Africa
Kenyan LGBTQ groups seek representation in government human rights body
New report documents lack of employment opportunities, limited access to financial system

Kenyan advocacy groups are demanding representation in the country’s government-funded human rights body in order to champion their interests in a bid to end inequality and discrimination against them.
The groups that advocate on behalf of lesbians, bisexuals, queer and gender non-conforming people in a report released in May note their exclusion from the Kenya National Commission on Human Rights representation has contributed to the elusive realization of equal rights that other citizens enjoy.
The report, dubbed “An Economic Justice Report for LBQGNC in Kenya,” details continued discrimination against LGBTQ Kenyans in employment opportunities, financial services and government social empowerment funding.
This situation is despite the country recording progressive women’s economic inclusion, whose rate, according to Kenya’s Bureau of Statistics data, is 40 percent in urban areas and 22 percent in parts of the country. This figure is attributed to favorable laws and policies that allow equal and active participation of women in economic activities.
The report notes discrimination against queer people in employment in both public and private sectors due to homophobia has forced most of them to become entrepreneurs, including models, with some benefiting from the government’s social empowerment funding.
“The Kenyan government should ensure that a minimum of one commissioner is included in the makeup of the Kenya National Commission on Human Rights whose focus will be to represent all members of the LGBTQ+ community,” the 52-page report reads.
The Kenya Human Rights Organization, which advocates for equal rights, regardless of one’s gender identity and sexual orientation, had made a similar demand to help address anti-LGBTQ discrimination.
The push to have an LGBTQ representative comes at a time when intersex people in Kenya have a commissioner on the KNHCR who advocates for their rights following their recognition in law last year as the country’s third sex.
To address the problem of discrimination in employment, the report wants the government and other relevant players to establish an employment agency for the queer community to help form networks among LGBTQ-friendly businesses.
“Financial institutions could also support LBQGNC businesses by providing attractive interest rates for loans and reasonable repayment deadlines. This can be better achieved through partnerships with LGBTQ+ organizations to help identify businesses run by LBQGNC persons,” the report reads.
It urges banks and other financial institutions to set up departments or teams in charge of identifying and addressing LGBTQ Kenyans’ financial needs, reviewing provisions that limit their access to certain products and services. This includes limitations to opening joint accounts that are only open to heterosexual married couples, the decriminalization of consensual same-sex sexual relations and legal recognition of same-sex partners.
The report, whose data collection entailed desktop research and interviewing of LGBTQ people in Nairobi, the Kenyan capital, and cities that include Mombasa and Kisumu, notes continued discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity continues to have an impact in education: LGBTQ people face expulsion from school, bullying and stigma.
The rejection and discrimination against LGBTQ people, according to the report, starts with the family, relatives and the community, where they are sometimes subjected to forced moral “conversion” to confirm to society.
“From a human rights perspective, practices such as conversion ‘therapy’ ought to be denounced, with many countries having taken steps towards ensuring its eradication within their jurisdictions,” the report reads.
The so-called conversion therapy methods are varied and may include electro-shock therapy and forced administration of medication to induce drowsiness and lethargy, one of the survivors who also almost died said.
“This is the sad reality faced by too many LBQGNC people in Kenya to this day, at the basis of which is the religious, cultural, and overall societal discrimination against the people in this community,” reads the report.
Kenya’s Education Ministry in March established a Chaplains Committee comprising religious leaders from various denominations to provide counseling to students who identify as LGBTQ to stop its so-called infiltration in schools. The controversial Supreme Court ruling in February that allowed LGBTQ NGOs to register prompted this decision.
The ruling, which has been appealed to the attorney general, sparked criticism from clerics and political leaders since Section 162 of the Penal Code criminalizes consensual same-sex acts with 14 years prison term.
The LGBTQ rights groups want Kenya’s new curriculum, especially on social ethics and religious education, reviewed and to embrace sexual orientation and gender identity by recognizing LGBTQ people as normal and not “social outcasts.”
“Additionally, ensure that the school environment fosters respect for all people, human rights, and each child’s family values in an atmosphere of understanding, tolerance, and equality,” the report states.
The report asks the government to require all schools to have anti-bullying policies that protect LGBTQ persons and teachers undergo training on diversity and inclusion to promote gender equality. The groups also want the government to guarantee equal access to reproductive healthcare and HIV/AIDS information and treatment that recognizes and respects the needs of LGBTQ people.
The report also seeks a policy paper to help health practitioners and medical students how to work with queer people.
Uganda
Ugandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow
Clare Byarugaba founded PFLAG-Uganda
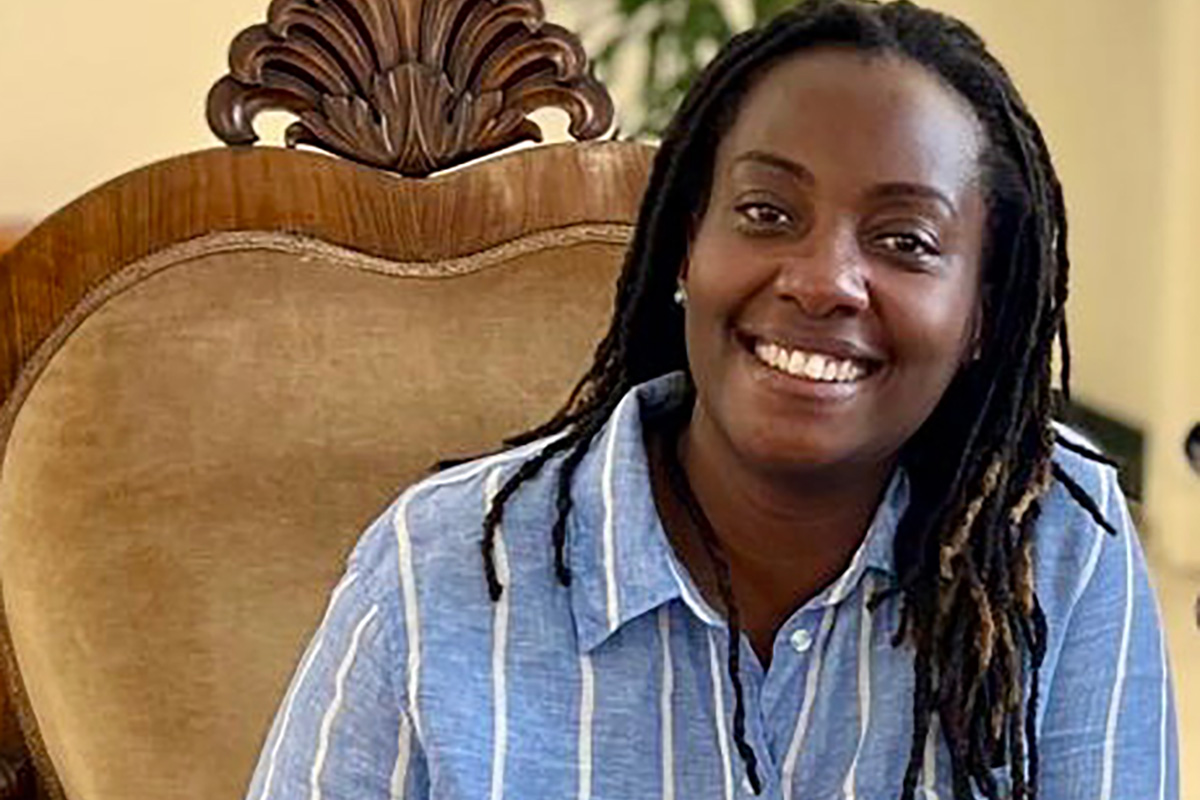

The Charles F. Kettering Foundation has named a prominent Ugandan LGBTQ activist as one of its 2026 fellows.
Clare Byarugaba, founder of PFLAG-Uganda, is one of the foundation’s five 2026 Global Fellows.
Byarugaba, among other things, has been a vocal critic of Uganda’s Anti-Homosexuality Act. Byarugaba in 2024 met with Pope Francis — who criticized criminalization laws during his papacy — at the Vatican.
The foundation on its website says it “is dedicated to bringing research and people together to make the promise of democracy real for everyone, everywhere.”
“Clare is the kind of hero who rushes toward the emergency to help,” said PFLAG CEO Brian K. Bond in a Feb. 27 statement to the Washington Blade. “She founded PFLAG-Uganda as the country pushed to criminalize homosexuality and those who support LGBTQ+ people. Yet, she never hesitated in her courage, telling us that families wanted to organize to keep their LGBTQ+ loved ones safe, and PFLAG was the way to do it. Clare Byarugaba not only deserves this honor, but she will use her compassion and experience to teach the world about LGBTQ+ advocacy as a Kettering Global Fellow.”
Africa
LGBTQ groups question US health agreements with African countries
Community could face further exclusion, government-sanctioned discrimination

Some queer rights organizations have expressed concern that health agreements between the U.S. and more than a dozen African countries will open the door to further exclusion and government-sanctioned discrimination.
The Trump-Vance administration since December has signed five-year agreements with Kenya, Uganda, and other nations that are worth a total of $1.6 billion.
Kenyan and Ugandan advocacy groups note the U.S. funding shift from NGO-led to a government-to-government model poses serious risks to LGBTQ people and other vulnerable populations in accessing healthcare due to existing discrimination based on sexual orientation.
Uganda Minority Shelters Consortium, Let’s Walk Uganda, the Kenya Human Rights Commission, and the Center for Minority Rights and Strategic Litigation note the agreements’ silence on vulnerable populations in accessing health care threatens their safety, privacy, and confidentiality.
“Many LGBTQ persons previously accessed HIV prevention and treatment, sexual and reproductive health services, mental health support, and psychosocial care through specialized clinics supported by NGOs and partners such as USAID (the U.S. Agency for International Development) or PEPFAR,” Let’s Walk Uganda Executive Director Edward Mutebi told Washington Blade.
He noted such specialized clinics, including the Let’s Walk Medical Center, are trusted facilities for providing stigma-free services by health workers who are sensitized to queer issues.
“Under this new model that sidelines NGOs and Drop-in Centers (DICs), there is a high-risk of these populations being forced into public health facilities where stigma, discrimination, and fear of exposure are prevalent to discourage our community members from seeking care altogether, leading to late testing and treatment,” Mutebi said. “For LGBTQ persons already living under criminalization and heightened surveillance, the loss of community-based service delivery is not just an access issue; it is a full-blown safety issue.”
Uganda Minority Shelters Consortium Coordinator John Grace said it is “deeply troubling” for the Trump-Vance administration to sideline NGOs, which he maintains have been “critical lifelines” for marginalized communities through their specialized clinics funded by donors like the Global Fund and USAID.
USAID officially shut down on July 1, 2025, after the White House dismantled it.
Grace notes the government-to-government funding framework will impact clinics that specifically serve the LGBTQ community, noting their patients will have to turn to public systems that remain inaccessible or hostile to them.
“UMSC is concerned that the Ugandan government, under this new arrangement, may lack both the political will and institutional safeguards to equitably serve these populations,” Grace said. “Without civil society participation, there is a real danger of invisibility and neglect.”
Grace also said the absence of accountability mechanisms or civil society oversight in the U.S. agreement, which Uganda signed on Dec. 10, would increase state-led discrimination in allocating health resources.
Center for Minority Rights and Strategic Litigation Legal Manager Michael Kioko notes the U.S. agreement with Kenya, signed on Dec. 4, will help sustain the country’s health sector, but it has a non-binding provision that allows Washington to withdraw or withhold the funding at any time without legal consequences. He said it could affect key health institutions’ long-term planning for specialized facilities for targeted populations whose independent operations are at stake from NGOS the new agreement sidelines.
“The agreement does not provide any assurance that so-called non-core services, such as PrEP, PEP, condoms, lubricants, targeted HIV testing, and STI prevention will be funded, especially given the Trump administration’s known opposition to funding these services for key populations,” Kioko said.
He adds the agreement’s exclusionary structure could further impact NGO-run clinics for key populations that have already closed or scaled down due to loss of the U.S. funding last year, thus reversing hard-won gains in HIV prevention and treatment.
“The socio-political implications are also dire,” Kioko said. “The agreement could be weaponized to incite discrimination and other LGBTQ-related health issues by anti-LGBTQ voices in the parliament who had called for the re-authorization of the U.S. funding (PEPFAR) funding in 2024, as a political mileage in the campaign trail.”
Even as the agreement fails to safeguard specialized facilities for key populations, the Kenya Human Rights Commission states continued access to healthcare services in public facilities will depend on the government’s commitment to maintain confidentiality, stigma-sensitive care, and targeted outreach mechanisms.
“The agreement requires compliance with applicable U.S. laws and foreign assistance policies, including restrictions such as the Helms Amendment on abortion funding,” the Kenya Human Rights Commission said in response to the Blade. “More broadly, funded activities must align with U.S. executive policy directives in force at the time. In the current U.S. context, where executive actions have narrowed gender recognition and reduced certain transgender protections, there is a foreseeable risk that funding priorities may shift.”
Just seven days after Kenya and the U.S. signed the agreement, the country’s High Court on Dec. 11 suspended its implementation after two petitioners challenged its legality on grounds that it was negotiated in secrecy, lacks proper parliamentary approval, and violates Kenyans’ data privacy when their medical information is shared with America.
The agreement the U.S. and Uganda signed has not been challenged.
Senegal
A dozen Senegalese men arrested for ‘unnatural acts’
Popular journalist and musician among those taken into custody
Senegalese police have charged a dozen men with committing “unnatural acts.”
The New York Times reported Pape Cheikh Diallo, a popular television reporter, and Djiby Dramé, a musician, are among the men who authorities arrested. They appeared in court in Dakar, the Senegalese capital, on Monday.
Le Soleil, a Senegalese newspaper, reported authorities arrested the men on Feb. 6 “for intentional transmission of HIV, unnatural acts, criminal conspiracy, and endangering others.” The newspaper further notes the men have been placed in “pre-trial detention.”
Senegal is among the countries in which consensual same-sex sexual relations remain criminalized.
Police in Kaolack, a town that is roughly 135 miles southeast of Dakar, in 2015 arrested 11 people who allegedly engaged in same-sex sexual acts during “a celebration of a gay marriage.” The National Assembly in 2021 rejected a bill that would have further criminalized homosexuality in the country.
-

 National5 days ago
National5 days ago13 HIV/AIDS activists arrested on Capitol Hill
-

 Photos5 days ago
Photos5 days agoPHOTOS: Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras Parade
-

 Florida3 days ago
Florida3 days agoFla. Senate passes ‘Anti-Diversity’ bill that could repeal local LGBTQ protections
-

 Uganda4 days ago
Uganda4 days agoUgandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow