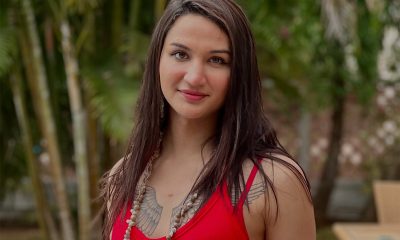World
Honduras government institutions ‘are murdering us’
Lack of opportunities, violence prompt LGBTQ people to migrate

Editor’s note: International News Editor Michael K. Lavers was on assignment for the Washington Blade in Honduras, El Salvador and Mexico from July 11-25.
LA CEIBA, Honduras — Leonela and Jerlín, her partner of 11 years, and their school-age daughter live in La Ceiba, a city on Honduras’ Caribbean coast.
Jerlín was a bus driver in San Pedro Sula, the country’s commercial capital, until gang members shot him three times in 2012 because he couldn’t pay the extortion money from which they demanded from him each month. Jerlín, Leonela and their daughter subsequently fled to La Ceiba, which is about three hours east of San Pedro Sula.
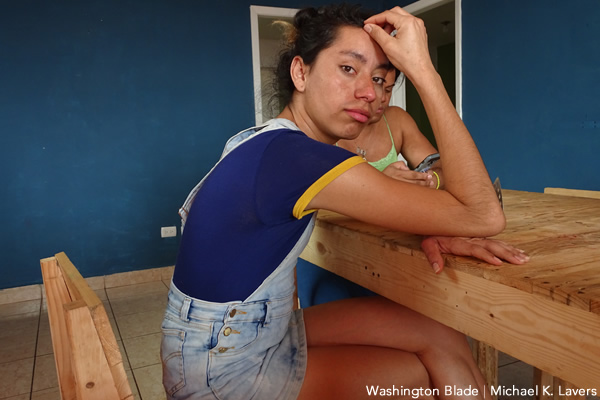
“We left,” Jerlín told the Washington Blade on July 20 during an interview at the offices of Organización Pro Unión Ceibeña (Oprouce), a La Ceiba-based advocacy group. “We fled from there.”
Jerlín migrated to Mexico in January 2019, but returned to Honduras less than a month later because Leonela was in the hospital. The couple and their daughter migrated to Mexico a year later.
Leonela asked for a Mexican humanitarian visa for her and her daughter once they arrived in Ciudad Hidalgo, a Mexican border city that is across the Suchiate River from Tecún Umán, Guatemala.
Leonela told the Blade that she planned to ask for asylum in Mexico and wanted to go to Tuxtla Gutiérrez, the capital of Mexico’s Chiapas state, to find work. Leonela said she and Jerlín instead decided to return to Honduras because they did not want their daughter to further endure the “inhumane” conditions of the migrant detention center in Tapachula, a city that is roughly 20 miles northwest of Ciudad Hidalgo, in which they were living.
“We decided it was better to allow them to deport us,” said Jerlín.

Jerlín, Leonela and their daughter returned to Honduras in May 2020. Someone shot at their house on July 10, 2020.
“They couldn’t even do what people wanted them to do, perhaps even buring us alive,” said Leonela.
Leonela and Jerlín are among the many LGBTQ Hondurans who have decided to leave Honduras in order to escape violence and discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity.
Vice President Kamala Harris and other Biden administration officials have acknowledged anti-LGBTQ violence is one of the “root causes” of migration from Honduras and neighboring Guatemala and El Salvador.
Title 42, a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention rule that closed the Southern border to most asylum seekers and migrants because of the coronavirus pandemic, remains in place. The White House has repeatedly told migrants not to travel to the U.S.
Roxsana Hernández, a trans Honduran woman with HIV, died at a New Mexico hospital on May 25, 2018, while in U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement custody.
Natasha, another trans Honduran woman, arrived in Matamoros, a Mexican border city that is across the Rio Grande from Brownsville, Texas, on Oct. 12, 2019. The previous administration forced her to pursue her U.S. asylum case in Mexico under its Migrant Protection Protocols. (The U.S. Supreme Court on Tuesday ordered the Biden administration to reinstate MPP.)
The Blade interviewed Natasha on Feb. 27 at a Matamoros shelter that Rainbow Bridge Asylum Seekers, a program for LGBTQ asylum seekers and migrants that Resource Center Matamoros, a group that provides assistance to asylum seekers and migrants in the Mexican border city, helped create. The U.S. less than two weeks later allowed Natasha to enter the country.

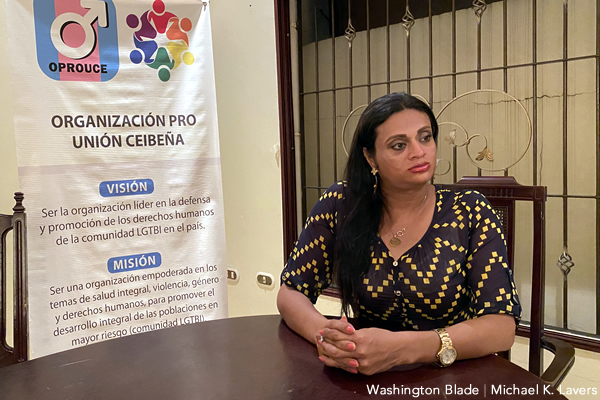
Oprouce Executive Director Sasha Rodríguez, who is trans, has participated in the State Department’s International Visitor Leadership Program.
She said a lack of employment and housing associated with the pandemic has prompted more Hondurans to migrate to the U.S., Mexico and Costa Rica. Rodríguez also told the Blade the U.S. and “our countries sell an American dream that doesn’t exist.”
“Why don’t these American organizations say don’t go,” she said, specifically referring to trans people who have decided to leave Honduras. “Here they see it as beautiful. They are already in the United States, but they were raped while trying to get there. They were kidnapped.”

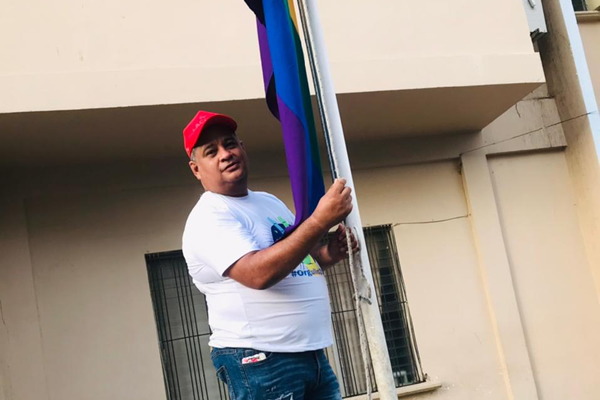
Alexa, a 27-year-old trans woman from La Ceiba, told the Blade she has friends who live in Mexico. Alexa said she would like to leave Honduras, but she doesn’t want to leave her mother alone.
“I don’t want to leave her alone and abandon her because I have always fought for her,” Alexa told the Blade during an interview at Oprouce. “She supports me as a woman.”
Alexa said she served a nearly 3-year prison sentence for attempted murder, even though she was defending herself against a woman who was hitting her in the face with a rock. Alexa began to sob when she started to tell the Blade about the Salvadoran man who raped her in prison. She said the warden then forced her to cut her hair and guards doused her with “ice cold water” in an isolation cell.
“I was a woman,” said Alexa. “They made me a man.”
Alexa told the Blade that other prisoners tried to kill her. She said she also tried to die by suicide several times until her release on Jan. 27.
Alexa said she has not been able to find a job since she left prison. She also told the Blade that gang members continue to threaten her.
“It is sometimes very difficult to lead the lifestyle that we lead as trans women in Honduras,” she said, referring to anti-trans discrimination and a lack of employment opportunities.
Venus, a 30-year-old trans woman who is also from La Ceiba, echoed Alexa.
“To be a trans person is synonymous with teasing, harassment, violence and even death,” Venus told the Blade at Oprouce.
Venus said Honduran soldiers regularly attack trans women. She told the Blade a lack of access to health care, machismo and patriarchal attitudes are among the myriad other issues that she and other trans Hondurans face.
“We don’t have access to education, to health (care), to a job,” said Venus. “Above all we are fighting for a gender-based law that recognizes us as women and men.”
Venus added she, like Alexa, would leave Honduras “if I was given the opportunity to do so.”
Landmark ruling finds Honduras responsible for trans woman’s murder
Red Lésbica Cattrachas, a lesbian feminist human rights group based in Tegucigalpa, the Honduran capital, notes 373 LGBTQ Hondurans were reported killed in the country between 2009-2020.
Statistics indicate 119 of those murdered were trans. Red Lésbica Cattrachas also noted 18 of the LGBTQ Hondurans who were reported killed were in Atlántida department in which La Ceiba is located.
Vicky Hernández was a trans activist and sex worker with HIV who worked with Colectivo Unidad Color Rosa, a San Pedro Sula-based advocacy group.
Hernández’s body was found in a San Pedro Sula street on June 29, 2009, hours after the coup that ousted then-President Manuel Zelaya from power. Hernández and two other trans women the night before ran away from police officers who tried to arrest them because they were violating a curfew.
The Inter-American Court of Human Rights in June issued a landmark ruling that found Honduras responsible for Hernández’s murder.
The ruling ordered Honduras to pay reparations to Hernández’s family and enact laws that protect LGBTQ people from violence and discrimination. The government of President Juan Orlando Hernández, whose brother, former Congressman Juan Antonio “Tony” Hernández, is serving a life sentence in the U.S. after a federal jury convicted him of trafficking tons of cocaine into the country, has not publicly responded to the ruling.
Rodríguez noted to the Blade that Oprouce and other advocacy groups have been fighting for a trans rights law in Honduras for more than a decade.
“We have had failure for 11 years, but I think that with what happened with the Inter-American Court, the recommendations that have come from the Vicky Hernández case could achieve something important,” said Rodríguez. “There are very good human rights recommendations for Honduras and there are good recommendations that Honduras could automatically apply to trans women.”
Rodríguez as she discussed the ruling reiterated trans Hondurans continue to face violence, discrimination and a lack of employment opportunities. Rodríguez also reiterated her sharp criticism of her country’s government and its institutions.
“Societal exclusion forces us to do sex work,” she said. “We are being harmed by our trade: Murder, persecution, hate crimes, torture, beatings.”
“I always say that it is an institutional death because state institutions are murdering us,” added Rodríguez.
‘My fight is here’
In spite of these challenges, Rodríguez said there has been progress.
Oprouce — which works on a variety of issues that include the prevention of gender-based violence and fighting HIV/AIDS — offers workshops to the Public Ministry, the Honduran Armed Forces and judges. Asociación de Prevención y Educación en Salud, Sexualidad, Sida y Derechos Humanos (Aprest), another advocacy group in Tela, a city that is about 60 miles west of La Ceiba, conducts similar trainings with local and national authorities.
Aprest Executive Director Leonel Barahona Medina told the Blade during an interview at a beachfront restaurant in Tela on July 20 that city officials have given him an office from which he and his colleagues can work. Barahona said they also supported activists who raised the Pride flag on June 27 in front of Tela City Hall.
A similar ceremony took place in a park in the center of La Ceiba.
“We have good relations with them,” said Barahona, referring to Tela officials.

Both Barahona and Rodríguez said their work will continue.
“My fight is here,” said Rodríguez. “My essence and my dreams are here.”
Abdiel Echevarría-Caban and Reportar sin Miedo contributed to this story.
Latin America
Protests, demands for rights define Pride month in Latin America
More than 3 million people participated in São Paulo march
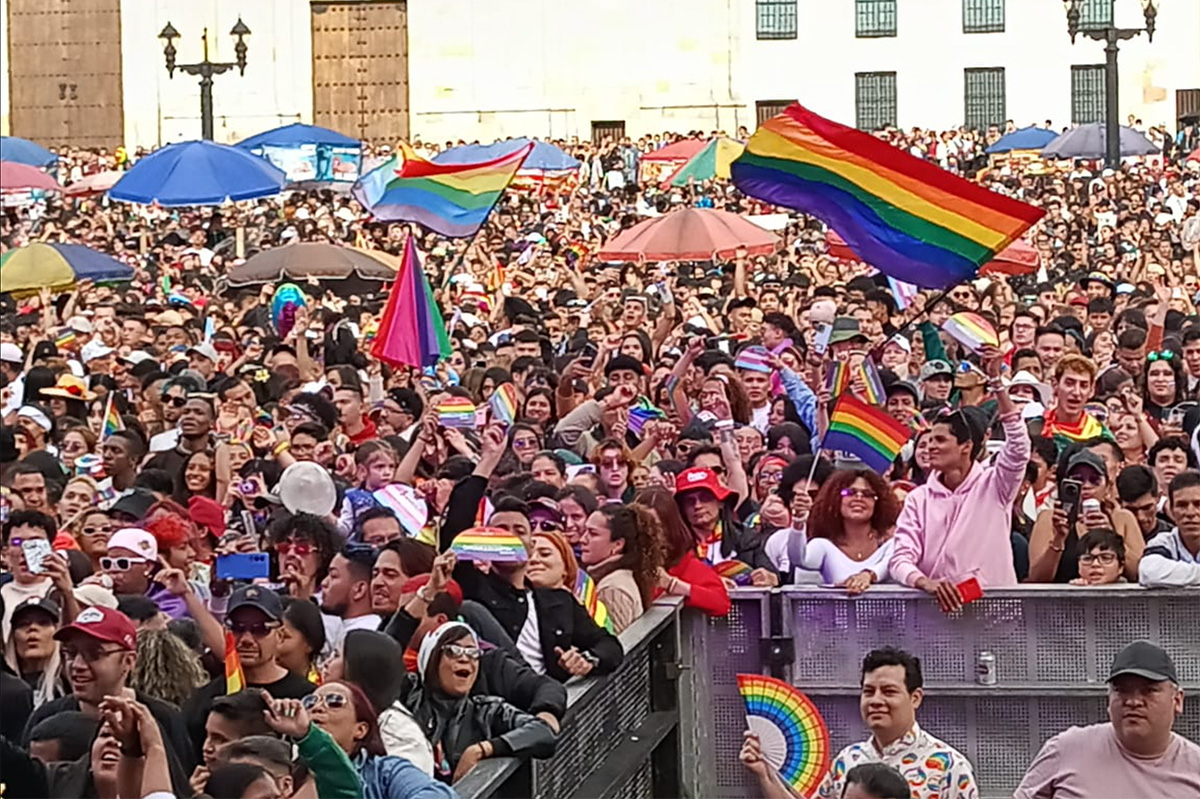

Activists across Latin America marked Pride month with massive demonstrations, cultural activities, and demands that their countries guarantee equality and protect LGBTQ people from violence.
From Santiago, Chile, to Mexico City, activists took to the streets to celebrate the rights that have been won and the many that are still pending.
Chile
The Pride march that the Movement for Homosexual Integration and Liberation (Movilh) and Fundación Iguales organized took place in downtown Santiago, the country’s capital, on June 22. Authorities and the two organizations say more than 120,000 people participated.
Under the slogan “Pride with memory and hope,” marchers demanded lawmakers approve a bill that would allow reparations for LGBTQ Chileans who Gen. Augusto Pinochet’s dictatorship targeted. There were also calls for the government to promote an LGBTQ-inclusive educational reform.
“This time we are marching on high alert,” said Movilh spokesperson Javiera Zúñiga. “For the first time in decades, we are losing achieved rights. We demand the state wake up. The reform of the Zamudio Law has been stalled for 13 years.”
Marches also took place in Valparaíso, Antofagasta, Temuco, and Concepción, highlighting the growing visibility of transgender groups and feminist organizations.
Mexico
Mexico City on June 29 was the epicenter of one of the region’s largest Pride marches.
More than 300,000 people participated in the march. Comité IncluyeT organized the 46th annual march under the slogan “Not one step back: rights are respected.”
Several organizations denounced the increase in hate crimes — Mexico’s National Observatory of Hate Crimes notes more than 80 LGBTQ people have been reported murdered in the last year. They also urged Mexican lawmakers to criminalize transfeminicides across the country.
Argentina
Although Buenos Aires’s official Pride march takes place in November, the Argentine LGBT+ Federation and other groups in the Argentine capital and in other cities across the country in June organized activities.
More than 5,000 people on June 24 marched from Plaza de Mayo to the Argentine Congress to reject the government’s dismantling of public policies. President Javier Milei’s decision to eliminate the country’s Women, Gender, and Diversity Ministry and cut sexual health programs were among the moves the protesters denounced.
“Today Pride is also resistance to the adjustment,” pointed out Comunidad Homosexual Argentina, an LGBTQ advocacy group.
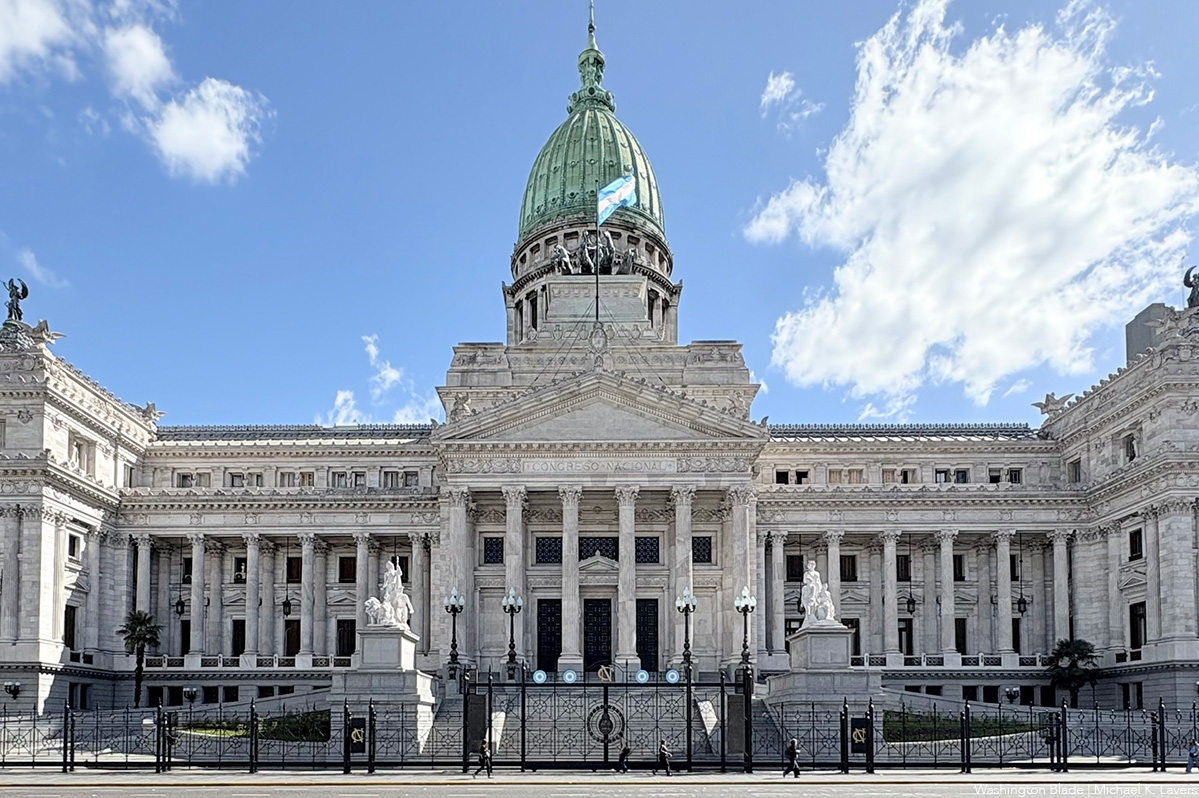

Colombia
Thousands of people in Bogotá, the Colombian capital, and the cities of Medellín, Cali, and Barranquilla marched on June 29.
The marchers’ slogan was “diversity is also peace,” in a context where violence against LGBTQ people remains high. Caribe Afirmativo, a Colombian LGBTQ rights group, notes more than 45 people from the community has been reported killed in the country over the last 12 months, with most of them trans women.
Organizations also demanded lawmakers resume debate of a bill that would extend comprehensive protections to LGBTQ Colombians. The measure has been stalled in Congress since 2023.
Brazil
More than 3 million people participated in the 28th São Paulo LGBTQ+ Pride Parade that took place on the city’s Paulista Avenue on June 22.
The parade took place under the slogan “LGBT+ social policies: we want the whole thing, not half of it.” Organizers demanded expanded access to health care, employment, and education for the most vulnerable communities, especially Black trans people. They also denounced ultraconservative figures who seek to curtail LGBTQ rights.
Peru and Paraguay
More than 15,000 people took part in a Pride march in Lima, the Peruvian capital, on June 28. Participants demanded lawmakers approve a trans rights law, which has been stalled in the Peruvian Congress since 2016, and recognition of civil unions.
Members of SomosGay, a Paraguayan LGBTQ rights group, and other organizations participated in a Pride march that took place in Asunción, the country’s capital, on June 29.
The march took place without incident, despite threats and anti-LGBTQ hate speech on social media. Participants demanded an end to anti-LGBTQ discrimination and rhetoric from social and religious groups.
Central America
Upwards of 2,000 people participated in a Pride march in Tegucigalpa, the Honduran capital, on June 22. A Pride demonstration took place in San Salvador, the capital of neighboring El Salvador, on June 28.
India
Anaya Bangar challenges ban on trans women in female cricket teams
Former Indian cricketer Sanjay Bangar’s daughter has received support
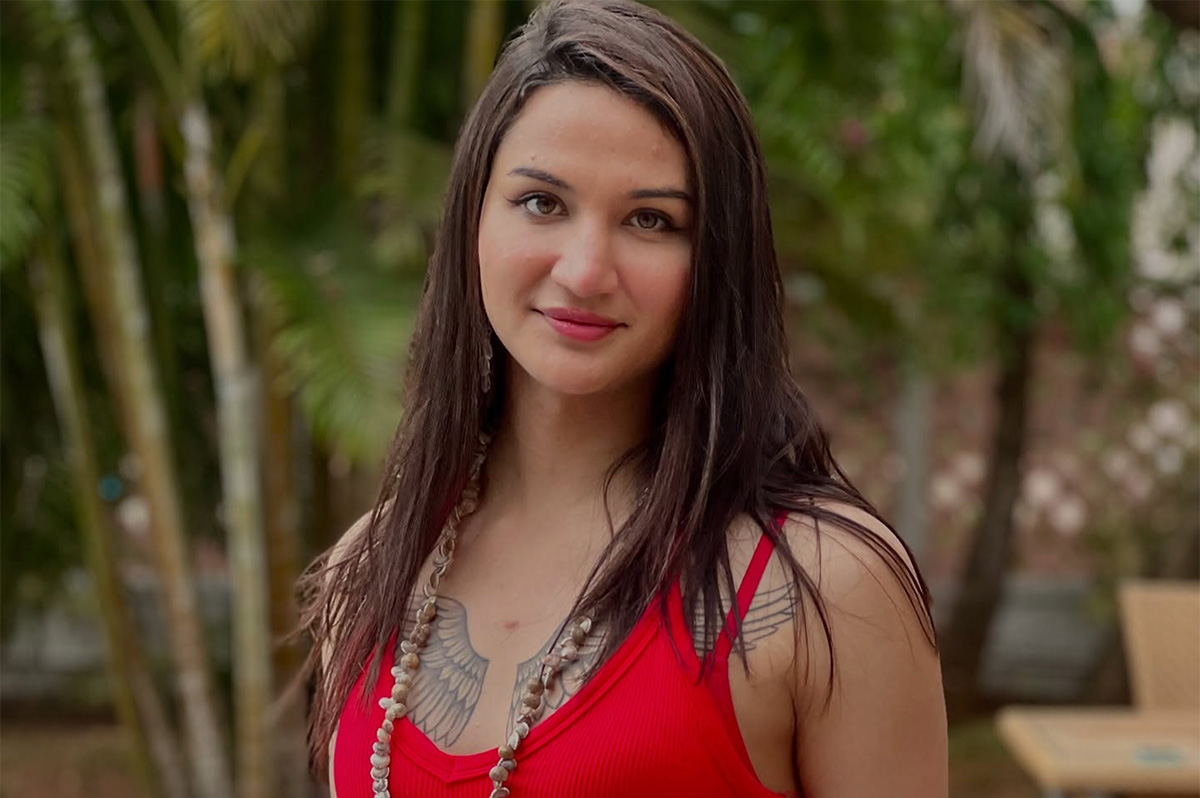
Anaya Bangar, the daughter of former Indian cricketer Sanjay Bangar, has partnered with the Manchester Metropolitan University Institute of Sport in the U.K. to assess her physiological profile following her gender-affirming surgery and undergoing hormone replacement therapy.
From January to March 2025, the 23-year-old underwent an eight-week research project that measured her glucose levels, oxygen uptake, muscle mass, strength, and endurance after extensive training.
The results, shared via Instagram, revealed her metrics align with those of cisgender female athletes, positioning her as eligible for women’s cricket under current scientific standards. Bangar’s findings challenge the International Cricket Council’s 2023 ban on transgender athletes in women’s cricket, prompting her to call for a science-based dialogue with the Board of Control for Cricket in India and the ICC to reform policies for trans inclusion.
“I am talking with scientific evidence in my hand,” Bangar said in an interview posted to her Instagram page. “So, I hope, this makes an impact and I will be hoping to BCCI and ICC talking with me and discussing this further.”
On Nov. 21, 2023, the ICC enacted a controversial policy barring trans women from international women’s cricket. Finalized after a board meeting in Ahmedabad, India, the regulation prohibits any trans player who has experienced male puberty from competing, irrespective of gender-affirming surgery or hormone therapy. Developed through a 9-month consultation led by the ICC’s Medical Advisory Committee, the rule aims to safeguard the “integrity, safety, and fairness” of women’s cricket but has drawn criticism for excluding athletes like Canada’s Danielle McGahey, the first trans woman to play internationally. The policy, which allows domestic boards to set their own rules, is slated for review by November 2025.
Bangar shared a document on social media verifying her participation in a physiological study at the Manchester Metropolitan University Institute of Sport, conducted from Jan. 20 to March 3, 2025, focused on cricket performance. The report confirmed that her vital metrics — including hemoglobin, blood glucose, peak power, and mean power — aligned with those of cisgender female athletes. Initially, her fasting blood glucose measured 6.1 mmol/L, slightly above the typical non-diabetic range of 4.0–5.9 mmol/L, but subsequent tests showed it normalized, reinforcing the study’s findings that her physical profile meets female athletic standards.
“I am submitting this to the BCCI and ICC, with full transparency and hope,” said Bangar. “My only intention is to start a conversation based on facts not fear. To build space, not divide it.”
In a letter to the BCCI and the ICC, Bangar emphasized her test results from the Manchester Metropolitan University study. She explained that the research aimed to assess how hormone therapy had influenced her strength, stamina, hemoglobin, glucose levels, and overall performance, benchmarked directly against cisgender female athletic standards.
Bangar’s letter to the BCCI and the ICC clarified the Manchester study was not intended as a political statement but as a catalyst for a science-driven dialogue on fairness and inclusion in cricket. She emphasized the importance of prioritizing empirical data over assumptions to shape equitable policies for trans athletes in the sport.
Bangar urged the BCCI, the world’s most influential cricket authority, to initiate a formal dialogue on trans women’s inclusion in women’s cricket, rooted in medical science, performance metrics, and ethical fairness. She called for the exploration of eligibility pathways based on sport-specific criteria, such as hemoglobin thresholds, testosterone suppression timelines, and standardized performance testing. Additionally, she advocated for collaboration with experts, athletes, and legal advisors to develop policies that balance inclusivity with competitive integrity.
“I am releasing my report and story publicly not for sympathy, but for truth. Because inclusion does not mean ignoring fairness, it means measuring it, transparently and responsibly,” said Bangar in a letter to the BCCI. “I would deeply appreciate the opportunity to meet with you or a representative of the BCCI or ICC to present my findings, discuss possible policy pathways, and work towards a future where every athlete is evaluated based on real data, not outdated perceptions.”
Before her transition, Bangar competed for Islam Gymkhana in Mumbai and Hinckley Cricket Club in the U.K., showcasing her talent in domestic cricket circuits. Her father, Sanjay Bangar, was a dependable all-rounder for the Indian national cricket team from 2001 to 2004, playing 12 test matches and 15 One Day Internationals. He later served as a batting coach for the Indian team from 2014 to 2019, contributing to its strategic development.
Cricket in India is a cultural phenomenon, commanding a fanbase of more than 1 billion, with more than 80 percent of global cricket viewership originating from the country.
The International Cricket Council, the sport’s governing body, oversees 12 full member nations and more than 90 associate members, with the U.S. recently gaining associate member status in 2019 and co-hosting the 2024 ICC Men’s T20 World Cup. The BCCI generated approximately $2.25 billion in revenue in the 2023–24 financial year, primarily from the Indian Premier League, bilateral series, and ICC revenue sharing. The ICC earns over $3 billion from media rights in India alone for the 2024–27 cycle, contributing nearly 90 percent of its global media rights revenue, with the BCCI receiving 38.5 percent of the ICC’s annual earnings, approximately $231 million per year.
Women’s cricket in India enjoys a growing fanbase, with over 300 million viewers for the Women’s Premier League in 2024, making it a significant driver of the sport’s global popularity. The International Cricket Council oversees women’s cricket in 12 full member nations and over 90 associate members, with the U.S. fielding a women’s team since gaining associate status in 2019 and competing in ICC events like the 2024 Women’s T20 World Cup qualifiers. The BCCI invests heavily in women’s cricket, allocating approximately $60 million annually to the WPL and domestic programs in 2024–25, while contributing to the ICC’s $20 million budget for women’s cricket development globally. India’s media market for women’s cricket, including WPL broadcasting rights, generated $120 million in 2024, accounting for over 50 percent of the ICC’s women’s cricket media revenue.
“As a woman, I feel when someone says that they are women, then they are, be trans or cis. A trans woman is definitely the same as a cis woman emotionally and in vitals, and specially, when someone is on hormone replacement therapy. Stopping Anaya Bangar from playing is discrimination and violation of her rights. It is really sad and painful that every trans woman need to fight and prove their identity everywhere,” said Indrani Chakraborty, an LGBTQ rights activist and a mother of a trans woman. “If ICC and BCCI is stopping her from playing for being transgender, then I will say this to be their lack of awareness and of course the social mindsets which deny acceptance.”
Chakraborty told the Blade that Bangar is an asset, no matter what. She said that the women’s cricket team will only benefit by participation, but the discriminating policies are the hindrance.
“Actually the transgender community face such discrimination in every sphere. In spite of being potent, they face rejection. This is highly inhuman. These attitudes is regressive and will never let to prosper. Are we really in 2025?,” said Chakraborty. “We, our mindset and the society are the issues. We, as a whole, need to get aware and have to come together for getting justice for Anaya. If today, we remain silent, the entire community will be oppressed. Proper knowledge of gender issues need to be understood.”
The BCCI and the International Cricket Council have not responded to the Blade’s repeated requests for comment.
El Salvador
La marcha LGBTQ desafía el silencio en El Salvador
Se realizó el evento en San Salvador bajo la lluvia, pero con orgullo
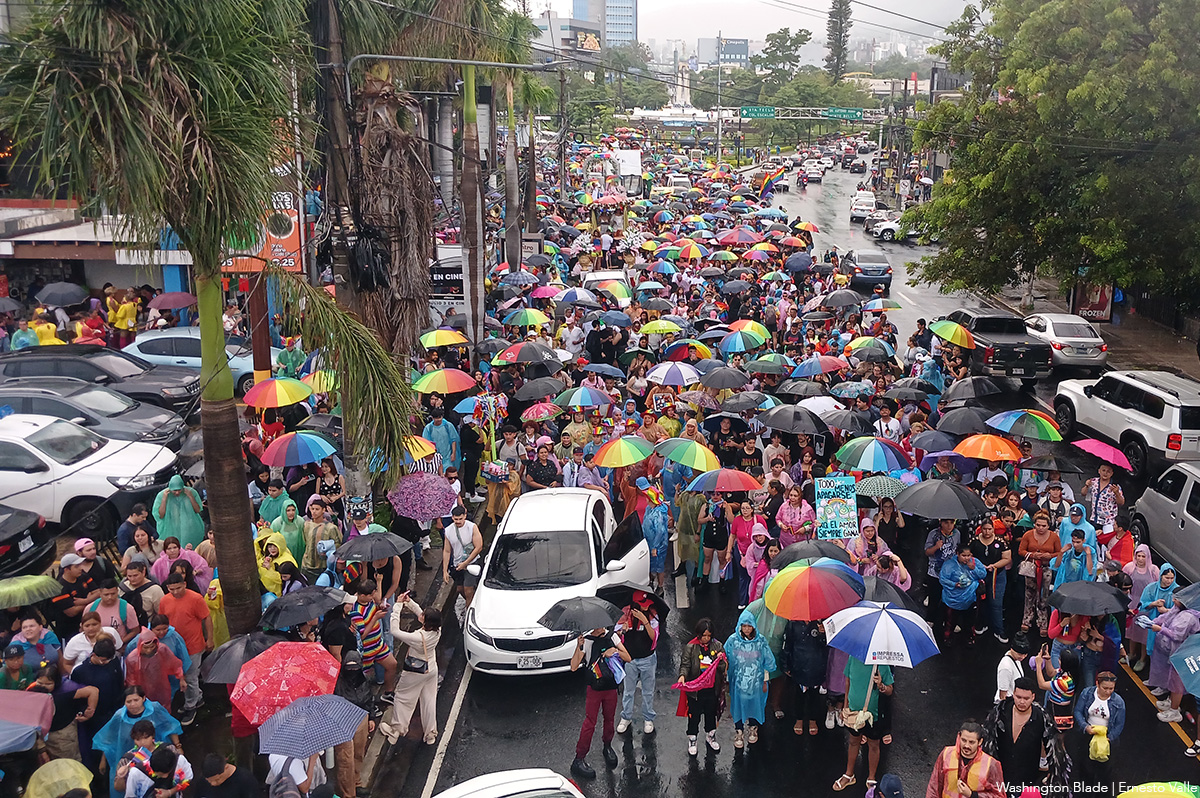

SAN SALVADOR, El Salvador — El reloj marcaba el mediodía cuando los primeros colores del arcoíris comenzaron a ondear frente a la emblemática Plaza del Divino Salvador del Mundo. A pesar de la incertidumbre generada en redes sociales, donde abundaban los rumores sobre una posible cancelación de la marcha por la diversidad sexual, la ciudad capital comenzaba a llenarse de esperanza, de resistencia y de orgullo.
Este año, la Marcha del Orgullo LGBTQ+ en El Salvador se desarrolló en un contexto tenso, en medio de un clima político que reprime y silencia a las voces disidentes.
“Aunque las estadísticas digan que no existimos, viviendo en El Salvador, un país donde hoy, después de décadas de avances, defender los derechos humanos es de nuevo una causa perseguida, criminalizada y silenciada”, afirmaron representantes de la Federación Salvadoreña LGBTQ+.
A pesar de la cancelación del festival cultural que usualmente acompaña la marcha, los colectivos decidieron seguir adelante con la movilización, priorizando el sentido original de la actividad: salir a las calles para visibilizarse, exigir respeto a sus derechos y recordar a quienes ya no están.
A la 1:30 p.m., una fuerte lluvia comenzó a caer sobre la ciudad. Algunas de las personas presentes corrieron a refugiarse, mientras otras, debajo de sombrillas y de los escasos árboles en la plaza, decidieron mantenerse firmes. Los comentarios pesimistas no se hicieron esperar: “a lo mejor la cancelan por el clima”, “no se ve tanta gente como otros años”. Sin embargo, lo que siguió fue una muestra de resistencia: a las 2:05 p.m. las voces comenzaron a llamar a tomar las calles.
Visibilidad como resistencia
La marcha arrancó bajo una llovizna persistente. La Avenida Roosevelt y la Alameda Juan Pablo II se tiñeron de colores con banderas arcoíris, trans, lésbicas, bisexuales y otras que representan a los diversos sectores de la población LGBTQ. Cada bandera alzada fue un acto político, cada paso una declaración de existencia.
Desde la Plaza del Divino Salvador del Mundo hasta la Plaza Gerardo Barrios, frente a Catedral Metropolitana y el Palacio Nacional, la marcha se convirtió en un carnaval de dignidad. Carteles con frases como “El amor no se reprime”, “Mi existencia no es delito” o “Marcho por quien ya no puede hacerlo” se alzaron entre las multitudes.
La movilización fue también un espacio para recordar a quienes han perdido la vida por la discriminación y el rechazo. Familias que marcharon por hijos, hijas o amigues que se suicidaron a causa del estigma. Personas que caminaron por quienes aún viven en el miedo, por quienes no pudieron salir del clóset, por quienes se han ido del país huyendo de la violencia.
Arte, fe y rebeldía
Una de las escenas más llamativas fue protagonizada por Nelson Valle, un joven gay que marchó vestido como sacerdote.
“Hay muchas personas que secretamente asisten a ritos religiosos como en Semana Santa, y les gusta vivir en lo oculto. Pero la fe debe ser algo libre porque Dios es amor y es para todos”, dijo.
Valle utilizó su vestimenta como una forma de protesta contra las estructuras religiosas que aún condenan la diversidad sexual.
“Un ejemplo de persona que abrió el diálogo del respeto fue el papa Francisco, abrió la mente y muy adelantado a su tiempo, porque dejó claro que hay que escuchar a toda persona que quiere encontrar a Dios”, agregó.
La marcha también incluyó bandas musicales, grupos de cachiporristas, carrozas artísticas, colectivos provenientes de distintos puntos del país, y manifestaciones de orgullo en todas sus formas. Fue un mosaico cultural que mostró la riqueza y diversidad de la población LGBTQ en El Salvador.
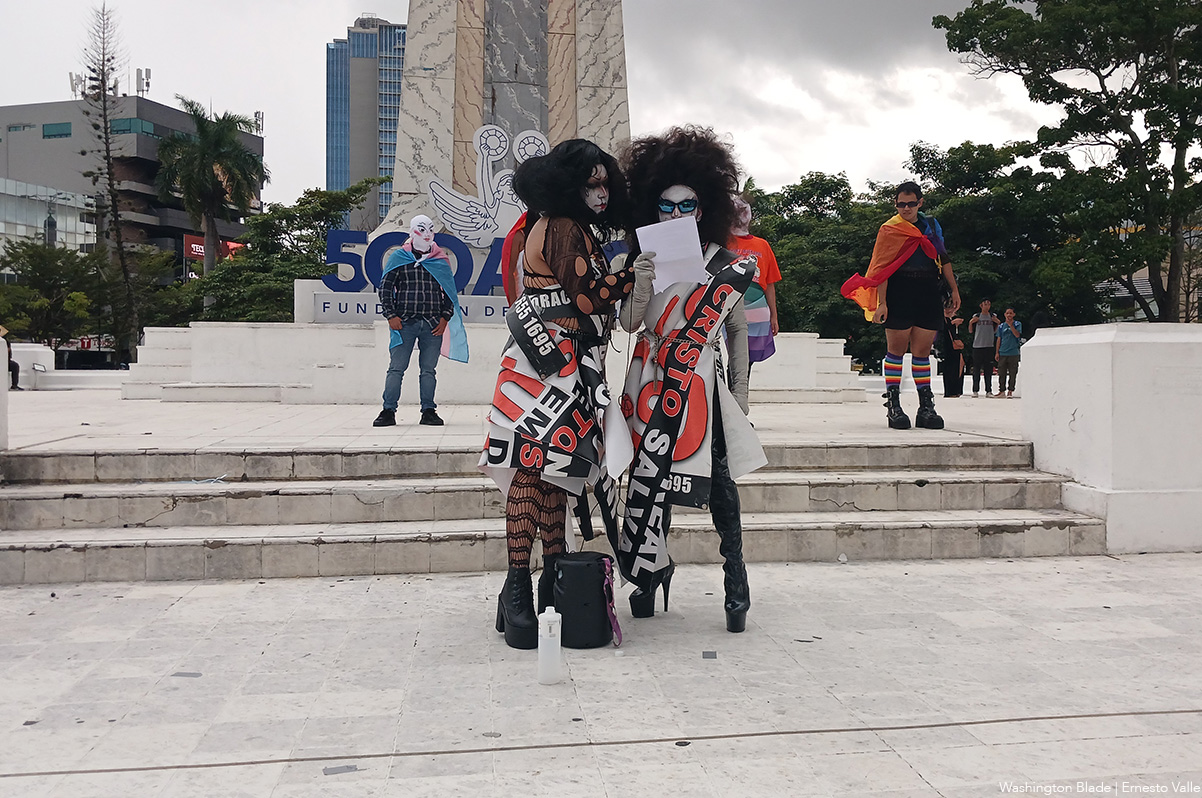

Una lucha que persiste
Las organizaciones presentes coincidieron en su mensaje: la lucha por la igualdad y el reconocimiento no se detiene, a pesar de los intentos del Estado por invisibilizarlos.
“Nuestros cuerpos se niegan a ser borrados y a morir en la invisibilidad de registros que no guardan nuestros nombres ni nuestros géneros”, declararon representantes de la Federación.
Además, agregaron: “Desde este país que nos quiere callar, levantamos nuestras voces: ¡La comunidad LGBTIQ+ no se borra! ¡El Salvador también es nuestro! Construyamos, entre todes, un país donde podamos vivir con Orgullo.”
El ambiente fue de respeto, pero también de desconfianza. La presencia de agentes policiales no pasó desapercibida. Aunque no hubo reportes oficiales de violencia, varias personas expresaron su temor por posibles represalias.
“Marchar hoy es también un acto de valentía”, comentó Alejandra, una joven lesbiana que viajó desde Santa Ana para participar. “Pero tenemos derecho a vivir, a amar, a soñar. Y si nos detenemos, les damos la razón a quienes nos quieren ver en silencio.”
Rumbo al futuro
Concluida la marcha frente a Catedral y el Palacio Nacional, muchas personas permanecieron en la plaza compartiendo abrazos, fotos y palabras de aliento. No hubo festival, no hubo escenario, pero hubo algo más valioso: una comunidad que sigue viva, que sigue resistiendo.
Los retos son muchos: falta de leyes de protección y que apoye las identidades de las personas trans, discriminación laboral, violencia por prejuicio, rechazo familiar, y una narrativa estatal que pretende que no existen. Pero la marcha del 28 de junio demostró que, aunque el camino sea cuesta arriba, la dignidad y el orgullo no se borran.
La lucha por un El Salvador más justo, más plural y más inclusivo continúa. En palabras de uno de los carteles más llamativos de ese día: “No estamos aquí para pedir permiso, estamos aquí para recordar que también somos parte de este país”.
-

 District of Columbia5 days ago
District of Columbia5 days agoActivists protest outside Hungarian Embassy in DC
-

 Virginia4 days ago
Virginia4 days agoSpanberger touts equality, reproductive rights in Arlington
-

 Books4 days ago
Books4 days agoTwo new books on dining out LGBTQ-style
-

 Theater4 days ago
Theater4 days ago‘Andy Warhol in Iran’ a charming look at intersection of art, politics