Health
Pre-AIDS conference events to focus on gay men’s health, sex workers rights
Gay Men’s Health Summit will take place at GWU on Friday and Saturday

With about 30,000 people expected in D.C. for the International AIDS Conference; a number of panels and other events are scheduled to take place in D.C. before AIDS 2012 officially opens on Sunday.
The Gay Men’s Health Summit will take place at George Washington University on Friday and Saturday. Whitman-Walker Health, Us Helping Us, the D.C. LGBT Community Center, The GWU School of Medicine and Health Sciences, the National Coalition for LGBT Health and Master Taino’s Leather Family co-sponsored the two-day gathering that will feature more than 40 workshops on a range of topics. These include coming out as an older adult, mental health and addiction among gay and bisexual men.
Activist and researcher Dan O’Neill and Brant Miller of the D.C. Center on Friday will present a workshop on the D.C. FUK!T campaign that uses sexually explicit messages to promote condom and lube use among men who have sex with men. HIV/AIDS activists in Seattle launched a similar initiative last year, but O’Neill told the Blade that he is optimistic that service providers in other cities will create their own FUK!T-inspired safer-sex campaigns.
“Hopefully with the diverse audience that will be there, they can recreate similar programs where they are if they aren’t already there,” he said.
Latino GLBT History Project President David Pérez and others on Saturday will present a workshop on the impact of HIV/AIDS on gay Hispanics. Frank Walker and DeAndre Roberts of Youth Pride Services and DeAndre Preston of Code Red will moderate a panel on young black gay men in the United States on Friday. This workshop will also coincide with the release of a national study that details the experiences of roughly 2,000 black LGBT youth from across the country and Puerto Rico.
“There is something there for everyone,” said Walker, referring to the summit and its focus on gay men’s health. “From what I’ve seen so far, it’s probably one of the best places to get that information with like-minded people.”
In addition to the Gay Men’s Health Summit, the Global Forum on MSM and HIV will take place on Saturday. The International Network of Religious Leaders Living with or Personally Affected by HIV/AIDS conference will take place at Howard University through tomorrow, while Youth Force’s annual gathering at Gallaudet University will conclude on the same day.
Helping Individual Prostitutes Survive will host a pre-conference strategy session at its Northeast Washington offices on Saturday in support of sex-workers’ rights. “The goal is to really get sex workers together to talk about our plans for the conference itself and moving our agenda forward,” said HIPS executive director Cyndee Clay.
Current U.S. immigration policy prohibits sex workers and drug users from entering the country—thousands of sex workers and their allies are expected to gather in Kolkata, India, for a conference that will take place during AIDS 2012. HIPS plans to live-stream this gathering at its Global Village exhibit during the D.C. conference.
Ending this ban is among the four issues outlined in a so-called call to action that urges the federal government to adopt policies that signatories hope will more effectively prevent the spread of HIV/AIDS among sex workers.
“The United Nations considers sex workers and their clients to be two of the populations most at risk for HIV infection,” reads the declaration. “Structural issues drive the HIV epidemic within the sex sector – criminalization and stigma compound health disparities already affecting those on the wrong end of racial, economic and gender inequality. Yet when they are empowered to be leaders, connected to services and resources, and supported to address social injustice, sex workers have been some of the most effective communities at curtailing the spread of AIDS. Currently, the U.S. imposes and continues to expand harmful policies affecting sex workers both domestically and abroad, putting them at increased risk for HIV.”
Health
Housewives head to Capitol Hill to promote PrEP coverage
Bravo’s Real Housewives stars to lobby lawmakers for expanded PrEP access.

Stars from Bravo’s hit franchise “The Real Housewives” are heading to Capitol Hill next week to advocate for expanded access to HIV prevention and treatment.
On March 18, several well-known cast members — including NeNe Leakes, Phaedra Parks, Candiace Dillard Bassett, Erika Jayne, Luann de Lesseps, Melissa Gorga, and Marysol Patton — will travel to D.C. to participate in an advocacy event aimed at increasing awareness and coverage for pre-exposure prophylaxis, commonly known as PrEP.
The event, dubbed “Housewives on the Hill,” is being organized by MISTR, the nation’s largest telehealth platform focused on sexual health. The group’s founder and CEO, Tristan Schukraft, will join the reality television stars as they meet with lawmakers and legislative staff to discuss the importance of maintaining and expanding access to HIV prevention tools.
PrEP is a medication regimen that can, if taken properly, reduce the risk of contracting HIV through sex by up to 99 percent according to public health officials. Advocates say wider access to the medication — including through insurance coverage and telehealth services — is critical to reducing new HIV infections across the United States.
During their day on Capitol Hill, the Housewives are expected to meet with members of Congress and participate in conversations about federal policies affecting HIV prevention and treatment. Organizers say the reality stars will also share personal reflections about the continued impact of HIV on communities across the country and the importance of keeping prevention resources accessible.
The “Housewives on the Hill” event aims to use the cultural influence of the Bravo stars to spotlight HIV prevention efforts and encourage lawmakers to protect and expand access to lifesaving medication and treatment options. Organizers say the goal is simple: ensure that more Americans can access the tools they need to prevent HIV and maintain their sexual health.
Health
Too afraid to leave home: ICE’s toll on Latino HIV care
Heightened immigration enforcement in Minneapolis is disrupting treatment

Uncloseted Media published this article on March 3.
This story was produced in collaboration with Rewire News Group, a nonprofit publication reporting on reproductive and sexual health, rights and justice.
This story was produced with the support of MISTR, a telehealth platform offering free online access to PrEP, DoxyPEP, STI testing, Hepatitis C testing and treatment and long-term HIV care across the U.S. MISTR did not have any editorial input into the content of this story.
By SAM DONNDELINGER and CAMERON OAKES | For two weeks, Albé Sanchez didn’t leave their house in South Minneapolis.
“[I was] forced into survival mode,” Sanchez told Uncloseted Media and Rewire News Group (RNG). “I felt like there was an invisible wall [to the outside world] that I couldn’t cross unless I really wanted to put myself in a place where there was a chance that I might not be able to come back.”
Queer and Mexican American, Sanchez was afraid of being targeted by the Immigration and Customs Enforcement presence in their neighborhood, even though they are a U.S. citizen.
“Every day is a risk,” they say, adding that even if they have paperwork, if they fit the profile, they are a target, making it scary to go even to work or the grocery store.
Sanchez, a 30-year-old sexual health care educator, has been taking oral PrEP, the daily preventive medication for HIV, for over a decade. But the mounting stress of ICE raids has made it harder to keep up with dosing.
“A missed dose here and there pushed me to make the appointment [for something more sustainable],” they say.
Sanchez says they felt like somebody would have their back at their local clinic. It was only a 10-minute drive from where they worked, they knew its staff from previous visits and community outreach, and they could count on finding Spanish-speaking staff and providers of Latino heritage. But not everybody has had that same experience accessing care.
Since ICE’s Operation Metro Surge began in early December, an increasing number of Latino patients in Minnesota are delaying or canceling what can be lifesaving care for the prevention and treatment of HIV.
These findings are particularly alarming for Latino communities, who, as of 2023, are 72 percent more likely than the general U.S. population to be diagnosed with HIV. And while overall infections have decreased, cases among Latinos increased by 24 percent between 2010 and 2022.
“I’m very concerned that there is going to be a sharp uptick in transmission,” says Alex Palacios, a community health specialist in the Minneapolis area.
In a January 2026 declaration as part of a lawsuit seeking to end Operation Metro Surge in the days following Renee Nicole Good’s killing, the commissioner of the Minnesota Department of Health said HIV testing among Latino populations has “dropped dramatically” and that “although grantee staff continue to go into the community to promote and provide testing, people are not showing up.”
Local clinics are reporting the same thing. The Aliveness Project, a community wellness center in Minneapolis specializing in HIV care, told Uncloseted Media and RNG they have seen more than a 50 percent decrease in new clients. The clinic serves a large number of Latino and undocumented clients, and while it usually sees 750 people walk through their door each week, according to providers, it reported seeing 100 fewer people each week since December.
Red Door, Minnesota’s largest STI and HIV clinic, has had a “modest uptick” in no-shows and missed appointments since December.
What happens when treatment stops
Today, there are multiple medications available that work to prevent HIV and dozens that treat it once a person tests positive. Many people who consistently take their medication have such low levels of the virus that they can’t transmit it through sex. But becoming undetectable requires patients to stay on their medication; otherwise, the virus replicates and mutates, weakening the immune system and increasing the risk of life-threatening infections.
“If patients aren’t on their medicines consistently, HIV can learn about the medication and become resistant to them. When this happens, the medicine will not work for the patient, and the new resistant virus could potentially be passed on to others,” says George Froehle, a physician assistant and provider at Aliveness Project. “Medication adherence is one of the most important aspects of HIV care.”
To maintain care and prevent dangerous, untreatable strains from spreading in Minnesota, providers at Aliveness Project have begun delivering medication to patients when possible, offering telehealth when they can, and pausing routine lab work to limit in-person appointments.
“The most important thing we can do from a public health perspective is to keep people undetectable so they don’t transmit HIV,” Froehle says, adding that providers in other cities targeted by ICE will need to make plans for missed injection visits, pivot to telehealth and prepare their teams for the “trauma that can occur.”
Sanchez understands the risks of inconsistent treatment, which is why they opted for the injectable preventative medication.
“I have a lot of risk [to HIV in my community],” Sanchez says. “With so much uncertainty about the future and whether HIV care will remain stable, I realized I couldn’t let this opportunity pass.”
But injectable HIV treatments are commonly dosed at two weeks to six months apart, and the medication must be administered in a clinic — a setting many patients are avoiding, according to providers.
“They have a two-week window” to get their shots, according to Froehle, who added that because patients are afraid to come in person, they have had to transition people off of their injectable HIV treatments. This has caused patients to return to oral HIV treatments without the testing they would normally receive had ICE not been in Minneapolis. “[Oral treatments] weren’t super successful [for these patients] to begin with and that’s why they were on injectables.”
Oral HIV medications, too, must be taken consistently to work. In response, providers have urged patients to have their pills with them at all times in case they get deported or detained.
The caution is not unfounded. Federal immigration facilities have a history of denying adequate medical care to people living with HIV, despite internal standards that require them to comply. Since 2025, at least two men living with HIV have been denied access to their medication in a Brooklyn jail, according to lawsuits obtained by THE CITY. One man said he was only given his medication after his lips broke open and he developed an open pustule on his leg. And in January 2025, another man died of HIV complications while in ICE custody in Arizona.
Beyond being detained without proper medication, patients are at risk of being deported to countries with limited access to HIV care, like Honduras and Venezuela, experts say.
“A lot of men [from Venezuela] told me they left because it wasn’t safe to be gay there and because they struggled to access HIV care,” says Froehle. “It’s a little heartbreaking to see new folks not only face the threat of deportation, but to places where they didn’t feel safe medically or identity-wise.”
“Some of these patients will die in their home country,” says Anna Person, the chair of the HIV Medicine Association. “It’s a death sentence.”
A ‘cascading disaster’
While ICE’s presence is threatening the infrastructure of HIV care that Minneapolis has built over decades, experts say there has always been a blind spot in HIV care for the city’s Latino community.
Vincent Guilamo-Ramos, executive director of the Institute for Policy Solutions at the Johns Hopkins University of Nursing, describes HIV in Latino communities as a “cascading disaster,” the result of years of compounding inequities.
“There’s been an invisible crisis among Latinos that hasn’t gotten traction,” he says. “The numbers have consistently gone up in terms of new infections, while nationally they’ve gone down. … That should be a big alarm.”
Numbers are rising because structural barriers and stigma are preventing Latinos from receiving care. A 2022 report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found that between 2018 and 2020, nearly 1 in 4 Hispanic people living with HIV reported experiencing discrimination in health care settings. Lack of representation among providers, language barriers and deep-rooted medical mistrust further complicate access to care, according to Guilamo-Ramos.
Beyond the medical system, stigma within Latino communities can be equally damaging. According to Human Rights Campaign data, more than 78 percent of Latino LGBTQ youth reported experiencing homophobia or transphobia within the Latino community in 2024.
Sanchez agrees that stigma and bias are already massive barriers to care, citing the strict gender norms and Catholic beliefs many Latino communities hold. They say ICE’s presence is threatening already delicate access to HIV care.
“This has caused so much damage to people,” Sanchez says. “Not being able to access your health care appointments is such a stab in the side. … Being able to navigate any of these things in normal circumstances already has so much difficulty to it.”
Palacios, who is Afro-Latine and living with HIV, says the heightened ICE presence is worsening barriers that have long undermined the Latino community’s access to HIV care.
“The horizon has always been stark and dim,” they say. “And this just feels like one more thing to address and to fight back against.”
Sliding backwards
Navigating HIV care is becoming more difficult across the board, as the federal government has decimated HIV funding, compromising decades of progress made in the fight against the virus since Donald Trump retook office just over a year ago.
In February 2026, three months into Operation Metro Surge, the Trump-Vance administration proposed slashing $600 million in HIV-related grants, targeting four blue states, including $42 million for Minnesota programs. A federal judge has temporarily blocked the cuts.
“This would completely decimate and gut all of our HIV prevention,” says Dylan Boyer, director of development at Aliveness Project. “That’s the reality that we live in.”
“We have all the tools, and yet we are staring down this rollback of infrastructure and research dollars, prevention efforts, treatment efforts, that are going to put us squarely back in the 1980s,” says Person, a national HIV expert who grew up in Minnesota. “[There] seems to be no other rationale for that besides cruelty, to be quite frank, since there’s no scientific reason for it.”
Repair and representation
Jenny Harding, director of advancement at a Minneapolis-area supportive housing program for people living with HIV, says that while ICE’s presence is lessening in the Twin Cities, the “damage is done.”
Person says that this mending will take time, especially between the medical community and patients, since HIV providers can have a “very fragile” relationship with their clients.
“It takes, sometimes, years to build that level of trust. And I do worry that folks are just going to say, ‘I don’t feel safe here anymore. The system does not have my best interest at heart, and I’m not coming back,’” she says. “This is not something that you can flip a switch and everything will go back to normal.”
“We need to hold our federal government accountable, particularly HHS, [and] we need to ensure that HIV funding remains intact,” Guilamo-Ramos says, adding that in order to lower rates of HIV in the Latino community, there should be more specialized efforts: such as bilingual and culturally aligned health care providers, community-based outreach programs co-located where risk is highest, trust-building initiatives to address medical mistrust, mobile clinics, and targeted programs to re-engage patients who have fallen out of care.
Aliveness Project’s patient numbers have increased in the last few weeks as the ICE operation has waned, but the clinic staff is keeping “a watchful eye” and is having “difficulty reaching folks who are understandably scared.”
“Our biggest focus right now is reconnecting with people through our outreach so no one has a lapse in their HIV medications or prevention care,” Boyer, of Aliveness Project, says.
For Sanchez, seeing providers who speak Spanish and are of Latin heritage at Aliveness Project built enough trust for them to reach out and make an appointment despite the risks. Sanchez feels optimistic about their new injectable prevention strategy with the support of their clinic.
“There’s many places where you can receive care here in the Twin Cities where you might not see your skin tone. … There’s still a lot of health care professionals that unfortunately carry bias. … Aliveness is the opposite of that,” they say. “Seeing that representation and knowing someone has that cultural context of how to meet you in moments of sensitivity, it’s crucial.”
District of Columbia
Trans activists arrested outside HHS headquarters in D.C.
Protesters demonstrated directive against gender-affirming care
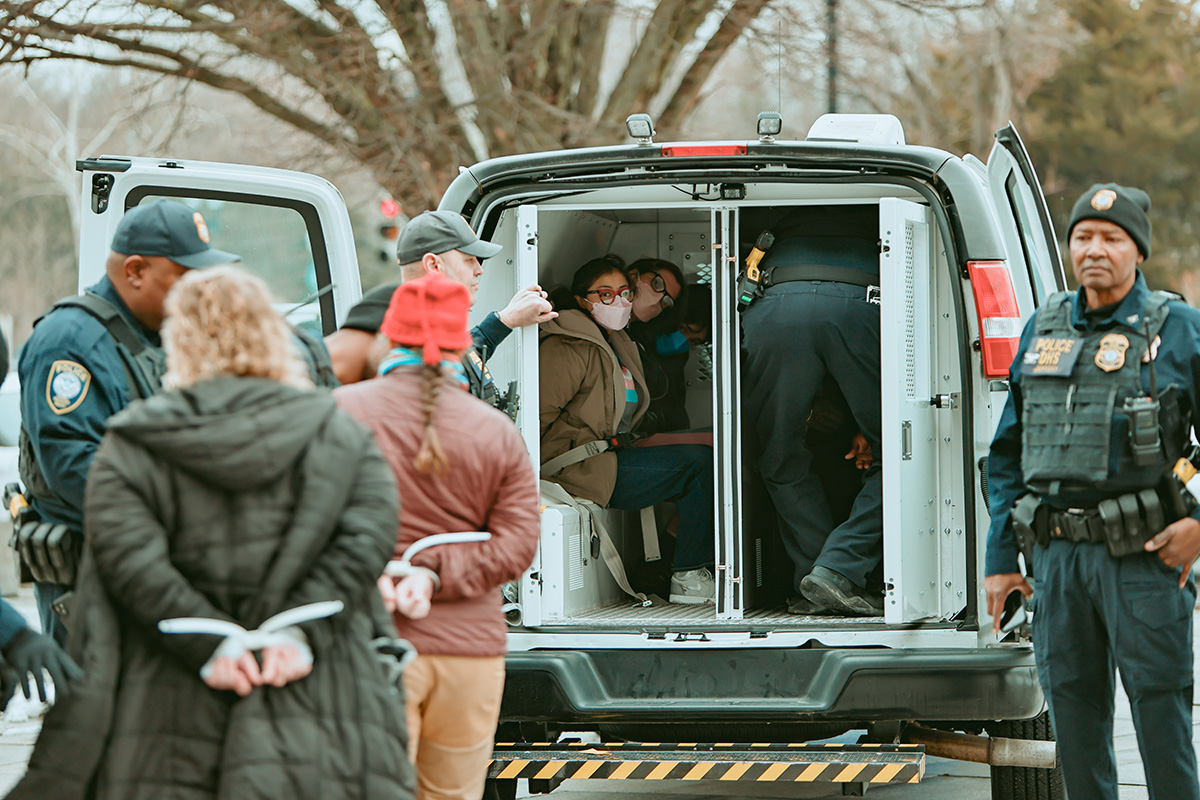

Authorities on Tuesday arrested 24 activists outside the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services headquarters in D.C.
The Gender Liberation Movement, a national organization that uses direct action, media engagement, and policy advocacy to defend bodily autonomy and self-determination, organized the protest in which more than 50 activists participated. Organizers said the action was a response to changes in federal policy mandated by Executive Order 14187, titled “Protecting Children from Chemical and Surgical Mutilation.”
The order directs federal agencies and programs to work toward “significantly limiting youth access to gender-affirming care nationwide,” according to KFF, a nonpartisan, nonprofit organization that provides independent, fact-based information on national health issues. The executive order also includes claims about gender-affirming care and transgender youth that critics have described as misinformation.
Members of ACT UP NY and ACT UP Pittsburgh also participated in the demonstration, which took place on the final day of the public comment period for proposed federal rules that would restrict access to gender-affirming care.
Demonstrators blocked the building’s main entrance, holding a banner reading “HANDS OFF OUR ‘MONES,” while chanting, “HHS—RFK—TRANS YOUTH ARE NO DEBATE” and “NO HATE—NO FEAR—TRANS YOUTH ARE WELCOME HERE.”
“We want trans youth and their loving families to know that we see them, we cherish them, and we won’t let these attacks go on without a fight,” said GLM co-founder Raquel Willis. “We also want all Americans to understand that Trump, RFK, and their HHS won’t stop at trying to block care for trans youth — they’re coming for trans adults, for those who need treatment from insulin to SSRIs, and all those already failed by a broken health insurance system.”
“It is shameful and intentional that this administration is pitting communities against one another by weaponizing Medicaid funding to strip care from trans youth. This has nothing to do with protecting health and everything to do with political distraction,” added GLM co-founder Eliel Cruz. “They are targeting young people to deflect from their failure to deliver for working families across the country. Instead of restricting care, we should be expanding it. Healthcare is a human right, and it must be accessible to every person — without cost or exception.”

Despite HHS’s efforts to restrict gender-affirming care for trans youth, major medical associations — including the American Medical Association, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Endocrine Society — continue to regard such care as evidence-based treatment. Gender-affirming care can include psychotherapy, social support, and, when clinically appropriate, puberty blockers and hormone therapy.
The protest comes amid broader shifts in access to care nationwide.
NYU Langone Health recently announced it will stop providing transition-related medical care to minors and will no longer accept new patients into its Transgender Youth Health Program following President Donald Trump’s January 2025 executive order targeting trans healthcare.
-

 Health4 days ago
Health4 days agoToo afraid to leave home: ICE’s toll on Latino HIV care
-

 Movies4 days ago
Movies4 days agoIntense doc offers transcendent treatment of queer fetish pioneer
-

 The White House3 days ago
The White House3 days agoTrump will refuse to sign voting bill without anti-trans provisions
-

 Colombia4 days ago
Colombia4 days agoClaudia López wins primary in Colombian presidential race