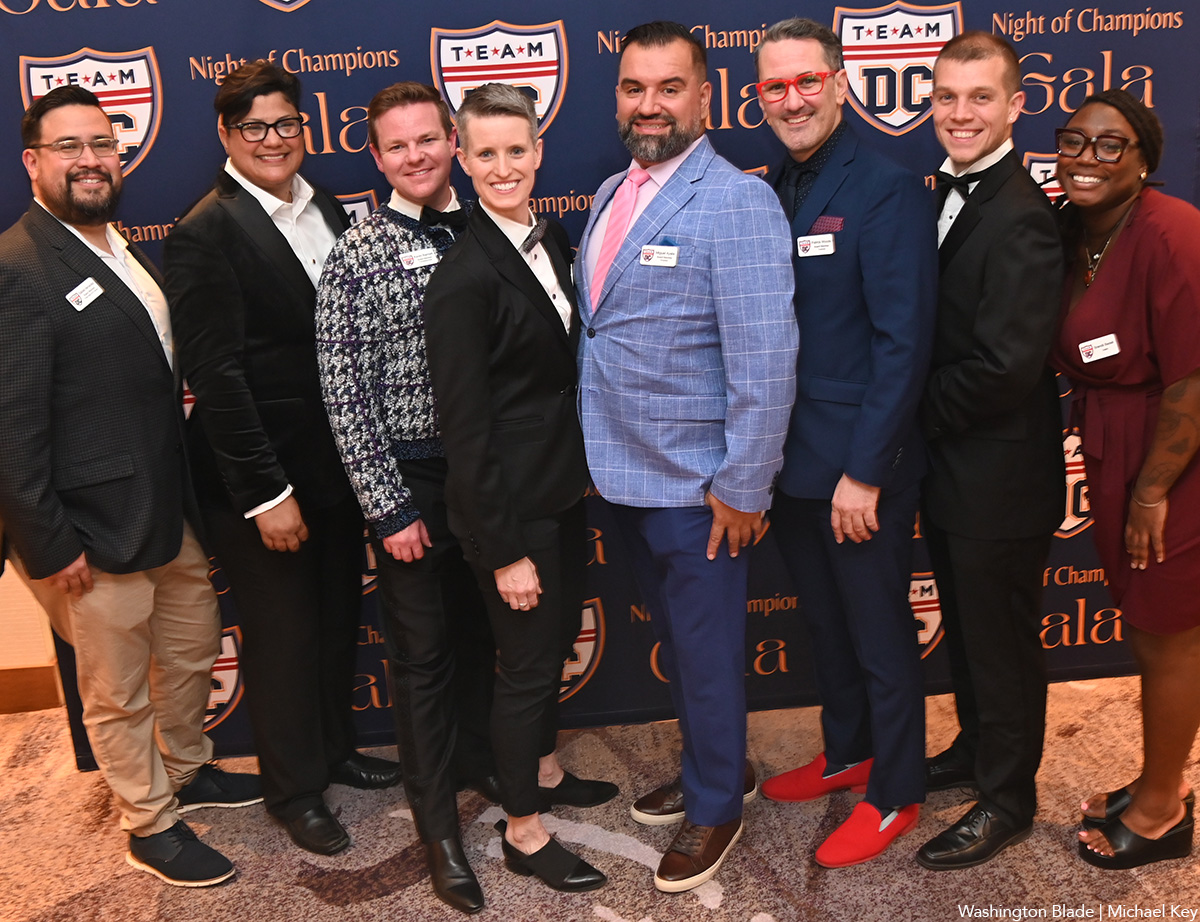
Team DC, the umbrella organization for LGBTQ-friendly sports teams and leagues in the D.C. area, held its annual Night of Champions Awards Gala on Saturday, April 20 at the Hilton National Mall. The organization gave out scholarships to area LGBTQ student athletes as well as awards to the Different Drummers, Kelly Laczko of Duplex Diner, Stacy Smith of the Edmund Burke School, Bryan Frank of Triout, JC Adams of DCG Basketball and the DC Gay Flag Football League.
(Washington Blade photos by Michael Key)




















The 2024 National Cannabis Festival was held at the Fields at RFK Stadium on April 19-20.
(Washington Blade photos by Michael Key)















Covering the @NatlCannaFest at RFK Stadium for @WashBlade . Stop by the LGBTQ+ booth and pick up a paper if you are here. pic.twitter.com/is7hnsaPns
— Michael Patrick Key (@MichaelKeyWB) April 20, 2024




















