U.S. Supreme Court
U.S. Supreme Court orders Title 42 to remain in place
Justices to hear oral arguments in case in February

The U.S. Supreme Court on Tuesday in a 5-4 ruling granted the request by 19 states led by Arizona and postponed lifting of Title 42 of the Public Health Services Act.
Title 42 was a coronavirus pandemic measure implemented by the Trump administration to suspend the entry of migrants as a public health threat at all U.S. borders.
The policy allowed U.S. Border Patrol and Immigration and Customs Enforcement agents to turn back migrants quickly, without giving them an opportunity to seek asylum in the U.S.
Arizona and 18 other Republican-led states argued that lifting the measure would create a humanitarian crisis which would imperil the safety and resources of the states particularly the states which border Mexico.
The high court has set oral arguments for the matter in February [2023.] Conservative Justice Neil Gorsuch joined the court’s three liberals in dissent.
The “current border crisis is not a COVID crisis,” he wrote in his dissent. “And courts should not be in the business of perpetuating administrative edicts designed for one emergency only because elected officials have failed to address a different emergency. We are a court of law, not policymakers of last resort.”
Reacting to the ruling by the Supreme Court, White House Press Secretary Karine Jean-Pierre issued the following statement:
“The Supreme Court’s order today keeps the current Title 42 policy in place while the court reviews the matter in 2023. We will, of course, comply with the order and prepare for the court’s review.
At the same time, we are advancing our preparations to manage the border in a secure, orderly and humane way when Title 42 eventually lifts and will continue expanding legal pathways for immigration. Title 42 is a public health measure, not an immigration enforcement measure, and it should not be extended indefinitely. To truly fix our broken immigration system, we need Congress to pass comprehensive immigration reform measures like the ones President Biden proposed on his first day in office.
Today’s order gives Republicans in Congress plenty of time to move past political finger-pointing and join their Democratic colleagues in solving the challenge at our border by passing the comprehensive reform measures and delivering the additional funds for border security that President Biden has requested.”
The Biden administration extended the Trump administration’s orders in August 2021, but in April of this year the government announced that it would end the policy, saying it was no longer necessary to protect public health.
But shortly before the policy was set to end in May, a federal judge in Louisiana ordered the Biden administration to continue the restrictions. U.S. District Judge Robert Summerhays concluded that the Biden administration had not provided proper notice of its decision to end the policy and an opportunity for the public to comment, as required by the federal law governing administrative agencies. The Biden administration appealed that decision to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 5th Circuit.
The dispute now before the Supreme Court, known as Arizona v. Mayorkas, is a separate case. It began as a challenge to the policy in federal court in D.C., by six families who crossed the U.S.-Mexico border without authorization and now seek asylum — on their own behalf but also as a class action on behalf of other families in the same position. In November, U.S. District Judge Emmet Sullivan ruled for the families and ordered the government to end the policy by Dec. 21.
The states asked to intervene in the D.C. case to defend the policy. If Sullivan’s ruling remains in effect, they argued, it will effectively nullify Summerhays’ ruling. But on Friday the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit rejected the states’ request to join the case on appeal.
The court explained that the states’ request came too late. The states should have known “long before now,” the court reasoned, that they did not have the same interest in continuing the policy as the Biden administration, especially when the Biden administration announced several months ago that it intended to end the policy.
Facing the termination of the policy prior to Christmas under Sullivan’s order, the states asked the justices to step in on an emergency basis and block that order from taking effect.
Additional reporting by Amy Howe, SCOTUSBlog
U.S. Supreme Court
Supreme Court upholds ACA rule that makes PrEP, other preventative care free
Liberal justices joined three conservatives in majority opinion

The U.S. Supreme Court on Friday upheld a portion of the Affordable Care Act requiring private health insurers to cover the cost of preventative care including PrEP, which significantly reduces the risk of transmitting HIV.
Conservative Justice Brett Kavanaugh authored the majority opinion in the case, Kennedy v. Braidwood Management. He was joined by two conservatives, Chief Justice John Roberts and Justice Amy Coney Barrett, along with the three liberal justices, Sonia Sotomayor, Elena Kagan, and Ketanji Brown-Jackson.
The court’s decision rejected the plaintiffs’ challenge to the Affordable Care Act’s reliance on the U.S. Preventative Services Task Force to “unilaterally” determine which types of care and services must be covered by payors without cost-sharing.
An independent all-volunteer panel of nationally recognized experts in prevention and primary care, the 16 task force members are selected by the secretary of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to serve four-year terms.
They are responsible for evaluating the efficacy of counseling, screenings for diseases like cancer and diabetes, and preventative medicines — like Truvada for PrEP, drugs to reduce heart disease and strokes, and eye ointment for newborns to prevent infections.
Parties bringing the challenge objected especially to the mandatory coverage of PrEP, with some arguing the drugs would “encourage and facilitate homosexual behavior” against their religious beliefs.
U.S. Supreme Court
Supreme Court rules parents must have option to opt children out of LGBTQ-specific lessons
Mahmoud v. Taylor case comes from Montgomery County, Md.

The U.S. Supreme Court on Friday ruled that public schools must give advance notice to parents and allow them the opportunity to opt their children out of lessons or classroom instruction on matters of gender and sexuality that conflict with their religious beliefs.
Mahmoud v. Taylor was decided 6-3 along party lines, with conservative Justice Samuel Alito authoring the majority opinion and liberal Justices Sonia Sotomayor, Elena Kagan, and Ketanji Brown-Jackson in dissent.
Parents from diverse religious backgrounds sued to challenge the policy in Maryland’s Montgomery County Public Schools when storybooks featuring LGBTQ characters were added to the elementary school English curriculum in 2022.
The school board argued in the brief submitted to the Supreme Court that “the storybooks themselves do not instruct about gender or sexuality. They are not textbooks. They merely introduce students to characters who are LGBTQ or have LGBTQfamily members, and those characters’ experiences and points of view.”
Advocacy groups dedicated to advancing free speech and expression filed amicus briefs in support of the district.
PEN America argued the case should be viewed in the context of broader efforts to censor and restrict what is available and allowable in public schools, for instance by passing book bans and “Don’t Say Gay” laws.
The ACLU said the policy of not allowing opt-outs is religion-neutral, writing that the Supreme Court should apply rational basis review, which requires only that the school district show that its conduct was “rationally related” to a “legitimate” government interest.
LGBTQ groups also objected to the challenge against the district’s policy, with many submitting amici briefs including: the National Center for Lesbian Rights, GLAD Law, Family Equality, COLAGE, Lambda Legal, the Leadership Conference on Civil and Human Rights, PFLAG., and the National Women’s Law Center.
The Human Rights Campaign did not submit a brief but did issue a statement by the group’s President Kelley Robinson: “LGBTQ+ stories matter. They matter so students can see themselves and their families in the books they read–so they can know they’re not alone.”
“And they matter for all students who need to learn about the world around them and understand that while we may all be different, we all deserve to be valued and loved,” she said. “All students lose when we limit what they can learn, what they can read, and what their teachers can say. The Supreme Court should reject this attempt to silence our educators and ban our stories.”
U.S. Supreme Court
Legal expert maps out how gender-affirming care bans may be challenged post-Skrmetti
Ruling leaves door open to state constitution claims
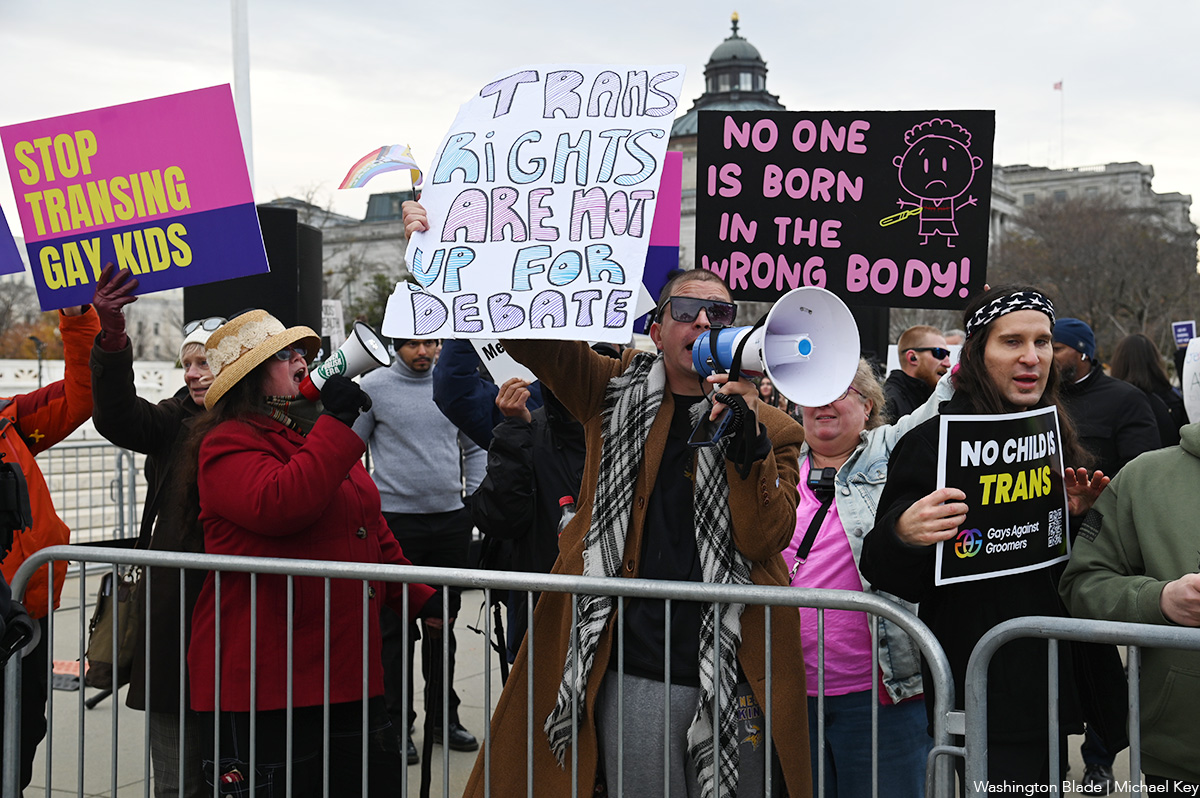
In a devastating loss for transgender youth and their families, the U.S. Supreme Court’s conservative supermajority on June 18 voted to uphold Tennessee’s law banning access to gender-affirming health care for minors in a 6-3 ruling that effectively shields similar restrictions in more than 20 other states.
Chase Strangio, a lead attorney for the plaintiffs in U.S. v. Skrmetti and the first trans lawyer to argue before the nation’s highest court, acknowledged the “setback” during a press call with reporters while stressing the need to “continue onward in the fight” because the avenues open to challenge laws like Tennessee’s Senate Bill 1 had not been fully extinguished.
Speaking with the Washington Blade on Monday, Professor Holning Lau of the University of North Carolina School of Law outlined the ramifications of the justices’ majority opinion and mapped out three ways in which cases aimed at striking down healthcare bans or other anti-trans policies and practices could play out in its wake.
An internationally recognized expert on equality rights, particularly in the contexts of sexuality, gender, and family life, Lau previously served as president of the ACLU of North Carolina’s board of directors and as a teaching fellow at UCLA’s Williams Institute on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity Law and Public Policy.
He is also the co-author of a recent paper that examines the exceptions to laws prohibiting medical interventions for gender transitions in minors that permit “so-called gender-normalizing surgeries, which are performed on intersex infants to conform their bodies to socially constructed expectations about the male/female binary.”
These carveouts, Lau and his colleague UNC Law School Associate Professor Barbara Fedders argue, cut against the reasoning cited by the lawmakers behind legislative restrictions targeting healthcare for trans youth like SB 1 and by the lawyers defending them in court.
Specifically, Lau told the Blade courts could interpret such “intersex exceptions” as evidence that gender affirming care bans were written with or are undergirded by sex stereotypes, unwarranted fears, and disgust — possible grounds to argue they should be struck down under the animus doctrine, which holds that government action motivated by hostility or prejudice towards a particular group is unconstitutional.
While there was some discussion of animus in the context of U.S. v. Skrmetti, notably in the concurring opinion by conservative Justice Amy Coney Barrett, the plaintiffs’ case focused primarily on “the sex discrimination argument because of Bostock v. Clayton County,” Lau said, referring to the 2020 Supreme Court case that determined sex-based discrimination in the context of employment, as defined by federal civil rights law, includes discriminatory conduct that is motivated by the victim’s sexual orientation or gender identity.
‘A huge, huge setback’
Five years after LGBTQ rights advocates were toasting their victory in the landmark case, which saw three of the conservatives on the High Court joining their liberal counterparts in a majority opinion written by Justice Neil Gorsuch, “a lot of folks may have reasonably thought that the logic of Bostock points towards this very straightforward sex discrimination argument,” Lau said, adding that liberal Justice Sonia Sotomayor “adopts that avenue of reasoning in her dissent” in Skrmetti.
“The way that the majority rejects the sex discrimination arguments in in the majority opinion of Skrmetti is not persuasive in my view,” he said. “I struggle for words to capture the reasoning of the majority opinion.”
Echoing Strangio’s remarks, Lau noted that Skrmetti “doesn’t completely close the door” to legal challenges but is nevertheless “a huge, huge setback.”
On the one hand, he said “lower courts might say that this was very much about the context of medical treatment and minors,” which means “there may still be cases that prevail having to do with transgender discrimination in other contexts, like the military ban or the restrictions on passports.”
At the same time, however, Lau cautioned that “you could also read this case as signaling more obstacles ahead, especially if a case gets back to the Supreme Court” since “three of the justices have already signaled in Skrmetti that they do not view gender identity discrimination as warranting heightened scrutiny.”
Litigation aside, young people and their families who will suffer the most direct and harmful consequences, namely the loss of access to medically necessary gender-affirming care, will have to navigate “a patchwork of state laws,” he said, which in many cases will mean relocating or traveling out of state for treatments that have been criminalized in the places where they live.
The Supreme Court’s 2022 decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, which overturned the nationwide right to abortion, led to many of these same outcomes, he said. In an email following Monday’s phone interview, Lau further explained that “Dobbs unleashed conflicts between states, and there are signs that similar conflicts will arise with respect to gender-affirming care for trans youth.”
For example, he said “A growing number of states might seek to penalize interstate travel for gender-affirming care — targeting families who travel across state lines and/or medical providers who provide care to such families.”
“There is ongoing litigation concerning the constitutionality of interstate bans and shield laws in the abortion context, and those cases will bear significance on interstate bans and shield laws regarding gender-affirming care,” Lau said.
Counsel for the plaintiffs in Skrmetti probably turned to Bostock because the case was “the most recent victory, and the most on point when it comes to gender identity,” Lau said.
The animus doctrine was an important element of cases that expanded equal rights and protections for LGBTQ people, he said, pointing to U.S. v. Windsor (2013), which struck down portions of the Defense of Marriage Act, a law that prohibited the federal government from recognizing same-sex marriages, and Romer v. Evans (1996) which struck down a Colorado constitutional amendment prohibiting the state from enacting any LGBTQ inclusive nondiscrimination rules.
Lau said those cases are examples of where the Supreme Court has found indirect evidence of impermissible animus in the laws under consideration by the way they were designed or structured, as opposed to more direct evidence like overt expressions of sex stereotypes, fear, and disgust toward a particular group that might arise during the legislative process.
These cases and the animus doctrine, Lau added, are closely associated with the late former Justice Anthony Kennedy, an appointee of President Ronald Reagan who was the “swing vote” responsible for ultimately deciding many of cases considered by the Roberts court where the justices were split 5-4.
Following his retirement in 2018 and the emergence of a 6-3 conservative majority, there is less certainty about how the justices might evaluate animus related arguments in the context of disputes over issues of gay or transgender rights, Lau said, especially relative to how they were expected to look at the reasoning central to the Bostock decision just five years ago.
“I would have liked to see more” engagement with animus in the Skrmetti opinions, Lau said. Barrett in her concurrence did address the question, writing that there was a rational basis for Tennessee legislators’ SB 1, in contrast with the court’s findings in Romer, where the “sheer breadth” of law was “so discontinuous with the reasons offered for it that the [law] seem[ed] inexplicable by anything but animus toward the class it affect[ed]”.)
“To be sure, an individual law ‘inexplicable by anything but animus’ is unconstitutional,” Barrett said. “But legislatures have many valid reasons to make policy in these areas, and so long as a statute is a rational means of pursuing a legitimate end, the Equal Protection Clause is satisfied.”
Lau said that notwithstanding her position on Skrmetti, the fact that Barrett “did make reference to the animus jurisprudence suggests that there is potentially a future for animus doctrine, even in the post-Kennedy Supreme Court.”
Rather than the animus doctrine or Bostock’s reasoning that gender identity discrimination constitutes sex based discrimination, the court relied on Geduldig v. Aiello (1974), Lau said, which found that pregnancy discrimination “is not a type of sex discrimination” and remains a case that “strikes so many people as being incorrectly decided.”
“Whenever I teach Geduldig v. Aiello, my students are shocked by the court’s reasoning,” he said, “and it’s so formalistic in its reasoning that it’s so divorced from people’s lived experiences.”
The same can be said for the majority opinion and concurrences in Skrmetti, Lau said, where the justices said “that even if transgender kids are the only ones seeking treatment for gender dysphoria, not all transgender kids are seeking this treatment, and kids can still get the treatment if they have a different type of diagnosis” such as any of the conditions delineated in the exceptions that were written into SB 1 and similar laws in other states.
“One day, I imagine teaching [Skrmetti] and my students will be, likewise, shocked at the Court’s exceedingly formalistic reasoning,” he added.
Legal challenges to anti-trans healthcare bans in a post-Skrmetti world
After Skrmetti, Lau said he expects to see cases challenging bans and restrictions on healthcare for trans youth that are based on state constitutional claims, noting “a case where there was a recent victory in Montana based on Montana’s constitution,” a win that came despite the fact that it was decided in a place that “might not strike you as particularly hospitable to transgender rights.”
“The state constitutional law claims are particularly promising,” he said, “but it’ll be very context specific,” with the cases ultimately turning on the language contained in these different constitutions and “what sort of jurisprudence we have in each particular state.”
Per Lambda Legal, “On Dec. 11, 2024, the Montana Supreme Court upheld a preliminary injunction that (Senate Bill) 99 was likely unconstitutional under the Montana state constitution’s privacy clause, which prohibits government intrusion on private medical decisions. The ruling rested entirely on state constitutional grounds, insulating transgender adolescents, their families and health care providers from any potential negative outcome at the U.S. Supreme Court.”
Lau said the remaining two primary avenues for challenging anti-trans healthcare restrictions are likely to be animus based claims and cases grounded in arguments about parental rights, a phrase that often crops up in the context of efforts to undermine rather than strengthen freedoms and protections for LGBTQ people.
The reasoning was cited in a 2023 decision by a federal judge in Idaho who temporarily struck down the state’s ban on gender affirming care for kids, writing: “Transgender children should receive equal treatment under the law … Parents should have the right to make the most fundamental decisions about how to care for their children.”
Asked whether he believes jurists will consider parental rights or animus the more persuasive argument, Lau demurred, telling the Blade “I would be hesitant to say which one is more promising,” noting that animus claims often turn on very specific evidence that might show for example that the lawmakers behind a ban or restriction on transgender medicine were driven by sex stereotypes, irrational fear, or disgust toward a particular group.
Animus and the intersex exceptions
Asked whether anti-trans legislators are being counseled to avoid overt expressions of anti-trans sentiment or prejudice for fear that they might provide grounds for a successful legal challenge against their gender affirming care bans, he said “I think that’s very possible,” adding that “legislators are savvier now in terms of concealing their motives and their biases.”
“Philosopher Martha Nussbaum was monumental and unpacking disgust as an element of animus,” Lau said. “And so in my article, I try to unpack it to help readers connect the dots that there is this visceral disgust towards both intersex children and transgender minors, and that that can be connected to the doctrine of animus.”
In their paper, Lau and Fedders focused on the potential for courts to find inferred animus in laws like Tennessee’s SB 1 based on how they are structured, with sweeping restrictions on the one hand coupled with exceptions on the other that would allow families to pursue medical interventions for their children only when they have certain conditions or diagnoses.
“If we couple that with evidence from the legislative record” pointing to animus “there may be a case to be made,” Lau said.
Both the opinions in Skrmetti and the language of the SB 1 statute address how the law allows otherwise prohibited treatments or interventions to be administered to minors when they are indicated for diagnoses other than gender dysphoria or used for purposes other than gender transitions.
“They don’t call them intersex exceptions,” Lau said, but rather “exceptions for congenital defects,” defined as “including DSDs, disorders in sexual development — or what many intersex advocates would now refer to as ‘differences’ in sexual development.”
Interact, an intersex rights organization, “filed an amicus brief in Skrmetti that dovetailed with my article in that they argued the intersex exceptions support the idea that there are sex stereotypes that undergird the gender affirming care bans,” he said.
“I would like to see more discussion of the interplay between transgender rights and intersex rights,” Lau added, noting how questions about intersex vis-a-vis trans identities are relevant beyond the context of healthcare restrictions. For instance, he pointed to the Trump-Vance administration’s directive for the State Department to not allow passport holders to have the gender markers on their documents changed to align with their gender identity, also removing the option to select ‘X’ rather than the male/female binary category.
“The restrictions on passports not only affect transgender folks, but also non-binary and intersex folks as well,” Lau said. “And with respect to the bans on gender affirming care, not only do they restrict transgender youth’s access to gender affirming care, but they reflect and reinforce this understanding of intersex conditions that is very harmful and damaging to intersex youth.”
-

 U.S. Supreme Court3 days ago
U.S. Supreme Court3 days agoSupreme Court upholds ACA rule that makes PrEP, other preventative care free
-

 U.S. Supreme Court3 days ago
U.S. Supreme Court3 days agoSupreme Court rules parents must have option to opt children out of LGBTQ-specific lessons
-

 National5 days ago
National5 days agoEvan Wolfson on the 10-year legacy of marriage equality
-
 Congress4 days ago
Congress4 days agoSenate parliamentarian orders removal of gender-affirming care ban from GOP reconciliation bill






