Africa
Kenya seeks to ban intersex athletes from lowering hormone levels to compete in sports
Country’s human rights body has put forth measure

Kenya’s state-funded human rights body does not want intersex athletes in the country to lower their hormone levels as a requirement to compete in any sport.
The Kenya National Commission on Human Rights in a proposal to the National Assembly notes it will ensure non-discrimination and fairness for intersex people in sports.
The proposal in the Intersex Persons Bill, 2024, is among numerous amendments to existing laws that seek to grant intersex people equal rights after the government in 2019 officially recognized them as a third sex.
According to the bill that would amend Kenya’s Sports Act of 2013, this will require the Sports and Youth Affairs Ministry’s Cabinet secretary and the National Council for Intersex Persons, which the measure would create, to develop measures that ensure fairness for sporting intersex people when enacted.
“The measures shall not require a person to alter their biological hormonal composition as a condition to participating in any sporting activity or program,” reads the bill.
Although the measures would apply nationally, they would contradict the World Athletics Council’s 2018 regulations that similarly bar female transgender athletes from participating in international competitions, such as the Olympic Games. Intersex Kenyan athletes have to abide by these rules at the global level.
The World Athletics through the regulations noted trans women who naturally have higher levels of testosterone compared to ordinary women have to undergo medication or surgery to lower their testosterone levels as a condition before competing in races of between 400 meters and a mile. Kenya’s National Olympic Committee supports these rules.
Some top female trans athletes barred from competing in the Olympic events from the World Athletics regulations due to their high natural testosterone levels include Margaret Wambui of Kenya, Caster Semenya of South Africa, Aminatou Seyni of Niger and and Francine Niyonsaba of Burundi.
The trans athletes opposed the World Athletics regulations with Semenya challenging them in court, but lost the case, even though the U.N. Human Rights Council in 2019 criticized the rules. UNHCR cautioned sports bodies not to “force, coerce or otherwise pressure women and girl athletes into undergoing unnecessary, humiliating and harmful medical procedures.”
Kenya National Commission on Human Rights Deputy Director Veronica Mwangi, who spoke with the Washington Blade about the bill’s controversial proposal, said Kenya, which is the only African country to recognize intersex people as a third sex, has started the conversation with a “bigger picture” for the international sporting bodies to create an alternative competition for them to exploit their talents without reducing their hormonal levels or interfering with their biological characteristics as the condition before competing.
“As KNCHR, we are very clear that we cannot afford to continue discriminating and marginalizing persons who are born as intersex, but rather we can promote conversations of inclusivity where the Semenya of South Africa, an equivalent of Semenya in Uganda and an equivalent in the U.S. or Kenya can have a special sporting event like the Paralympics for persons living with disabilities,” Mwangi said.
She also questioned the fairness of World Athletics and other international sporting bodies in demanding “the Semenyas or talented intersex persons” to undergo hormonal therapy which then affects the athletes’ well-being after interfering with their biological anatomy.
“These governing sporting bodies should not come back to us that it is the intersex persons to carry the blame,” Mwangi said. “It is not the responsibility of the intersex (person) but they are duty-bearers and should think of mechanisms to grow their talents and not find an easy way out of demanding to change who they are.”
Mwangi disclosed the proposal is driven by KNCHR’s special task force report that found most intersex school children are talented and perform well in sports.
Kenya’s Intersex Persons Implementation Coordination Committee is already identifying talented intersex people, including those in schools, to support their growth in sports. Kenya’s 2019 Census found there are 1,524 intersex people in the country.
Other amendments to the Intersex Persons Bill include an employment provision that would cap an intersex person’s monthly income tax at 25 percent of wages, compared to other Kenyans whose maximum taxable income stands at 35 percent, depending on one’s monthly total earnings.
“Capping the income tax or wages for intersex persons at 25 percent is a tax consideration in the form of an affirmative action to uplift them in economic development and it is similar to that of persons living with disability who are tax exempted as marginalized groups,” Mwangi said.
The bill further seeks to amend the Health Act for any parent with an intersex child born at home to report the birth at the nearest government administration office or risk a fine of not more than $1,000 or a six-month prison term, or both, after being found guilty of concealing an intersex child’s identity.
The proposed law, moreover, seeks to create the National Council for Intersex Persons, whose mandates would include the creation of initiatives and programs to prevent discrimination against intersex people, creating a database for all intersex people and accrediting the group for employment purposes.
Uganda
Ugandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow
Clare Byarugaba founded PFLAG-Uganda
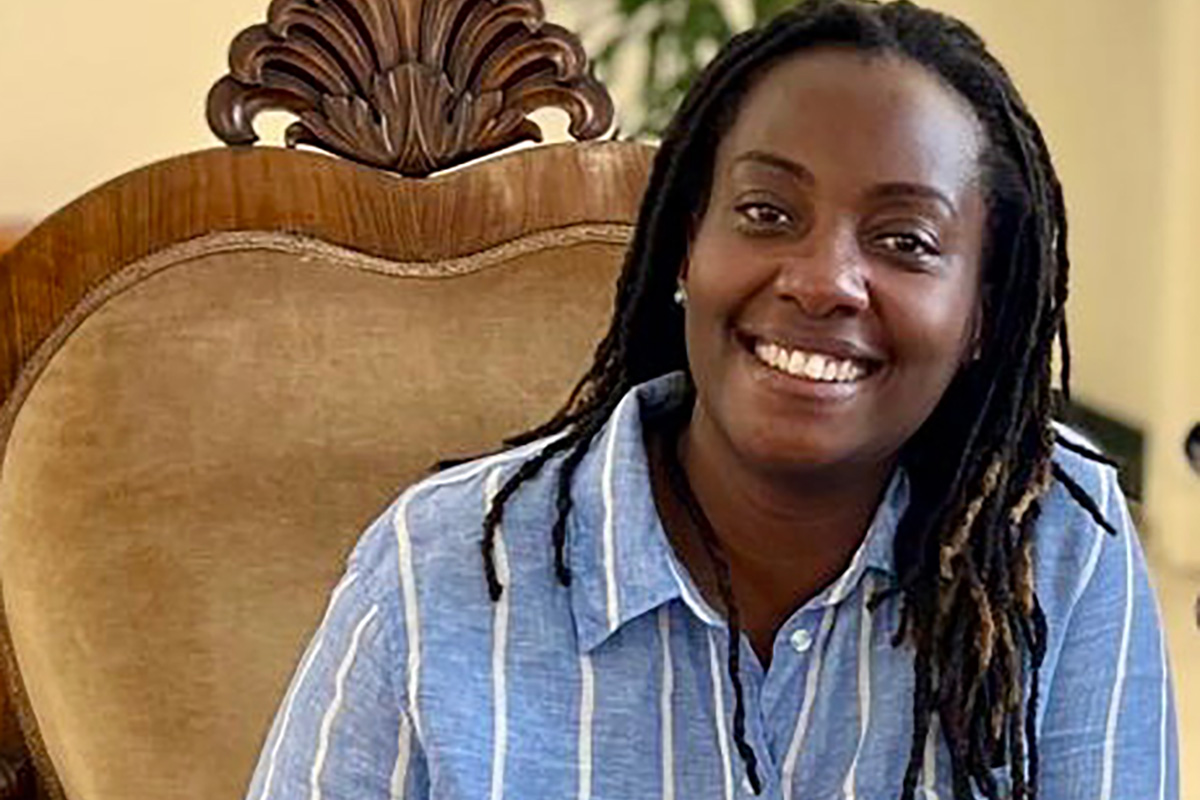

The Charles F. Kettering Foundation has named a prominent Ugandan LGBTQ activist as one of its 2026 fellows.
Clare Byarugaba, founder of PFLAG-Uganda, is one of the foundation’s five 2026 Global Fellows.
Byarugaba, among other things, has been a vocal critic of Uganda’s Anti-Homosexuality Act. Byarugaba in 2024 met with Pope Francis — who criticized criminalization laws during his papacy — at the Vatican.
The foundation on its website says it “is dedicated to bringing research and people together to make the promise of democracy real for everyone, everywhere.”
“Clare is the kind of hero who rushes toward the emergency to help,” said PFLAG CEO Brian K. Bond in a Feb. 27 statement to the Washington Blade. “She founded PFLAG-Uganda as the country pushed to criminalize homosexuality and those who support LGBTQ+ people. Yet, she never hesitated in her courage, telling us that families wanted to organize to keep their LGBTQ+ loved ones safe, and PFLAG was the way to do it. Clare Byarugaba not only deserves this honor, but she will use her compassion and experience to teach the world about LGBTQ+ advocacy as a Kettering Global Fellow.”
Africa
LGBTQ groups question US health agreements with African countries
Community could face further exclusion, government-sanctioned discrimination

Some queer rights organizations have expressed concern that health agreements between the U.S. and more than a dozen African countries will open the door to further exclusion and government-sanctioned discrimination.
The Trump-Vance administration since December has signed five-year agreements with Kenya, Uganda, and other nations that are worth a total of $1.6 billion.
Kenyan and Ugandan advocacy groups note the U.S. funding shift from NGO-led to a government-to-government model poses serious risks to LGBTQ people and other vulnerable populations in accessing healthcare due to existing discrimination based on sexual orientation.
Uganda Minority Shelters Consortium, Let’s Walk Uganda, the Kenya Human Rights Commission, and the Center for Minority Rights and Strategic Litigation note the agreements’ silence on vulnerable populations in accessing health care threatens their safety, privacy, and confidentiality.
“Many LGBTQ persons previously accessed HIV prevention and treatment, sexual and reproductive health services, mental health support, and psychosocial care through specialized clinics supported by NGOs and partners such as USAID (the U.S. Agency for International Development) or PEPFAR,” Let’s Walk Uganda Executive Director Edward Mutebi told Washington Blade.
He noted such specialized clinics, including the Let’s Walk Medical Center, are trusted facilities for providing stigma-free services by health workers who are sensitized to queer issues.
“Under this new model that sidelines NGOs and Drop-in Centers (DICs), there is a high-risk of these populations being forced into public health facilities where stigma, discrimination, and fear of exposure are prevalent to discourage our community members from seeking care altogether, leading to late testing and treatment,” Mutebi said. “For LGBTQ persons already living under criminalization and heightened surveillance, the loss of community-based service delivery is not just an access issue; it is a full-blown safety issue.”
Uganda Minority Shelters Consortium Coordinator John Grace said it is “deeply troubling” for the Trump-Vance administration to sideline NGOs, which he maintains have been “critical lifelines” for marginalized communities through their specialized clinics funded by donors like the Global Fund and USAID.
USAID officially shut down on July 1, 2025, after the White House dismantled it.
Grace notes the government-to-government funding framework will impact clinics that specifically serve the LGBTQ community, noting their patients will have to turn to public systems that remain inaccessible or hostile to them.
“UMSC is concerned that the Ugandan government, under this new arrangement, may lack both the political will and institutional safeguards to equitably serve these populations,” Grace said. “Without civil society participation, there is a real danger of invisibility and neglect.”
Grace also said the absence of accountability mechanisms or civil society oversight in the U.S. agreement, which Uganda signed on Dec. 10, would increase state-led discrimination in allocating health resources.
Center for Minority Rights and Strategic Litigation Legal Manager Michael Kioko notes the U.S. agreement with Kenya, signed on Dec. 4, will help sustain the country’s health sector, but it has a non-binding provision that allows Washington to withdraw or withhold the funding at any time without legal consequences. He said it could affect key health institutions’ long-term planning for specialized facilities for targeted populations whose independent operations are at stake from NGOS the new agreement sidelines.
“The agreement does not provide any assurance that so-called non-core services, such as PrEP, PEP, condoms, lubricants, targeted HIV testing, and STI prevention will be funded, especially given the Trump administration’s known opposition to funding these services for key populations,” Kioko said.
He adds the agreement’s exclusionary structure could further impact NGO-run clinics for key populations that have already closed or scaled down due to loss of the U.S. funding last year, thus reversing hard-won gains in HIV prevention and treatment.
“The socio-political implications are also dire,” Kioko said. “The agreement could be weaponized to incite discrimination and other LGBTQ-related health issues by anti-LGBTQ voices in the parliament who had called for the re-authorization of the U.S. funding (PEPFAR) funding in 2024, as a political mileage in the campaign trail.”
Even as the agreement fails to safeguard specialized facilities for key populations, the Kenya Human Rights Commission states continued access to healthcare services in public facilities will depend on the government’s commitment to maintain confidentiality, stigma-sensitive care, and targeted outreach mechanisms.
“The agreement requires compliance with applicable U.S. laws and foreign assistance policies, including restrictions such as the Helms Amendment on abortion funding,” the Kenya Human Rights Commission said in response to the Blade. “More broadly, funded activities must align with U.S. executive policy directives in force at the time. In the current U.S. context, where executive actions have narrowed gender recognition and reduced certain transgender protections, there is a foreseeable risk that funding priorities may shift.”
Just seven days after Kenya and the U.S. signed the agreement, the country’s High Court on Dec. 11 suspended its implementation after two petitioners challenged its legality on grounds that it was negotiated in secrecy, lacks proper parliamentary approval, and violates Kenyans’ data privacy when their medical information is shared with America.
The agreement the U.S. and Uganda signed has not been challenged.
Senegal
A dozen Senegalese men arrested for ‘unnatural acts’
Popular journalist and musician among those taken into custody
Senegalese police have charged a dozen men with committing “unnatural acts.”
The New York Times reported Pape Cheikh Diallo, a popular television reporter, and Djiby Dramé, a musician, are among the men who authorities arrested. They appeared in court in Dakar, the Senegalese capital, on Monday.
Le Soleil, a Senegalese newspaper, reported authorities arrested the men on Feb. 6 “for intentional transmission of HIV, unnatural acts, criminal conspiracy, and endangering others.” The newspaper further notes the men have been placed in “pre-trial detention.”
Senegal is among the countries in which consensual same-sex sexual relations remain criminalized.
Police in Kaolack, a town that is roughly 135 miles southeast of Dakar, in 2015 arrested 11 people who allegedly engaged in same-sex sexual acts during “a celebration of a gay marriage.” The National Assembly in 2021 rejected a bill that would have further criminalized homosexuality in the country.
-

 Florida4 days ago
Florida4 days agoFla. Senate passes ‘Anti-Diversity’ bill that could repeal local LGBTQ protections
-

 Uganda4 days ago
Uganda4 days agoUgandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow
-

 Celebrity News4 days ago
Celebrity News4 days agoLiza Minnelli makes surprise appearance at GLAAD Media Awards
-

 Opinions4 days ago
Opinions4 days agoCapital Pride must be transparent about sexual misconduct investigation