Real Estate
Assessing discount brokerages
Is the risk really worth it?


Scoring a lower commission with a discount brokerage may end up costing you more in the long run.
Lately, it seems like the real estate wheel is constantly trying to be reinvented. New models promising to change the brokerage landscape with venture capital, rapidly evolving technology, and promises of discounts to the consumer while still offering the same amount of service are almost too perfect. Discount brokerages have used tricks through large ad campaigns as smoke and mirrors for buyers and sellers alike. As I would say to a market like DC’s, if the wheel is working, don’t fix it!
Discount brokerages are on the rise nationwide with promises to change the real estate game, put the power back in the hands of the consumer with flashy technologies and marketing campaigns that promise to be the future of the real estate market. These brokerages may offer a subsidy to the buyer at closing, reduced commission to seller, or a flat fee for their services. Each of these discounted models may appear attractive, but what lies beneath may be a lesson in cutting corners.
To address the subject head on: is the discount really worth it?
Let’s look at a real example in the District with a medium size condo building located on Champlain Street NW (for the sake of anonymity between brokerages, we won’t disclose the building’s address). The building is a luxury condominium in the heart of Adams Morgan, with high-end lofts delivered in the mid-2000s. Of the 14 sales the past two years, nearly all listings in the building sell for or over list price within two weeks.
For listings, this condo building currently has 2 active listings and 1 under contract. The listing under contract was on market for 5 days and was listed by a full-service brokerage. The two active listings have been on market for 34 days and 113 days. Both active units are listed by discount brokerages. Both active listings have gone through price reductions (one of which was over 10 percent) and are currently vacant. A seller on a discounted 1 to 1.5 percent listing agreement has easily paid out the additional 1.5 percent in mortgage and condo fees over the days on the market. That one percent reduction in commission leads to less support, less marketing and visibility on the market, and in return, poorer results.
Now, what about the buyers? Let’s take the same example from Champlain Street NW. Each of the three listings may offer a buyer’s agent commission, even if they are listed by a discount brokerage. Buyers working with full service agents may not offer the buyer a rebate, but will take the buyer from contract to closing every step of the way. Buyers with a discount brokerage may see a lack of service as their agents move on to the next client with less of a focus on the contract phase, leaving the listing agent to take on all of the work.
In addition, a seller who is given the opportunity to choose between a buyer’s agent from a full-service brokerage or a discount brokerage may sway toward to the full-service agent. Why? The answer is simple: in a transaction where one party is discounted, the other side must pick up all of the work for both parties, while only one side is benefitted with a rebate. Thus, the industry’s perception of discounted brokerages leads to a stigma of poor service to the client.
Sure, everyone likes a good deal, but that doesn’t mean that every deal is a good one. In situations like our example here, discount brokerages can do lasting damage to how a market operates. For our Champlain Street example, the average days on market this year will skyrocket because of these two listings. The neighborhood will see a skewed list to sales price ratio, and the sellers will be burned from their experience of working with a discounted broker. All of this damage likely done to make a quick buck on commissions that never fully came to fruition in the full buying and selling process.
Full disclosure, I am a Realtor with a full service brokerage. Perhaps the answer seems intuitive to me, but I’ll let the consumer be the judge. When making one of the most personal decisions of your life in purchasing real estate, are we really willing to take a chance to score a quick buck?
Tim Savoy is a real estate agent with Coldwell Banker Residential Brokerage, Dupont Circle. The views expressed in this article are his, and do not reflect the opinions of the Washington Blade. Reach him at 202-400-0534 or [email protected].

Valentine’s Day is often portrayed as a celebration of romantic love — flowers, chocolates, and candlelit dinners. But for many LGBTQ+ individuals and couples, Valentine’s Day can also be a moment to reflect on something deeper: the love that creates a safe, welcoming home.
For LGBTQ+ home buyers and sellers, homeownership is more than a financial milestone—it is an act of belonging, resilience, and pride. Owning a home can mean finally having a place where you can hold hands with your partner on the front porch, decorate with your authentic style, and build a life free from judgment. In this way, buying or selling a home is one of the most meaningful love stories many LGBTQ+ people will ever write.
This Valentine’s Day, whether you’re a first-time gay home buyer, a same-sex couple upgrading your space, or an LGBTQ+ seller moving on to your next chapter, it’s worth thinking about how love, identity, and real estate intersect—and how to navigate that journey with confidence, protection, and the right support.
Love, Identity, and the Meaning of ‘Home’
For generations, LGBTQ+ people were denied equal access to housing, homeownership, and legal protections. Even today, many LGBTQ+ home buyers still face subtle bias, uncomfortable interactions, or outright discrimination in the real estate process.
That’s why finding LGBTQ+ friendly real estate and an affirming gay friendly realtor or lesbian realtor matters so much. A home isn’t just a building—it’s a personal sanctuary. Working with LGBTQ+ real estate agents who understand your lived experience can make all the difference between a stressful transaction and a joyful one.
For over 30 years, GayRealEstate.com has been the leading gay real estate network, connecting LGBTQ+ home buyers and sellers with gay real estate agents, lesbian real estate agents, and LGBTQ+ friendly realtors who truly “get it.” Their mission has always been simple yet powerful: to ensure that every LGBTQ+ person has access to safe, respectful, and inclusive real estate services.
Finding Your Match: Choosing the Right LGBTQ+ Friendly Realtor
Much like dating, finding the right real estate agent is about compatibility, trust, and communication. Here are some key tips for choosing the best LGBTQ+ real estate representation:
- Look for experience with LGBTQ+ clients. Search for a gay realtor near me or lesbian realtor near me through GayRealEstate.com, where agents are vetted for cultural competency and community commitment.
- Ask about their experience with same-sex couple home buying. A strong agent should understand issues like joint ownership, legal protections, and financing considerations.
- Choose someone who listens. You should feel safe sharing your priorities—whether that includes proximity to LGBTQ+ nightlife, affirming schools, or lesbian-friendly neighborhoods.
- Prioritize respect and transparency. Your agent should advocate for you, not just push a quick sale.
The right gay friendly real estate agent isn’t just helping you buy a house—they’re helping you find a place to build your life.
Best Cities for LGBTQ+ Home Buyers
If love is your compass, location is your map. Some of the best cities for LGBTQ+ home buyers consistently offer strong community presence, legal protections, and welcoming neighborhoods:
- Wilton Manors, Florida – A hub for LGBTQ+ culture with thriving LGBTQ+ real estate opportunities
- Palm Springs, California – A long-standing LGBTQ+ retirement and second-home destination
- Provincetown, Massachusetts – Historic LGBTQ+ community with progressive housing protections
- Asheville, North Carolina – Growing market with inclusive real estate services
- Fort Lauderdale, Florida – Diverse, welcoming, and highly sought-after for LGBTQ+ home ownership
Working with GayRealEstate.com allows you to connect with local LGBTQ+ real estate experts who know these markets inside and out.
Navigating Legal Protections in LGBTQ+ Real Estate
Love is universal—but legal protections are not always consistent. Understanding your rights is essential when buying or selling a home as an LGBTQ+ person.
Key protections include:
- Fair Housing Act (FHA): Prohibits discrimination based on sex, which courts have increasingly interpreted to include sexual orientation and gender identity.
- State and local protections: Many cities and states offer additional safeguards against LGBTQ+ housing discrimination.
- Same-sex couple legal considerations: If you are married, joint ownership is typically straightforward. If not, consult an attorney about co-ownership agreements.
A knowledgeable LGBTQ+ friendly realtor from GayRealEstate.com can help guide you through these complexities and connect you with trusted legal professionals when needed.
Buying a Home as an LGBTQ+ Person: Practical Tips
If you’re embarking on your home-buying journey this Valentine’s season, here are smart, practical steps to take:
- Clarify your priorities. Do you want a vibrant LGBTQ+ neighborhood, quiet suburbs, or access to queer community spaces?
- Get pre-approved for a mortgage. This strengthens your position in competitive markets.
- Work with an LGBTQ+ real estate agent. Searching “finding a gay real estate agent” or “finding a lesbian real estate agent” through GayRealEstate.com is a great first step.
- Research inclusive communities. Some neighborhoods are more welcoming than others.
- Know your rights. If you experience bias, document it and seek legal guidance.
Buying a home is an act of self-love—and community love.
Selling a Home as an LGBTQ+ Person
Selling can be just as emotional as buying, especially if your home represents years of memories with your partner, friends, or chosen family.
When selling a home as an LGBTQ+ person, consider:
- Working with a gay friendly realtor who will market your home inclusively
- Highlighting LGBTQ+ community appeal in listings
- Being prepared for potential buyer bias (and knowing how to respond)
- Leaning on GayRealEstate.com’s LGBTQ+ real estate services for trusted guidance
Your story—and your home—deserve respect.
Real Estate for LGBTQ+ Families
More LGBTQ+ couples are raising children, fostering, or building blended families. This makes homeownership even more meaningful.
When searching for real estate for LGBTQ+ families, consider:
- LGBTQ+ affirming school districts
- Family-friendly queer communities
- Safe neighborhoods with inclusive values
- Access to LGBTQ+ resources and social networks
GayRealEstate.com specializes in helping LGBTQ+ families find homes that truly fit their lives.
Love, Pride, and Homeownership
At its core, Valentine’s Day is about connection. For LGBTQ+ people, homeownership can be one of the most profound expressions of love—love for yourself, your partner, your family, and your future.
Whether you are a first-time gay home buyer, a same-sex couple relocating, or an LGBTQ+ seller moving forward, you deserve an experience rooted in dignity, fairness, and celebration.
For over three decades, GayRealEstate.com has stood as the leading source for LGBTQ+ real estate, gay real estate, lesbian real estate, and LGBTQ+ home buying and selling representation. Their nationwide network of gay real estate agents, lesbian-friendly real estate agents, and LGBTQ+ friendly realtors ensures that your real estate journey is guided by professionals who understand your heart—and your home.
This Valentine’s Day, let your next chapter be written in a place where you can truly belong. Because when love leads the way, home is never far behind.
Scott Helms is president and owner of Gayrealestate.com.
Real Estate
New year, new housing landscape for D.C. landlords
Several developments expected to influence how rental housing operates

As 2026 begins, Washington, D.C.’s rental housing landscape continues to evolve in ways that matter to small landlords, tenants, and the communities they serve. At the center of many of these conversations is the Small Multifamily & Rental Owners Association (SMOA), a D.C.–based organization that advocates for small property owners and the preservation of the city’s naturally occurring affordable housing.
At their December “DC Housing Policy Summit,” city officials, housing researchers, lenders, attorneys, and housing providers gathered to discuss the policies and proposals shaping the future of rental housing in the District. The topics ranged from recent legislative changes to emerging ballot initiatives and understanding how today’s policy decisions will affect housing stability tomorrow.
Why Housing Policy Matters in 2026
If you are a landlord or a tenant, several developments now underway in D.C., are expected to influence how rental housing operates in the years ahead.
One of the most significant developments is the Rebalancing Expectations for Neighbors, Tenants and Landlords (RENTAL) Act of 2025, a sweeping piece of legislation passed last fall and effective December 31, 2025, which updates a range of housing laws. This broad housing reform law will modernize housing regulations and address long-standing court backlogs, and in a practical manner, assist landlords with shortened notice and filing requirements for lawsuits. The Act introduces changes to eviction procedures, adjusts pre-filing notice timelines, and modifies certain tenant protections under previous legislation, the Tenant Opportunity to Purchase Act.
At the same time, the District has expanded its Rent Registry, to have a better overview of licensed rental units in the city with updated technology that tracks rental units subject to and exempt from rent control and other related housing information. Designed to improve transparency and enforcement, Rent Registry makes it easier for all parties to verify rent control status and compliance.
Looking ahead to the 2026 election cycle, a proposed ballot initiative for a two-year rent freeze is generating significant conversation. If it qualifies for the ballot and is approved by voters, the measure would pause rent increases across the District for two years. While still in the proposal phase, it reflects the broader focus on tenant affordability that continues to shape housing policy debates.
What This Means for Rental Owners
Taken together, these changes underscore how closely policy and day-to-day operations are connected for small landlords. Staying informed about notice requirements, registration obligations, and evolving regulations isn’t just a legal necessity. It’s a key part of maintaining stable, compliant rental properties.
With discussions underway about rent stabilization, voucher policies, and potential rent freezes, long-term revenue projections will be influenced by regulatory shifts just as much as market conditions alone. Financial and strategic planning becomes even more important to protect your interests.
Preparing for the Changes
As the owner of a property management company here in the District, I’ve spent much of the past year thinking about how these changes translate from legislation into real-world operations.
The first priority has been updating our eviction and compliance workflows to align with the RENTAL Act of 2025. That means revising how delinquent rent cases are handled, adjusting notice procedures, and helping owners understand how revised timelines and court processes may affect the cost, timing, and strategy behind enforcement decisions.
Just as important, we’re shifting toward earlier, more proactive communication around compliance and regulatory risk. Rather than reacting after policies take effect, we’re working to flag potential exposure in advance, so owners can make informed decisions before small issues become costly problems.
A Bigger Picture for 2026
Housing policy in Washington, D.C., has always reflected the city’s values from protecting tenants to preserving affordability in rapidly changing neighborhoods. As those policies continue to evolve, the challenge will be finding the right balance between stability for renters and sustainability for the small property owners who provide much of the city’s housing.
The conversations happening now at policy summits, in Council chambers, and across neighborhood communities will shape how rental housing is regulated. For landlords, tenants, and legislators alike, 2026 represents an opportunity to engage thoughtfully, to ask hard questions, and to create a future where compliance, fairness, and long-term stability go hand-in-hand.
Real Estate
Unconventional homes becoming more popular
HGTV show shines spotlight on alternatives to cookie cutter

While stuck in the house surrounded by snow and ice, I developed a new guilty pleasure: watching “Ugliest House in America” on HGTV. For several hours a day, I looked at other people’s unfortunate houses. Some were victims of multiple additions, some took on the worst décor of the ‘70s, and one was even built in the shape of a boat.
In today’s world, the idea of what a house should look like has shifted dramatically. Gone are the days of cookie-cutter suburban homes with white picket fences. Instead, a new wave of architects, designers, and homeowners are pushing the boundaries of traditional housing to create unconventional and innovative spaces that challenge our perceptions of what a home can be.
One of the most popular forms of alternative housing is the tiny house. These pint-sized dwellings are typically fewer than 500 square feet and often are set on trailers to allow for mobility. Vans and buses can also be reconfigured as tiny homes for the vagabonds among us.
These small wonders offer an affordable and sustainable living option for those wishing to downsize and minimize their environmental footprint. With clever storage solutions, multipurpose furniture, and innovative design features, tiny homes have become a creative and functional housing solution for many, although my dogs draw the line at climbing Jacob’s Ladder-type steps.
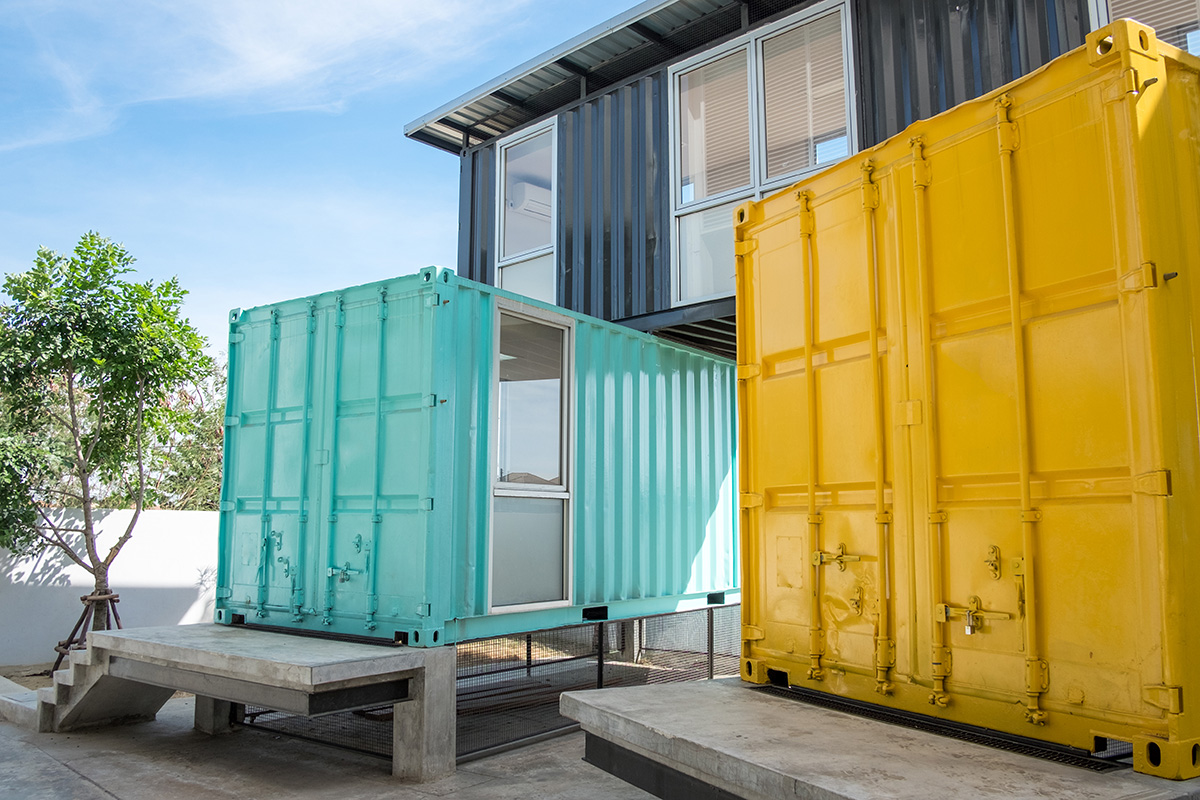
Another unusual type of housing gaining popularity is the shipping container home. Made from repurposed shipping containers, these homes offer a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to create modern and sleek living spaces. With their industrial aesthetic and modular design, shipping container homes are a versatile option for those contemplating building a unique and often multi-level home.
For those looking to connect with nature, treehouses are a whimsical and eccentric housing option. Nestled high up in the trees, these homes offer a sense of seclusion and tranquility that is hard to find in traditional housing. With their distinctive architecture and stunning views, treehouses can be a magical retreat for those seeking a closer connection to the natural world.
For a truly off-the-grid living experience, consider an Earthship home. These self-sustaining homes use recycled construction materials and rely on renewable energy sources like solar power and rainwater harvesting. With their passive solar design and natural ventilation systems, Earthship homes are a model of environmentally friendly living.
For those with a taste for the bizarre, consider a converted silo home. These cylindrical structures provide an atypical canvas for architects and designers to create modern and minimalist living spaces. With curved walls and soaring ceilings, silo homes offer a one-of-a-kind living experience that is sure to leave an impression.
Barn homes have gained popularity in recent years. These dwellings take the rustic charm of a traditional barn and transform it into a modern and stylish living space. With their open, flexible floor plans, lofty ceilings, and exposed wooden beams, barn homes offer a blend of traditional and contemporary design elements that create a warm and inviting atmosphere, while being tailored to the needs and preferences of the homeowner.
In addition to their unique character, barn homes also offer a sense of history and charm that is hard to find in traditional housing. Many of them have a rich and storied past, with some dating back decades or even centuries.
If you relish life on the high seas (or at a marina on the bay), consider a floating home. These aquatic abodes differ from houseboats in that they remain on the dock rather than traverse the waterways. While most popular on the West Coast (remember “Sleepless in Seattle”?), you sometimes see them in Florida, with a few rentals available in Baltimore’s Inner Harbor and infrequent sales at our own D.C. Wharf. Along with the sense of community found in marinas, floating homes offer a peaceful retreat from the hustle and bustle of city life.
From tiny homes on wheels to treehouses in the sky or homes that float, these distinctive dwellings offer a fresh perspective on how we live and modify traditional thoughts on what a house should be. Sadly, most of these homes rely on appropriate zoning for building and placement, which can limit their use in urban or suburban areas.
Nonetheless, whether you’re looking for a sustainable and eco-friendly living option or a whimsical retreat, there is sure to be an unconventional housing option that speaks to your sense of adventure and creativity. So, why settle for a run-of-the-mill ranch or a typical townhouse when you can live in a unique and intriguing space that reflects your personality and lifestyle?
Valerie M. Blake is a licensed Associate Broker in D.C., Maryland, and Virginia with RLAH @properties. Call or text her at 202-246-8602, email her at [email protected] or follow her on Facebook at TheRealst8ofAffairs.