Asia
Chinese government forces Beijing LGBT Center to close
Shutdown is part of a broader crackdown
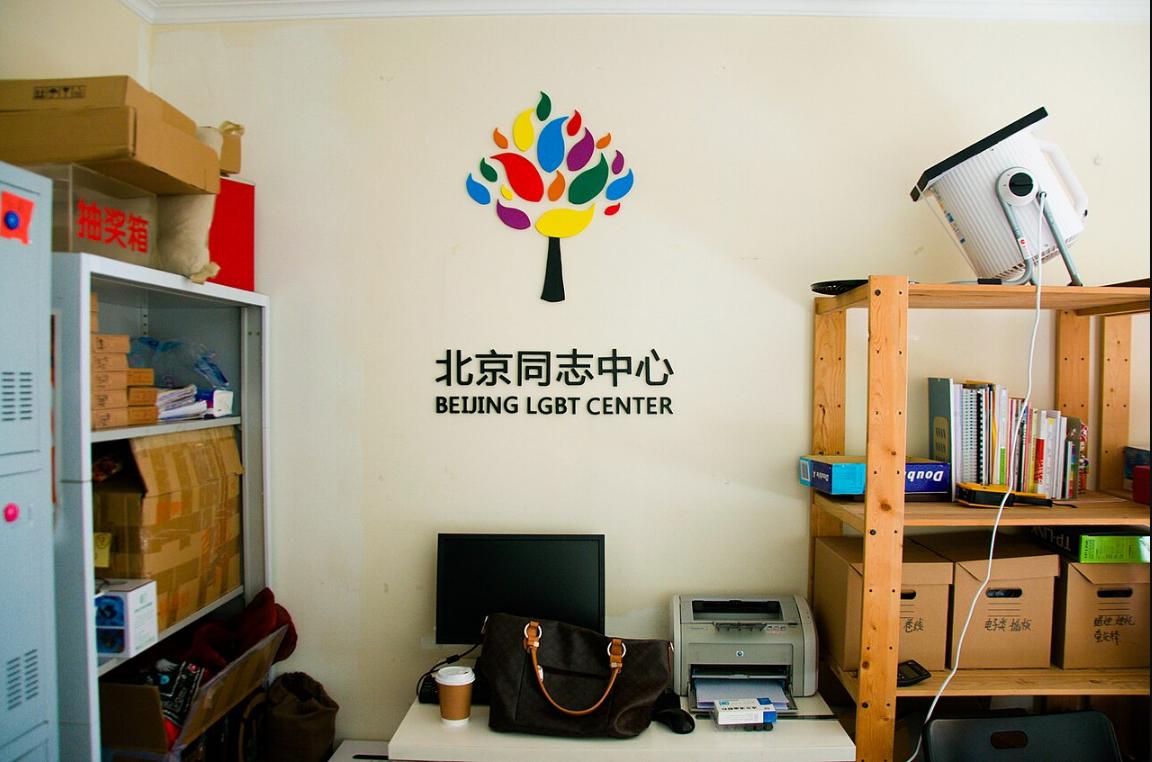

The government of Chinese President Xi Jinping continued its crackdown on the country’s LGBTQ minority, abruptly forcing closure of the Beijing LGBT Center on Monday.
In a brief message posted to the Sina Weibo microblogging website and on its WeChat account the center stated: “We very regretfully announce, due to forces beyond our control, the Beijing LGBT Center will stop operating today.”
With its closure, the Beijing LGBT Center, which has been operating for 15 years since it was founded in 2008, leaves China’s LGBTQ people with few resources to turn to. In November 2021, prominent LGBTQ equality rights legal group LGBT Rights Advocacy China, co-founded by Peng Yanzi and A. Qiang in the city of Guangzhou in 2013, and focused its efforts on securing legal rights for LGBTQ individuals through strategic lawsuits in China’s legal system, indefinitely suspended operations.
That suspension taking place after previously in July 2021, the Cyberspace Administration of China permanently disabled and deleted dozens of LGBTQ student organizations’ WeChat accounts across China.
The accounts, which were primarily managed by students, advocate LGBTQ and gender equality, and providing support to LGBTQ students on university and college campuses.
The pages of those accounts now display the message: “According to internet regulations, we have screened all content and suspended this account.” The names of the accounts have been changed to “Unnamed.”
In a early morning phone call Wednesday local time to an activist in the Chinese capital who asked to not be identified, the Blade was told that there was an accelerated push by Xi’s government to rein in LGBTQ groups and activists. The activist indicated that the center had published an article commemorating its 15 years of dedicated work last week, which “likely caught the scrutiny of both the Ministry of Civil Affairs and the Ministry of Public Security.”
“They are not the first group, nor are they the largest, but because Beijing LGBT Center was in Beijing, it represented China’s LGBT movement,” said another Chinese activist who requested anonymity out of fear for his safety to the Associated Press. “In our political, economic and cultural center, to have this type of organization. It was a symbol of the LGBT movement’s presence.”
A human rights activist from Hong Kong, who spoke to the Washington Blade on the condition of remaining anonymous, pointed out that in recent years the government has moved towards becoming more intolerant and homophobic towards LGBTQ people.
Acceptance of LGBTQ individuals in China has varied historically. In modern China, homosexuality is neither a crime nor officially regarded as an illness in China. For decades, the legal status of consensual same-sex activity between men was ambiguous, although at one point consensual sexual acts between people of the same sex were banned under a law on hooliganism in 1979 with punishments ranging from imprisonment to execution. That was cleared up in the revised criminal code of 1997 as China moved to decriminalize homosexuality.
In 2001, the Chinese Society of Psychiatry removed homosexuality from its list of mental disorders. This is consistent with the consensus of global medical associations that homosexuality is not a medical condition. But same-sex marriage is still illegal and the topic remains taboo socially.
Chinese government officials increasingly push the narrative that LGBTQ culture is an imported “Western” idea, while expressing concern that the country’s big tech platforms are spreading subversive views and ideas that could upend traditional ideas of gender.
In an action promulgated by Xi’s government this week, China’s National Radio and Television Administration ordered broadcasters to “resolutely put an end to sissy men and other abnormal esthetics.”
In the directive, the NRTA used the term “niang pao” which means “girlie guns” — more commonly translated as “sissy” an offensive description of effeminate men. The directive is seen as taking direct aim at the idols of the Chinese music industry who tend to be in their late teens to mid 20s, are thin, and dress in what could be loosely deemed an androgynously ambiguous manner.
The nationwide crackdown on human rights lawyers and activists started in 2015 after Xi came to power.
Speaking with the AP, the activist noted that police pressure on rights groups increased in the past few years, the activist said. Police often invited LGBTQ groups to “drink tea” — a euphemism for unofficial meetings that police use to keep track of certain targets. That used to happen in public spaces, but started taking place in private spaces, such as directly in front of activists’ homes. Police also started taking activists to the police station for these “teas.”
The Beijing LGBT Center has faced ongoing challenges to stay open throughout its existence, with obstacles arising from both funding limitations and political pressures. LGBTQ groups cannot register as non-governmental organizations in China, making it difficult to obtain government approval for events and secure external funding.
Because of those restrictions, groups like the center have been forced to create fundraising events at local bars and or receive direct financial support from groups outside of China. The Center also began to rent out its space to other, related organizations on weekdays at below-market rates, effectively tapping into its biggest asset — its real estate.
In addition to this there was direct financial support from the center’s sister organization, the Los Angeles LGBT Center.
This latest move is seen by some China watchers as another in a decades long battle by Beijing to combat Western influences on the younger generations of Chinese.
Conservatives in Chinese society and government charge that young Chinese youth are turning into ‘soft boys,’ reflecting concern that the Chinese pop stars who have embraced the pop-culture phenomenon in part due to the influence of the South Korean pop music and all-encompassing genre known as K-Pop, are failing to encourage China’s young men to be masculine enough.
In some government circles the source told the Blade its seen as overtly homosexual and targeting young Chinese males. One area that has raised the ire of officials is video games.
Game developers already were required to submit new titles for government approval before they could be released. Officials have called on them to add nationalistic themes, the AP reported.
“There is a tendency in China for some people to relate homosexuality and LGBT people to Western lifestyles or capitalistic, bourgeois decadence, so this was in line with a moral panic,” said Hongwei Bao, an associate professor of media studies at the University of Nottingham and specialist in queer politics in China.
“Especially now, there’s tension between China-West relations, so there is likely to be a heightened sense of nationalism which sees LGBT issues, feminist issues, as Western, as unfit for China.”
A closeted gay government source told the Blade that world events factor in to the crackdowns. Citing the rising tensions with Taiwan and its closest ally, the U.S. as an example.
He noted that in addition to gay men and lesbians, the center had opened its doors and resources to bisexual and transgender individuals, who themselves are minorities within the LGBT community and, as a result, face particular challenges.
“Their shutdown makes one feel very helpless. As groups large and small shut down or stop hosting events, there’s no longer a place where one can see hope,” said another Chinese activist who requested anonymity for fear of government retribution told the AP.
India
Anaya Bangar challenges ban on trans women in female cricket teams
Former Indian cricketer Sanjay Bangar’s daughter has received support
Anaya Bangar, the daughter of former Indian cricketer Sanjay Bangar, has partnered with the Manchester Metropolitan University Institute of Sport in the U.K. to assess her physiological profile following her gender-affirming surgery and undergoing hormone replacement therapy.
From January to March 2025, the 23-year-old underwent an eight-week research project that measured her glucose levels, oxygen uptake, muscle mass, strength, and endurance after extensive training.
The results, shared via Instagram, revealed her metrics align with those of cisgender female athletes, positioning her as eligible for women’s cricket under current scientific standards. Bangar’s findings challenge the International Cricket Council’s 2023 ban on transgender athletes in women’s cricket, prompting her to call for a science-based dialogue with the Board of Control for Cricket in India and the ICC to reform policies for transgender inclusion.
“I am talking with scientific evidence in my hand,” Bangar said in an interview posted to her Instagram page. “So, I hope, this makes an impact and I will be hoping to BCCI and ICC talking with me and discussing this further.”
On Nov. 21, 2023, the ICC enacted a controversial policy barring trans women from international women’s cricket. Finalized after a board meeting in Ahmedabad, India, the regulation prohibits any trans player who has experienced male puberty from competing, irrespective of gender-affirming surgery or hormone therapy. Developed through a 9-month consultation led by the ICC’s Medical Advisory Committee, the rule aims to safeguard the “integrity, safety, and fairness” of women’s cricket but has drawn criticism for excluding athletes like Canada’s Danielle McGahey, the first trans woman to play internationally. The policy, which allows domestic boards to set their own rules, is slated for review by November 2025.
Bangar shared a document on social media verifying her participation in a physiological study at the Manchester Metropolitan University Institute of Sport, conducted from Jan. 20 to March 3, 2025, focused on cricket performance. The report confirmed that her vital metrics — including haemoglobin, blood glucose, peak power, and mean power — aligned with those of cisgender female athletes. Initially, her fasting blood glucose measured 6.1 mmol/L, slightly above the typical non-diabetic range of 4.0–5.9 mmol/L, but subsequent tests showed it normalized, reinforcing the study’s findings that her physical profile meets female athletic standards.
“I am submitting this to the BCCI and ICC, with full transparency and hope,” said Bangar. “My only intention is to start a conversation based on facts not fear. To build space, not divide it.”
In a letter to the BCCI and the ICC, Bangar emphasized her test results from the Manchester Metropolitan University study. She explained that the research aimed to assess how hormone therapy had influenced her strength, stamina, haemoglobin, glucose levels, and overall performance, benchmarked directly against cisgender female athletic standards.
Bangar’s letter to the BCCI and the ICC clarified the Manchester study was not intended as a political statement but as a catalyst for a science-driven dialogue on fairness and inclusion in cricket. She emphasized the importance of prioritizing empirical data over assumptions to shape equitable policies for trans athletes in the sport.
Bangar urged the BCCI, the world’s most influential cricket authority, to initiate a formal dialogue on trans women’s inclusion in women’s cricket, rooted in medical science, performance metrics, and ethical fairness. She called for the exploration of eligibility pathways based on sport-specific criteria, such as haemoglobin thresholds, testosterone suppression timelines, and standardized performance testing. Additionally, she advocated for collaboration with experts, athletes, and legal advisors to develop policies that balance inclusivity with competitive integrity.
“I am releasing my report and story publicly not for sympathy, but for truth. Because inclusion does not mean ignoring fairness, it means measuring it, transparently and responsibly,” said Bangar in a letter to the BCCI. “I would deeply appreciate the opportunity to meet with you or a representative of the BCCI or ICC to present my findings, discuss possible policy pathways, and work towards a future where every athlete is evaluated based on real data, not outdated perceptions.”
Before her transition, Bangar competed for Islam Gymkhana in Mumbai and Hinckley Cricket Club in the U.K., showcasing her talent in domestic cricket circuits. Her father, Sanjay Bangar, was a dependable all-rounder for the Indian national cricket team from 2001 to 2004, playing 12 test matches and 15 One Day Internationals. He later served as a batting coach for the Indian team from 2014 to 2019, contributing to its strategic development.
Cricket in India is a cultural phenomenon, commanding a fanbase of more than 1 billion, with more than 80 percent of global cricket viewership originating from the country.
The International Cricket Council, the sport’s governing body, oversees 12 full member nations and more than 90 associate members, with the U.S. recently gaining associate member status in 2019 and co-hosting the 2024 ICC Men’s T20 World Cup. The BCCI generated approximately $2.25 billion in revenue in the 2023–24 financial year, primarily from the Indian Premier League, bilateral series, and ICC revenue sharing. The ICC earns over $3 billion from media rights in India alone for the 2024–27 cycle, contributing nearly 90 percent of its global media rights revenue, with the BCCI receiving 38.5 percent of the ICC’s annual earnings, approximately $231 million per year.
Women’s cricket in India enjoys a growing fanbase, with over 300 million viewers for the Women’s Premier League in 2024, making it a significant driver of the sport’s global popularity. The International Cricket Council oversees women’s cricket in 12 full member nations and over 90 associate members, with the U.S. fielding a women’s team since gaining associate status in 2019 and competing in ICC events like the 2024 Women’s T20 World Cup qualifiers. The BCCI invests heavily in women’s cricket, allocating approximately $60 million annually to the WPL and domestic programs in 2024–25, while contributing to the ICC’s $20 million budget for women’s cricket development globally. India’s media market for women’s cricket, including WPL broadcasting rights, generated $120 million in 2024, accounting for over 50 percent of the ICC’s women’s cricket media revenue.
“As a woman, I feel when someone says that they are women, then they are, be trans or cis. A trans woman is definitely the same as a cis woman emotionally and in vitals, and specially, when someone is on hormone replacement therapy. Stopping Anaya Bangar from playing is discrimination and violation of her rights. It is really sad and painful that every transwoman need to fight and prove their identity everywhere,” said Indrani Chakraborty, an LGBTQ rights activist and a mother of a trans woman. “If ICC and BCCI is stopping her from playing for being transgender, then I will say this to be their lack of awareness and of course the social mindsets which deny acceptance.”
Chakraborty told the Blade that Bangar is an asset, no matter what. She said that the women’s cricket team will only benefit by participation, but the discriminating policies are the hindrance.
“Actually the transgender community face such discrimination in every sphere. In spite of being potent, they face rejection. This is highly inhuman. These attitudes is regressive and will never let to prosper. Are we really in 2025?,” said Chakraborty. “We, our mindset and the society are the issues. We, as a whole, need to get aware and have to come together for getting justice for Anaya. If today, we remain silent, the entire community will be oppressed. Proper knowledge of gender issues need to be understood.”
The BCCI and the International Cricket Council have not responded to the Blade’s repeated requests for comment.
India
Indian court rules a transgender woman is a woman
Activists across the country celebrated landmark decision

The Andhra Pradesh High Court on June 16 issued a landmark ruling that says Indian law cannot deny transgender women recognition as women solely because they cannot bear children.
Justice Venkata Jyothirmai Pratapa, who presided over the case, rejected arguments that tie womanhood exclusively to reproductive capacity, declaring such views “legally unsustainable” and contrary to the Indian constitution’s guarantees of dignity, equality, and identity. The decision, rooted in the Supreme Court’s 2014 National Legal Services Authority v. Union of India ruling that recognized individuals as a “third gender” with equal fundamental rights, marks a significant step toward gender justice in India.
“A trans woman, born male and later transitioning to female, is legally entitled to recognition as a woman,” Pratapa declared.
The court emphasized this recognition is enshrined in Articles 14, 15, and 21 of the constitution; which guarantee equality before the law, prohibit discrimination based on sex, and protect the right to life and personal liberty respectively. Pratapa further clarified that trans women are entitled to the same protections as cisgender women under Section 498A of the Indian penal code, which addresses cruelty by a husband or his relatives.
“Denying such protection by questioning their womanhood amounts to discrimination,” said the High Court in its ruling.
The ruling came in response to a petition filed by Viswanathan Krishnamurthy and his parents, who sought to dismiss a dowry harassment case brought by Pokala Sabhana, a trans woman. Shabana alleged that Krishnamurthy and his family subjected her to cruelty and demanded dowry, charges that prompted her to seek protection under Section 498A.
The court’s decision to uphold her legal standing as a woman ensures that trans women can access critical protections against domestic abuse, setting a precedent for future cases.
Section 498A’s applicability to trans women, as the court affirmed, extends critical protections against domestic cruelty to marginalized groups. Trans women can now seek legal recourse under this provision for physical, emotional, or economic abuse, including dowry-related harassment, by their husbands or in-laws. This recognition ensures access to police intervention, potential arrest of perpetrators, and penalties under the Indian penal code, aligning trans women’s marital protections with those afforded to cisgender women. By including trans women under Section 498A, the ruling strengthens their ability to combat domestic violence and assert their rights within familial structures.
Shabana and Krishnamurthy lived together in Ongole, a city in Andhra Pradesh, for a short time before Krishnamurthy relocated to Chennai and ceased communication, according to the court document the Washington Blade obtained.
Shabana filed a complaint at the Ongole Women’s Police Station, alleging her in-laws threatened her life and that Krishnamurthy abused her. Based on her accusations, the police registered a case against Krishnamurthy and his parents under Section 498A.
Krishnamurthy and his parents in 2022 petitioned the Andhra Pradesh High Court to dismiss the case, arguing that Shabana, as a trans woman, could not invoke Section 498A, a provision typically applied to cisgender women.
The petitioners’ counsel argued that trans women, due to their inability to conceive, do not meet the legal definition of a woman and thus cannot invoke Section 498A. They also contended Shabana’s cruelty and dowry harassment allegations were baseless and lacked evidentiary support.
The Andhra Pradesh High Court rejected the petitioners’ arguments, ruling that gender identity does not hinge on the ability to bear children and other biological factors. The court affirmed that trans women, like Shabana, have the right to file complaints under Section 498A and are entitled to all constitutional protections afforded to women under the constitution.
While affirming that trans women are legally recognized as women, the Andhra Pradesh High Court dismissed the case against Krishnamurthy and his family, citing insufficient evidence rather than gender-based arguments.
The court noted Shabana’s claims of dowry demands and cruelty lacked supporting material. It ruled that proceeding with the trial without prima facie evidence would constitute a misuse of the judicial process.
“I am relieved, the delighted and thank the Andhra Pradesh High Court and the judge for upholding our basic human right to be identified as what we want. What better reason could that be for celebrating this Pride Month,” said Kalki Subramaniam, a prominent trans activist and artist. “For transgender community, especially trans women this verdict means a lot.”
Subramaniam told the Blade that the verdict is a momentous achievement. She described it as a significant stride toward justice, dignity, and equality for trans people throughout India.
“By affirming their legal status as women, the court has shattered discriminatory barriers and reinforced the fundamental principle that identity is valid and deserving of full legal protection,” said Subramaniam. “This ruling marks a significant moment of progress, sending a clear message that our legal frameworks are evolving to be more inclusive and reflective of the diverse realities of our society. It is a victory of human rights and a beacon of hope for a more equitable future.”
Meera Parida, a prominent trans activist in Odisha, told the Blade the ruling is a significant triumph.
“Only because a trans woman cannot bear a child, she is not a woman — that’s not good,” she said.
“This is a respectful judgement for all of us,” added Parida. “This is restoring equality and somewhere because of this verdict the stigmatization wall will fall and people will respect us. I respect this verdict.”
“This verdict is very progressive and a crucial step forward to the transgender community and gender equality,” Rani Patel, president and founder of Aarohan, an organization that works to address educational disparities among underprivileged communities and advocates for LGBTQ rights, told the Blade. “People said that we should give them separate toilets and classrooms, but that totally excludes them from the community. Many women also cannot give birth to a child, so that is totally different.”
“If someone is carrying themselves as female, they should be honored with their status,” added Patel. “Since the purpose of the verdict is to recognize trans women as women, they will get all the status and rights as cisgender women in dowry and harassment cases.”

Authorities in the Indonesian city of Bogor on June 22 arrested 75 people after they raided a “gay party.”
Amnesty International in a press release notes the party was taking place at a villa in the city’s Puncak neighborhood. A local police chief reportedly said officers raided the gathering “following reports from the public regarding ‘gay activities.'”
“The police claimed to have secured a number of pieces of evidence, among them sex toys, four condoms, and a sword used for a dance performance,” said Amnesty International.
Bogor is roughly 40 miles south of Jakarta, the Indonesian capital, on the country’s Java island.
Officers took the 74 men and one woman they arrested to police headquarters. Amnesty International says they “were subjected to further examination, including health checks, and HIV tests.”
“The Indonesian authorities must end these hate-based and humiliating raids,” said Amnesty International. “No one should be subjected to arrest, intimidation, or public shaming because of their actual or perceived sexual orientation or gender identity.”
“The police must immediately release all those arrested,” it added. “Indonesia’s government must also take urgent steps to ensure accountability for human rights violations committed by the police, and work toward creating an environment where LGBTI individuals and their allies can live free from fear and harassment.”
Amnesty International notes authorities in Jakarta on May 24 raided a “gay sex party” at a hotel and arrested nine people. Indonesian police on Feb. 1 detained 56 people in a different Jakarta hotel after they raided “a gay party.”
Jakarta authorities in 2017 arrested 51 people who were attending a “gay party” at a sauna.
“These raids have increased in frequency in the first half of the year,” an Indonesian LGBTQ activist told the Washington Blade on Wednesday.
Amnesty International in its press release notes those arrested in the raids could face up to 15 years in prison for violating Indonesia’s Pornography Law.
“The Pornography Law defines pornography broadly, encompassing material that contravenes norms of community morality,” says Amnesty International. “Ambiguously worded laws on pornography are often exploited to deliberately target LGBTI people, denying them the basic right to privacy and the right to enter into consensual relationships.”
-

 U.S. Supreme Court3 days ago
U.S. Supreme Court3 days agoSupreme Court upholds ACA rule that makes PrEP, other preventative care free
-

 U.S. Supreme Court3 days ago
U.S. Supreme Court3 days agoSupreme Court rules parents must have option to opt children out of LGBTQ-specific lessons
-

 India5 days ago
India5 days agoIndian court rules a transgender woman is a woman
-

 National4 days ago
National4 days agoEvan Wolfson on the 10-year legacy of marriage equality












