News
Sen. Warren’s new bill could give gay couples refund on back taxes
Refund Equality Act allows for reconsideration of marriages prior to DOMA ruling
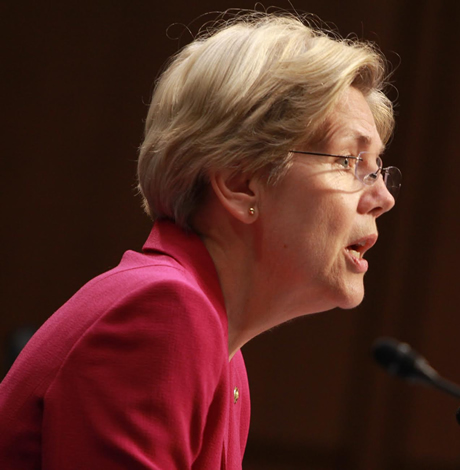
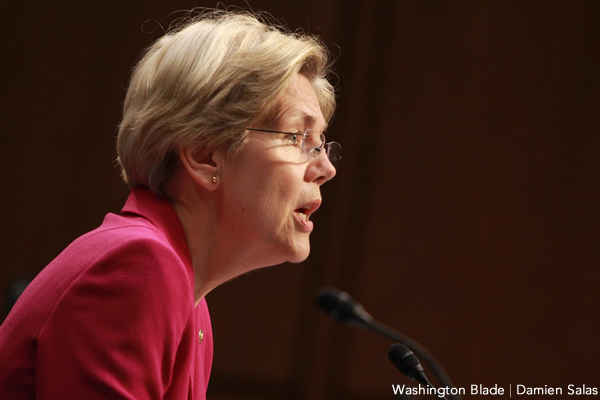


Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-has introduced legislation that could gay couples a refund on back taxes.
(Washington Blade photo by Damien Salas)
A new bill led by Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass.) in the U.S. Senate would make gay couples potentially eligible for a refund on their back taxes if they married more than three years before the U.S. Supreme Court struck down the anti-gay Defense of Marriage Act.
The legislation, called the Refund Equality Act, would same-sex couples married in places like Massachusetts, which had marriage equality before the Supreme Court decision in the Obergefell case, could file amended tax returns back to the date of their marriage.
“For nearly a decade, legally married same-sex couples had to file their taxes as single persons, often paying more taxes than they would owe if they could file as married,” Warren said in a statement. “This bill is a simple fix to allow same-sex couples to claim the tax refunds they earned but were denied because of who they love.”
After the Supreme Court ruled against DOMA in 2013, then-President Obama directed his administration to extend federal spousal benefits to same-sex couples to the furthest extent possible under the law. Former Treasury Secretary Jack Lew allowed married same-sex couples throughout the country — even those in states at the time without marriage equality — to file taxes jointly for the first time.
Additionally, same-sex couples could file an amended return if they feel they would’ve receive a refund in one or more prior tax years for up to three years in the past: 2010, 2011, and 2012. Under some circumstances, such as signing an agreement with the Internal Revenue Service to keep the statute of limitations open, these couple might have been able to seek a refund from an earlier time.
The Refund Equality Act would extend the window period for a refund further back in time. Same-sex couples could file a joint return to seek a refund dating to the time of their marriage, which in Massachusetts could be as early as 2004.
Same-sex couples who wed in jurisdictions with marriage equality more than three years before the DOMA decision — Massachusetts, Connecticut, California, Iowa, New Hampshire, Vermont, and D.C. — could be eligible for a refund under the Refund Equality Act.
According to Warren’s office, an estimated $67 million in refunds could be available to married same-sex couples if the legislation becomes law.
It’s possible that under some circumstances, same-sex couples would have had to pay more in taxes if DOMA weren’t in place as a result of filing as married as opposed to single. Low and high-income couples can incur hefty marriage penalties — often when both spouses have similar incomes. It seems unlikely those couples would be eligible for a refund under the Refund Equality Act.
In the Senate, the legislation is co-sponsored by 30 senators — all Democrats. Among them are Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-N.Y.), lesbian Sen. Tammy Baldwin (D-Wis.), Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), Sen. Tim Kaine (D-Va.) and Sen. Kamala Harris (D-Calif.).
Rep. Richard Neal (D-Mass.) leads the legislation in the U.S. House, where 39 other lawmakers have co-sponsored the bill.
“All legally married couples in this country deserve to be treated equally,” Neal said in a statement. “This bill would codify into law an important correction that would enable same-sex married couples to go back and claim the tax refunds and credits for which they qualify. The Supreme Court has ruled as such, and now it’s time for Congress to act and make sure all Americans are treated with the fairness and equality they deserve under the law.”
Read a fact sheet on the Refund Equality Act here.
District of Columbia
Bowser appoints first nonbinary person to Cabinet-level position
Peter Stephan named Office of Disability Rights interim director

D.C. Mayor Muriel Bower has named longtime disability rights advocate Peter L. Stephan, who identifies as nonbinary, as interim director of the D.C. Office of Disability Rights.
The local transgender and nonbinary advocacy group Our Trans Capital and the LGBTQ group Capital Stonewall Democrats issued a joint statement calling Stephan’s appointment an historic development as the first-ever appointment of a nonbinary person to a Cabinet-level D.C. government position.
“This milestone appointment recognizes Stephan’s extensive expertise in disability rights advocacy and marks a historic advancement for transgender and nonbinary representation in District government leadership,” the statement says.
The statement notes that Stephan, an attorney, held the position of general counsel at the Office of Disability Rights immediately prior to the mayor’s decision to name him interim director.
The mayor’s office didn’t immediately respond to a question from the Washington Blade asking if Bowser plans to name Stephan as the permanent director of the Office of Disability Rights. John Fanning, a spokesperson for D.C. Council member Anita Bonds (D-At-Large), said the office’s director position requires confirmation by the Council.
Stephan couldn’t immediately be reached for comment.
“At a time when trans and nonbinary people ae under attack across the country, D.C. continues to lead by example,” said Stevie McCarty, president of Capital Stonewall Democrats. “This appointment reflects what we have always believed that our community is always strongest when every voice is represented in government,” he said.
“This is a historic step forward,” said Vida Rengel, founder of Our Trans Capital. “Interim Director Stephan’s career and accomplishments are a shining example of the positive impact that trans and nonbinary public servants can have on our communities,” according to Rangel.
Bulgaria
Top EU court issues landmark transgender rights ruling
Member states must allow name, gender changes on ID documents

The European Union’s highest court on Thursday ruled member states must allow transgender people to legally change their name and gender on ID documents.
The EU Court of Justice in Luxembourg issued the ruling in the case of “Shipova,” a trans woman from Bulgaria who moved to Italy.
“Shipova” had tried to change her gender and name on her Bulgarian ID documents, but courts denied her requests for nearly a decade.
A ruling the Bulgarian Supreme Court of Cassation issued in 2023 essentially banned trans people from legally changing their name and gender on ID documents. Two Bulgarian LGBTQ and intersex rights groups — the Bilitis Foundation and Deystvie — and ILGA-Europe and TGEU – Trans Europe and Central Asia supported the plaintiff and her lawyers.
“Because her life in Italy also depended on her Bulgarian documents, the lack of documents reflecting her lived gender creates an obstacle to her right to move and reside within EU member states,” said the groups in a press release. “This mismatch between her gender identity and expression and her gender marker in her official documents leads to discrimination in all areas of life where official documents are required. This includes everyday activities such as going to the doctor and paying for groceries by card, finding employment, enrolling in education, or obtaining housing.”
Denitsa Lyubenova, a lawyer with Desytvie, in the press release said the case “concerns the dignity, equality, and legal certainty of trans people in Bulgaria.” TGEU Senior Policy Officer Richard Köhler also praised the ruling.
“Today, the EU Court of Justice has taken an important step towards a right to legal gender recognition in the EU,” said Köhler. “Member states must allow their nationals living in another member state to change their gender data in public registries and identity cards to ensure they can fully enjoy their freedom of movement. National laws or courts cannot stand in their way.”
“Thousands of trans people in the EU are breathing a sigh of relief today,” added Köhler.
Senegal
Senegalese lawmakers approve bill to further criminalize homosexuality
A dozen men arrested in February for ‘unnatural acts’
Senegalese lawmakers on Wednesday approved a bill that would further criminalize consensual same-sex sexual relations in the country.
The Associated Press notes the measure that Prime Minister Ousmane Sonko introduced in February would increase the penalty for anyone convicted of engaging in consensual same-sex sexual relations from one to five years in prison to five to 10 years. The AP further indicates the bill would prohibit the “promotion” or “financing” of homosexuality in the country.
The bill passed with near unanimous support. Only three of 135 MPs abstained.
President Bassirou Diomaye Faye is expected to sign the measure.
The National Assembly in 2021 rejected a bill that would have further criminalized homosexuality in Senegal.
Senegalese police last month arrested a dozen men and charged them with committing “unnatural acts.”
Volker Türk, the U.N. high commissioner for human rights, in a statement described the bill as “deeply worrying.”
“It flies in the face of the sacrosanct human rights we all enjoy: the rights to respect, dignity, privacy, equality and freedoms of expression, association, and peaceful assembly,” he said.
Türk also urged Faye not to sign the bill.
“I urge the president not to sign this harmful law into effect, and for authorities to repeal the existing discriminatory law and to uphold the human rights of all in Senegal, without discrimination,” said Türk.
-

 Health4 days ago
Health4 days agoToo afraid to leave home: ICE’s toll on Latino HIV care
-

 Movies4 days ago
Movies4 days agoIntense doc offers transcendent treatment of queer fetish pioneer
-

 The White House3 days ago
The White House3 days agoTrump will refuse to sign voting bill without anti-trans provisions
-

 Colombia4 days ago
Colombia4 days agoClaudia López wins primary in Colombian presidential race