National
Racial disparities persist in monkeypox outbreak despite equity efforts
Percentage of cases for Black men grows amid overall decline
Racial disparities persist in response to the monkeypox outbreak as the numbers of Black and Latino men contracting the disease are now disproportionately high, but that inequity is getting new attention as overall cases drop.
Although overall new cases in the monkeypox outbreak are steadily on the decline after numbers peaked in the summer, a growing share of the continuing numbers belong to men who have sex with men who are racial minorities.
The latest numbers show the racial disparity dramatically. In the week of Sept. 4, Black people consisted of 41 percent of the cases and Latinos consisted of 27 percent, while 26 percent were white and three percent were Asian, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control.
Black people among the new cases of monkeypox were much smaller when numbers were first reported earlier in the summer. For example, the percentage was 18 on June 22 and as low as 8 percent June 8. The percentage of Latinos, as with white people, has been on the decline, although they’re still overrepresented in new cases in the context of their demographics in the U.S. population at large.
The disproportionate impact of new monkeypox cases on racial minorities hasn’t gone unnoticed. As a result, health officials are attempting to shift the focus of the monkeypox outbreak away from gay and bisexual men and other men who have sex with men more broadly and more toward men of color who are sexual minorities.
Sean Cahill, director of health policy research at the Boston-based Fenway Institute, said in an interview with the Washington Blade the racial disparities in the monkeypox outbreak are largely the result of Black and Latino men being “less likely to get vaccinated than their proportion of the population.”
“So they’re more vulnerable to monkeypox, and they’re less likely to get the vaccine,” Cahill said. “So that’s a real problem, and it’s really critical that you know, federal, state and local partners come together and really center equity in the response and try to reduce the burden on Black and Latino gay men, but also increase access to the vaccine to ensure that people can protect themselves.”
The Fenway Institute last week issued a blueprint calling for a more effective federal response to monkeypox, accusing the U.S. government of failing to effectively mobilize existing public health infrastructure to aid communities affected by the virus. The document outlines a range of possible actions, but also concludes marginalized communities are having difficulty accessing vaccines and treatments, which are concentrated at well-resourced institutions less accessible to communities of color.
Cahill, asked to characterize whether the numbers demonstrating racial disparity have changed over time or have remained stagnant, said any trends are difficult to determine because the data on racial demographics has been available only recently and “it’s very imperfect data.”
“I don’t know if it’s getting worse or better, the disproportionate racial ethnic impact,” Cahill said. “But it’s definitely there, and it doesn’t seem to be going away.”
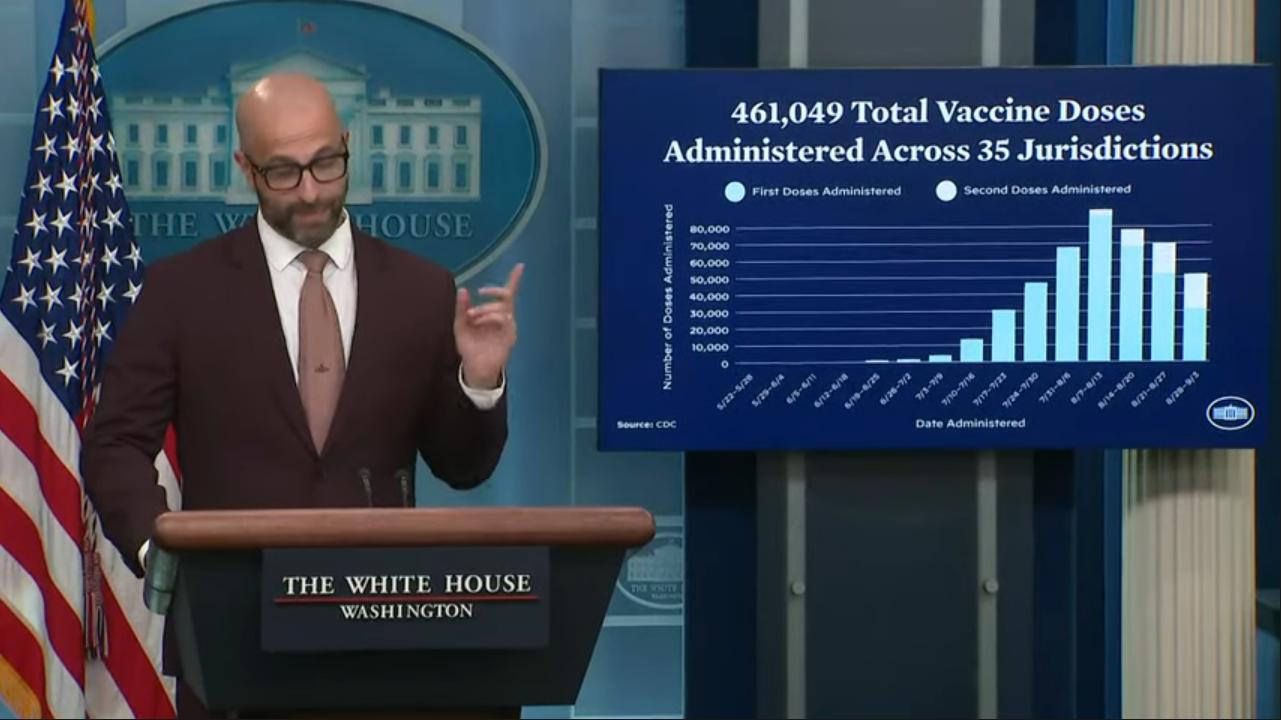
The Biden administration, while touting the 20 percent decline in overall cases in the monkeypox outbreak, has also started to recognize the continued disproportionate impact of monkeypox on Black and Latino men who have sex with men.
Rochelle Walensky, director for the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, said during a conference call with reporters the U.S. government approaches the decline with “cautious optimism.”
“Over the past several weeks, we have also seen the racial and ethnic makeup of this outbreak evolve,” Walensky said. “While monkeypox cases were first seen predominantly in non-Hispanic white men, in the last week, among the cases for which we have race and ethnicity data, non-Hispanic Black men represented 38 percent of cases, Latino or Hispanic men represented 25 percent of cases, and non-Hispanic white men represented 26 percent of cases.”
Among the efforts the Biden administration has undertaken is a pilot program for vaccines reserved for large events and equity. Monkeypox vaccines have been administered to more than 10,000 people, including at Southern Decadence in New Orleans, Atlanta Black Gay Pride, Charlotte Pride, Boise Pride Festival, and Oakland Pride and Pridefest.
Demetre Daskalakis, the face of LGBTQ outreach for the Biden administration in monkeypox efforts and deputy director the White House monkeypox task force, was among those promoting the pilot program in equity efforts during a conference call with reporters.
“Health departments will use their local experience and connection to the community to identify hyperlocal strategies to improve vaccine access to communities of color, specifically those that are overrepresented in this outbreak,” Daskalakis said.
David Johns, executive director of the National Black Justice Coalition, said in the racial disparities in the monkeypox outbreak are consistent with other trends in public health.
“There have been so many opportunities to learn ways to address health inequities before they grow,” Johns said. “That Black people continue to be disproportionately impacted by this newest health epidemic is additional evidence of how white supremacy works and the importance of democratized responses to crises.”
Biden health officials, asked by the Washington Blade during the virtual meeting why the administration’s stated goal of equity in managing the monkeypox outbreak isn’t producing racial equity among new cases, restated their efforts and talked about the difficulty in achieving that goal.
Walensky, who has also had a lead role in the Biden administration combating the coronavirus pandemic, said racial disparities in the monkeypox outbreak “is not uncommon for many infectious diseases, quite unfortunately,” and defended the U.S. government’s approach to monkeypox.
“And it is exactly for these reasons why we started on these pilot projects before we even saw the shifts in data, as that is often the case in infectious diseases that we have more vulnerable population — racial and ethnic minorities — who are most impacted later on,” Walensky added. “And so, we anticipated this. We have embarked on these activities to address this in exactly this moment.”
Daskalakis, following up in defense of the Biden administration’s efforts on equity, said he’s “spoken to providers on the ground and also promoters at these events who have noted that this effort is really unprecedented in terms of reaching deeply into these communities.”
“I think all of our commitment in the administration is to really focus efforts on equity to resolve the issues that we’re seeing. It is a hard effort and it’s a challenge,” Daskalakis added. “And I think that the way to address equity is intentionally, and this is an example of intentional work to address equity.”
With the racial disparity in the monkeypox outbreak ongoing, health observers say additional efforts are needed to reach out to marginalized communities to ensure they have access to public messaging and vaccinations.
Cahill said although people of color in urban areas go to LGBTQ centers to receive health care, many of them are also getting care through other facilities that aren’t LGBTQ-specific, such as emergency rooms and urgent care clinics .
“I think providing some training and technical assistance to those healthcare organizations in how to provide affirming care to bisexual men could be an important approach and could make it so that people might be more likely to disclose same-sex behavior in those contexts,” Cahill said.
U.S. Supreme Court
As Supreme Court weighs trans sports bans, advocate and former athlete speaks out
PFLAG staffer Diego Sanchez competed at University of Georgia in 1970s

The U.S. Supreme Court will hear two cases Tuesday addressing the legality of banning transgender women and girls from participating in sports under the 14th Amendment.
Though the two cases differ slightly in their fact patterns, they ultimately pose the same constitutional question: whether laws that limit participation in women’s sports to only cisgender women and girls violate the Equal Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment.
In both cases — Little v. Hecox and West Virginia v. B.P.J. — trans girls filed lawsuits against their respective states, Idaho and West Virginia, arguing that the bans violate their right to equal protection under the law by subjecting them to different standards than cisgender girls.
Lindsay Hecox, now 24, filed her lawsuit in 2020 while attending Boise State University. That same year, Idaho enacted the “Fairness in Women’s Sports Act,” which barred trans women from participating in any sport in public schools, from kindergarten through college. Although Hecox underwent hormone therapy that significantly lowered her testosterone levels, she was still excluded under the law when she attempted to try out for the women’s track and cross-country teams.
The second case centers on B.P.J., a 15-year-old trans girl who has identified as female since third grade and has been on puberty blockers since the onset of puberty. In 2021, West Virginia enacted the “Save Women’s Sports Act,” which requires sports teams to be designated by “biological sex” rather than gender identity. B.P.J.’s mother filed suit on her behalf after her daughter was barred from participating on her school’s girls’ cross-country and track teams.
A key distinction between the two cases is that attorneys for B.P.J. have argued that because puberty blockers were part of her development, her body is more aligned with that of a cisgender girl than a cisgender boy. Despite these differences, both cases raise the same constitutional issue: whether it is lawful to bar someone from participation in sports based on sex assigned at birth.
The Washington Blade spoke with PFLAG Vice President of Policy and Government Affairs Diego Sanchez.
Sanchez is a trans elder with firsthand experience as a college athlete at the University of Georgia and later became the first openly trans legislative staff member on Capitol Hill.
His dual experience — as a former athlete and a longtime policy expert deeply familiar with constitutional law — gives him a unique perspective on the questions now before the Supreme Court. Sanchez will also be one of the featured speakers at a rally on the steps of the court as the justices hear arguments.
When asked how attitudes toward trans athletes differ from when he competed at the University of Georgia from 1976-1980 to today — when 29 states have passed laws restricting trans participation in sports — Sanchez said the contrast is stark.
“I had the good experience of being supported by my teammates and my coach,” Sanchez said. “The thing that’s so different today is that these [trans] kids are able to go home and get kisses and hugs from their parents, being lauded in the stands by their families, and then being told that who they are doesn’t necessarily fit with who they’re allowed to be in their expression at the moment, and that to me, seems a terrible injustice.”
Sanchez emphasized that sports offer lessons that extend far beyond competition.
“When you’re an athlete, you learn an awful lot of things about life,” he said. “You learn about leadership, but you also learn that your best effort becomes part of a team effort … how you feel as an individual contributor is affected by what ends up being part of how you live your life as an adult.”
After his time as an athlete, Sanchez began working in government, eventually serving as senior policy advisor to then-U.S. Rep. Barney Frank (D-Mass.) until Frank’s retirement in 2013. Sanchez said that one of the most important aspects of his role was simply being visible as a trans person in spaces where many lawmakers had never knowingly met one before.
“My job was to make sure that no one, no legislator, could say that they had never met a trans person,” Sanchez said.
Sanchez also addressed the broader implications the Supreme Court’s decision could have on how gender is treated within institutional systems.
“I don’t think it affects how people perceive their own gender or express their own gender, but I do think that it could create barriers if it doesn’t welcome the way that community and society actually are,” he said. “The most important thing for people to know … is to remember that every person is an individual, and that the right to contribute to society should be something that is supported by the government, not hindered.”
He added that the court’s role must be understood within the framework of checks and balances established by the Constitution.
“The risk, of course, here is always remembering that we have three branches of government, so that this action by the judiciary branch may or may not have implications on whether or how things can be perceived or executed at other branches,” Sanchez said. “I would hope that our government is interested in letting the future generations and current generations be the best that they can be as well.”
“Do people get to live their lives as they are, or is the government an obstruction or a support?”
When asked what message he would share with young trans athletes watching the Supreme Court take up these cases, Sanchez said community support remains critical, regardless of how the justices rule.
“Make sure that the environment that you put yourself in is something that honors who you know you are and supports you becoming the best person you can be, and that anything that takes away from that is purely dissonance,” he said.
“What we do with dissonance is what distinguishes us as whether we excel or doubt.”
That same sense of community, Sanchez said, is what rallies — like the one planned outside the Supreme Court — are meant to reinforce, even as decisions are made inside the building.
“Rallies, including tomorrow’s, are about people knowing they’re not alone, and hearing from other people who support who they are,” he said. “There is support across the country … I wish that I had had someone my age now that I could have looked to, but I am the role model, but I didn’t have any.”
Looking ahead to the possibility that the court could uphold bans on trans athletes, Sanchez said the immediate challenge will be ensuring that families and communities continue to affirm trans youth amid legal uncertainty.
“Having the endorsement of being supported who you are, it helps you so much,” he said. “You cannot put the issue of rights back into the genie’s bottle once people experience what freedom and welcoming is.”
For Sanchez, whose life has spanned decades of change in both sports and government, the cases before the Supreme Court represent a pivotal moment — not just legally, but culturally.
“Living your life, for me, does not require bravery,” he said. “It’s just taking one step and then another.”
U.S. Military/Pentagon
HRC holds retirement ceremony for ousted transgender servicemembers
White House executive order bans openly trans military personnel
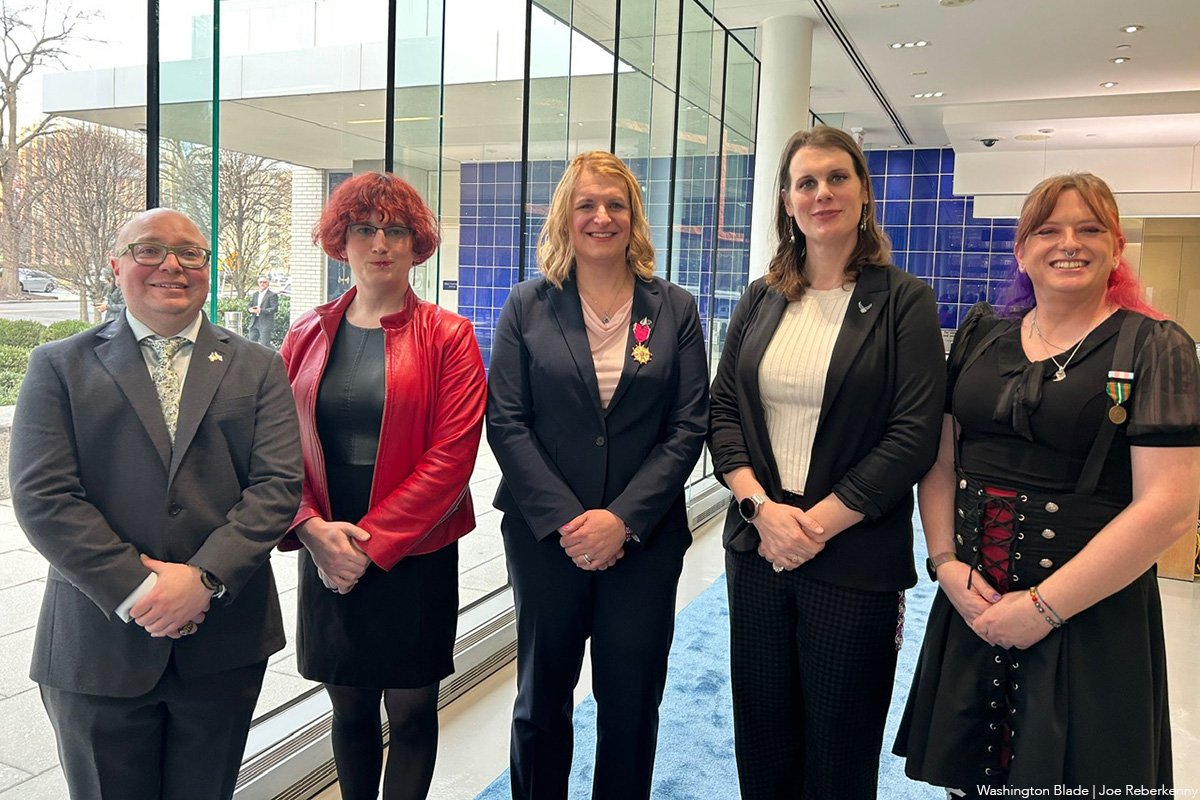

When retirement celebrations are planned — especially military ones — crowded rooms are usually filled with joyous energy: smiling people celebrating over glasses of champagne and stories of “the good old days,” marking the moment when service members decide it is the right time to step back from work. This retirement event, however, felt more like a funeral than a major life milestone.
The Human Rights Campaign Foundation hosted an event on Jan. 8 in D.C. to commemorate the forced retirement of transgender servicemembers. The event was a direct result of President Donald Trump’s 2025 Executive Order 14183, titled “Prioritizing Military Excellence and Readiness,” which directed the Pentagon to adopt policies prohibiting trans, nonbinary, and gender-nonconforming people from serving in the military.
In the heart of the nation’s capital, mere blocks from where the president signed that executive order, five military members followed the traditional pomp and circumstance that military retirement celebrations demand — the U.S. Army’s passing of the NCO sword, the U.S. Navy’s reading of “The Watch,” speeches from colleagues and bells ringing, flags folded tightly while family members, and bosses talk about the peaks of their careers and sacrifices made to protect the Constitution. But the tears that could be heard and seen were not bittersweet, as they often are for the millions of Americans who came before them. They were tears of sadness, fear, and ultimately of acceptance — not agreement — that they were removed from their posts because of their gender identity.
Thousands of trans servicemembers were forced out of all six branches of the military after Executive Order 14183, joined by a February memo from Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth stating that trans and nonbinary individuals would no longer be eligible to join the military. The memo also directed that all trans people currently serving be separated from service because their gender identity supposedly goes against the military’s accession requirements and that, as a collective group, they “lack the selflessness and humility” required for military service.
For many trans servicemembers, their careers had suddenly come to an end. Unlike the five on stage on Jan. 8, they would not have a ceremony, the ability to say goodbye to a job they didn’t want to leave, or a packed room of supporters clapping and crying alongside them.
Colonel Bree B. Fram from the U.S. Space Force, Commander Blake Dremann from the U.S. Navy, Lt. Col. (Ret.) Erin Krizek from the U.S. Air Force, Chief Petty Officer (Ret.) Jaida McGuire U.S. from the Coast Guard, and Sgt. First Class (Ret.) Catherine Schmid from the Army were granted the chance to say goodbye to more than 100 years of combined service to the country.
“This ceremony is unprecedented — not because their careers fell short in any way, but because they shined so brightly in a military that cast them aside as unworthy,” said Maj. Gen. Tammy Smith (Ret.), who was the master of ceremonies for the roughly 5-hour event. “For every one of them, there are thousands of other transgender service members who were denied the opportunity to even reach this moment of retirement, despite records that mark them as among the best of the best.”
Shawn Skelly, former assistant secretary of defense for readiness under President Joe Biden and member of HRC’s board of directors, also spoke at the event. She emphasized that this is not a result of anything a trans servicemember did — or didn’t do — but rather a country trying to villainize them.
“Trans service members … are on the front lines, canaries in the coal mine of our democracy as to who can be seen as not just American, but among the best that America has to offer,” Skelly said.
Two members of Congress who have been at the heart of the fight for ensuring LGBTQ rights for Americans also addressed the crowd and the retiring officers: the first openly gay non-white member of the U.S. House of Representatives, U.S. Rep. Mark Takano (D-Calif.), and the first openly trans member of Congress, U.S. Rep. Sarah McBride (D-Del.).
“I want to begin by apologizing to our [trans] servicemembers and reiterating that your service and commitment to our nation does not go unnoticed,” Takano said. “I am sorry this administration has chosen to target you for no reason other than cruelty.”
“Each of you answered the call to serve. Each of you met the standards. And each of you served and led with integrity, professionalism, and courage,” said McBride. “Each of you are brave, honorable, and committed patriots who also dared to have the courage to say out loud that you’re transgender.”
Former Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall also gave a speech, noting that there was no reason for thousands of trans military members to lose their jobs and for the country to lose invaluable personnel that make the Armed Forces the best in the world.
“As I read the biographies of each of our retirees today, one thing came across to me,” former Kendall said. “It was how similar these read to those of all other retirees, and to others still serving. … It is a huge injustice, and an enormous loss to our nation that [they] … are not being allowed to continue to serve their country in uniform.”
Each service member had an introducer highlight their accomplishments before they gave their own heartfelt and pointed speeches, all of which can be watched in full on HRC’s YouTube page.
“I joined the military to be part of the solution … I learned that living authentically proved far more truthful and beneficial to not only myself but also my units than pretending to be someone else,” McGuire told the audience of family members, friends, LGBTQ rights activists, and former military personnel. “Being transgender never kept me from deploying, and I never failed to fulfill my duties.”
Despite the circumstances, McGuire said she would use this moment as an opportunity to continue serving.
“Even when it was forced upon you with no choice or discussion, [retirement] is still a new chapter … I’ll keep advocating for the rights and freedoms we all cherish,” McGuire said.
Schmid from the Army spoke about accepting the feeling of institutional betrayal after giving so much of herself to the service.
“The Army taught me what honor and integrity meant, and that integrity cost me the only thing I’ve ever really known how to do — it cost me being a soldier,” Schmid said. “Institutions fail people, but institutions are made of people, and that’s what I keep going back to … the soldiers, the people — that’s the Army that matters.”
Presik from the Air Force went next.
“Over my career, I’ve been called a hero and thanked for my service … I did all those things for the hope that I was making this country a better place for my three children and for your children and your families and your hopes as well,” Presik said, emphasizing that this was a fundamental policy failure, not a personal failure. “Now I have been separated from the Air Force, not because my performance, commitment, or ideals were found lacking, but because the policy changed on who could serve — and that reality is difficult to say out loud.”
“You matter. Your service matters, and you are not alone … transgender airmen are surrounded daily by so many fellow Americans who serve quietly and professionally,” Presik added, acknowledging that some trans people will continue to serve their country, even if it means hiding a piece of themselves until this policy is remedied.
Draiman from the Navy was fourth, emphasizing that his work serving the American people would continue despite retirement.
“I have spent my entire career pushing back against systems that too often treated my sex, my sexuality, or my gender as a measure of my capability under the guise of readiness,” Draiman told the crowd. “The work of dismantling hate and building better systems is far from over, and I still have more to give as I step out of uniform.”
Fram from the Space Force went last.
“My service was real. My dedication was real, and the years I gave to this country were given fully, honorably, and especially at the end with great pride,” she said with tears welling in her eyes — as did most of those in the audience. “Transgender service members are persons of character, not caricatures, and a society that justifies exclusion by denying our humanity needs to learn its lesson better from the Civil Rights Movement.”
“The uniform may come off, but the values it represents never will.”
Across the five branches of the military represented, each retiree carried countless honors and awards, evidence of their strength and dedication to protecting a country that elected a president who has now attempted to strip them of their service in both of his terms in office.
After the ceremony, the Washington Blade sat down with HRC Senior Vice President of Campaigns and Communications Jonathan Lovitz, to discuss why HRC decided to honor these five servicemembers.
“Why do this? Because they deserve nothing less. These are our heroes. These are our fellow Americans who have done more to serve this country than anyone who has been attacking them for that service,” Lovitz said. “These five are stand-ins for the thousands more, many of whose stories we’re never going to know, but it’s our obligation to find and uplift every single one of them.”
Multiple times during the ceremony, it was noted that military members vow to protect the Constitution rather than any individual in the White House. For Lovitz, that is the crux of why HRC felt the need to act.
“Civil rights protect all of us — or at least they’re supposed to. That’s at the heart of the Constitution … and that includes, and especially includes, our heroes who fight, sometimes die, to protect even those who would try to erase them.”
He ended the conversation by sharing a private moment with one of the retirees.
“I just hugged one of the honorees, and she said to me, ‘We never should have had to do this, but if we had to do it, this was the way.’ So I feel great that they feel loved and honored and seen and celebrated, and that so many leaders in the community were able to be here to lift them up.”
The White House
Hundreds protest ICE killing of Renee Nicole Good in D.C.
Married queer woman shot in Minneapolis on Wednesday
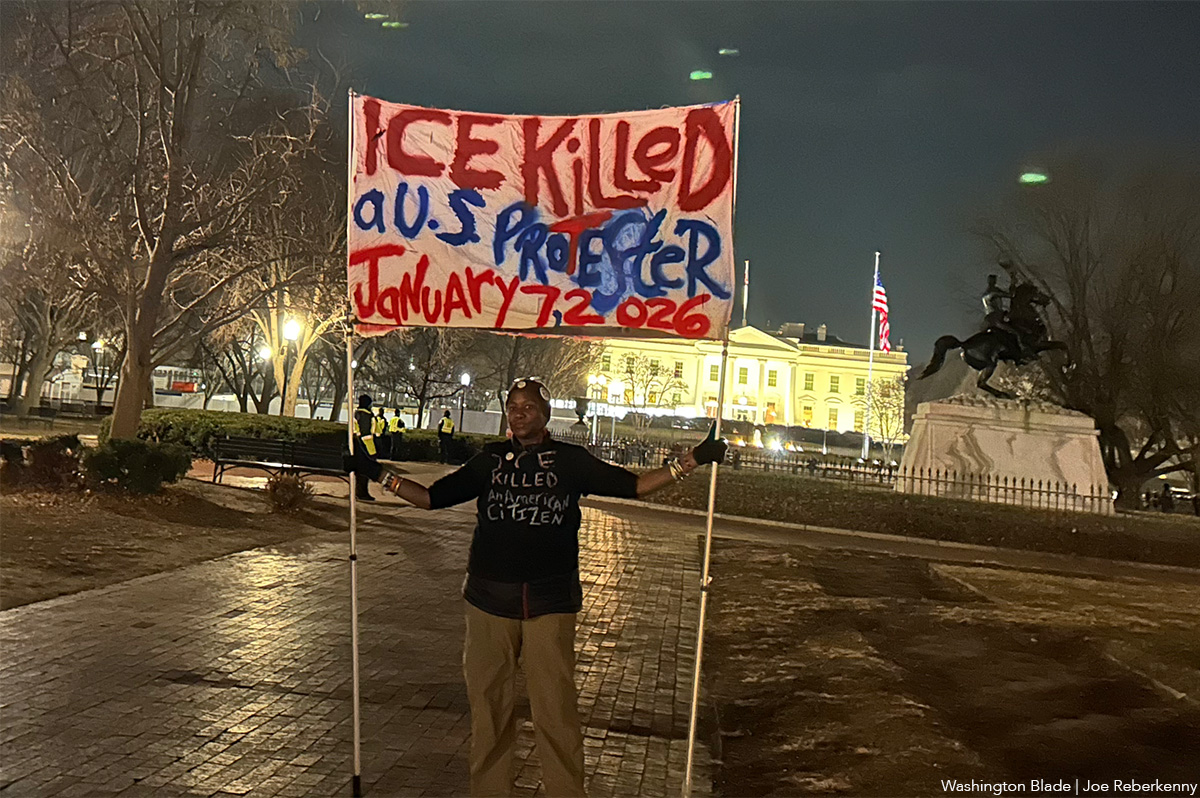
Hundreds of people took to the streets of D. C. on Thursday night to protest the killing of a U.S. citizen by a U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement agent.
Protests began at the busy — and increasingly queer — intersection of 14th and U Streets, N.W. There, hundreds of people held signs, shouted, and made their way to the White House to voice their dissent over the Trump-Vance administration’s choice to increase law enforcement presence across the country.
The protest, which also occurred simultaneously in cities large and small across the country, comes in the wake of the death of Minneapolis resident Renne Nicole Good at the hands of ICE Agent Jonathan Ross. Good left behind two children and a wife, Rebecca Good.
Records obtained by the Associated Press found that Ross was an Iraq War veteran and nearly two decades into his career with U.S. Border Patrol and ICE.
Good was gunned down just blocks away from where George Floyd was killed by police in 2020, sparking weeks of national protests. Minnesota officials say the FBI has blocked their access to an investigation into the fatal shooting, according to a BBC story published on Friday.
In the nation’s capital, protesters marched from the intersection of 14th and U Street to Lafayette Square, right outside the White House. Multiple D.C. organizations led the protest, most notably Free DC, a nonprofit that works to ensure the right of “self-determination” for District residents, as many local laws can be reviewed, modified, or overturned by Congress. Free DC had organized multiple protests since the Trump-Vance administration was elected.
The Washington Blade spoke to multiple protesters towards the tail end of the protest about why they came out.
Franco Molinari, from Woodbridge, Va., crossed the Potomac to partake in his first-ever protest.
“I don’t appreciate ICE and the use of federal agents being pretty much militarized against America,” Molinari said while holding a “Justice for Renee” sign. “The video of Renee being executed cartel style in her car was enough for me to want to come out, to at least do something.”
Molinari, like many others the Blade spoke with, found out about the protest on Instagram.
“It was my friend there, Sarah … had sent a link regarding the protest to a group chat. I saw it in the morning, and I thought, ‘You know what, after work, I’m head out.’”
He also shared why protesting at the White House was important.
“I already saw the response that the president gave towards the murder of Renee, and it was largely very antagonizing,” Molinari said.
President Donald Trump, along with federal leaders under him, claimed that Good “violently, willfully and viciously ran over the ICE officer.” The president’s claims have been widely discredited through multiple videos of the incident, which show Good was attempting to leave the scene rather than attacking the officer.
“I hope that anybody would be able to see that and see the response and see for themselves that it just is not correct,” Molinari said.
The Blade also spoke with leftist influencer Dave the Viking, who has more than 52,000 followers on TikTok, where he posts anti-fascist and anti-Trump videos.
“We’re out here to make sure that this regime can’t rewrite history in real time, because we all know what we saw … we’re not going to allow them to run with this narrative that they [ICE agents] were stuck in the snow and that that poor woman tried to weaponize her car, because we all saw video footage that proves otherwise,” he told the Blade. “We’re not going to let this regime, the media, or right-wing influencers try to rewrite history in real time and try to convince us we didn’t all see what we know we saw.”
Dave the Viking continued, saying he believes the perceived power of ICE and other law enforcement to act — oftentimes in deadly and unjustifiable ways — is a product of the Trump-Vance administration.
“There’s a line between fascism and anti-fascism. These motherfuckers have been pushing that envelope, trying to label an idea a terrorist organization, to the point of yesterday, crossing that line hardcore. You face the point of looking at history and saying there was this 1989, 2003 America, where we’re just going in, raiding resources. Where is this fucking 1930s Germany, where we’re going in and we’re about to just start clearing shit and pulling knots? Yeah, nope. We proved that shit yesterday.”
Two people were injured in another shooting involving federal agents, this time Border Patrol in Portland, Ore., on Thursday afternoon.
KC Lynch, who lives near American University, also spoke about her choice to protest with a group.
“I came out today because everything that ICE has done is absolutely unacceptable, not only killing this one woman, but also the fact that they’ve been imprisoning people in places that are literally, that have been literally on record by international organizations shown to be human rights violating. It’s unbelievably evil.”
Lynch also echoed Dave’s opinion about parallels between the Trump-Vance administration and the rise of Adolf Hitler in Nazi Germany.
“It’s literally what happened before the Holocaust. We should all be scared. We should all be angry. I’m so angry about it … even talking about it — I’m sorry,” she said before getting choked up.
Lynch emphasized that despite the circumstances in which people were protesting together, the sense of community was strong and powerful.
“I feel like it’s important for people to know that we’re angry, even if no policy changes come out of it, and it’s just nice to yell and be angry about it, because I feel like we’ve probably all been feeling this way, and it’s nice to be around people that are like minded and to like have a sense of community.”
-

 Opinions5 days ago
Opinions5 days agoJust say no to the felon in the White House
-

 Minnesota5 days ago
Minnesota5 days agoReports say woman killed by ICE was part of LGBTQ community
-

 Maryland5 days ago
Maryland5 days agoSteny Hoyer, the longest-serving House Democrat, to retire from Congress
-

 National5 days ago
National5 days agoU.S. in midst of ‘genocidal process against trans people’: study