National
U.S. health officials expand approach to monkeypox vaccines as cases crest
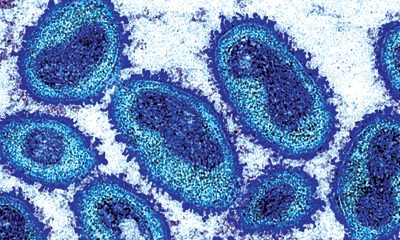
At the end of a summer when the number of cases in the monkeypox outbreak rose sharply, the increase in reported infections now appears to be cresting amid increased public messaging and access to vaccines, prompting U.S. health officials to expand their strategy with a new equity-based effort to combat the disease.
Although the reported number of cases, according to most data from the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, has reached 18,417 in the United States, the number of additional cases decreased from the high at the start of the month, suggesting a downward trajectory in the spread of the disease as vaccines become more readily available.
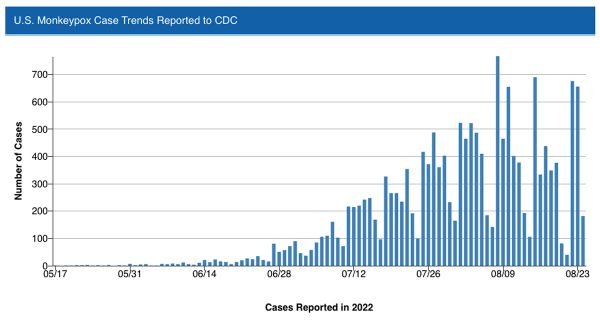
The numbers are also consistent with a new study finding a significant number of gay and bisexual men, as well as other men who have sex with men, have been limiting contact with casual sex partners, which has been the driving force in the spread of monkeypox. The report from the CDC last week found limiting one-time sexual encounters can significantly reduce the transmission of monkeypox virus, while about half of men who have sex with men are cutting down on sexual activity amid the outbreak, including one-night stands and app hookups.
With the trajectory of monkeypox on the decline, the Biden administration announced a new initiative with the goal of ensuring vaccine distribution is consistent with the value of equity, including on the basis of geographic, racial, and ethnic lines. A total of 10,000 doses of vaccines in the federal government’s supply will be earmarked for localities that have used 50 percent of their allocated supply to support equity interventions, such as outreach to Black and Latino communities, which have been disproportionately affected by the disease or a specific event and celebration for LGBTQ people, health officials announced Tuesday.
Demetre Daskalakis, the Biden administration’s face of LGBTQ outreach for monkeypox and deputy coordinator for the White House monkeypox task force, laid out the details for the new equity-based supplementary initiative in a conference call Tuesday with reporters.
“So what we mean by an equity intervention is what works in your state, county, or city to reach people who we may not be reaching, especially people of color and members of the LGBTQI+ population,” Daskalakis said. “What it means is: It can be working with a specific group or venue that reaches the right people for monkeypox prevention. Once these innovative strategies have been reviewed by CDC, vaccines will be supplied to jumpstart these ideas and accelerate reach deeper into communities.”
The additional equity-based approach to monkeypox vaccine distribution is consistent with the Biden administration’s efforts in recent weeks to distribute additional shots to localities hosting large-scale events for LGTBQ people at the end of the summer, such as Black Pride in Atlanta and Southern Decadence in New Orleans.
Louisiana Gov. John Bel Edwards joined the conference call with reporters on Tuesday and had high praise for the Biden administration for making the additional 6,000 doses of monkeypox vaccine available in time for Southern Decadence, which takes place in the final week of August through Labor Day weekend.
“This is an example — I think a really solid example — of what a federal-state-local partnership and — and then the community providers as well,” Bel Edwards said. “Because the public health folks in New Orleans have been tremendous, but also the community providers.”
Bel Edwards said health officials in the Biden administration have, in addition to providing more vaccines, sent down multidisciplinary teams to New Orleans to help the state organize and prepare as well as set up testing and vaccination sites “that are going to be convenient for the at-risk population.”
A reporter from the New Orleans Advocate on the conference call, however, asked a pointed question on the recent distribution of vaccines to New Orleans in advance of Southern Decadence: The current approach to vaccine administration requires a series of shots, and even with new distribution most people won’t have even had their second shot by that time, so how can Southern Decadence think they will be protected, especially when vaccines take time to become fully effective?
Daskalakis, while promoting the equity-based approach to vaccine distribution, said the Biden administration has been “very clear” that first shot of the monkeypox vaccine “doesn’t mean that you’re protected for the event.”
“We’re going to talk to them about lots of other strategies that they can reduce risk of acquiring monkeypox, but also make it clear that that shot is not for today; it’s for four weeks from now, plus two weeks after that second dose when you get maximum protection,” Daskalakis said.
First death of monkeypox patient reported
Although the number of cases is cresting, concern about monkeypox continues as well as the potential danger of the disease. Case in point: The death of a hospital patient in Texas who had monkeypox, but may have to succumbed to other factors, has drawn attention amid a conventional understanding the skin disease isn’t fatal. The case represents the first time in the United States that a patient with monkeypox died while having the condition.
The patient, as confirmed by the Texas Department of State Health Services on Tuesday, was an adult resident of Harris County who was “severely immunocompromised” and state health officials reviewing the case said it is under investigation to determine what role monkeypox played in the death.
Jenny McQuiston, a CDC official who specializes in research on zoological diseases that spread from animals to people, said in response to a question on the casualty that health officials are also evaluating the death and the role monkeypox played.
“I think it’s important to emphasize that deaths due to monkeypox, while possible, remain very rare,” McQuiston said. “In most cases, people are experiencing infection that resolves over time. And there have been very few deaths even recorded globally. Out of over 40,000 cases around the world, only a handful of fatalities have been reported.”
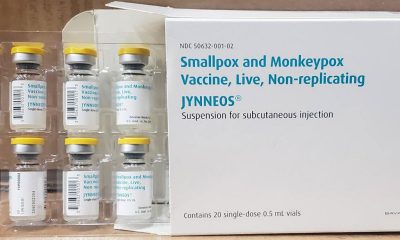
Despite the cresting in the number of cases, many health experts aren’t sold on the new approach to vaccines announced earlier this month by the Biden administration, which sought to expand existing doses of vaccines fivefold as supply hasn’t met demand. The new vaccine approach calls for injecting the JYNNEOS vaccine from the subcutaneous route (delivery of the vaccine under the fat layer underneath the skin) to the intradermal route (delivery of the vaccine into the layer of skin just underneath the top layer).
Bob Fenton, a regional administrator for FEMA and the response coordinator for the White House task force, said about 75 percent of jurisdictions have already adopted the new approach to vaccine injection, while an additional 20 percent are working toward a “fully operational intradermal method.”
“We continue to be laser-focused on doing everything within our power to help jurisdictions and clinicians get shots in arms,” Fenton said. “We’re seeing more and more jurisdictions adopt the intradermal administration.”
Data of this new intradermal approach, critics have said, is insufficient to support the idea it will be as effective as subcutaneous injections, although the Biden administration continues to give assurances the new route for injections is tested and safe. According to a report earlier this month in the Washington Post, the manufacturer of the JYNNEOS vaccine in Denmark, Bavaria Nordic, privately threatened to cut off supply of the shots based on a conversation with health officials on objections the vaccine hasn’t been approved for intradermal use.
McQuiston, in response to a question on whether or not U.S. health officials are collecting newly available real-world information on the results of the new vaccine approach, said U.S. health officials continue to receive data on monkeypox and soon onboard information from additional states.
“CDC operates a system called VAERS — or the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System — and we’re actively looking at…different types of events that might be reported post-vaccination,” McQuiston said. ” And we are actively gathering information from the different jurisdictions and states and cities about which vaccines they’re administering — whether it’s subcutaneous or intradermal — and we are gathering those data now, as we speak.”
Federal Government
Gay Venezuelan man ‘forcibly disappeared’ to El Salvador files claim against White House
Andry Hernández Romero had asked for asylum in US
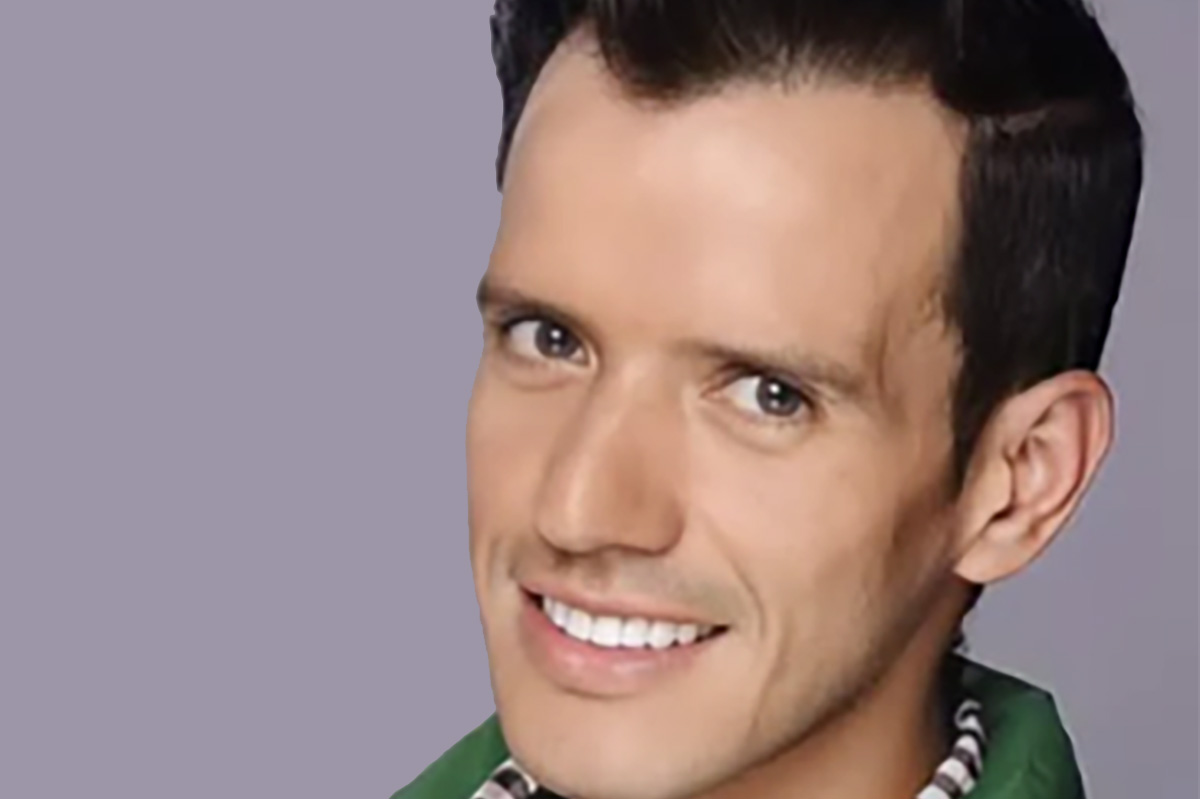

A gay Venezuelan asylum seeker who the U.S. “forcibly disappeared” to El Salvador has filed a claim against the federal government.
Immigrant Defenders Law Center, who represents Andry Hernández Romero, on Friday announced their client and five other Venezuelans who the Trump-Vance administration “forcibly removed” to El Salvador under the Alien Enemies Act of 1798, filed “administrative claims” under the Federal Tort Claims Act.
The White House on Feb. 20, 2025, designated Tren de Aragua, a Venezuelan gang, as an “international terrorist organization.”
President Donald Trump less than a month later invoked the Alien Enemies Act of 1798, which the Associated Press notes allows the U.S. to deport “noncitizens without any legal recourse.” The White House then “forcibly removed” Hernández, who had been pursuing his asylum case in the U.S., and more than 250 other Venezuelans to El Salvador.
Immigrant Defenders Law Center disputed claims that Hernández is a Tren de Aragua member.
Hernández was held at El Salvador’s Terrorism Confinement Center, a maximum-security prison known by the Spanish acronym CECOT, until his release on July 18, 2025. Hernández, who is back in Venezuela, claims he suffered physical and sexual abuse while at CECOT.
“As a Venezuelan citizen with no criminal record anywhere in the world, I would like to tell not only the government of the United States but governments everywhere that no human being is illegal,” said Hernández in the Immigrant Defenders Law Center press release. “The practice of judging whole communities for the wrongdoing of a single individual must end. Governments should use their power to help every person in the nation become more aware and informed, to strengthen our cultures and build a stronger generation with principles and values — one that multiplies the positive instead of destroying unfulfilled dreams and opportunities.”
Immigrant Defenders Law Center filed claims on behalf of Hernández and the five other Venezuelans less than three months after American forces seized then-Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro and his wife, Cilia Flores, at their home in Caracas, the Venezuelan capital.
Maduro and Flores have pleaded not guilty to federal drug charges. Delcy Rodríguez, who was Maduro’s vice president, is Venezuela’s acting president.
‘Due process and accountability cannot be optional’
Immigrant Defenders Law Center on Friday also made the following demands:
- The Trump administration must officially release the names of all people the United States sent to CECOT to ensure that everyone has been or will be released.
- The federal government must clear the names of the 252 men wrongfully labeled as criminal gang members of Tren de Aragua.
- DHS (Department of Homeland Security) must end the practice of outsourcing torture through third‑country removals, restore humanitarian parole, and rebuild a functioning, humane asylum system.
- DHS must reinstate Temporary Protected Status for all individuals who cannot safely return to their home countries, halt mass deportations and unlawful raids and arrests, and guarantee due process for everyone navigating the immigration system.
- Congress must pass the Neighbors Not Enemies Act, which would repeal the Alien Enemies Act.
“In all my years as an immigration attorney, I have never seen a client simply vanish in the middle of their case with no explanation,” said Immigration Defenders Legal Fund Legal Services Director Melissa Shepard. “In court, the government couldn’t even explain where he was — he had been disappeared.”
“When the government detains and transfers people in secrecy, without transparency or access to the courts, it tears at the basic protections a democracy is supposed to guarantee,” added Shepard. “What this experience makes painfully clear is that due process and accountability cannot be optional. They are the only safeguards standing between people and the kind of lawlessness our clients suffered. We must end third country transfers, restore the asylum system, and humanitarian parole, and reinstate temporary protective status so this nightmare never happens again.”
The White House
Trump proclamation targets trans rights as State Dept. shifts visa policy
Recent policy actions from the White House limit transgender rights in sports, immigration visas, and overarching federal policy.

In a proclamation issued by the Trump White House Thursday night, the president said he would, among other things, “restore public safety” and continue “upholding the rule of law,” while promoting policies that restrict the rights of transgender people.
“We are keeping men out of women’s sports, enforcing Title IX as it was originally written, and ensuring colleges preserve — and, where possible, expand — scholarships and roster opportunities for female athletes,” the proclamation reads. “At the same time, we are restoring public safety and upholding the rule of law in every city so women, children, and families can feel safe and secure.”
The statement comes amid a broader series of actions by the Trump administration targeting transgender people across multiple federal policy areas, including education, health care, and immigration. A nearly complete list of policies the current administration has put forward can be found on KFF.org.
One day before the proclamation was issued, the U.S. State Department announced changes to visa regulations that could impact transgender and gender-nonconforming people seeking entry into the United States.
The policy, published March 11 and scheduled to take effect April 10, introduces changes to the Diversity Immigrant Visa Program, commonly known as the “DV Program.” The rule is framed by the department as an effort to strengthen oversight and prevent fraud within the visa lottery system, which allocates a limited number of immigrant visas annually to applicants from countries with historically low rates of immigration to the United States.
However, the updated language also standardizes the use of the term “sex” in federal regulations in place of “gender,” a change that LGBTQ advocates say could create additional barriers for transgender and gender-diverse applicants.
The policy states: “The Department of State (‘Department’) is amending regulations governing the Diversity Immigrant Visa Program (‘DV Program’) to improve the integrity of, and combat fraud in, the program. These amendments require a petitioner to the DV Program to provide valid, unexpired passport information and to upload a scan of the biographic and signature page in the electronic entry form or otherwise indicate that he or she is exempt from this requirement. Additionally, the Department is standardizing and amending its regulations to add the word ‘shall’ to simplify guidance for consular officers; ensure the use of the term ‘sex’ in lieu of ‘gender’; and replace the term ‘age’ in the DV Program regulations with the phrase ‘date of birth’ to accurately reflect the information collected and maintained by the Department during the immigrant visa process.”
Advocates say the shift toward using “sex” rather than “gender” in federal immigration rules reflects a broader push by the administration to roll back recognition of transgender identities in federal policy.
According to the National Center for Transgender Equality, an estimated 15,000 to 50,000 undocumented transgender immigrants currently live in the United States, with many entering the country to seek refuge from persecution and hostile governments in their home countries.
Florida
Fla. House passes ‘Anti-Diversity’ bill
Measure could open door to overturning local LGBTQ rights protections

The Florida House of Representatives on March 10 voted 77-37 to approve an “Anti-Diversity in Local Government” bill that opponents have called an extreme and sweeping measure that, among other things, could overturn local LGBTQ rights protections.
The House vote came six days after the Florida Senate voted 25-11 to pass the same bill, opening the way to send it to Republican Gov. Ron DeSantis, who supports the bill and has said he would sign it into law.
Equality Florida, a statewide LGBTQ advocacy organization that opposed the legislation, issued a statement saying the bill “would ban, repeal, and defund any local government programming, policy, or activity that provides ‘preferential treatment or special benefits’ or is designed or implemented with respect to race, color, sex, ethnicity, sexual orientation, or gender identity.”
The statement added that the bill would also threaten city and county officials with removal from office “for activities vaguely labeled as DEI,” with only limited exceptions.
“Written in broad and ambiguous language, the bill is the most extreme of its kind in the country, creating confusion and fear for local governments that recognize LGBTQ residents and other communities that contribute to strength and vibrancy of Florida cities,” the group said in a separate statement released on March 10.
The Miami Herald reports that state Sen. Clay Yarborough (R-Jacksonville), the lead sponsor of the bill in the Senate, said he added language to the bill that would allow the city of Orlando to continue to support the Pulse nightclub memorial, a site honoring 49 mostly LGBTQ people killed in the 2016 mass shooting at the LGBTQ nightclub.
But the Equality Florida statement expresses concern that the bill can be used to target LGBTQ programs and protections.
“Debate over the bill made expressly clear that LGBTQ people were a central target of the legislation,” the group’s statement says. “The public record, the bill sponsors’ own statements, and hours of legislative debate revealed the animus driving the effort to pressure local governments into pulling back from recognizing or resourcing programs targeting LGBTQ residents and other historically marginalized communities,” the statement says.
But the statement also notes that following outspoken requests by local officials, sponsors of the bill agreed to several amendments “ensuring local governments can continue to permit Pride festivals, even while navigating new restrictions on supporting or promoting them.”
The statement adds, “Florida’s LGBTQ community knows all too well how to fight back against unjust laws. Just as we did, following the passage of Florida’s notorious ‘Don’t Say Gay or Trans’ law, we will fight every step of the way to limit the impact of this legislation, including in the courts.”
-

 Health5 days ago
Health5 days agoToo afraid to leave home: ICE’s toll on Latino HIV care
-

 Colombia5 days ago
Colombia5 days agoClaudia López wins primary in Colombian presidential race
-

 The White House4 days ago
The White House4 days agoTrump will refuse to sign voting bill without anti-trans provisions
-

 Iran4 days ago
Iran4 days agoMan stuck in Lebanon as Iran war escalates