Books
‘Oscar Wars’ an exhilarating read for film critics and fans alike
Awards a conflict zone for issues of race, gender, representation
‘Oscar Wars: A History of Hollywood in Gold, Sweat, and Tears’
By Michael Schulman
c.2023, Harper
$40/589 pages
Get out the guacamole! The game, beloved by millions — especially queers — is being played. This Sunday, the 95th Academy Awards ceremony at the Dolby Theatre in Los Angeles will be seen worldwide.
Few have written more compellingly about the ego, campiness, politics, and intrigue of the Academy Awards than Michael Schulman in his new book “Oscar Wars: A History of Hollywood in Gold, Sweat, and Tears.”

The Oscars are “the closest thing America has to royalty,” writes Schulman, a staff writer at The New Yorker. “They’re the only thing forcing Hollywood to factor art into commerce.”
Schulman likens the Oscars to a horse race and a relic. The Academy Awards prop up Hollywood, a multibillion-dollar business, canonize movies and showcase fashion, he notes.
“They’re an orgy of self-congratulation by rich and famous people who think too highly of themselves.” Schulman adds, “They’re the Gay Super Bowl.”
You can bet that every year, something will throw the Oscars off their game. Last year, it was the Slap (when Will Smith, upset by Chris Rock’s joke about his wife Jada Pinkett Smith, hit the comedian).
There are the insipid production numbers and lackluster hosts. More seriously, there is the continuing racism and sexism in Hollywood.
You have to keep the Academy Awards in perspective, Schulman wryly notes. “The Oscars … are always getting it wrong,” he writes, “Twenty-four centuries after Euripides came in third place at the Athenian dramatic festival, Brokeback Mountain lost Best Picture to Crash, and the outcry will probably last another twenty-four centuries.”
It’s tempting to view the Academy Awards annual bash as enjoyable froth. To lap up the glam, glitz, and camp. But in “Oscar Wars,” Schulman persuasively argues that the Oscars should, also, be taken seriously.
“The Oscars are a battlefield,” Schulman writes, “where cultural forces collide and where the victors aren’t always as clear as the names drawn from the envelopes.”
“In recent years,” he adds, “the Oscars have become a conflict zone for issues of race, gender, and representation, high profile signifiers of whose stories get told and whose don’t.”
Thankfully, Schulman’s nearly 600-page book isn’t an Oscars encyclopedia. Volumes of Oscar facts and trivia already exist. Even if you’re a movie buff, these books will make your eyes glaze over. “Oscar Wars” is filled with Schulman’s painstaking research and in-depth reporting. It’s not surprising that he’s said in interviews that he worked on the book for four years.
Schulman, author of “”Her Again: Becoming Meryl Streep,” is a powerhouse. While writing “Oscar Wars,” Schulman produced numerous hard-to-put-down profiles at his New Yorker day job. Tongues are still wagging over his profile of actor Jeremy Strong (Kendall Roy in “Succession”).
In 11 intriguing installments, Schulman illuminates how, from the first Academy Awards in 1929 to our present #OscarsSoWhite and #MeToo era, conflict has been embedded in the Oscars.
The Academy Awards was started in an effort to squelch labor unions in Hollywood. Spoiler alert: the effort of Louis B. Mayer and other Hollywood moguls to stop the unions flopped as the awards caught on.
There’s much in “Oscar Wars” to engage Old Hollywood aficionados. There’s the sad tale of Peg Entwistle, a 24-year-old actress, who, in 1932, played Hazel in “Thirteen Women, a movie about a group of former sorority sisters. Hazel stabs her husband. Entwistle’s 16 minutes in the movie were cut to four, Schulman writes, because the Hays office felt “that her scenes with another actress had unacceptable lesbian undertones.” After a series of horrible events, the actress killed herself.
There is the story of how one of Bette Davis’s husbands divorced her because she read too much.
It’s well-known among cinephiles that Bette Davis (for “All About Eve”) and Gloria Swanson (for “Sunset Boulevard”) were up against each other in 1951 for the Oscar and lost to Judy Holliday (for “Born Yesterday”). But Schulman brings new depth and insight into this saga.
The Academy Awards are steeped in Hollywood and entertainment. But Schulman makes it clear that the Oscars, from the Black List of the 1940s-1950s to the racism of “Gone with the Wind” to sexism to homophobia, are entwined with cultural attitudes and politics.
“Citizen Kane” was one of the greatest films ever made. Yet, there was no way it could have won an Oscar because the newspaper tycoon William Randolph Hearst was furious that “Kane’s” protagonist was based on him.
One of the most campy, but poignant, accounts in the book is that of Allan Carr, who produced the 1989 Oscars. Carr, who was gay, dreamed up a tasteless, unintentionally campy production number. It featured Rob Lowe and Snow White (Google it.) Yet, he created, Schulman reports, some innovations that are still part of the Oscars (such as the red carpet).
“Oscar Wars” is an exhilarating read for everyone from film critics to fans.
The Blade may receive commissions from qualifying purchases made via this post.
Books
Love or fear flying you’ll devour ‘Why Fly’
New book chronicles a lifetime obsession with aircraft

‘Why Fly’
By Caroline Paul
c. 2026, Bloomsbury
$27.99/256 pages
Tray table folded up.
Check. Your seat is in the upright position, the airflow above your head is just the way you like it, and you’re ready to go. The flight crew is making final preparations. The lights are off and the plane is backing up. All you need now is “Why Fly” by Caroline Paul, and buckle up.

When she was very young, Paul was “obsessed” with tales of adventure, devouring accounts written by men of their derring-do. The only female adventure-seeker she knew about then was Amelia Earhart; later, she learned of other adventuresome women, including aviatrix Bessie Coleman, and Paul was transfixed.
Time passed; Paul grew up to create a life of adventure all her own.
Then, the year her marriage started to fracture, she switched her obsession from general exploits to flight.
Specifically, Paul loves experimental aircraft, some of which, like her “trike,” can be made from a kit at home. Others, like Woodstock, her beloved yellow gyrocopter, are major purchases that operate under different FAA rules. All flying has rules, she says, even if it seems like it should be as freewheeling as the birds it mimics.
She loves the pre-flight checklist, which is pure anticipation as well as a series of safety measures; if only a relationship had the same ritual. Paul loves her hangar, as a place of comfort and for flight in all senses of the word. She enjoys thinking about historic tales of flying, going back before the Wright Brothers, and including a man who went aloft on a lawn chair via helium-filled weather balloons.
The mere idea that she can fly any time is like a gift to Paul.
She knows a lot of people are terrified of flying, but it’s near totally safe: generally, there’s a one in almost 14 million chance of perishing in a commercial airline disaster – although, to Paul’s embarrassment and her dismay, it’s possible that both the smallest planes and the grandest loves might crash.
If you’re a fan of flying, you know what to do here. If you fear it, pry your fingernails off the armrests, take a deep breath, and head to the shelves. “Why Fly” might help you change your mind.
It’s not just that author Caroline Paul enjoys being airborne, and she tells you. It’s not that she’s honest in her explanations of being in love and being aloft. It’s the meditative aura you’ll get as you’re reading this book that makes it so appealing, despite the sometimes technical information that may flummox you between the Zen-ness. It’s not overwhelming; it mixes well with the history Paul includes, biographies, the science, heartbreak, and exciting tales of adventure and risk, but it’s there. Readers and romantics who love the outdoors, can’t resist a good mountain, and crave activity won’t mind it, though, not at all.
If you own a plane – or want to – you’ll want this book, too. It’s a great waiting-at-the-airport tale, or a tuck-in-your-suitcase-for-later read. Find “Why Fly” and you’ll see that it’s an upright kind of book.
The Blade may receive commissions from qualifying purchases made via this post.
Books
New book profiles LGBTQ Ukrainians, documents war experiences
Tuesday marks four years since Russia attacked Ukraine
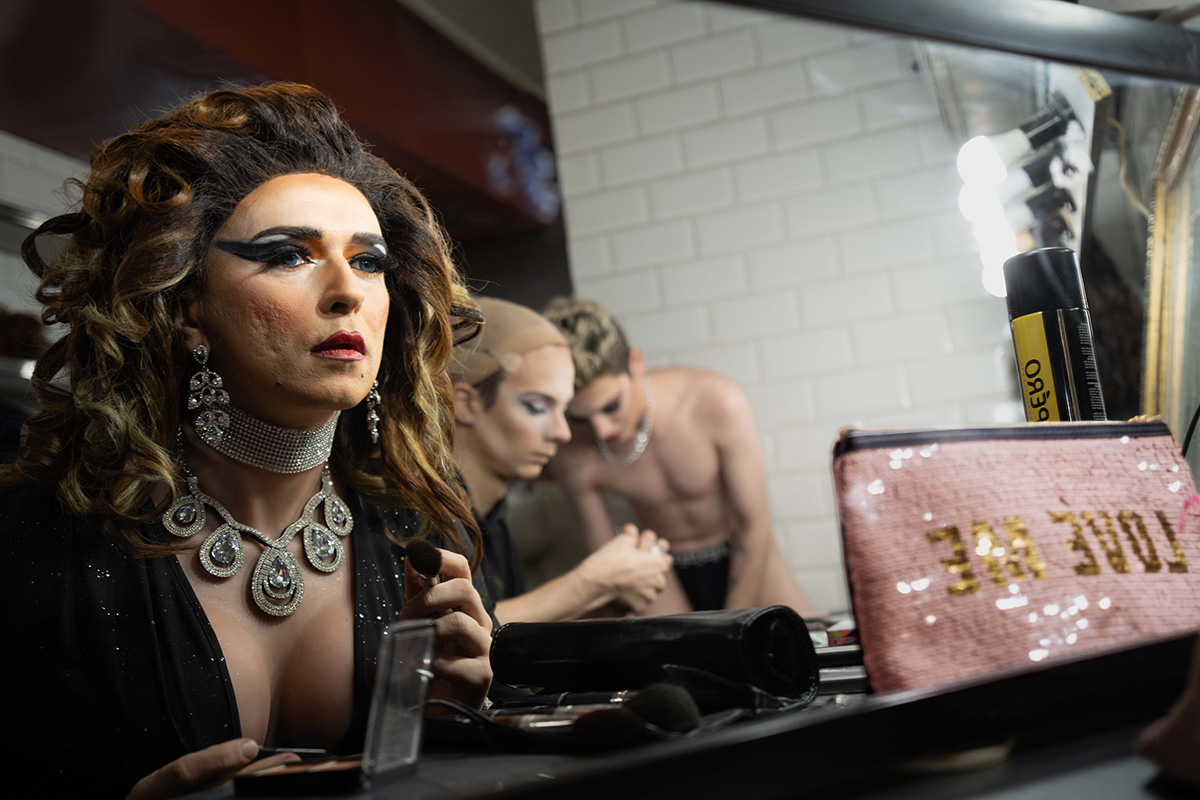

Journalist J. Lester Feder’s new book profiles LGBTQ Ukrainians and their experiences during Russia’s war against their country.
Feder for “The Queer Face of War: Portraits and Stories from Ukraine” interviewed and photographed LGBTQ Ukrainians in Kyiv, the country’s capital, and in other cities. They include Olena Hloba, the co-founder of Tergo, a support group for parents and friends of LGBTQ Ukrainians, who fled her home in the Kyiv suburb of Bucha shortly after Russia launched its war on Feb. 24, 2022.
Russian soldiers killed civilians as they withdrew from Bucha. Videos and photographs that emerged from the Kyiv suburb showed dead bodies with their hands tied behind their back and other signs of torture.
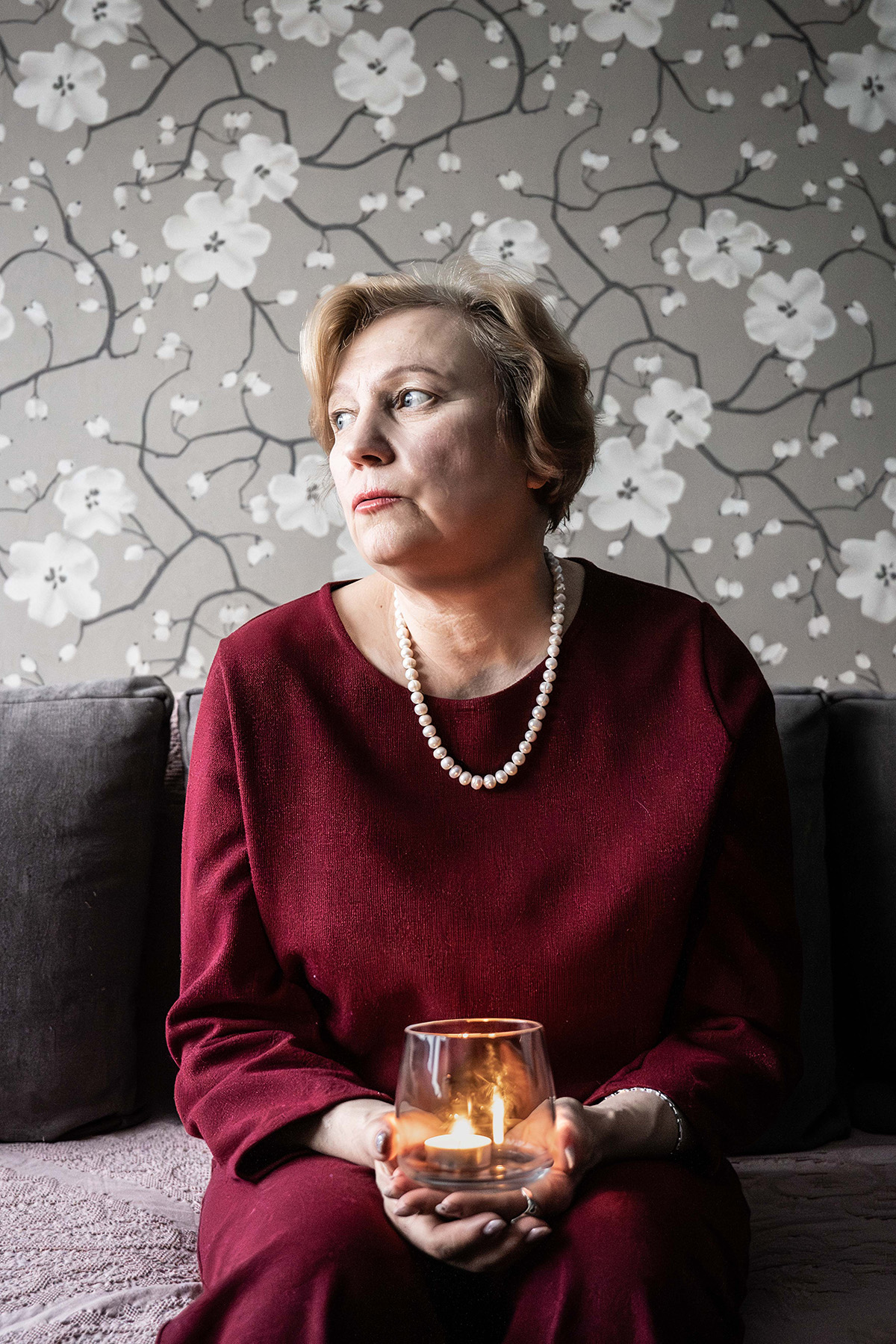

Olena Shevchenko, chair of Insight, a Ukrainian LGBTQ rights group, wrote the book’s forward.
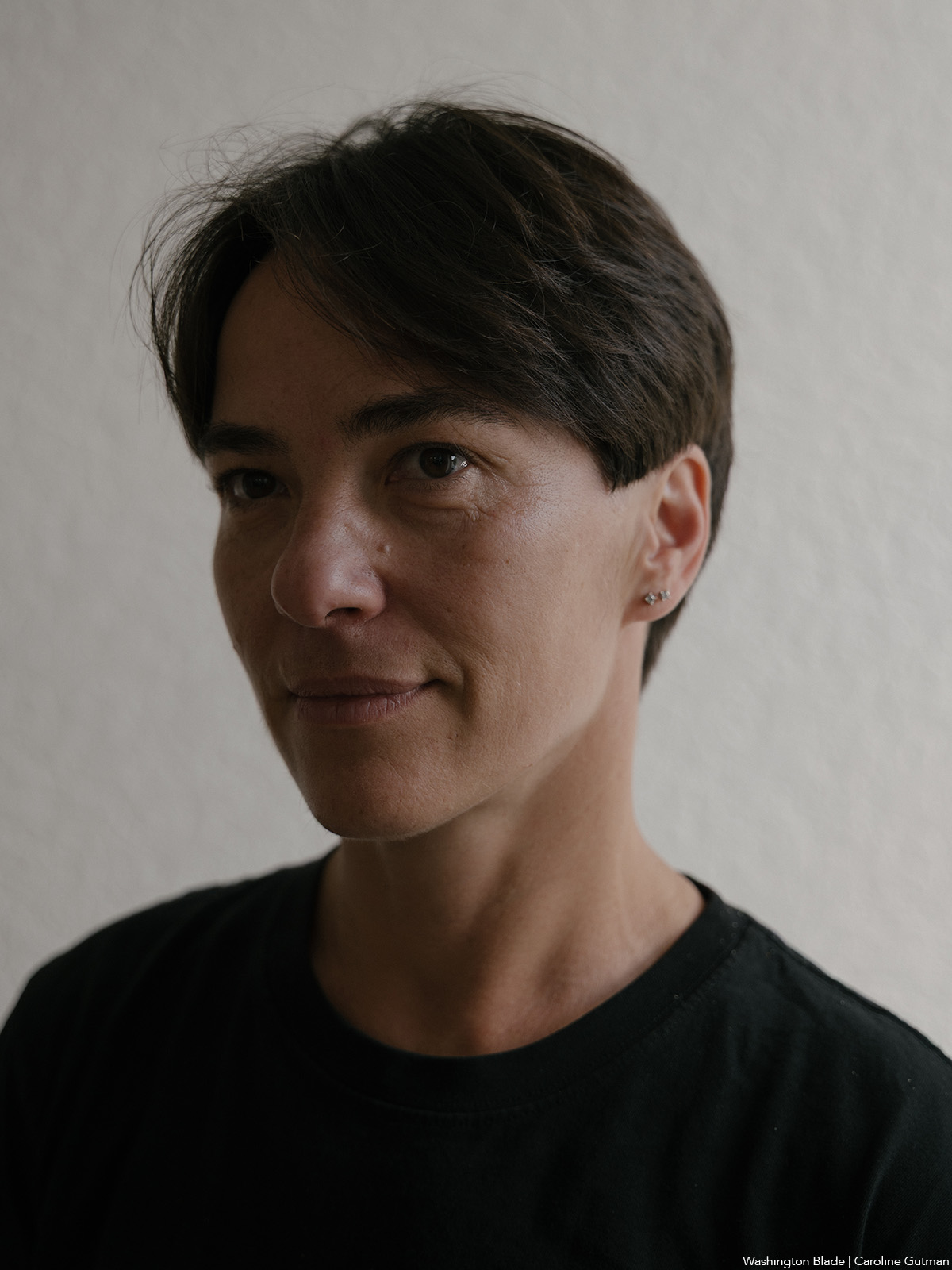

The book also profiles Viktor Pylypenko, a gay man who the Ukrainian military assigned to the 72nd Mechanized Black Cossack Brigade after the war began. Feder writes Pylypenko’s unit “was deployed to some of the fiercest and most important battles of the war.”
“The brigade was pivotal to beating Russian forces back from Kyiv in their initial attempt to take the capital, helping them liberate territory near Kharkiv and defending the front lines in Donbas,” wrote Feder.
Pylypenko spent two years fighting “on Ukraine’s most dangerous battlefields, serving primarily as a medic.”
“At times he felt he was living in a horror movie, watching tank shells tear his fellow soldiers apart before his eyes,” wrote Feder. “He held many men as they took their final breaths. Of the roughly one hundred who entered the unit with him, only six remained when he was discharged in 2024. He didn’t leave by choice: he went home to take care of his father, who had suffered a stroke.”
Feder notes one of Pylypenko’s former commanders attacked him online when he came out. Pylypenko said another commander defended him.
Feder also profiled Diana and Oleksii Polukhin, two residents of Kherson, a port city in southern Ukraine that is near the mouth of the Dnieper River.
Ukrainian forces regained control of Kherson in November 2022, nine months after Russia occupied it.
Diana, a cigarette vender, and Polukhin told Feder that Russian forces demanded they disclose the names of other LGBTQ Ukrainians in Kherson. Russian forces also tortured Diana and Polukhin while in their custody.
Polukhim is the first LGBTQ victim of Russian persecution to report their case to Ukrainian prosecutors.

Feder, who is of Ukrainian descent, first visited Ukraine in 2013 when he wrote for BuzzFeed.
He was Outright International’s Senior Fellow for Emergency Research from 2021-2023. Feder last traveled to Ukraine in December 2024.
Feder spoke about his book at Politics and Prose at the Wharf in Southwest D.C. on Feb. 6. The Washington Blade spoke with Feder on Feb. 20.
Feder told the Blade he began to work on the book when he was at Outright International and working with humanitarian groups on how to better serve LGBTQ Ukrainians. Feder said military service requirements, a lack of access to hormone therapy and documents that accurately reflect a person’s gender identity and LGBTQ-friendly shelters are among the myriad challenges that LGBTQ Ukrainians have faced since the war began.
“All of these were components of a queer experience of war that was not well documented, and we had never seen in one place, especially with photos,” he told the Blade. “I felt really called to do that, not only because of what was happening in Ukraine, but also as a way to bring to the surface issues that we’d had seen in Iraq and Syria and Afghanistan.”

Feder also spoke with the Blade about the war’s geopolitical implications.
Russian President Vladimir Putin in 2013 signed a law that bans the “promotion of homosexuality” to minors.
The 2014 Winter Olympics took place in Sochi, a Russian resort city on the Black Sea. Russia annexed Crimea from Ukraine a few weeks after the games ended.
Russia’s anti-LGBTQ crackdown has continued over the last decade.
The Russian Supreme Court in 2023 ruled the “international LGBT movement” is an extremist organization and banned it. The Russian Justice Ministry last month designated ILGA World, a global LGBTQ and intersex rights group, as an “undesirable” organization.
Ukraine, meanwhile, has sought to align itself with Europe.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy after a 2021 meeting with then-President Joe Biden at the White House said his country would continue to fight discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity. (Zelenskyy’s relationship with the U.S. has grown more tense since the Trump-Vance administration took office.) Zelenskyy in 2022 publicly backed civil partnerships for same-sex couples.
Then-Ukrainian Ambassador to the U.S. Oksana Markarova in 2023 applauded Kyiv Pride and other LGBTQ and intersex rights groups in her country when she spoke at a photo exhibit at Ukraine House in D.C. that highlighted LGBTQ and intersex soldiers. Then-Kyiv Pride Executive Director Lenny Emson, who Feder profiles in his book, was among those who attended the event.
“Thank you for everything you do in Kyiv, and thank you for everything that you do in order to fight the discrimination that still is somewhere in Ukraine,” said Markarova. “Not everything is perfect yet, but you know, I think we are moving in the right direction. And we together will not only fight the external enemy, but also will see equality.”
Feder in response to the Blade’s question about why he decided to write his book said he “didn’t feel” the “significance of Russia’s war against Ukraine” for LGBTQ people around the world “was fully understood.”
“This was an opportunity to tell that big story,” he said.
“The crackdown on LGBT rights inside Russia was essentially a laboratory for a strategy of attacking democratic values by attacking queer rights and it was one as Ukraine was getting closet to Europe back in 2013, 2014,” he added. “It was a strategy they were using as part of their foreign policy, and it was one they were using not only in Ukraine over the past decade, but around the world.”
Feder said Republicans are using “that same strategy to attack queer people, to attack democracy itself.”
“I felt like it was important that Americans understand that history,” he said.
Books
New book explores homosexuality in ancient cultures
‘Queer Thing About Sin’ explains impact of religious credo in Greece, Rome

‘The Queer Thing About Sin’
By Harry Tanner
c.2025, Bloomsbury
$28/259 pages
Nobody likes you very much.
That’s how it seems sometimes, doesn’t it? Nobody wants to see you around, they don’t want to hear your voice, they can’t stand the thought of your existence and they’d really rather you just go away. It’s infuriating, and in the new book “The Queer Thing About Sin” by Harry Tanner, you’ll see how we got to this point.
When he was a teenager, Harry Tanner says that he thought he “was going to hell.”
For years, he’d been attracted to men and he prayed that it would stop. He asked for help from a lay minister who offered Tanner websites meant to repress his urges, but they weren’t the panacea Tanner hoped for. It wasn’t until he went to college that he found the answers he needed and “stopped fearing God’s retribution.”
Being gay wasn’t a sin. Not ever, but he “still wanted to know why Western culture believed it was for so long.”
Historically, many believe that older men were sexual “mentors” for teenage boys, but Tanner says that in ancient Greece and Rome, same-sex relationships were common between male partners of equal age and between differently-aged pairs, alike. Clarity comes by understanding relationships between husbands and wives then, and careful translation of the word “boy,” to show that age wasn’t a factor, but superiority and inferiority were.
In ancient Athens, queer love was considered to be “noble” but after the Persians sacked Athens, sex between men instead became an acceptable act of aggression aimed at conquered enemies. Raping a male prisoner was encouraged but, “Gay men became symbols of a depraved lack of self-control and abstinence.”
Later Greeks believed that men could turn into women “if they weren’t sufficiently virile.” Biblical interpretations point to more conflict; Leviticus specifically bans queer sex but “the Sumerians actively encouraged it.” The Egyptians hated it, but “there are sporadic clues that same-sex partners lived together in ancient Egypt.”
Says Tanner, “all is not what it seems.”
So you say you’re not really into ancient history. If it’s not your thing, then “The Queer Thing About Sin” won’t be, either.
Just know that if you skip this book, you’re missing out on the kind of excitement you get from reading mythology, but what’s here is true, and a much wider view than mere folklore. Author Harry Tanner invites readers to go deep inside philosophy, religion, and ancient culture, but the information he brings is not dry. No, there are major battles brought to life here, vanquished enemies and death – but also love, acceptance, even encouragement that the citizens of yore in many societies embraced and enjoyed. Tanner explains carefully how religious credo tied in with homosexuality (or didn’t) and he brings readers up to speed through recent times.
While this is not a breezy vacation read or a curl-up-with-a-blanket kind of book, “The Queer Thing About Sin” is absolutely worth spending time with. If you’re a thinking person and can give yourself a chance to ponder, you’ll like it very much.




















