Africa
For queer Nigerians, being on gay dating apps is still a risk
Homophobes target users for violence

Gay hookup apps like Grindr, and dating apps like Tinder and Bumble have managed to proliferate queer communities in countries like Nigeria.
Those who seek one night stands find what they want while those looking for love equally find what they seek. These platforms have managed to position themselves as safe spaces for queer people in anti-gay Nigeria. In recent times, however, it is proving to be unsafe, as homophobic people are quickly learning about the apps, and opening accounts that either seek to outrightly threaten queer people, or pretend to be queer, have long chats with gay people, invite them over, and inflict violence on them.
Take the case of Biodun, a queer Nigerian man who joined Grindr to meet up with guys like him.
After Biodun had built a connection and agreed to meet with someone whose display name was “Mamba,” they decided to meet up only for him to be met with violence. Apparently, Mamba ran a catfish account.
“I’ll never forget that day,” Biodun, who asked the Washington Blade not to use his last name because of safety concerns, said. “I still think about it, and sometimes blame myself for being very careless, even though Grindr was supposed to be our safe space.”
Biodun’s experience isn’t peculiar to him.
In Nigeria, draconian laws that criminalize same-sex relationships exist, making queer people turn to the digital realm to explore their identities and seek connections beyond the confines of societal oppression that comes with the physical environment. Gay dating apps such as Grindr, therefore, have emerged as virtual sanctuaries, offering spaces for queer Nigerians to forge friendships, find solidarity, and pursue romantic or sexual relationships. Spaces like this, however, have morphed into a landscape fraught with danger, as homophobic people have weaponized these platforms to perpetuate hate and violence.
“Sometimes, I often wonder how they learned about these platforms,” Daniel, which is not his real name, told the Blade. “You would think that it is just us in the platforms, until you find out that the accounts are rooted in homophobia.”
One time, someone’s bio read, “I’m only here to deal with the gay people. I know all of you, and I will find and kill you. We no want una for here (translates to we do not want you here, in English.)” It was a stark reminder that these spaces are no longer LGBTQ-friendly for Nigerians. In 2014, there was the passage of the Same-Sex Marriage Prohibition Act by former President Goodluck Jonathan, which not only criminalized same-sex unions, but also imposed severe penalties on anyone involved in LGBTQ advocacy or support.
This law catalyzed a surge in discrimination and violence against queer Nigerians; emboldening regular civilians, religious extremists, and even law enforcement agencies to target individuals perceived as deviating from traditional gender and sexual norms. Again, amid this hostile environment, gay dating apps emerged as lifelines for many queer Nigerians, offering avenues for discreet communication, community building, and the pursuit of intimate relationships.
The very anonymity and freedom these apps provided, however, became double-edged swords.
The advent of screenshot and screen-recording capabilities on these apps, for example, reduced the risks of exposure, strengthening the safety and privacy of users. However, this also comes with its own lapses, as queer people using Grindr have often relied on screenshots and screen recordings to confirm the identities of potentials with their friends, before accepting to meet.
“Before the removal of the screenshot option, I usually shared photos of others with my trusted friends,” Biodun shared. “But since that was taken off, there was no way for me to do that.”
Although, according to Grindr’s terms and conditions, the removal came with privacy concerns, as it was to facilitate a safe dating experience.
This erosion of digital safe spaces is depriving queer Nigerians of vital avenues for self-expression and affirmation,and is exacerbating the psychological toll of living in a society that continues to systematically demonize their identities. Moreover, the normalization of homophobic rhetoric and violence in both physical and digital realms has perpetuated a cycle of fear and oppression, and is reinforcing this notion that LGBTQ individuals are inherently unworthy of dignity and respect. Despite these challenges, though, the resilience of queer Nigerians continue to persist, as they defy societal norms and assert their right to love and be loved.
Egypt
Iran, Egypt object to playing in Seattle World Cup ‘Pride Match’
Game to take place on June 26

Iran and Egypt have objected to playing in a “Pride Match” that will take place in Seattle during the 2026 World Cup.
The Egyptian Football Association on Tuesday said it told FIFA Secretary General Mattias Grafström in a letter that “it categorically rejects holding any activities related to supporting (homosexuality) during the match between the Egyptian national team and Iran, scheduled to be held in Seattle, USA, on June 26, 2026, in the third round of the group stage of the 2026 World Cup.” Football Federation Islamic Republic of Iran President Mehdi Taj told ISNA, a semi-official Iranian news agency that both his country and Egypt “protested this issue.”
The 2026 World Cup will take place in the U.S., Canada, and Mexico. The draw took place at the Kennedy Center on Dec. 5.
Iran is among the handful of countries in which consensual same-sex sexual relations remain punishable by death.
The State Department’s 2023 human rights report notes that while Egyptian law “did not explicitly criminalize consensual same-sex sexual activity, authorities regularly arrested and prosecuted LGBTQI+ persons on charges including ‘debauchery,’ prostitution, and ‘violating family values.’” Egyptian authorities “also reportedly prosecuted LGBTQI+ individuals for ‘misuse of social media.’”
“This resulted in de facto criminalization of same-sex conduct and identity,” notes the report.
The 2024 human rights report the State Department released earlier this year did not include LGBTQ-specific references.
Soccer has ‘unique power to unite people across borders, cultures, and beliefs’
The June 26 match between Iran and Egypt coincides with Seattle Pride. The Washington Post reported the Seattle FIFA World Cup 2026 Local Organizing Committee decided to hold the “Pride Match” before last week’s draw.
“As the Local Organizing Committee, SeattleFWC26’s role is to prepare our city to host the matches and manage the city experience outside of Seattle Stadium,” said SeattleFWC26 Vice President of Communications Hana Tadesse in a statement the committee sent to the Washington Blade on Wednesday. “SeattleFWC26 is moving forward as planned with our community programming outside the stadium during Pride weekend and throughout the tournament, partnering with LGBTQ+ leaders, artists, and business owners to elevate existing Pride celebrations across Washington.”
“Football has a unique power to unite people across borders, cultures, and beliefs,” added Tadeese. “The Pacific Northwest is home to one of the nation’s largest Iranian-American communities, a thriving Egyptian diaspora, and rich communities representing all nations we’re hosting in Seattle. We’re committed to ensuring all residents and visitors experience the warmth, respect, and dignity that defines our region.”
The 2034 World Cup will take place in Saudi Arabia.
Consensual same-sex sexual relations remain punishable by death in the country. The 2022 World Cup took place in neighboring Qatar, despite concerns over the country’s anti-LGBTQ rights record.
Eswatini
PEPFAR delivers first doses of groundbreaking HIV prevention drug to two African countries
Lenacapavir now available in Eswatini and Zambia.

The State Department on Tuesday announced PEPFAR has delivered the first doses of a groundbreaking HIV prevention drug to two African countries.
The lenacapavir doses arrived in Eswatini and Zambia.
The State Department in September unveiled an initiative with Gilead Sciences to bring lenacapavir “to market in high-burden HIV countries.”
Lenacapavir users inject the drug twice a year.
The State Department in its September announcement noted everyone who participated in Gilead’s clinical trials remained HIV negative. It also said lenacapavir “has the potential to be particularly helpful for pregnant and breastfeeding mothers, as it safely protects them during and after pregnancy to prevent mother-to-child transmission.”
“In our new America First Global Health Strategy, the Department of State is establishing a first-of-its-kind innovation fund to support American-led research, market-shaping, and other dynamic advancements in global health,” said PEPFAR on Tuesday in a press release.
“The arrivals of the first doses of lenacapavir in Eswatini and Zambia mark an important milestone in HIV prevention and reflect our commitment to supporting communities with the greatest need,” added Gilead CEO Daniel O’Day. “For the first time, a new HIV medicine is reaching communities in sub-Saharan Africa in the same year as its U.S. approval.”
The September announcement came against the backdrop of widespread criticism over the Trump-Vance administration’s reported plans to not fully fund PEPFAR and to cut domestic HIV/AIDS funding. The Washington Blade has previously reported PEPFAR-funded programs in Kenya and other African countries have been forced to curtail services or even close because of U.S. funding cuts.
Botswana
The first courageous annual Palapye Pride in Botswana
Celebration was a beginning rooted in courage, community, and love.
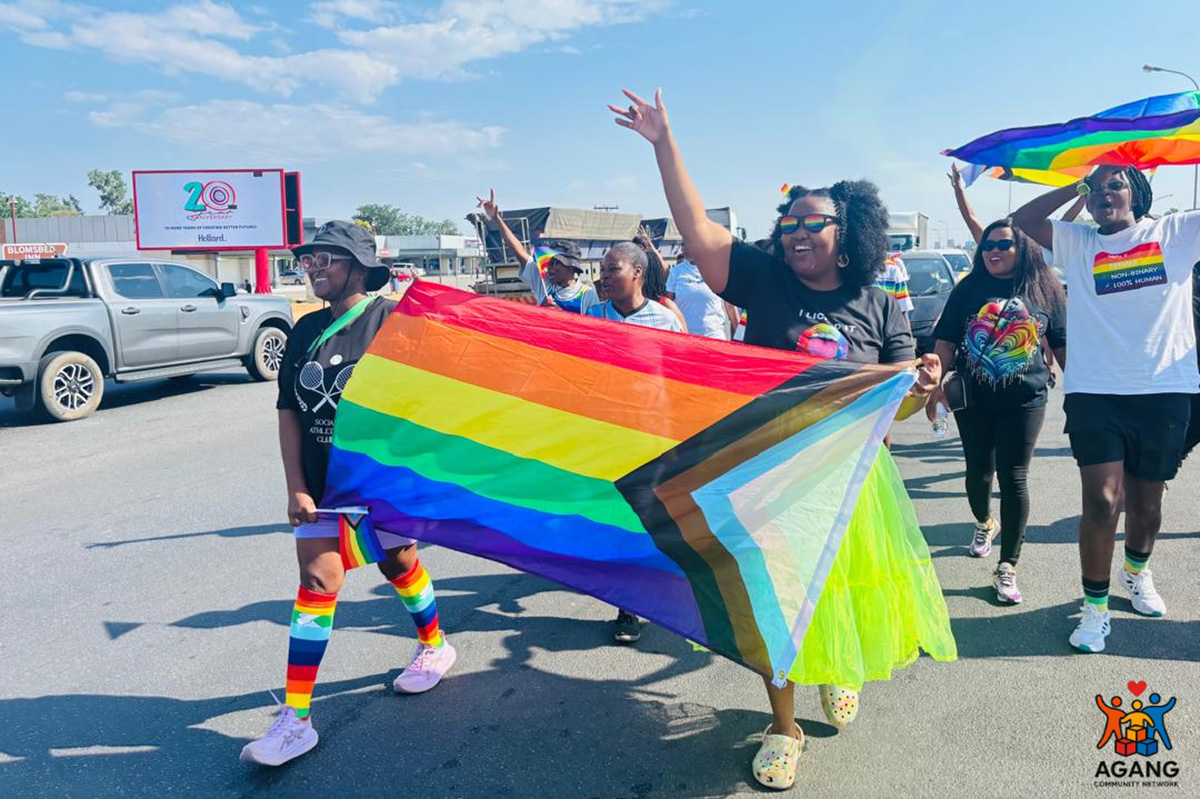

“When the sun rose on 1 Nov., 2025, Pride morning in Palapye, the open space where the march was scheduled to begin was empty. I stood there trying to look calm, but inside, my chest felt tight. I was worried that no one would come. It was the first-ever Pride in Palapye, a semi-urban village where cultural norms, religious beliefs, and tradition are deeply woven into everyday life.
I kept asking myself if we were being naive. Maybe people weren’t ready. Perhaps fear was going to win. For the first 30 minutes, it was me, a couple of religious leaders and a handful of parents. That was it. The silence was loud, and every second felt like it stretched into hours. I expected to see the queer community showing up in numbers, draped in color and excitement. Instead, only the wind was moving.
But slowly, gently, just like courage often arrives, people started to show up with a rainbow flag appearing from behind a tree and a hesitant wave from someone standing at a distance.
That’s when I understood that people weren’t late, just that they were afraid. And their fear made sense. Showing up openly in a small community like Palapye is a radical act. It disrupts silence. It challenges norms. It forces visibility. Visibility is powerful, but it is never easy. We marched with courage, pulling from the deepest parts of ourselves. We marched with laughter that cracked through the tension. We marched not because it was easy, but because it was necessary,” narrates activist Seipone Boitshwarelo from AGANG Community Network, which focuses on families and friends of LGBTIQ+ people in Botswana. She is also a BW PRIDE Awards nominee for the Healing and Justice Award, a category which acknowledges contributions to wellness, mental health, and healing for the LGBTIQ+ community across Botswana.
Queer Pride is Botswana Pride!
Pride is both a celebration and a political statement. It came about as a response to systemic oppression, particularly the criminalization and marginalization of LGBTIQ+ people globally, including in Botswana at some point. It is part of the recognition, equality, and assertion of human rights. It also reminds us that liberation and equality are not automatically universal, and continued activism is necessary. A reminder of the famous saying by Fannie Lou Hamer, “Nobody is free until everybody’s free.”
The 2023 Constitutional Review process made one thing evident, which is that Botswana still struggles to acknowledge the existence of LGBTIQ+ people as full citizens. Instead of creating a democratic space for every voice, the process sidelined and erased an entire community. In Bradley Fortuin’s analysis of the Constitutional review and its final report, he highlighted how this erasure directly contradicts past court decisions that explicitly affirmed the right of LGBTIQ+ people to participate fully and openly in civic life. When the state chooses to ignore court orders and ignore communities, it becomes clear that visibility must be reclaimed through alternative means. This is why AGANG Community Network embarked on Palapye Pride. It is a radical insistence on belonging, rooted in community and strengthened through intersectionality with families, friends, and allies who refuse to let our stories be erased.
Motho ke motho ka batho!
One of the most strategic decisions made by the AGANG Community Network was to engage parents, religious leaders, and local community members, recognizing their value in inclusion and support. Thus, their presence in the march was not symbolic, but it was intentional.
Funding for human rights and LGBTIQ+ advocacy has been negatively impacted since January 2025, and current funding is highly competitive, uneven and scarce, especially for grassroots organizations in Botswana. The Palapye Pride event was not funded, but community members still showed up and donated water, a sound system, and someone even printed materials. This event happened because individuals believed in its value and essence. It was a reminder that activism is not always measured in budgets but in willingness and that “motho ke motho ka batho!” (“A person is a person because of other people!”).
Freedom of association for all
In March 2016, in the the Attorney General of Botswana v. Rammoge and 19 Others case, also known as the LEGABIBO registration case, the Botswana Court of Appeal stated that “members of the gay, lesbian, and transgender community, although no doubt a small minority, and unacceptable to some on religious or other grounds, form part of the rich diversity of any nation and are fully entitled in Botswana, as in any other progressive state, to the constitutional protection of their dignity.” Freedom of association, assembly, and expression is a foundation for civic and democratic participation, as it allows all citizens to organize around shared interests, raise their collective voice, and influence societal and cultural change, as well as legislative reform.
The Botswana courts, shortly after in 2021, declared that criminalizing same-sex sexual relations is unconstitutional because they violated rights to privacy, liberty, dignity, equality, and nondiscrimination. Despite these legal wins, social stigma, cultural, and religious opposition continue to affect the daily lived experience of LGBTIQ+ people in Botswana.
The continuation of a declaration
AGANG Community Network is committed to continuing this work and creating safe and supportive spaces for LGBTIQ+ people, their families, friend, and allies. Pride is not just a day of fun. It is a movement, a declaration of queer existence and recognition of allyship. It is healing and reconciliation while amplifying queer joy.
Seipone Boitshwarelo is a feminist, activist, social justice healer, and founder of AGANG Community Network. Bradley Fortuin is a social justice activist and a consultant at the Southern Africa Litigation Center.