Health
Cornell University study on impact of discrimination on LGBTQ of color
Around 25% of LGBTQ youth have attempted suicide, but the rates are starkly higher for LGBTQ youth of color than their white counterparts

ITHACA, NY. – Cornell University’s What We Know Project in conjunction with a coalition of leading LGBTQ rights groups last month published a comprehensive curation of data on studies that chart the intersection of anti-LGBTQ and racial discrimination.
The findings found that discrimination inflicts profoundly greater harm on LGBTQ people of color in a wide range of areas, including grossly disproportionate rates of: experiencing discrimination over the past year, poorer mental and physical health, greater economic insecurity, and attempts to die by suicide.
In addition, LGBTQ people of color are more likely than white LGBTQ people to live in states without protections against discrimination and that state anti-LGBTQ laws harm LGBTQ people.
“This research brief makes clear the tangible harms that discrimination inflicts on LGBTQ people of color, and the urgent need for public policy that reflects what the research tells us about how we can reduce those harms,” said Dr. Nathaniel Frank, the study’s author.
Highlights of the research brief’s findings include:
LGBTQ people are more likely than non-LGBTQ people to be people of color, and Black LGBTQ Americans are disproportionately likely to live in states without protections against discrimination. For example, 42% of LGBT people are people of color compared to 32% of non-LGBT people and the majority of Black LGBT Americans live in the South (51.4%, more than twice the share of any other region), where most states lack anti-discrimination protections.
LGBTQ people of color face higher odds of discrimination than both non-LGBTQ individuals and LGBTQ white people. For example, LGBTQ people of color are more than twice as likely to experience anti-LGBTQ discrimination (slurs or other verbal abuse) when applying for jobs than white LGBTQ individuals (32% vs. 13%). LGBTQ people of color are more than twice as likely as white LGBTQ people to experience anti-LGBTQ discrimination when interacting with the police (24% vs. 11%).
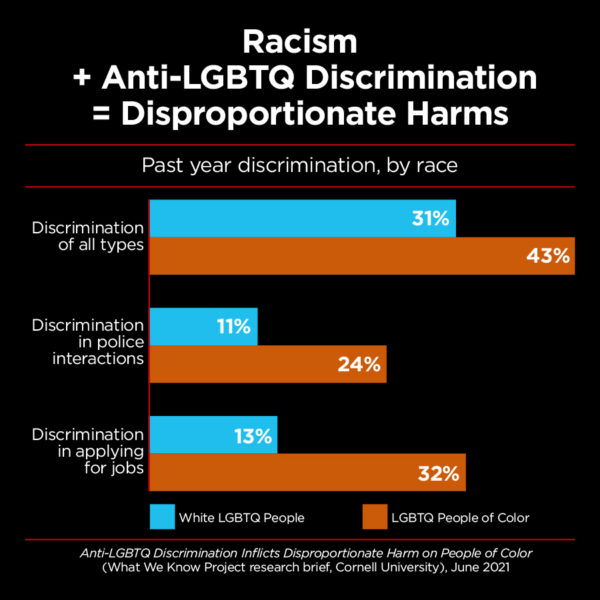
Black LGBT Americans are more likely to experience economic insecurity than Black non-LGBT Americans. For example, the majority of Black LGBT people (56%) live in low-income households (below 200% of the federal poverty level) compared to 49% of Black non-LGBT Americans, and Black LGBT adults are also more likely to experience food insecurity than Black non-LGBT adults (37% compared to 27%).
Hundreds of studies conclude that experiencing anti-LGBTQ discrimination increases the risks of poor mental and physical health, including depression, anxiety, suicidality, PTSD, substance use, and psychological distress.
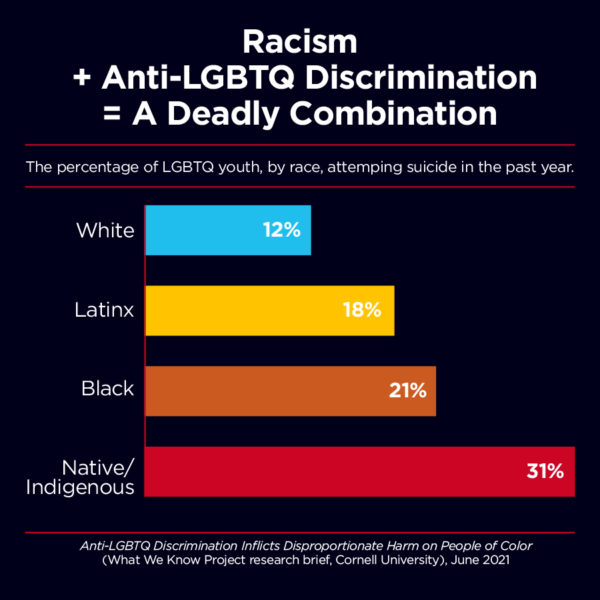
LGBTQ people of color face disproportionate odds of suicidality, which is linked to discrimination. For example, while 12% of white LGBTQ youth attempted suicide, the rate is 31% for LGBTQ Native/Indigenous youth, 21% for LGBTQ Black youth, and 18% of LGBTQ Latinx youth.
While supportive laws, family, and peers lower the risk of poor health outcomes for LGBTQ people of color, anti-LGBTQ state laws inflict tangible harm on sexual minority populations. For example, states with “denial of service” laws that give license to discriminate against LGBT residents between 2014 and 2016 were linked with a 46% increase in LGBT mental distress. Black LGBTQ youth who reported high levels of support from at least one person, or who had access to an LGBTQ-affirming space, reported attempting suicide at lower rates than those who lacked such support (16% vs. 24%).

Supportive laws, family, and peers lower the risk of poor health outcomes for LGBTQ people of color.
• Suicide attempts by LGBT youth dropped by 7 percent in states that legalized same-sex marriage.22
• The corollary is that anti-LGBTQ state laws inflict tangible harm on sexual minority populations. States with “denial of service” laws that give license to discriminate against LGBT residents were linked with a 46% increase in LGBT mental distress.23
• Black LGBTQ youth who reported high levels of support from at least one person, or who had access to an LGBTQ-affirming space, reported attempting suicide at lower rates than those who lacked such support (16% vs. 24%). Those with high levels of family support had rates of past-year attempted suicide nearly one third as high as those who lacked such support (22% vs. 8%).24
• Protective measures that have been found to help reduce anxiety, depression, and suicidality among LGBTQ youth include: Establishing inclusive practices and anti-discrimination policies; peer, community, and family support, including dedicated school groups; access to affirmative mental health and social services; societal confrontation of attitudes and norms that exacerbate minority stress; and practitioner training and interventions designed to disrupt negative coping responses and build resilience.
Experiencing discrimination is associated with greater odds of harm to psychological and economic well-being, which is reflected in data on disparities for LGBTQ people of color.
• Hundreds of studies conclude that experiencing anti-LGBTQ discrimination increases the risks of poor mental and physical health, including depression, anxiety, suicidality, PTSD, substance use, and psychological distress.
• LGBT people of color have work-place experiences that are more negative than those of white LGBT employees, reporting that their success and work-life balance are fostered less extensively, they have less transparent evaluations, and they are respected less by supervisors.
• Among LGBTQ people surveyed, 51% of Black respondents say discrimination harms their ability to be hired, compared with 33% of white respondents; 41% say it has an impact on their ability to retain employment, compared with 31% of white respondents; 77% of Black respondents report that discrimination impacts their psychological well-being, a rate nearly 50% higher than the total LGBTQ survey population.
• While racial discrimination on its own is not associated with mental health disorders, the combination of racial discrimination with gender and/or sexual orientation discrimination is significantly associated with increased odds of a past-year mental health disorder.
LGBTQ people of color face disproportionate odds of suicidality, which is linked to discrimination.
• Around 25% of LGBTQ youth of all races have attempted suicide, but the rates are starkly higher for LGBTQ youth of color than their white counterparts: While 12% of white LGBTQ youth have attempted suicide, the rate is 31% for LGBTQ Native/Indigenous youth, 21% for LGBTQ Black youth, and 18% for LGBTQ Latinx youth.
• In a 95%-non-white LGBT sample, those who report experiencing anti-LGBT victimization (such as bullying and harassment) are 2.5 times more likely to report a past-year suicide attempt compared to those who do not report victimization.
• Black LGBTQ youth who experience anti-LGBTQ discrimination face twice the rate of past year suicide attempts compared to youth who do not (27% vs. 12%). Black LGBTQ youth who experience race-based discrimination also face higher odds of attempting suicide than those who do not (20% vs. 14%).
• Black LGB adults are over 40% more likely to have made a serious suicide attempt in their lifetime than white LGB adults.
• Latinx and Native American/Pacific Islander LGBT youth are 50% more likely to attempt suicide than white LGBT youth. Latinx LGBT girls are nearly twice as likely to attempt suicide than white LGBT youth.
• LGBTQ students who experience discrimination “based on multiple social identities” report more use of deliberate self-harm compared to LGBTQ students who experience racial discrimination alone or who do not experience significant discrimination of any kind.
Reflecting on the study’s findings, key executives from participating LGBTQ Advocacy groups weighed in:
“These painful figures highlight an indisputable link between discrimination, economic security, mental and physical health. People with multiple stigmatized, marginalized social and political identities, particularly Black LGBTQ+/Same Gender Loving people, bear a disproportionate amount of the weight illustrated by the data in this study. Statutory equality for LGBTQ+ people nationwide is a necessary foundation to remove the gaps in existing civil rights laws if we are to ever live up to our country’s founding promises of life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness for all,” said David Johns, Executive Director, National Black Justice Coalition.
The majority of Black LGBTQ people live in the South, with nearly half (44%) of all Black women couples raising children. Even today, most of these states still do not protect LGBTQ people from discrimination and have overtly discriminatory laws on their books. It is no wonder the disparities are so profound and it is a testament to the strength and resilience of our people that they are doing as well as they are. For our community and for our children it’s time for federal action!” said Kierra Johnson, Executive Director, National LGBTQ Task Force.
“This important brief only further solidifies what we have known for a very long time—the combination of racism and anti-LGBTQ discrimination has serious and long-lasting effects for the health and well-being of LGBTQ people of color. This research highlights why federal non-discrimination protections are overdue and vital to protecting the most some of the most underrepresented and vulnerable members of our community. Federal anti-discrimination protections are absolutely necessary in protecting and supporting all LGBTQ people, and this is especially true for LGBTQ people of color,” said Imani Rupert-Gordon, Executive Director, National Center for Lesbian Rights.
“Study after study shows that nondiscrimination protections improve economic opportunities, public safety, and physical and mental well-being of LGBTQ people. It is well past time for the essential protections available only in some of our states and cities to be extended to all LGBTQ Americans, especially LGBTQ people of color, who are disproportionately burdened by the lack of protections, ” said Kasey Suffredini, CEO and National Campaign Director, Freedom for All Americans.
District of Columbia
Trans activists arrested outside HHS headquarters in D.C.
Protesters demonstrated directive against gender-affirming care
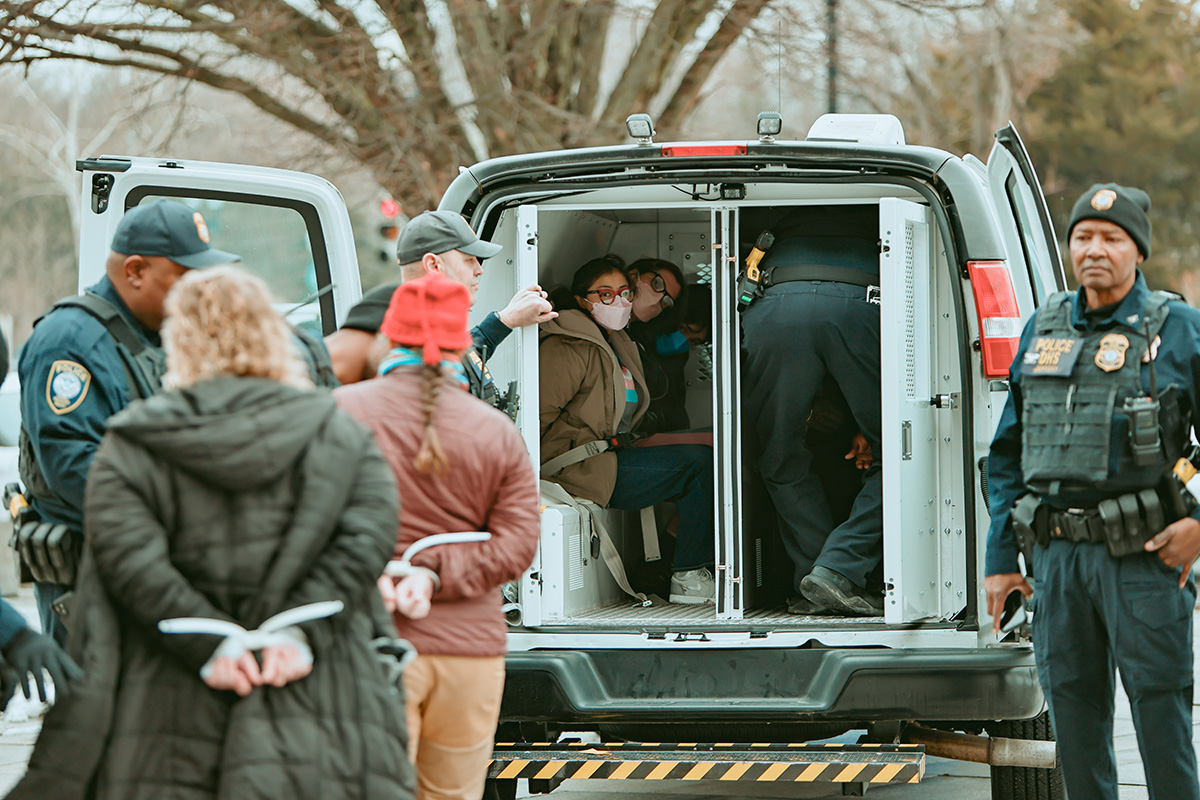

Authorities on Tuesday arrested 24 activists outside the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services headquarters in D.C.
The Gender Liberation Movement, a national organization that uses direct action, media engagement, and policy advocacy to defend bodily autonomy and self-determination, organized the protest in which more than 50 activists participated. Organizers said the action was a response to changes in federal policy mandated by Executive Order 14187, titled “Protecting Children from Chemical and Surgical Mutilation.”
The order directs federal agencies and programs to work toward “significantly limiting youth access to gender-affirming care nationwide,” according to KFF, a nonpartisan, nonprofit organization that provides independent, fact-based information on national health issues. The executive order also includes claims about gender-affirming care and transgender youth that critics have described as misinformation.
Members of ACT UP NY and ACT UP Pittsburgh also participated in the demonstration, which took place on the final day of the public comment period for proposed federal rules that would restrict access to gender-affirming care.
Demonstrators blocked the building’s main entrance, holding a banner reading “HANDS OFF OUR ‘MONES,” while chanting, “HHS—RFK—TRANS YOUTH ARE NO DEBATE” and “NO HATE—NO FEAR—TRANS YOUTH ARE WELCOME HERE.”
“We want trans youth and their loving families to know that we see them, we cherish them, and we won’t let these attacks go on without a fight,” said GLM co-founder Raquel Willis. “We also want all Americans to understand that Trump, RFK, and their HHS won’t stop at trying to block care for trans youth — they’re coming for trans adults, for those who need treatment from insulin to SSRIs, and all those already failed by a broken health insurance system.”
“It is shameful and intentional that this administration is pitting communities against one another by weaponizing Medicaid funding to strip care from trans youth. This has nothing to do with protecting health and everything to do with political distraction,” added GLM co-founder Eliel Cruz. “They are targeting young people to deflect from their failure to deliver for working families across the country. Instead of restricting care, we should be expanding it. Healthcare is a human right, and it must be accessible to every person — without cost or exception.”

Despite HHS’s efforts to restrict gender-affirming care for trans youth, major medical associations — including the American Medical Association, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Endocrine Society — continue to regard such care as evidence-based treatment. Gender-affirming care can include psychotherapy, social support, and, when clinically appropriate, puberty blockers and hormone therapy.
The protest comes amid broader shifts in access to care nationwide.
NYU Langone Health recently announced it will stop providing transition-related medical care to minors and will no longer accept new patients into its Transgender Youth Health Program following President Donald Trump’s January 2025 executive order targeting trans healthcare.
Health
CMS moves to expand HIV-positive organ transplants
HIV/AIDS activists welcome potential development

The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services is pushing forward a proposed rule that would make it not only easier for people with HIV in need to get organ transplants from HIV-positive donors, but also make it a priority where there was often a barrier.
The Washington Blade sat down with people familiar with this topic — from former heads of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, to HIV activists and to the first HIV-positive person to donate an organ — about what this proposed change could mean.
HIV is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system, particularly targeting the body’s T-cells, which makes it harder to fight off infection and disease. If left untreated, HIV can become AIDS. Without treatment, AIDS can lead to death within a few months or years. The virus is spread through direct contact with bodily fluids — often through sex, unclean needles, or from mother to baby during pregnancy.
According to HIV.gov, a website managed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, approximately 1.2 million people in the U.S. were living with HIV in 2022. Of those 1.2 million, 13 percent don’t know they have it.
The virus disproportionately impacts men who have sex with men and people of color.
The CDC’s statistics show men are most affected, making up almost 80 percent of diagnoses, with gay and bisexual men accounting for the majority. Racial disparities also are present — Black people make up 38 percent of diagnoses. The World Health Organization estimates that around 44.1 million people have died from AIDS-related illnesses globally as of 2024.
Since the virus was first detected 45 years ago, scientists have been working on ways to treat and prevent its spread. In 1987, the first breakthrough in fighting HIV came as the U.S. approved the first HIV medication, AZT — marking the beginning of antiretroviral therapy. This medicine — and later descendants of it, like today’s widely prescribed Biktarvy — stop the HIV virus from reproducing and allow the body to keep its T-cells.
Then in 2012, another big step toward minimizing the scope of the potentially fatal disease came as the CDC approved the first HIV prevention medication, Truvada, more commonly known as PrEP. As of 2024, nearly 600,000 people in the U.S. are using PrEP, according to AIDSVu, which uses data from Gilead Sciences (manufacturers of Truvada and Biktarvy) and is compiled by researchers at the Rollins School of Public Health at Emory University.
The following year, in 2013, the HIV Organ Policy Equity (HOPE) Act was signed into law, enabling the use of organs from HIV-positive donors for transplants into HIV-positive recipients, overturning a 1988 ban.
There are an estimated 123,000 people waiting for organ transplants in the U.S. The number of HIV-positive people on that list is estimated to be smaller, harder to precisely quantify, but they are still in dire need.
A study from the New England Journal of Medicine, published in 2024, analyzed the outcomes of 198 kidney transplantations to people with HIV at 26 medical centers across the U.S. from 2018 to 2021.
Results from the study showed that for kidney transplants performed using organs from 99 donors with HIV and 99 without HIV, one-year survival rates for HIV-positive recipients were nearly identical (94 percent and 95 percent, respectively). Three-year survival rates were also similar (85 percent and 87 percent). Organ rejection rates were also numerically on par after three years (21 percent and 24 percent). Other measures for surgical outcomes, including the number of side effects that occurred, were also roughly the same for both groups.
This shows that, overall, HIV-positive-to-HIV-positive transplants are nearly identical in outcome to transplants between HIV-negative donors and recipients.
Where we are now
Now in 2026, CMS is pushing past the clinical trial testing phase it has been in, making HIV-positive-to-HIV-positive organ transplants more widespread and more accessible.
Adrian Shanker, the former deputy assistant secretary for health policy and senior advisor on LGBTQ health equity at HHS, explained to the Blade that the HOPE Act was a step in the right direction, but this policy change from CMS will expand the ability to help HIV-positive patients in need.
“The original HOPE Act asked for scientific research,” Shanker explained. “There were 10 years of clinical trials. The Biden administration promulgated a rule that removed clinical trial requirements for kidney and liver transplants between people living with HIV. This proposed rule is further implementation on the CMS side with the organ procurement organizations to ensure they’re carrying out the stated intent of the HOPE Act law. It’s building on consensus that has existed through multiple administrations.”
The proposed change would go into effect on July 1, and, according to Shanker, would help everyone in need of an organ — not just HIV-positive people.
“People living with HIV, their ability to receive organs from other people living with HIV in a more streamlined way means that the overall organ waitlist is sped up as well,” he added. “So it benefits everyone on the waitlist.”
Shanker, who was also a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on HIV/AIDS, spoke about how this is a rare moment of bipartisanship.
“There’s no secret that the Trump administration has been quite adversarial to LGBTQI plus health, and to the health of people living with HIV/HIV prevention resources as well … From destabilizing PEPFAR to shutting down one of the primary implementation partners, which is USAID, to firing almost the entire staff of the Office of Infectious Disease and HIV Policy at HHS … But what this is is a glimmer of hope that we can have bipartisan solutions that improve quality of life for people living with HIV.”
Harold Phillips, the CEO of NMAC, a national HIV/AIDS organization that pushes policy education and public engagement to end the HIV epidemic, and an HIV-positive American, sees this as a huge gain for the HIV-positive community.
“For a number of years, we were excluded from that pool of potential donors,” Phillips said. “Many people living with HIV were excluded from being able to get organ transplants. So this opens up that door. This is a positive step forward that will help save lives.”
That “open door,” Phillips said, does more than just provide life-saving organs to people in the most need. It provides a sense of being able to support their community.
“I remember when I was no longer able to check that box on my driver’s license,” Phillips recalled during his interview with the Blade. “I remember what that meant — that my organs might not be able to save a life. The potential that now they could is really exciting for me.”
“To think about people living with HIV donating their organs to other people living with HIV and helping extend their health and well-being — that’s an exciting moment in our history. It reinforces that HIV is not a death sentence anymore.”
Human Rights Campaign Senior Public Policy Advocate Matt Rose also sat down with the Blade to explain the realities of HIV-positive people in the U.S. right now who are looking for a transplant.
“If you’re HIV positive and on the waitlist for an organ right now, your chance of getting one is slim to nil,” Rose said. “This at least gives you a real shot.”
He went on to explain that while the HOPE Act started to move in the right direction, it hasn’t done enough for HIV-positive people in dire need.
“This bill [HOPE] was supposed to fix that — and it never really has. But every administration, we keep chipping away at the next hurdle,” he said. “This latest move will drastically expand the ability for someone who is HIV positive to donate an organ.”
That slow chipping away, in addition to the non-stop trials being done to prove the efficacy and ability for HIV-positive people’s bodies to accept organ donation, is part of the broader push to normalize this practice and remove outdated restrictions.
Shanker elaborated, explaining all that time was necessary to figure out the efficacy of HIV-positive-to-HIV-positive organ transplants but now that the data has been collected — its time to expand the availability.
“There were over a decade of clinical trials between the original HOPE Act law being signed by President Obama and our rule being promulgated at the end of the Biden administration. It was to allow those clinical trials to run their course,” Shanker said.
Nina Martinez is the first HIV-positive person to donate an organ to another person with HIV.
She explained that the stigma and lack of understanding from the general public is another hurdle that those working to improve the quality of life for people living with HIV have to deal with.
“People don’t generally understand that treatment works,” Martinez said, who became the first person to undergo HIV-positive organ donation in 2019. “When you have access to antiretroviral therapy, it lowers the virus in your bloodstream to levels so low that lab tests can’t detect it. Clinically, that correlates to good health and an inability to transmit HIV sexually. I was healthy enough to pass the same evaluation as any other living donor without HIV.”
She continued explaining:
“Just by having a diagnosis of HIV, they’re labeling donors as medically complex, and that’s not accurate. Every donor with HIV has to pass the same evaluation as donors without HIV,” she said. “If someone passes that evaluation and still isn’t allowed to donate, that’s discrimination. If a patient is willing to accept that organ and you block it because of preconceived notions, you’re denying someone care based on disability. That runs counter to basic fairness.”
When asked about her decision to become a donor and what message she hopes it sends, Martinez emphasized that the choice should remain personal.
“I didn’t undertake this endeavor to say that people with HIV should donate. This is a community that’s been through a lot and has contributed to science — we have served. But for people who wanted a way to leave a legacy, and that is what I wanted, they should be supported in that. There shouldn’t be arcane scientific perceptions and myths getting in the way of that.”
National Donor Day, which raises awareness of organ donation, is on Feb. 14. To become an organ donor, visit registerme.org.
Health
CVS Health agrees to cover new HIV prevention drug
‘Groundbreaking’ PrEP medication taken by injection once every six months

CVS Health, the nation’s second largest pharmacy benefit manager company that plays a key role in deciding which drugs are covered by health insurance policies, has belatedly agreed to cover the new highly acclaimed HIV prevention drug yeztugo.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the use of yeztugo as an HIV prevention or “PrEP” medication in June 2025 as the first such drug to be taken by injection just once every six months. AIDS activists hailed the drug as a major breakthrough in the longstanding effort to end the HIV epidemic.
“We are pleased that CVS Health has finally decided to cover this groundbreaking new PrEP mediation,” said Carl Schmid, executive director of the HIV+ Hepatitis Policy Institute.
“Four months ago, 63 HIV organizations joined us in sending a letter to CVS’s president urging them to reconsider their refusal to cover Yeztugo and reminding them of their legal obligation to cover PrEP and describe the important benefits the drug would bring to preventing HIV in the U.S.,” Schmid said in a statement.
He noted that CVS Health now joins other leading pharmacy benefit manager companies and insurers in covering yeztugo. Gilead Sciences, the pharmaceutical company that developed and manufactures yeztugo, has said 85 percent of all people with health insurance in the U.S. now have coverage for the drug, according to Schmid.
“However, coverage does not automatically translate into access and usage,” Schmid said in his statement. “Too many people are being forced to pay copays while other payers, including employers, are failing to cover all forms of PrEP,” he said.
According to Schmid, the HIV+ Hepatitis Policy Institute is joining other HIV advocacy organizations in urging federal and state government officials to engage in “aggressive enforcement of PrEP insurance coverage requirements and sustained funding of state, local, and community HIV prevention programs.”
-

 National5 days ago
National5 days agoLGBTQ activists mourn the Rev. Jesse Jackson
-

 Massachusetts4 days ago
Massachusetts4 days agoEXCLUSIVE: Markey says transgender rights fight is ‘next frontier’
-

 New York4 days ago
New York4 days agoLawsuit to restore Stonewall Pride flag filed
-

 Opinions4 days ago
Opinions4 days agoGay Treasury Secretary’s silence on LGBTQ issues shows he is scum


















