World
Out in the World: LGBTQ news from Europe and Asia
South Korea court upheld criminalization of same-sex relations in the military

South Korea
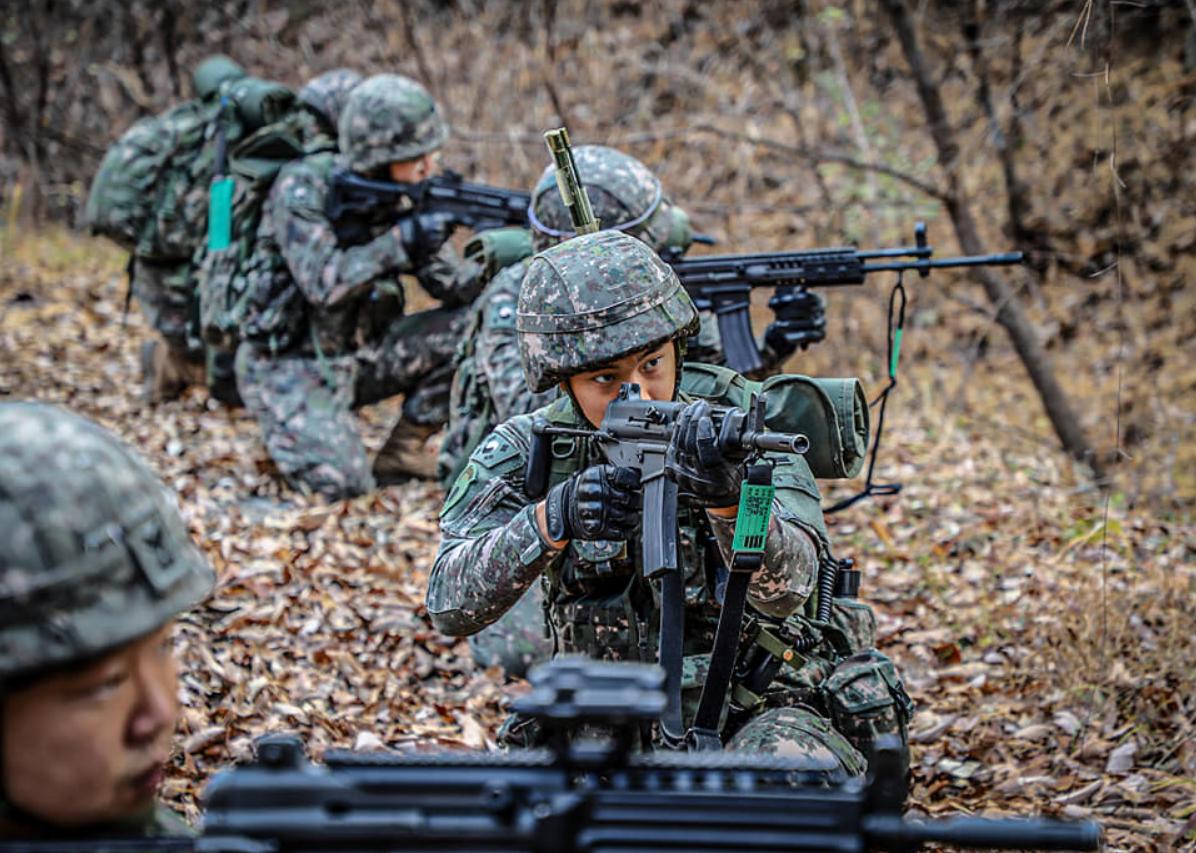

This past week on Oct. 27, the second highest court in South Korea upheld an earlier ruling for the fourth time, the Military Criminal Act, that criminalizes same-sex relations in the military.
The Constitutional Court of South Korea, in a 5-4 vote, ruled that article 92-6 of the military criminal act was constitutional. Justices in their ruling stated that same-sex activities might undermine discipline and harm the combat capabilities of the military. Same-sex activities between civilians however, is not a crime.
Article 92-6 of the Military Criminal Act (“Article 92-6”) provides that a person who commits anal intercourse or any other indecent act with “a military person” shall be punished by imprisonment for not more than two years.
Human rights activists have noted that the South Korean military has invoked Article 92-6 to punish sexual acts between male servicemen with sentences of up to two years in prison — regardless of whether the acts were consensual or whether they happened within or outside of military facilities.
Several of South Korea’s allies including the U.S. and the U.K. have repealed provisions similar to Article 92-6 of the Military Act of South Korea in order to align with international obligations to protect against the discrimination of LGBTQ people.
The executive director of the Center for Military Human Rights Korea, which provides legal assistance to soldiers including those accused of breaking the anti-sodomy law, Lim Tae-hoon said the decision was “absurd, illogical, regressive and driven by prejudice.
“While the world has been making progress in abolishing discrimination against minorities over the past 20 years, the minds of the judges have not advanced even a single step,” he added.
Lim pointed out that: “this law can be abused at any time to harass many sexual minority soldiers due to their sexual orientation. In addition, among the constitutional appeal cases supported by the Military Sexual Violence Counseling Center affiliated with the Military Human Rights Center, there is one case in which the military prosecutors believed the words of the perpetrator of same-sex sexual violence and suspended indictment by claiming that the sexual intercourse was consensual with the victim.
“The perpetrator was sentenced to three years in prison by the final ruling of the Supreme Court and is currently serving his sentence. Constitutional Court judges argue that the law of indecent assault should remain in place to protect victims of same-sex sexual violence in the military, but in reality, it is being abused as a means of imprisoning and punishing victims. Without understanding how the world works or how the law operates, they were caught up in prejudice and stubbornness and made regressive decisions.”
Japan

Last week on Oct. 25, Japan’s highest court ruled in a unanimous decision that the country’s law mandating sterilization surgery for transgender people as a requirement for legal gender recognition was unconstitutional.
In the ruling, the 15 justices wrote: “Being forced to undergo sterilization surgery … constitutes a significant constraint on freedom from invasive procedures” in violation of the Japanese Constitution.
Human Rights Watch Japanese Director Kanae Doi noted that since 2004, trans people in Japan who want to legally change their gender must appeal to a family court. Under the Gender Identity Disorder Special Cases Act, applicants must undergo a psychiatric evaluation, be surgically sterilized, and “have a physical form that is endowed with genitalia that closely resemble the physical form of an alternative gender.” They also must be single and without children who are younger than 18.
In May 2023, the Supreme Court ruled in favor of the right of a trans woman government employee to use the restrooms in accordance with her gender identity. In November 2022, the government in Japan’s Kanagawa prefecture awarded another trans woman workplace compensation after recognizing her depression was the result of harassment she faced from her supervisor.
Earlier this month, a local family court ruled in favor of a trans man, Gen Suzuki, who requested to have his gender legally changed without undergoing the surgery, the BBC reported.
The family court judge, Takehiro Sekiguchi, said the current law violated Article 13 of the constitution that stipulates all people shall be respected as individuals.
According to the Japanese government’s statistics, sexual minorities (LGBTQ) make up for 3 to 8 percent of the population and that at most, the statistics estimate that around 0.7 percent of the population is trans.
They are an overwhelming minority. The overwhelming majority of people do not know about trans people, and various prejudices are widespread.
The “LGBT Understanding Promotion Act,” which was passed by the Japanese Parliament in June 2023, includes the sentence “we will take care to ensure that all citizens can live their lives with peace of mind,” but according to Japanese trans activist Aya Nishida, the background to this is “If you say you are a woman at heart, you are a man. This is because some people have discriminatory views such as, “If transgender people’s human rights are recognized, women’s human rights will be threatened.”
Nishida provides training on the human rights of trans people to local governments, about issues surrounding trans people.
While the Supreme Court has ruled against the sterilization requirement, it has asked a lower court to review the requirement to have “genitalia that closely resemble the physical form of an alternative gender.”

As of Oct. 1, 26 local governments in at least 12 prefectures across the country have enacted ordinances that codifies the prohibition of “outing,” which is the act of disclosing a person’s sexual orientation or gender identity without their consent.
According to a study conducted by the Research Institute of Local Government in Tokyo, these efforts highlights that some municipalities have made to protect the human rights of LGBTQ people since passage of the Act to Promote Understanding of LGBT and Other Sexual Minorities by Parliament this past June. That does not explicitly prohibit acts such as outing.
According to human rights groups and LGBTQ advocacy organizations, outing constitutes a serious human rights violation and it was defined as a form of abuse of power in the guidelines for legislation.
The Kyodo News reported that in July this year, it was disclosed that a man had been deemed eligible for compensation from his employer by a Tokyo labor office last year after his boss revealed he was gay without his consent, but the current law is limited in scope to the workplace.
The harmful consequences of outing hit the national consciousness in 2015, when a graduate student of Hitotsubashi University in Tokyo died after plunging from a school building in an apparent suicide after being outed as gay.
In the wake of that incident, the city of Kunitachi, which hosts the university, became the first local government to enforce an ordinance banning the outing of LGBTQ people in April 2018.
In a statement to media outlets in Japan, Yuichi Kamiya, the executive director of the LGBT Law Federation said:
“Outing is considered harassment and must be prevented in the workplace, but there are no laws in place for other settings such as schools and medical care, so it is difficult to know what constitutes it and what specific details are required. There is still not widespread understanding of how to respond.
It is important to clearly state the prohibition in ordinances, and it can also lead to public awareness, prevention and relief in the event of damage. The more discriminatory the environment surrounding the person concerned, the greater the impact of outing. Further awareness is needed in each field to prevent further damage. When someone comes out, the first thing you should do is ask them who they can talk about and how much they can talk about. If you have any concerns, please consult with a specialist who respects confidentiality obligations.”
Currently, none of the ordinances passed across Japan have criminal law penalties.
Hungary
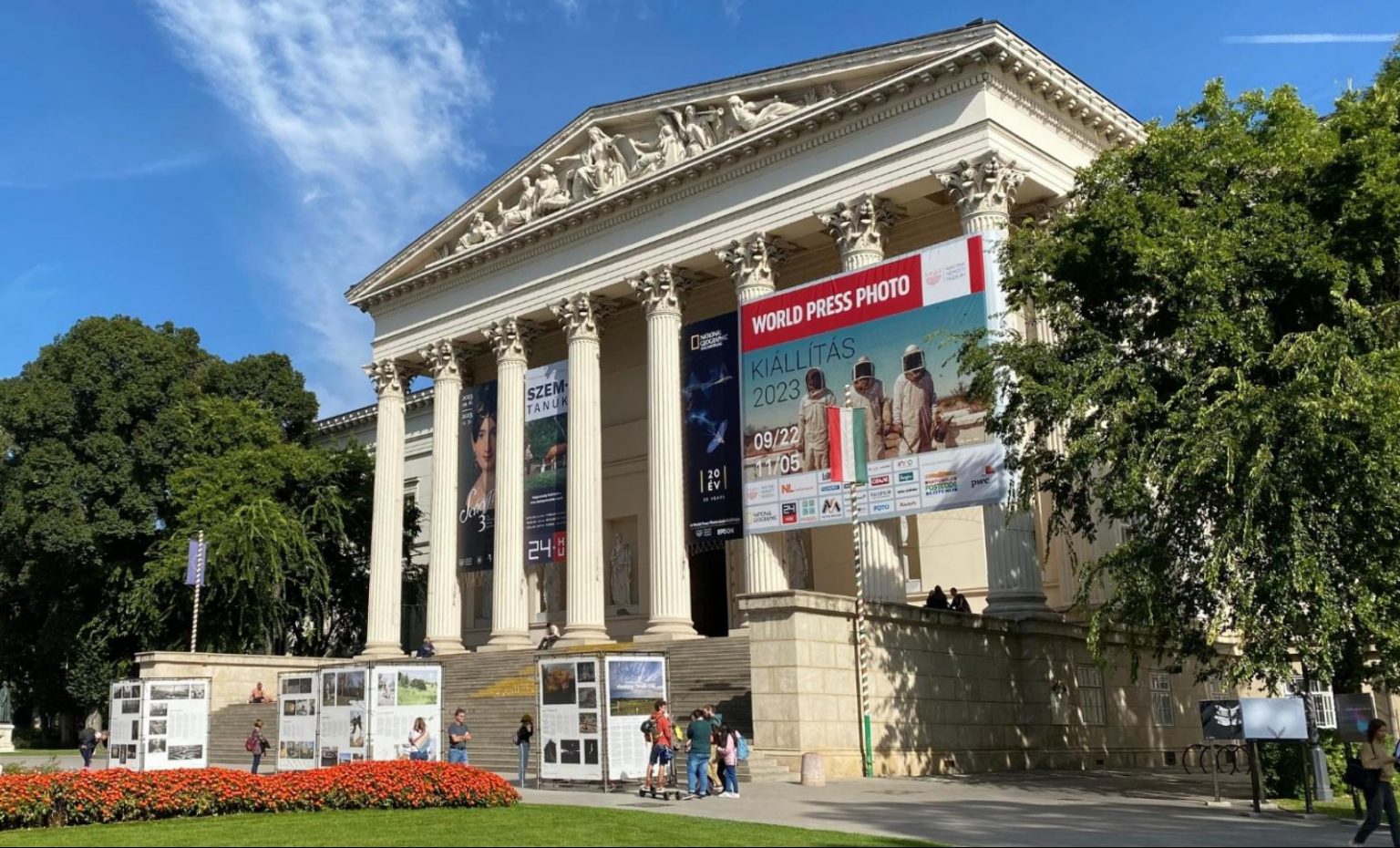

The far-right anti-LGBTQ government of Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orbán has banned children under the age of 18 from visiting the World Press Photo exhibition Hungarian National Museum in Budapest, citing LGBTQ content in some of the photos.
Since taking power, Orbán and his ruling party have waged an unceasing campaign to restrict the rights of LGBTQ Hungarians. In July 2021, the government passed a law that bans the promotion of homosexuality and sex-reassignment surgery to minors in the country.
This past summer Hungary’s second-largest bookstore chain was fined for violating the 2021 law that limits the access of minors to books, media content and advertisements that “promotes or portrays” the so-called “divergence from self-identity corresponding to sex at birth, sex change or homosexuality.”
The chain was fined for selling copies of British author Alice Oseman’s LGBTQ graphic novel series “Heartstopper,” a global phenomena due to the runaway hit Netflix show based on her books in the series.
According to the interpretation of the Háttér Society, a Hungarian organization focused on LGBTQ rights, a parent could break the law solely by buying a child a young adult novel that features an LGBTQ character.
Reuters reported that this past Saturday, the museum stopped selling tickets for the photo exhibition for youngsters after the far-right Our Homeland party had initiated a government inquiry, the party said.
“Based on the initiative of Mi Hazank, youngsters under 18 cannot visit the exhibition at the National Museum as it violates the child protection law,” the far-right party told state news agency MTI. The new rule was posted on the museum’s website later on Saturday.
Neither the museum nor the Our Homeland party responded to requests for comment.
The Vatican
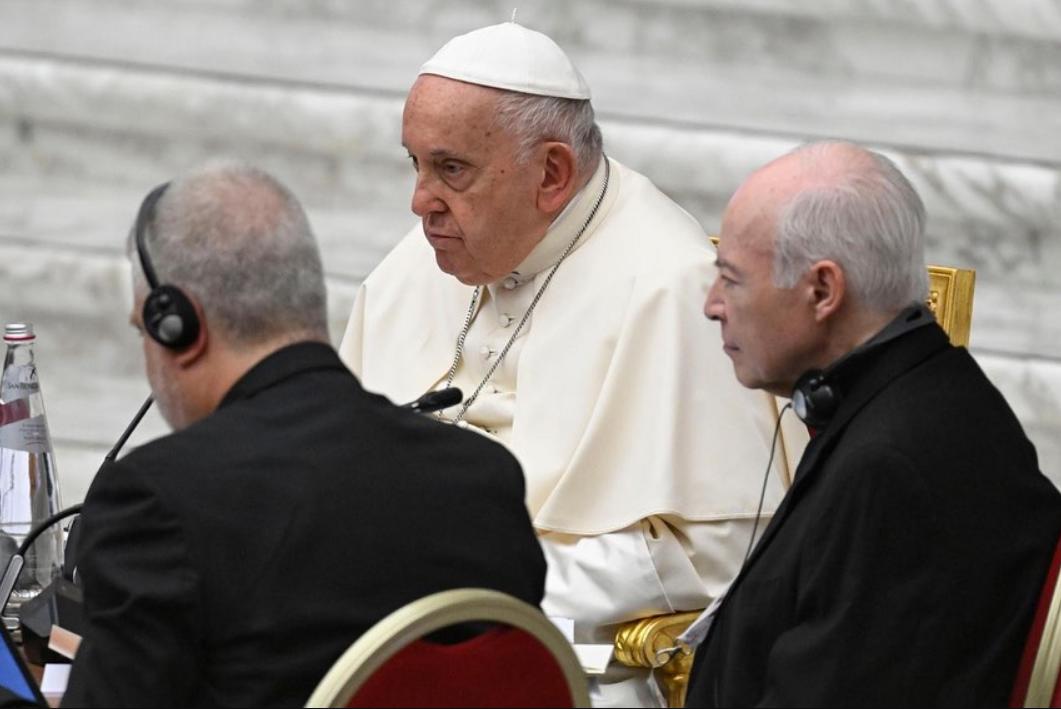

The month-long conference held in the Paul VI Hall at the Vatican regarding the future of the world-wide Roman Catholic Church ended on Saturday, without a clear course of action for the church on the issues of ordaining women as deacons or the treatment and care for its LGBTQ members.
The gathering, known as a Synod of Bishops, followed an unprecedented two-year canvassing of rank-and-file Catholics. The 365 synod participants included 300 bishops along with lay men and about 50 women who were mostly lay people, Reuters reported.
At the synod, the pope gave women and lay people a vote on church affairs for the first time. The participants meet for a final session in a year, then the pope will write a document on issues facing the church.
A 41-page report, approved and published Saturday at the close of the conference, called for the results of earlier papal and theological commissions on women deacons to be presented for further consideration at the next assembly of the Synod of Bishops, to be held in October 2024.
The report, titled “A synodal church in mission,” did not take a stand on LGBTQ issues despite discussion beforehand that the synod might call on the church to be more welcoming to the LGBTQ community, Reuters reported.
During a press briefing after the publication of the final report, Cardinal Mario Grech, who heads the Vatican’s synod office, on a question regarding LGBTQ Catholics, said that the assembly felt a need to “respect everyone’s pace.” He added: “It doesn’t mean if your voice is stronger it will prevail.”
Jesuit Fr. James Martin, a popular spiritual author and editor of the LGBTQ Catholic publication Outreach who took part in the synod as a voting member, told the National Catholic Reporter he was “disappointed but not surprised” by the result for LGBTQ Catholics.
“There were widely diverging views on the topic,” said Martin. “I wish, however, that some of those discussions, which were frank and open, had been captured in the final synthesis.”
United Kingdom
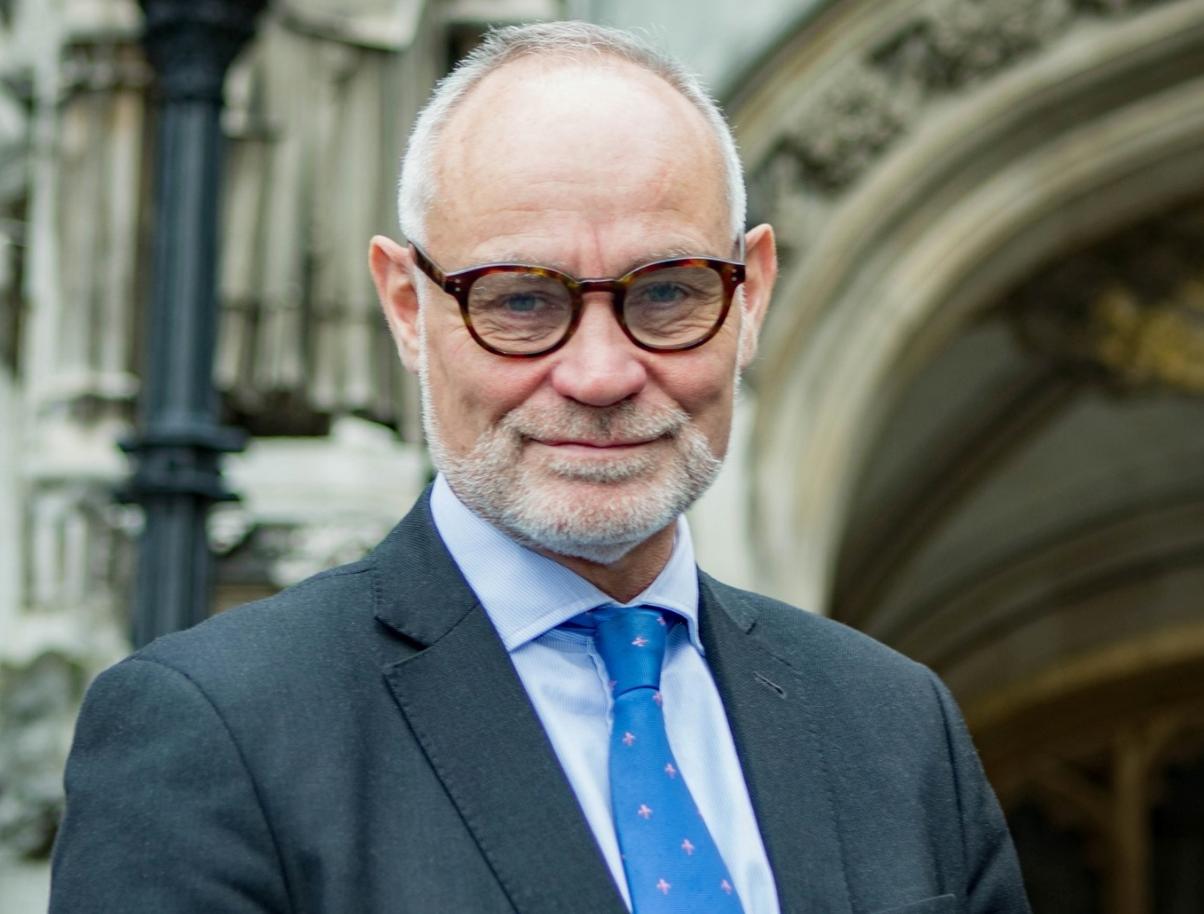

Crispin Blunt, the openly gay Conservative MP for Reigate was arrested in connection with an allegation of rape and possession of a controlled substance earlier this month at his home in Horley by the Surrey Police.
Blunt, served for two years as a justice minister and two years as chair of the Foreign Affairs Committee in the House of Commons, publicly came out as gay in 2010, announcing that he had separated from his wife and was “coming to terms with his homosexuality.”
British media outlet The Telegraph reported Blunt claimed in a statement that Surrey Police had begun an investigation three weeks ago when he reported “concerns over extortion.” The Conservative Party confirmed on Thursday night the 63-year-old has been stripped of the party designation, effectively meaning he has been expelled from the Conservative Party. He will now sit in the House of Commons in Parliament as an Independent member.
Taking to X, formerly Twitter, Blunt posted a statement saying, “The fact of the arrest requires a formal notification of the speaker and then my chief whip.
I have now been interviewed twice in connection with this incident, the first time three weeks ago, when I initially reported my concern over extortion. The second time was earlier this morning under caution following arrest.”
“The arrest was unnecessary as I remain ready to cooperate fully with the investigation that I am confident will end without charge,” Blunt continued. “I do not intend to say anything further on this matter until the police have completed their inquiries,” he added.
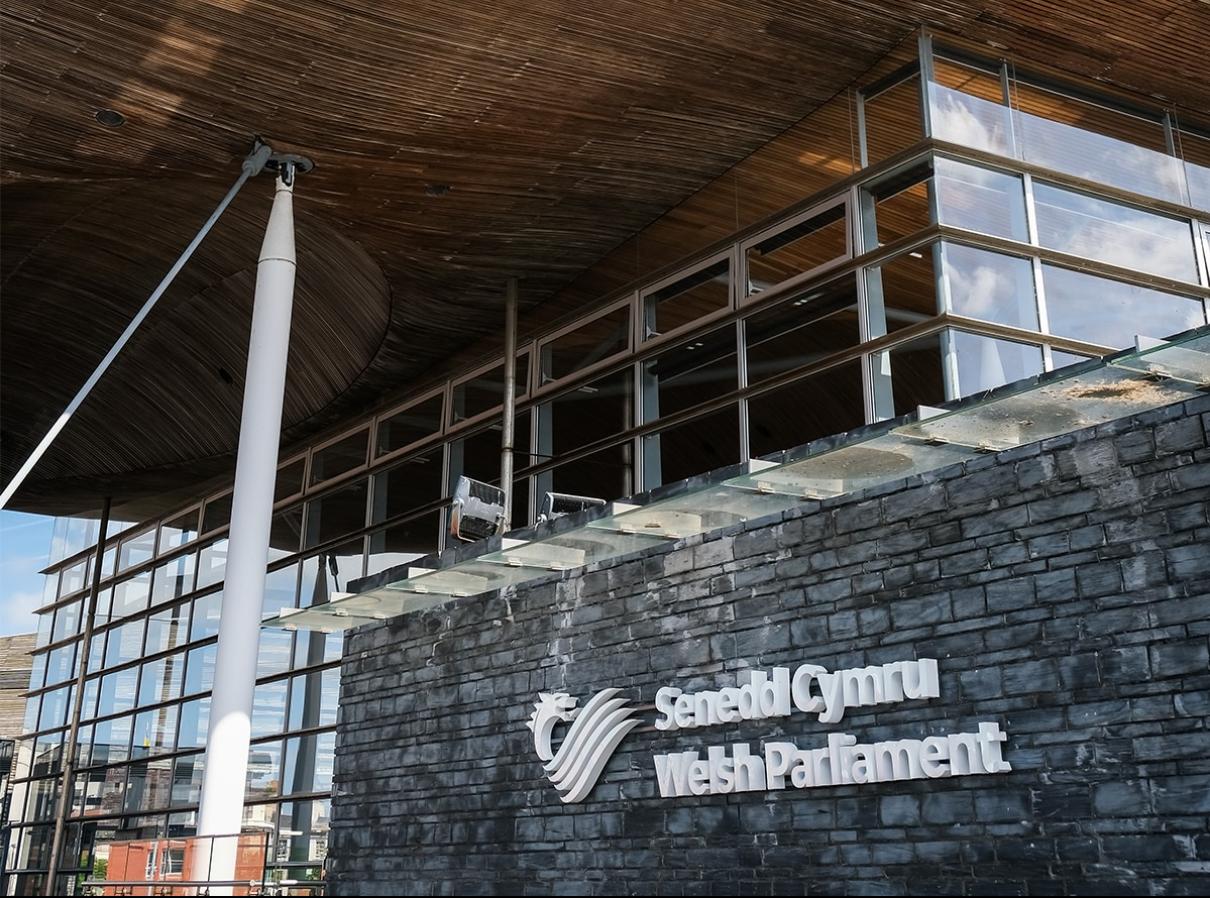

The Welsh government appears to be setting itself on a potential collision course with Prime Minister Rishi Sunak’s government after the leak of a draft of the Welsh government’s Gender Quotas Bill Sunday evening, which would allow people to self-identify their gender when running for the Welsh Parliament.
The Telegraph reported that the bill proposes plans for a gender-balanced Parliament by having set equal quotas for male and female political candidates. Under this draft bill, the definition of a woman will be updated, so that the female quota of party candidates running for office may include trans women.
The definition further stated that trans meant “a person who is proposing to undergo, is undergoing or has undergone a process (or part of a process) for the purpose of reassigning [their] sex to female by changing physiological or other attributes of sex.”
Reaction from transphobic opponents included an outspoken “gender critical” leader, Cathy Larkman from Women’s Rights Network Wales, who said in an emailed statement:
“We know from bitter experience that Welsh government is not listening to the concerns of women in Wales. We, along with other groups, have been shut out time and again. Unfortunately, the reasons for this are now apparent.
The government is now intent on driving a highly contested ideological agenda and this is clearly their first step. It is astonishing that the government is spending public funds and using a Gender Quotas Bill to promote an agenda which undermines the rights of half the population of Wales.
It is shameful that they are high-jacking legislation that should benefit women and increase female participation in political life, to embed a toxic and misogynistic ideology. We believe that the intention of the Welsh government is to introduce gender self-identification and put it on a statutory footing.
We believe this is the first step towards a full self-ID bill which would have serious implications for women and girls in particular as it would impact on single-sex services and spaces such as changing rooms, intimate care, hospital wards and domestic violence services.
It is unforgivable that the first minister and his government, aided and abetted by Plaid Cymru [a political party] intend to betray the women of Wales in this underhand way.”
PinkNewsUK noted that this bill echoes a similar plan put forward by the Scottish government in January that would have made it easier for people to legally change their gender, which was blocked by the UK government.
The leak has had a mixed response from the public. While the trans community and its advocates are pleased with the progressive step forward, anti-trans hate groups and so-called women’s rights groups are up in arms.
Commenting on the leaked bill, a spokesperson for the Welsh government told the Telegraph that it did not represent the latest version of the Gender Quotas Bill, though they did not say whether that had to do with the redefinition of women.
“Our proposed model for quotas is designed to maximize the chances of achieving a Senedd comprised of at least 50 percent women. Work is ongoing on the bill,” said the spokesperson.
The first minister of Wales, Mark Drakeford, has been a longtime defender of trans rights, and has repeatedly shared his pro-trans beliefs in Parliament, PinkNewsUK also reported.
Additional reporting by the Kyodo News, the BBC, Reuters, Agence France-Presse, the Telegraph and PinkNewsUK
Iran
Man stuck in Lebanon as Iran war escalates
Mario was traveling to India when conflict began on Feb. 28
The Washington Blade on March 6 spoke with a man who remains stuck in Lebanon because of the escalating Iran war.
Mario, who asked the Blade not to publish his last name, lives in the U.S., but was born in Lebanon. He decided to stop in the country to see his doctor before traveling to India for work.
Mario was about to board a flight at Rafic Hariri International Airport in Beirut, the Lebanese capital, on Feb. 28 when airline personnel announced “we cannot fly anymore” because authorities had closed the country’s airspace.
The U.S. and Israel earlier that day launched airstrikes against Iran.
One of them killed Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. Iran in response launched missiles and drones against Israel and Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Azerbaijan, Cyprus, and other countries.
An Iranian drone that hit a command center in Kuwait on March 1 killed six U.S. soldiers: Sgt. Declan Coady, Sgt. 1st Class Nicole Amor, Capt. Cody Khork, Sgt. 1st Class Noah Tietjens, Chief Warrant Officer 3 Robert Marzan, and Maj. Jeffrey O’Brien. Another American servicemember, Sgt. Benjamin Pennington, died on Sunday, a week after Iranian drones and missiles targeted the Prince Sultan Air Base in Saudi Arabia.
Iranian drones and missiles have also damaged civilian infrastructure, including hotels and airports in Dubai in the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait. An Iranian missile on March 1 killed nine people and injured 27 others in Beit Shemesh, Israel.
The war has left Mario and hundreds of thousands of others stranded in the Middle East.
“I had to come back home,” Mario told the Blade.
“Luckily, I’m with family,” he added.
‘War is between Israel and Hezbollah’
Hezbollah, an Iran-backed Shia militant group the U.S. and Israel have designated a terrorist organization, after Khamenei’s death launched rockets at Israel. The Jewish State in response has carried out airstrikes against Hezbollah targets across Lebanon.
Hamas militants on Oct. 7, 2023, killed upwards of 1,200 people when they launched a surprise attack against Israel from the Gaza Strip. Hezbollah the following day began to launch rockets into Israel.
An Israeli airstrike in Beirut on Sept. 27, 2024, killed Hassan Nasrallah, Hezbollah’s long-time leader. Iran four days later launched upwards of 200 ballistic missiles at Israel.
The U.S. helped broker a ceasefire between Israel and Lebanon that took effect on Nov. 27, 2024. Israel nevertheless continued to carry out airstrikes in Lebanon.
Israel on June 13, 2025, launched airstrikes against Iran that targeted the country’s nuclear and military facilities. The subsequent war, which lasted 12 days, prompted the cancellation of the annual Tel Aviv Pride parade.
Mario noted the Israeli airstrikes have targeted Hezbollah infrastructure in Dahiyah, a Beirut suburb that is predominantly Shia, and in southern Lebanon.
His family’s home is about five miles from downtown Beirut. Mario said there is a mountain “that separates me from the area that is being bombed, so I don’t even hear the sounds.”
“Lebanon is such an interesting juxtaposition, because depending on which area you are in, your quality of life can be different during these times,” he said. “Right now, the war is not between Israel and Lebanon as a government. The war is between Israel and Hezbollah.”
“If you are in the areas where Hezbollah is concentrated, then you are severely impacted,” added Mario. “If you are in other areas, even if they are Shia or … Muslims that usually align themselves with Hezbollah, you’re still relatively in a safe place, in a safe location.”
Israeli evacuation orders have prompted hundreds of thousands of people to flee their homes in Dahiyah and in southern Lebanon.
Mario said many of the evacuees are sleeping in their cars, or on the street. He also noted a video that showed a shepherd with his sheep and goats on a highway in downtown Beirut.
“He took his animals with him because he had to vacate where he was living,” said Mario. “That’s the first time you see in downtown Beirut maybe 100 goats walking the streets with two people sitting on jackasses and herding them.”
“It is very absurd,” he added.
The Lebanese government has opened schools and public shelters for people who have been displaced, but Mario said many of them do not have enough food. He also said gas prices have increased, and people are afraid to drive.
“It really saddens me seeing the kids affected by it,” said Mario. “Hezbollah made this decision, and it was a unilateral decision.”
“I doubt that the Shia people support them,” he added, referring to Hezbollah. “They cannot say it out loud that they do not support them, but I doubt people are happy within less than two years, for the second time in a row, to have to leave their homes and try to find a place to stay.”
Lebanese government urged to develop LGBTQ-inclusive plan for displaced people
Article 534 of Lebanon’s Penal Code states “any sexual intercourse contrary to the order of nature is punishable” by up to a year in prison. Several judges in recent years have opted not to use the statute to prosecute LGBTQ people who have been charged under it.
Helem, a Lebanese LGBTQ and intersex rights group, on March 4 called upon the Lebanese government and international NGOs to develop a response to the Israeli airstrikes that is “comprehensive, fair, and inclusive of all groups, without exception or discrimination.
“The experience of the previous war demonstrated that state response plans were not sufficiently inclusive of displaced LGBTQ+ individuals,” said Helem. “Many faced compounded challenges, including the inability to access state collective shelters, exposure to harassment or violence, difficulty accessing health and psychosocial services, and fear of disclosing their gender identity or sexual orientation due to stigma and discrimination.”
“Any emergency plan that fails to take the most vulnerable groups into account exposes their lives and dignity to additional risks,” added the group.
Helem also made the following requests:
• Integrating a rights-based and nondiscrimination approach in all stages of planning and implementation, ensuring safe and equal access to assistance and services.
• Training staff working in shelters and emergency response on principles of protection from gender-based violence and discrimination, including issues related to gender identity and sexual orientation.
• Reassessment of the currently adopted shelter model, which relies exclusively on the concept of the “traditional family” aligned with a specific social structure. In practice, this leads to the systematic exclusion of non-traditional families and individuals who do not belong to conventional family units, including LGBTQ+ individuals, survivors of domestic violence, migrant workers, and people without supportive family networks.
• Involving civil society organizations specialized in gender issues and LGBTQ+ rights in the design, implementation, and monitoring of the emergency response plan.
• Establishing clear monitoring and accountability standards to ensure that violations or discriminatory practices do not occur during the implementation of the emergency plan.
“Disasters and conflicts do not justify the suspension of rights or the neglect of marginalized groups. On the contrary, the need for a humanitarian approach grounded in dignity and equality becomes even more urgent in times of crisis.”
“Helem places its expertise and experience at the disposal of relevant authorities and affirms its readiness to cooperate to ensure that the emergency plan is more just, effective, and inclusive,” said Helem. “Dignity is indivisible, and protection must include everyone without exception.”
Colombia
Claudia López wins primary in Colombian presidential race
Former Bogotá mayor’s wife lost reelection bid on Sunday

Former Bogotá Mayor Claudia López on Sunday won her primary in the race to succeed Colombian President Gustavo Petro.
López, a centrist who is running as an independent, defeated Leonardo Huerta in the “Consulta de las Soluciones” primary.
López was the Colombian capital’s mayor from 2020-2023. She was a member of the Colombian Senate from 2014-2018.
López is running to succeed Petro, the country’s first leftist president who cannot seek a second consecutive term under Colombia’s constitution. Other presidential candidates who won their respective parties’ primaries on Sunday include Sen. Iván Cepeda, a member of Petro’s Historic Pact party, and Sen. Paloma Valencia of the conservative Democratic Center, the country’s main opposition party that former President Álvaro Uribe leads.
Juan Daniel Oviedo, who finished second in the Democratic Center’s primary, is openly gay.
The first-round of Colombia’s presidential election will take place on May 31.
Polls indicate López is trailing Cepeda and Valencia, who are considered the two frontrunners.
A second round will take place is no candidate receives at least 50 percent of the vote on May 31. López would become Colombia’s first female and first lesbian president if she wins the election.
López’s wife loses Senate seat
Colombia’s congressional elections also took place on Sunday.
Former Congressman Mauricio Toro, a member of the center-left Green Alliance party, in 2018 became the first openly gay man elected to Colombian Congress when he won a seat in the House of Representatives.
He lost his reelection bid in 2022. Voters on Sunday elected Toro for a second term.
Congresswoman María del Mar Pizarro, a bisexual Historic Pact member, won re-election.
Caribe Afirmativo, a Colombian LGBTQ and intersex rights group, notes only two of the 33 openly LGBTQ congressional candidates won their respective races. Among those who lost is Sen. Angélica Lozano, a bisexual woman who in 2018 became the first openly LGBTQ person elected to the Colombian Senate.
Lozano is married to López.
Lozano in a message posted to her Instagram page expressed “heartfelt gratitude to everyone for their support and love.”
“I will end my work in Congress on a high note by ensuring (the) child support and service contractor protection bills will become a reality in June,” she said.
Uganda
Ugandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow
Clare Byarugaba founded PFLAG-Uganda
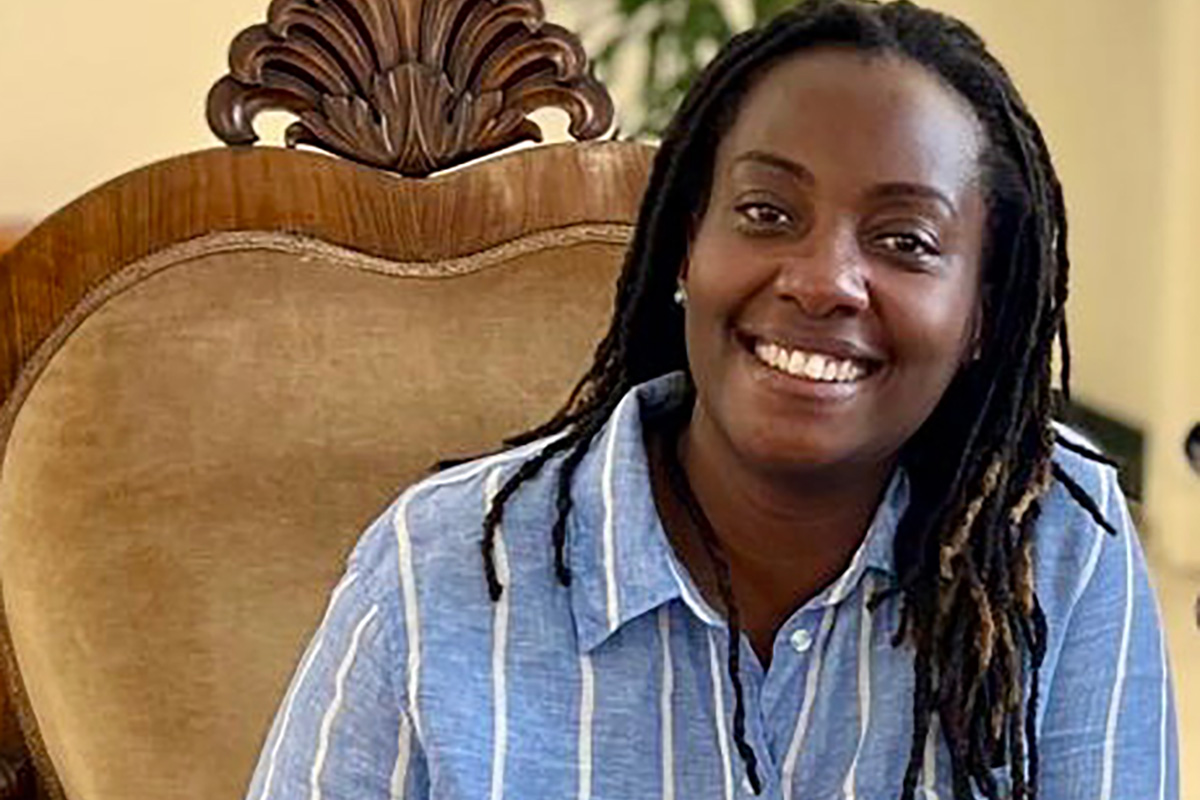

The Charles F. Kettering Foundation has named a prominent Ugandan LGBTQ activist as one of its 2026 fellows.
Clare Byarugaba, founder of PFLAG-Uganda, is one of the foundation’s five 2026 Global Fellows.
Byarugaba, among other things, has been a vocal critic of Uganda’s Anti-Homosexuality Act. Byarugaba in 2024 met with Pope Francis — who criticized criminalization laws during his papacy — at the Vatican.
The foundation on its website says it “is dedicated to bringing research and people together to make the promise of democracy real for everyone, everywhere.”
“Clare is the kind of hero who rushes toward the emergency to help,” said PFLAG CEO Brian K. Bond in a Feb. 27 statement to the Washington Blade. “She founded PFLAG-Uganda as the country pushed to criminalize homosexuality and those who support LGBTQ+ people. Yet, she never hesitated in her courage, telling us that families wanted to organize to keep their LGBTQ+ loved ones safe, and PFLAG was the way to do it. Clare Byarugaba not only deserves this honor, but she will use her compassion and experience to teach the world about LGBTQ+ advocacy as a Kettering Global Fellow.”




















