Asia
Inside Seoul’s hidden lesbian nightclubs
For a few hours, women can gather without fear of discrimination
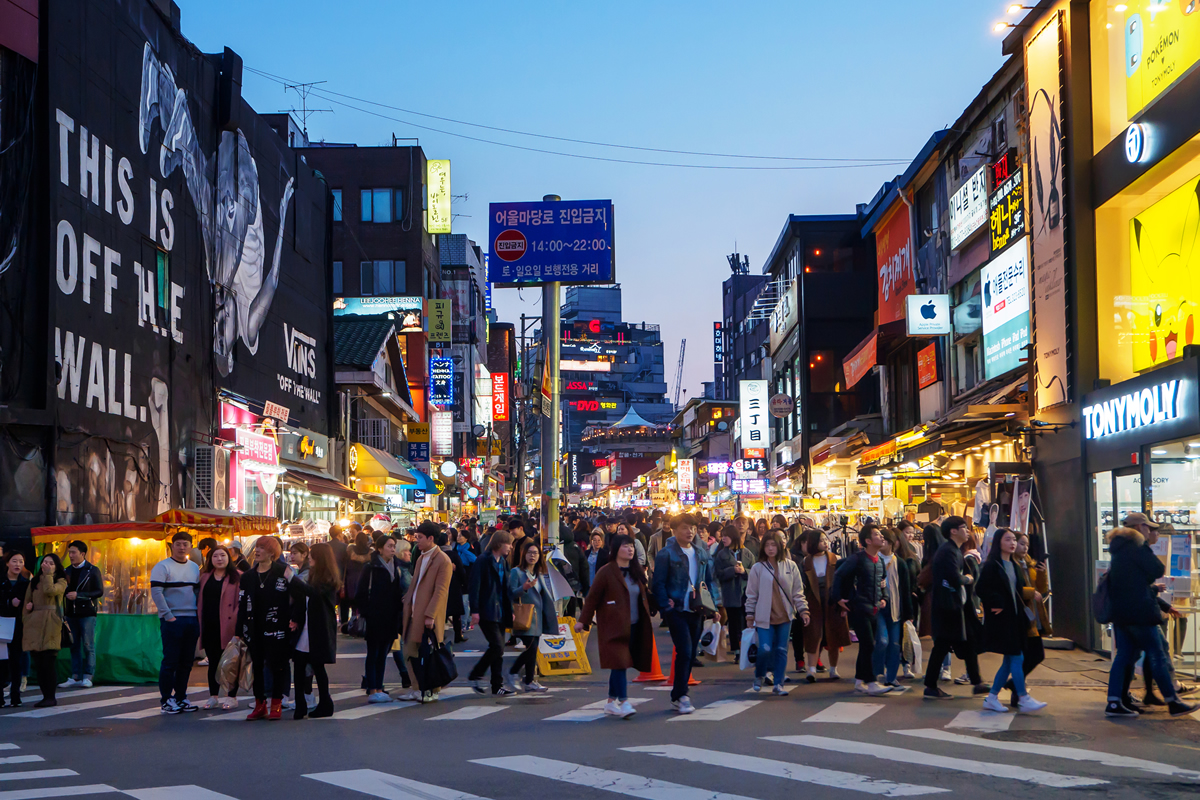

SEOUL, South Korea — Hongdae, a neighborhood in Seoul, South Korea, is known for its vibrant nightlife and indie music scene. By day, it’s a shopping and café mecca. By night it’s a crazy, alcohol-fueled playground. What’s easy to miss — and not even many Koreans living in Hongdae know about — is that hidden in plain sight, there are also secret lesbian clubs where women can gather and be themselves without fear of judgment or discrimination.
“Hongdae is the lesbian area of Seoul?!” my good friend blurted out when I told him over dinner. He’s been a resident of Hongdae for more than seven years but had never noticed. Most Koreans don’t know any LGBTQ people as Korean society is conservative and not accepting of homosexuality. Hongdae’s reputation as a more free-thinking, hipster haven makes it a perfect location for openness — albeit in private.
In South Korea, homosexuality is not illegal, but it is not widely accepted, especially in more conservative areas of the country. Seoul is more open compared to the countryside but not open enough for lesbians to be open. Same-sex couples cannot legally marry or adopt children and discrimination against the LGBTQ community is still prevalent.
Allen, a Korean woman in her 20s says, “There is a very strong homophobic atmosphere [in Korea] regardless of generation.”
Despite these challenges, the LGBTQ community in South Korea has been gradually (very gradually) gaining some visibility and acceptance in recent years such as an LGBTQ dating reality show “Merry Queer” following lesbian, gay and transgender couples. Seoul’s gay Pride parade — which last year drew thousands of participants despite protests from conservative religious groups — shows a shift in thinking too. However, it’s not enough progress as lesbian and bisexual women are still meeting in the dark.
One way in which the community has been able to connect and support each other is through secret lesbian clubs. Goon Young* is a Seoul freelancer in her mid-20s. Growing up she was constantly told that being straight is “natural” which left her feeling confused about her sexuality. “I thought I was bisexual when I was in college. I figured out that I don’t like men only about two years ago.” Goon Young enjoys hanging out at Hongdae’s lesbian club scene regularly.
These clubs are not advertised openly and are often hidden in inconspicuous side-streets, or in basements behind mainstream clubs.
One of these secret clubs is close to an infamous drinking spot for foreigners and when some foreign men were turned away for not being women, they looked visibly confused. It’s a large, luxe club with a strict no photograph rule. There’s table service and the DJ blasts Korean rap such as Jay Park and Zico.
This club and most of the others won’t easily pop up when you search on your phone’s map so usually lesbians need to get to know another lesbian to ask around for the exact location. This typically involves going to an LGBTQ bar first, or meet-up group and making friends there, as blurting out to your work buddies “Oh, by the way, is anyone else here gay?” wouldn’t go down too well in Korea. Goon Young concurs, “I’m pretty open to people that I love, someone like my mom or friends, but you can’t really tell people who are coworkers or someone [you] just met.”
Discrimination and stigma against the LGBTQ community persist in many areas of South Korean society, including the workplace and school. Many LGBTQ individuals still face rejection from their families and friends, and some even resort to conversion therapy to try and change their sexual orientation.
Luckily Goon Young’s mom is supportive, but not entirely convinced. “I came out to my mom — who loves me — last year. She still loves me and cheers me up when I have heartbreaks with girlfriends. But she says she still can’t take it seriously and gay things are not ‘natural,’ she always tells me to meet some good guys and date them even though I always reply to her that I don’t like men.”
The lesbian nightlife scene’s purpose is truly to create a safe space and respect the privacy of all. There’s so much trust in these clubs that “lonely heart” style personal ads are displayed on the big projector screen behind the DJ in the first club where I partied. After all, queer dating isn’t as straight-forward in a country that prizes straightness.
Inside these clubs, women let their guard down and can be themselves. They can dance, drink, and socialize without fear of being judged or harassed. Legally speaking, South Korea doesn’t have comprehensive LGBTQ anti-discrimination laws so the fear of physical safety for the LGBTQ community really means that a “safe space” carries much more weight than a “safe space” in a country where there’s more acceptance of gay rights.
Another safe space was a tiny club a little walk away from the big, “lonely hearts personals” club. What it lacked in size it made up for in chaotic ENERGY! Nobody was sitting in a corner here and after picking up my free drink included with the entry fee (every club did this), it was hit after hit from rapper Lil Nas X to K-pop group BLACKPINK.
Although lesbian and bi women were dancing wildly, enjoying the night, even within these safe spaces, many club-goers still feel the need to remain cautious as the fear of being outed can be overwhelming.
The last club I went to carried this caution. Located on an inconspicuous street, women were looking over their shoulders when paying in. That is, right up until the elevator doors shut. Once shut, women let their guards down and asked me how I found out about this place. Once inside — free drink handled (every club did Budweiser as a free drink option) — it was a playground of EDM, large opulent bottle service with half-undressed bartenders. One of them was even passing around free shots from one of the stripper pole podiums.
If there’s a lesbian heaven, I think I caught a glimpse of it here.
The cool air hit me as I left for home but nobody walking past suspected that the women leaving this club were not heterosexual. The fact that these clubs are still a secret highlights the need for greater acceptance and visibility of the LGBTQ community in South Korea. While progress has been made in recent years, there is still a long way to go before LGBTQ individuals can openly express their identities without fear of discrimination or being attacked.
“Young people in Korea are pretty open to LGBTQ, [but] of course, there are [some] who hate LGBTQ people. Most of the old people just can’t take it”, Goon Young says.
The existence of secret lesbian clubs in Hongdae and other parts of Seoul is a testament to the resilience and strength of the LGBTQ community in South Korea, also. Despite facing significant challenges and obstacles, these women have found a way to connect and support each other, creating safe spaces where they can be themselves.
Hongdae’s secret world of lesbian clubs offers a glimpse behind the curtain. Despite many hurdles, on a late, spring night in underground Hongdae clubs, women danced and flirted freely for the few hours they could be themselves.
(Editor’s note: Some names have been changed to protect identities of sources. Ash Potter is a freelance journalist based in Seoul.)
India
Anaya Bangar challenges ban on trans women in female cricket teams
Former Indian cricketer Sanjay Bangar’s daughter has received support
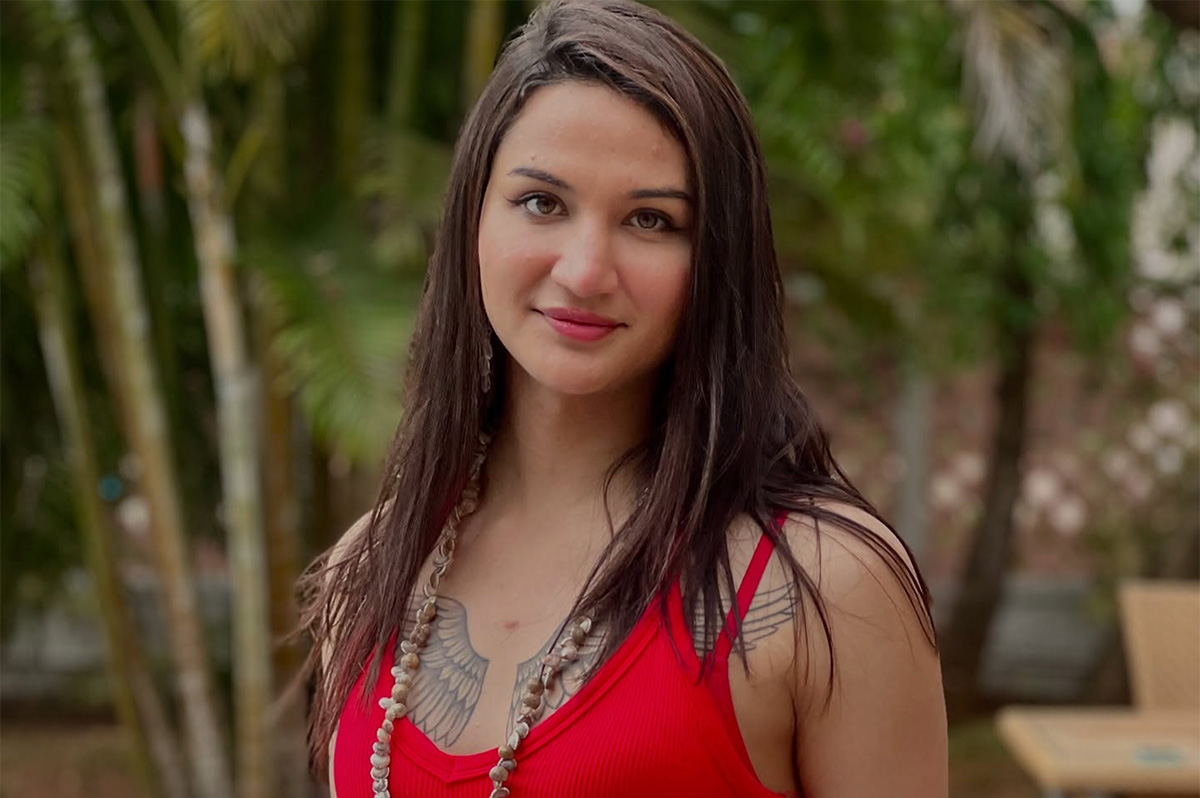
Anaya Bangar, the daughter of former Indian cricketer Sanjay Bangar, has partnered with the Manchester Metropolitan University Institute of Sport in the U.K. to assess her physiological profile following her gender-affirming surgery and undergoing hormone replacement therapy.
From January to March 2025, the 23-year-old underwent an eight-week research project that measured her glucose levels, oxygen uptake, muscle mass, strength, and endurance after extensive training.
The results, shared via Instagram, revealed her metrics align with those of cisgender female athletes, positioning her as eligible for women’s cricket under current scientific standards. Bangar’s findings challenge the International Cricket Council’s 2023 ban on transgender athletes in women’s cricket, prompting her to call for a science-based dialogue with the Board of Control for Cricket in India and the ICC to reform policies for trans inclusion.
“I am talking with scientific evidence in my hand,” Bangar said in an interview posted to her Instagram page. “So, I hope, this makes an impact and I will be hoping to BCCI and ICC talking with me and discussing this further.”
On Nov. 21, 2023, the ICC enacted a controversial policy barring trans women from international women’s cricket. Finalized after a board meeting in Ahmedabad, India, the regulation prohibits any trans player who has experienced male puberty from competing, irrespective of gender-affirming surgery or hormone therapy. Developed through a 9-month consultation led by the ICC’s Medical Advisory Committee, the rule aims to safeguard the “integrity, safety, and fairness” of women’s cricket but has drawn criticism for excluding athletes like Canada’s Danielle McGahey, the first trans woman to play internationally. The policy, which allows domestic boards to set their own rules, is slated for review by November 2025.
Bangar shared a document on social media verifying her participation in a physiological study at the Manchester Metropolitan University Institute of Sport, conducted from Jan. 20 to March 3, 2025, focused on cricket performance. The report confirmed that her vital metrics — including hemoglobin, blood glucose, peak power, and mean power — aligned with those of cisgender female athletes. Initially, her fasting blood glucose measured 6.1 mmol/L, slightly above the typical non-diabetic range of 4.0–5.9 mmol/L, but subsequent tests showed it normalized, reinforcing the study’s findings that her physical profile meets female athletic standards.
“I am submitting this to the BCCI and ICC, with full transparency and hope,” said Bangar. “My only intention is to start a conversation based on facts not fear. To build space, not divide it.”
In a letter to the BCCI and the ICC, Bangar emphasized her test results from the Manchester Metropolitan University study. She explained that the research aimed to assess how hormone therapy had influenced her strength, stamina, hemoglobin, glucose levels, and overall performance, benchmarked directly against cisgender female athletic standards.
Bangar’s letter to the BCCI and the ICC clarified the Manchester study was not intended as a political statement but as a catalyst for a science-driven dialogue on fairness and inclusion in cricket. She emphasized the importance of prioritizing empirical data over assumptions to shape equitable policies for trans athletes in the sport.
Bangar urged the BCCI, the world’s most influential cricket authority, to initiate a formal dialogue on trans women’s inclusion in women’s cricket, rooted in medical science, performance metrics, and ethical fairness. She called for the exploration of eligibility pathways based on sport-specific criteria, such as hemoglobin thresholds, testosterone suppression timelines, and standardized performance testing. Additionally, she advocated for collaboration with experts, athletes, and legal advisors to develop policies that balance inclusivity with competitive integrity.
“I am releasing my report and story publicly not for sympathy, but for truth. Because inclusion does not mean ignoring fairness, it means measuring it, transparently and responsibly,” said Bangar in a letter to the BCCI. “I would deeply appreciate the opportunity to meet with you or a representative of the BCCI or ICC to present my findings, discuss possible policy pathways, and work towards a future where every athlete is evaluated based on real data, not outdated perceptions.”
Before her transition, Bangar competed for Islam Gymkhana in Mumbai and Hinckley Cricket Club in the U.K., showcasing her talent in domestic cricket circuits. Her father, Sanjay Bangar, was a dependable all-rounder for the Indian national cricket team from 2001 to 2004, playing 12 test matches and 15 One Day Internationals. He later served as a batting coach for the Indian team from 2014 to 2019, contributing to its strategic development.
Cricket in India is a cultural phenomenon, commanding a fanbase of more than 1 billion, with more than 80 percent of global cricket viewership originating from the country.
The International Cricket Council, the sport’s governing body, oversees 12 full member nations and more than 90 associate members, with the U.S. recently gaining associate member status in 2019 and co-hosting the 2024 ICC Men’s T20 World Cup. The BCCI generated approximately $2.25 billion in revenue in the 2023–24 financial year, primarily from the Indian Premier League, bilateral series, and ICC revenue sharing. The ICC earns over $3 billion from media rights in India alone for the 2024–27 cycle, contributing nearly 90 percent of its global media rights revenue, with the BCCI receiving 38.5 percent of the ICC’s annual earnings, approximately $231 million per year.
Women’s cricket in India enjoys a growing fanbase, with over 300 million viewers for the Women’s Premier League in 2024, making it a significant driver of the sport’s global popularity. The International Cricket Council oversees women’s cricket in 12 full member nations and over 90 associate members, with the U.S. fielding a women’s team since gaining associate status in 2019 and competing in ICC events like the 2024 Women’s T20 World Cup qualifiers. The BCCI invests heavily in women’s cricket, allocating approximately $60 million annually to the WPL and domestic programs in 2024–25, while contributing to the ICC’s $20 million budget for women’s cricket development globally. India’s media market for women’s cricket, including WPL broadcasting rights, generated $120 million in 2024, accounting for over 50 percent of the ICC’s women’s cricket media revenue.
“As a woman, I feel when someone says that they are women, then they are, be trans or cis. A trans woman is definitely the same as a cis woman emotionally and in vitals, and specially, when someone is on hormone replacement therapy. Stopping Anaya Bangar from playing is discrimination and violation of her rights. It is really sad and painful that every trans woman need to fight and prove their identity everywhere,” said Indrani Chakraborty, an LGBTQ rights activist and a mother of a trans woman. “If ICC and BCCI is stopping her from playing for being transgender, then I will say this to be their lack of awareness and of course the social mindsets which deny acceptance.”
Chakraborty told the Blade that Bangar is an asset, no matter what. She said that the women’s cricket team will only benefit by participation, but the discriminating policies are the hindrance.
“Actually the transgender community face such discrimination in every sphere. In spite of being potent, they face rejection. This is highly inhuman. These attitudes is regressive and will never let to prosper. Are we really in 2025?,” said Chakraborty. “We, our mindset and the society are the issues. We, as a whole, need to get aware and have to come together for getting justice for Anaya. If today, we remain silent, the entire community will be oppressed. Proper knowledge of gender issues need to be understood.”
The BCCI and the International Cricket Council have not responded to the Blade’s repeated requests for comment.
India
Indian court rules a transgender woman is a woman
Activists across the country celebrated landmark decision

The Andhra Pradesh High Court on June 16 issued a landmark ruling that says Indian law cannot deny transgender women recognition as women solely because they cannot bear children.
Justice Venkata Jyothirmai Pratapa, who presided over the case, rejected arguments that tie womanhood exclusively to reproductive capacity, declaring such views “legally unsustainable” and contrary to the Indian constitution’s guarantees of dignity, equality, and identity. The decision, rooted in the Supreme Court’s 2014 National Legal Services Authority v. Union of India ruling that recognized individuals as a “third gender” with equal fundamental rights, marks a significant step toward gender justice in India.
“A trans woman, born male and later transitioning to female, is legally entitled to recognition as a woman,” Pratapa declared.
The court emphasized this recognition is enshrined in Articles 14, 15, and 21 of the constitution; which guarantee equality before the law, prohibit discrimination based on sex, and protect the right to life and personal liberty respectively. Pratapa further clarified that trans women are entitled to the same protections as cisgender women under Section 498A of the Indian penal code, which addresses cruelty by a husband or his relatives.
“Denying such protection by questioning their womanhood amounts to discrimination,” said the High Court in its ruling.
The ruling came in response to a petition filed by Viswanathan Krishnamurthy and his parents, who sought to dismiss a dowry harassment case brought by Pokala Sabhana, a trans woman. Shabana alleged that Krishnamurthy and his family subjected her to cruelty and demanded dowry, charges that prompted her to seek protection under Section 498A.
The court’s decision to uphold her legal standing as a woman ensures that trans women can access critical protections against domestic abuse, setting a precedent for future cases.
Section 498A’s applicability to trans women, as the court affirmed, extends critical protections against domestic cruelty to marginalized groups. Trans women can now seek legal recourse under this provision for physical, emotional, or economic abuse, including dowry-related harassment, by their husbands or in-laws. This recognition ensures access to police intervention, potential arrest of perpetrators, and penalties under the Indian penal code, aligning trans women’s marital protections with those afforded to cisgender women. By including trans women under Section 498A, the ruling strengthens their ability to combat domestic violence and assert their rights within familial structures.
Shabana and Krishnamurthy lived together in Ongole, a city in Andhra Pradesh, for a short time before Krishnamurthy relocated to Chennai and ceased communication, according to the court document the Washington Blade obtained.
Shabana filed a complaint at the Ongole Women’s Police Station, alleging her in-laws threatened her life and that Krishnamurthy abused her. Based on her accusations, the police registered a case against Krishnamurthy and his parents under Section 498A.
Krishnamurthy and his parents in 2022 petitioned the Andhra Pradesh High Court to dismiss the case, arguing that Shabana, as a trans woman, could not invoke Section 498A, a provision typically applied to cisgender women.
The petitioners’ counsel argued that trans women, due to their inability to conceive, do not meet the legal definition of a woman and thus cannot invoke Section 498A. They also contended Shabana’s cruelty and dowry harassment allegations were baseless and lacked evidentiary support.
The Andhra Pradesh High Court rejected the petitioners’ arguments, ruling that gender identity does not hinge on the ability to bear children and other biological factors. The court affirmed that trans women, like Shabana, have the right to file complaints under Section 498A and are entitled to all constitutional protections afforded to women under the constitution.
While affirming that trans women are legally recognized as women, the Andhra Pradesh High Court dismissed the case against Krishnamurthy and his family, citing insufficient evidence rather than gender-based arguments.
The court noted Shabana’s claims of dowry demands and cruelty lacked supporting material. It ruled that proceeding with the trial without prima facie evidence would constitute a misuse of the judicial process.
“I am relieved, the delighted and thank the Andhra Pradesh High Court and the judge for upholding our basic human right to be identified as what we want. What better reason could that be for celebrating this Pride Month,” said Kalki Subramaniam, a prominent trans activist and artist. “For transgender community, especially trans women this verdict means a lot.”
Subramaniam told the Blade that the verdict is a momentous achievement. She described it as a significant stride toward justice, dignity, and equality for trans people throughout India.
“By affirming their legal status as women, the court has shattered discriminatory barriers and reinforced the fundamental principle that identity is valid and deserving of full legal protection,” said Subramaniam. “This ruling marks a significant moment of progress, sending a clear message that our legal frameworks are evolving to be more inclusive and reflective of the diverse realities of our society. It is a victory of human rights and a beacon of hope for a more equitable future.”
Meera Parida, a prominent trans activist in Odisha, told the Blade the ruling is a significant triumph.
“Only because a trans woman cannot bear a child, she is not a woman — that’s not good,” she said.
“This is a respectful judgement for all of us,” added Parida. “This is restoring equality and somewhere because of this verdict the stigmatization wall will fall and people will respect us. I respect this verdict.”
“This verdict is very progressive and a crucial step forward to the transgender community and gender equality,” Rani Patel, president and founder of Aarohan, an organization that works to address educational disparities among underprivileged communities and advocates for LGBTQ rights, told the Blade. “People said that we should give them separate toilets and classrooms, but that totally excludes them from the community. Many women also cannot give birth to a child, so that is totally different.”
“If someone is carrying themselves as female, they should be honored with their status,” added Patel. “Since the purpose of the verdict is to recognize trans women as women, they will get all the status and rights as cisgender women in dowry and harassment cases.”

Authorities in the Indonesian city of Bogor on June 22 arrested 75 people after they raided a “gay party.”
Amnesty International in a press release notes the party was taking place at a villa in the city’s Puncak neighborhood. A local police chief reportedly said officers raided the gathering “following reports from the public regarding ‘gay activities.'”
“The police claimed to have secured a number of pieces of evidence, among them sex toys, four condoms, and a sword used for a dance performance,” said Amnesty International.
Bogor is roughly 40 miles south of Jakarta, the Indonesian capital, on the country’s Java island.
Officers took the 74 men and one woman they arrested to police headquarters. Amnesty International says they “were subjected to further examination, including health checks, and HIV tests.”
“The Indonesian authorities must end these hate-based and humiliating raids,” said Amnesty International. “No one should be subjected to arrest, intimidation, or public shaming because of their actual or perceived sexual orientation or gender identity.”
“The police must immediately release all those arrested,” it added. “Indonesia’s government must also take urgent steps to ensure accountability for human rights violations committed by the police, and work toward creating an environment where LGBTI individuals and their allies can live free from fear and harassment.”
Amnesty International notes authorities in Jakarta on May 24 raided a “gay sex party” at a hotel and arrested nine people. Indonesian police on Feb. 1 detained 56 people in a different Jakarta hotel after they raided “a gay party.”
Jakarta authorities in 2017 arrested 51 people who were attending a “gay party” at a sauna.
“These raids have increased in frequency in the first half of the year,” an Indonesian LGBTQ activist told the Washington Blade on Wednesday.
Amnesty International in its press release notes those arrested in the raids could face up to 15 years in prison for violating Indonesia’s Pornography Law.
“The Pornography Law defines pornography broadly, encompassing material that contravenes norms of community morality,” says Amnesty International. “Ambiguously worded laws on pornography are often exploited to deliberately target LGBTI people, denying them the basic right to privacy and the right to enter into consensual relationships.”
-

 U.S. Supreme Court3 days ago
U.S. Supreme Court3 days agoSupreme Court to consider bans on trans athletes in school sports
-

 Out & About3 days ago
Out & About3 days agoCelebrate the Fourth of July the gay way!
-

 Virginia3 days ago
Virginia3 days agoVa. court allows conversion therapy despite law banning it
-

 Maryland5 days ago
Maryland5 days agoLGBTQ suicide prevention hotline option is going away. Here’s where else to go in Md.