India
Marriage equality proponents make case to India Supreme Court
Hearing to resume on Tuesday

The Indian Supreme Court on April 18 started hearing a case on whether to extend marriage rights to same-sex couples in the country.
Chief Justice Dhananjay Yeshwant Chandrachud is heading a panel of five judges to decide if the time is now to extend marriage rights to same-sex couples in the country where being LGBTQ is not a crime, but a same sex couple cannot marry.
The marriage equality case on the first day of the hearing started with a heated exchange between Solicitor General Tushar Mehta, the country’s second highest legal official, and Chandrachud. The solicitor general argued which forum should be the only constitutional forum that could adjudicate the marriage equality law. Chandrachud wanted to hear the merits of the case first. Mehta insisted on hearing the issue first.
“I am in charge. I will decide. We will hear the petitioners first,” said Chandrachud.” “I will not allow anyone to dictate how proceedings will happen in this court.”
Judges felt a little shocked when Mehta said that if that is the case, let him then take time to see if the government should participate in the hearing. Justice Sanjay Kishan Kaul, one of the five judges who is currently hearing the validity of marriage equality in India, asked Mehta if he meant that the government would not participate in the hearing.
“None of us know what a farmer in south India thinks or a businessman thinks in North India,” said Mehta.
Chandrachud argued that the court would consider any request other than adjournment. After the heated argument in the court, senior lawyer Mukul Rohtagi opened the case for petitioners.
“We are persons of the same sex, and we have the same rights as like the heterosexual groups of the society this has been held so, and we need not reinvent the wheel and only stumbling block was Section 377, and our actions were subject to criminality, and now it is gone,” said Rohtagi, who represents the plaintiffs. “If our rights are identical and then we should enjoy full array of rights as under Articles 14, 15 and 21.”
Article 14 of the Indian constitution deals with equality before the law.
The article says that the state shall not deny to any person equality before the law or the equal protection of the laws within Indian territory based on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth. Article 15 prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth. Article 21 says no person shall be deprived of his life or personal liberty except according to a procedure established by law.
Rohtagi argued that the court should not wait for legislative action when fundamental rights are involved.
“Our lives are getting passed,” said Rohtagi. “We are getting old, and we need to be respected as in a marriage. Call them queer, call them gay. People look at them differently, and that is a violation of Article 21. A violation of right to life with dignity and also violation of Article 15 when there can be no discrimination based on caste, sex.”
While arguing, Rohtagi brought up the Respect for Marriage Act in the U.S. to support his argument about the validity of marriage equality. When the court was hearing the validity of the marriage equality case, Chandrachud made a note to restrict the discussion on the gender-neutral interpretation and evolve a civil union concept.
Menaka Guruswamy, a senior lawyer, while arguing for the plaintiffs, said she could not designate her life partner for life insurance and that people like her would keep coming to the court to redress individual grievances.
The Washington Blade last November reported that the Life Insurance Corporation of India, a public sector insurance company under India’s Finance Ministry, had said that there is no legal bar for anyone to make their same sex partner a beneficiary in insurance policies in the name of that person.
Mehta during the middle of the hearing said that the question is not granting a socio-legal sanction. It has been clearly saying no one shall discriminate against the trans person, including unfair treatment and denial of employment, and here trans includes LGBTQ and intersex and not what is understood in the conventional sense. He also said that Hindus and Muslims will be affected, and that is why states should be heard.
Chandrachud said that the notion of biological man and biological woman is absolute. The chief justice also said that it is not a question of genitals because the Special Marriage Act’s definition of man and woman is not restricted to genitals.
The Special Marriage Act is an Indian marriage law enacted in 1954 that provides a legal framework for the marriage of people belonging to different religions or castes.
Mehta argued other laws will be redundant if the marriage equality law takes effect. He also requested the Supreme Court consult all states in India for their response as marriage laws are listed in the concurrent list of the constitution that states union governments and state governments can make laws on the subjects enlisted under the concurrent list. Marriage falls under the concurrent list of the Indian constitution.
Kapil Sibal, a senior lawyer for Jamiat Ulema-I-Hind, a leading Islamic scholar organization in India, told the Supreme Court he believes in the autonomy of an individual and that everyone needs to celebrate the union of two people. But Sibal also argued that if same-sex marriage is allowed who will take care of the child? Who will be the father? Who will be the mother? Sibal said that in international examples countries reform all other laws to accommodate these things.
“I am all for same sex marriage but not in this fashion,” said Sibal. “If this is not done as a whole then let it not be done at all.”
Rohatgi said before the bench that the LGBTQ and intersex community has a fundamental right to get married and have it registered like heterogenous brethren of the society.
“I was amazed to hear that we are not equals and we need to be equal to stigmatized lot, and that is why court should step in, and that is why even after 377 judgment we are here,” said Rohatgi. “That is why state is telling us here that we are not equals.”
While highlighting equality and justice for everyone, Chandrachud, said that justice is to each of us, liberty to each of us, equality to each of us, and fraternity for all of us.
On April 19, the second day of the hearing, the central government filed a fresh application and urged the judges to take into account the state governments’ views since “marriage” is on the concurrent list. The central government in its application said that the Department of Legal Affairs has also written to all chief secretaries of state to submit their views on same-sex marriage in case notice is not issued to them. The central government also said that states should submit their views in 10 days so that center can present the case before the Supreme Court.
Rohatgi said that the LGBTQ and intersex community suffers under the majority. He said it is not the law, but a mindset that is bothering LGBTQ and intersex people in their daily life. Rohatgi also said that society accepts what the law is and highlighted to the judges that the LGBTQ and intersex community has no representation in the Parliament and that’s why the community has approached the court. Rohatgi also argued that constitutional morality would become a habit for the people when the same is upheld by the Supreme Court.
“State cannot discriminate against an individual on the basis of a characteristic over which the individual does not have control,” said Chandrachud. “When you see it is innate characteristics, then it counter urban elitist concept. Urban perhaps because more people are coming out of the closet. Government does not have any data also to show that same sex marriage is an urban elitist concept.”
On the third day of hearing, senior lawyer K.V. Vishwanathan appeared for the plaintiffs and argued that if one can be a son, daughter, sister, father-in-law, uncle, aunt and partner, then what holds the court to give marital status to the same-sex couples.
“It is only the sexual orientation which is beyond my control and it is not in conformity with heterosexual norms and thus will not accord you protection like the normal married couples,” said Vishwanathan. “Procreation is a valid defense to negate the right to marriage.”
Vishwanathan also argued that marriage is the coming together of two souls and to be told that it is to be looked at from procreation purpose is fallacious.
“What happens when there is a heterosexual couple when there is domestic violence. What kind of impact on children? So much for being heterosexual,” noted Chandrachud. “What about father coming back home drunk thrashing up the mother and asking money for alcohol? there is nothing absolute at the cost of being trolled. Answers to what we say in court is in trolls and not in court.”
The Supreme Court of the land also noted that the government does not have the data to prove that same-sex marriage is an urban elitist concept.
“People come out of closet,” noted the Supreme Court.
The central government, in its application, had highlighted that the concept of marriage equality is an ‘urban elitist’ notion.
The hearing on LGBTQ and intersex marriage rights has attracted reactions from across the nation.
Ranvir Shorey, a Bollywood actor, reacted to Supreme Court’s hearing and said that there is no fixed way to be a man or a woman.
“Better to think of it in terms of polarity, or scale. Those who fuss over binaries ought to remember there is an infinity between the two too,” said Shorey in a tweet. “Jurisprudence is derived from human understanding of nature’s principles. Laws exist so a society can function as a collective, while trying to preserve the rights of the individual. The more our laws move away from nature, the more at conflict we will be with ourselves.”
The Vishwa Hindu Parishad has opposed the marriage equality rights petition and said the “haste” with which the Supreme Court is hearing the petitions for legal recognition of same-sex marriage is not appropriate. The organization also said that the court should have asked for the opinion of religious leaders and experts from diverse fields.
The Bar Council of India, a statutory body that regulates legal practices and education in the country, on Sunday held a joint meeting with all the state Bar Councils in the country and passed a resolution concerning marriage equality. The Bar Council of India has requested the Supreme Court to leave the issue of marriage equality for legislative consideration.
“India is one of the most socio-religiously diverse countries in the world consisting of a mosaic of beliefs. Hence, any matter which is likely to tinker with the fundamental social structure, a matter which has a far-reaching impact on our socio-cultural and religious beliefs should necessarily come through the legislative process only, the meeting unanimously opined. Any decision by the Apex Court in such a sensitive matter may prove very harmful for the future generation of our country.” the release stated.
The Bar Council of India also said that more than 99.9 percent of people in the country are opposed to the idea of marriage equality. The Supreme Court will start hearing the government’s arguments on Tuesday.
Ankush Kumar is a reporter who has covered many stories for Washington and Los Angeles Blades from Iran, India and Singapore. He recently reported for the Daily Beast. He can be reached at mohitk@opiniondaily.news. He is on Twitter at @mohitkopinion.
India
Anaya Bangar challenges ban on trans women in female cricket teams
Former Indian cricketer Sanjay Bangar’s daughter has received support
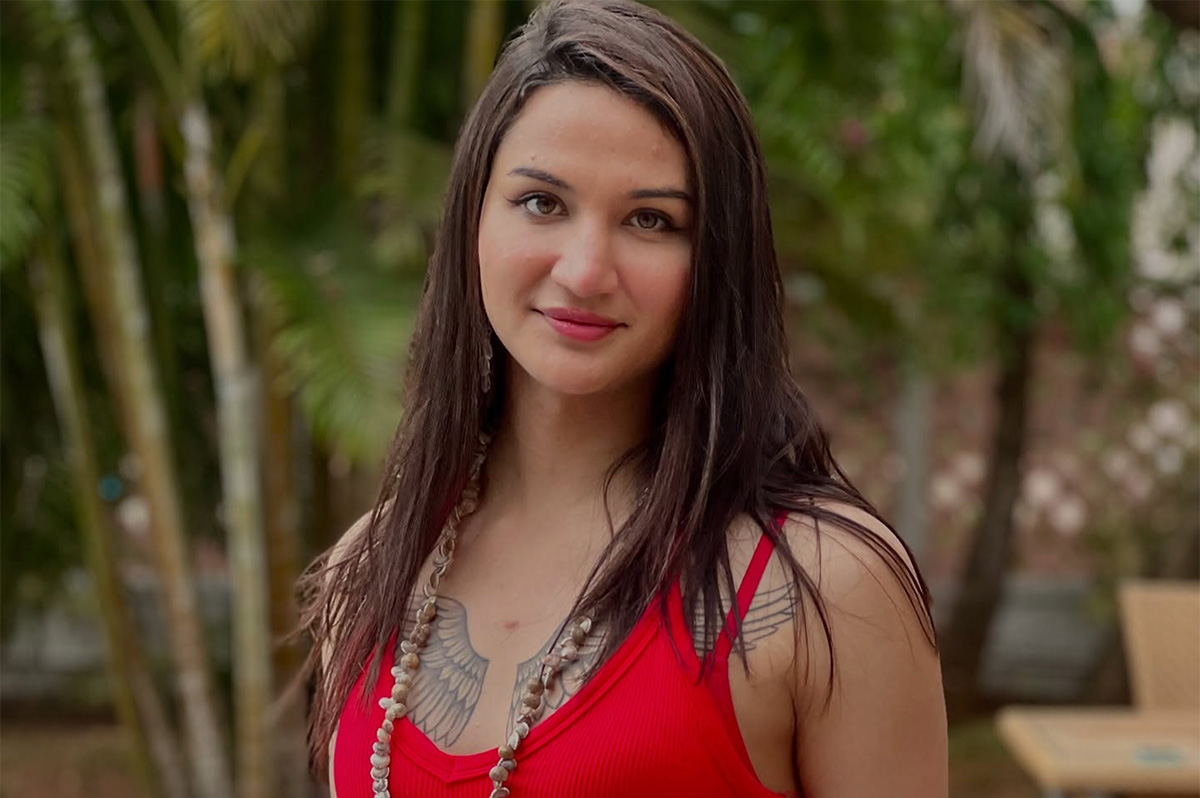
Anaya Bangar, the daughter of former Indian cricketer Sanjay Bangar, has partnered with the Manchester Metropolitan University Institute of Sport in the U.K. to assess her physiological profile following her gender-affirming surgery and undergoing hormone replacement therapy.
From January to March 2025, the 23-year-old underwent an eight-week research project that measured her glucose levels, oxygen uptake, muscle mass, strength, and endurance after extensive training.
The results, shared via Instagram, revealed her metrics align with those of cisgender female athletes, positioning her as eligible for women’s cricket under current scientific standards. Bangar’s findings challenge the International Cricket Council’s 2023 ban on transgender athletes in women’s cricket, prompting her to call for a science-based dialogue with the Board of Control for Cricket in India and the ICC to reform policies for trans inclusion.
“I am talking with scientific evidence in my hand,” Bangar said in an interview posted to her Instagram page. “So, I hope, this makes an impact and I will be hoping to BCCI and ICC talking with me and discussing this further.”
On Nov. 21, 2023, the ICC enacted a controversial policy barring trans women from international women’s cricket. Finalized after a board meeting in Ahmedabad, India, the regulation prohibits any trans player who has experienced male puberty from competing, irrespective of gender-affirming surgery or hormone therapy. Developed through a 9-month consultation led by the ICC’s Medical Advisory Committee, the rule aims to safeguard the “integrity, safety, and fairness” of women’s cricket but has drawn criticism for excluding athletes like Canada’s Danielle McGahey, the first trans woman to play internationally. The policy, which allows domestic boards to set their own rules, is slated for review by November 2025.
Bangar shared a document on social media verifying her participation in a physiological study at the Manchester Metropolitan University Institute of Sport, conducted from Jan. 20 to March 3, 2025, focused on cricket performance. The report confirmed that her vital metrics — including hemoglobin, blood glucose, peak power, and mean power — aligned with those of cisgender female athletes. Initially, her fasting blood glucose measured 6.1 mmol/L, slightly above the typical non-diabetic range of 4.0–5.9 mmol/L, but subsequent tests showed it normalized, reinforcing the study’s findings that her physical profile meets female athletic standards.
“I am submitting this to the BCCI and ICC, with full transparency and hope,” said Bangar. “My only intention is to start a conversation based on facts not fear. To build space, not divide it.”
In a letter to the BCCI and the ICC, Bangar emphasized her test results from the Manchester Metropolitan University study. She explained that the research aimed to assess how hormone therapy had influenced her strength, stamina, hemoglobin, glucose levels, and overall performance, benchmarked directly against cisgender female athletic standards.
Bangar’s letter to the BCCI and the ICC clarified the Manchester study was not intended as a political statement but as a catalyst for a science-driven dialogue on fairness and inclusion in cricket. She emphasized the importance of prioritizing empirical data over assumptions to shape equitable policies for trans athletes in the sport.
Bangar urged the BCCI, the world’s most influential cricket authority, to initiate a formal dialogue on trans women’s inclusion in women’s cricket, rooted in medical science, performance metrics, and ethical fairness. She called for the exploration of eligibility pathways based on sport-specific criteria, such as hemoglobin thresholds, testosterone suppression timelines, and standardized performance testing. Additionally, she advocated for collaboration with experts, athletes, and legal advisors to develop policies that balance inclusivity with competitive integrity.
“I am releasing my report and story publicly not for sympathy, but for truth. Because inclusion does not mean ignoring fairness, it means measuring it, transparently and responsibly,” said Bangar in a letter to the BCCI. “I would deeply appreciate the opportunity to meet with you or a representative of the BCCI or ICC to present my findings, discuss possible policy pathways, and work towards a future where every athlete is evaluated based on real data, not outdated perceptions.”
Before her transition, Bangar competed for Islam Gymkhana in Mumbai and Hinckley Cricket Club in the U.K., showcasing her talent in domestic cricket circuits. Her father, Sanjay Bangar, was a dependable all-rounder for the Indian national cricket team from 2001 to 2004, playing 12 test matches and 15 One Day Internationals. He later served as a batting coach for the Indian team from 2014 to 2019, contributing to its strategic development.
Cricket in India is a cultural phenomenon, commanding a fanbase of more than 1 billion, with more than 80 percent of global cricket viewership originating from the country.
The International Cricket Council, the sport’s governing body, oversees 12 full member nations and more than 90 associate members, with the U.S. recently gaining associate member status in 2019 and co-hosting the 2024 ICC Men’s T20 World Cup. The BCCI generated approximately $2.25 billion in revenue in the 2023–24 financial year, primarily from the Indian Premier League, bilateral series, and ICC revenue sharing. The ICC earns over $3 billion from media rights in India alone for the 2024–27 cycle, contributing nearly 90 percent of its global media rights revenue, with the BCCI receiving 38.5 percent of the ICC’s annual earnings, approximately $231 million per year.
Women’s cricket in India enjoys a growing fanbase, with over 300 million viewers for the Women’s Premier League in 2024, making it a significant driver of the sport’s global popularity. The International Cricket Council oversees women’s cricket in 12 full member nations and over 90 associate members, with the U.S. fielding a women’s team since gaining associate status in 2019 and competing in ICC events like the 2024 Women’s T20 World Cup qualifiers. The BCCI invests heavily in women’s cricket, allocating approximately $60 million annually to the WPL and domestic programs in 2024–25, while contributing to the ICC’s $20 million budget for women’s cricket development globally. India’s media market for women’s cricket, including WPL broadcasting rights, generated $120 million in 2024, accounting for over 50 percent of the ICC’s women’s cricket media revenue.
“As a woman, I feel when someone says that they are women, then they are, be trans or cis. A trans woman is definitely the same as a cis woman emotionally and in vitals, and specially, when someone is on hormone replacement therapy. Stopping Anaya Bangar from playing is discrimination and violation of her rights. It is really sad and painful that every trans woman need to fight and prove their identity everywhere,” said Indrani Chakraborty, an LGBTQ rights activist and a mother of a trans woman. “If ICC and BCCI is stopping her from playing for being transgender, then I will say this to be their lack of awareness and of course the social mindsets which deny acceptance.”
Chakraborty told the Blade that Bangar is an asset, no matter what. She said that the women’s cricket team will only benefit by participation, but the discriminating policies are the hindrance.
“Actually the transgender community face such discrimination in every sphere. In spite of being potent, they face rejection. This is highly inhuman. These attitudes is regressive and will never let to prosper. Are we really in 2025?,” said Chakraborty. “We, our mindset and the society are the issues. We, as a whole, need to get aware and have to come together for getting justice for Anaya. If today, we remain silent, the entire community will be oppressed. Proper knowledge of gender issues need to be understood.”
The BCCI and the International Cricket Council have not responded to the Blade’s repeated requests for comment.
India
Indian court rules a transgender woman is a woman
Activists across the country celebrated landmark decision

The Andhra Pradesh High Court on June 16 issued a landmark ruling that says Indian law cannot deny transgender women recognition as women solely because they cannot bear children.
Justice Venkata Jyothirmai Pratapa, who presided over the case, rejected arguments that tie womanhood exclusively to reproductive capacity, declaring such views “legally unsustainable” and contrary to the Indian constitution’s guarantees of dignity, equality, and identity. The decision, rooted in the Supreme Court’s 2014 National Legal Services Authority v. Union of India ruling that recognized individuals as a “third gender” with equal fundamental rights, marks a significant step toward gender justice in India.
“A trans woman, born male and later transitioning to female, is legally entitled to recognition as a woman,” Pratapa declared.
The court emphasized this recognition is enshrined in Articles 14, 15, and 21 of the constitution; which guarantee equality before the law, prohibit discrimination based on sex, and protect the right to life and personal liberty respectively. Pratapa further clarified that trans women are entitled to the same protections as cisgender women under Section 498A of the Indian penal code, which addresses cruelty by a husband or his relatives.
“Denying such protection by questioning their womanhood amounts to discrimination,” said the High Court in its ruling.
The ruling came in response to a petition filed by Viswanathan Krishnamurthy and his parents, who sought to dismiss a dowry harassment case brought by Pokala Sabhana, a trans woman. Shabana alleged that Krishnamurthy and his family subjected her to cruelty and demanded dowry, charges that prompted her to seek protection under Section 498A.
The court’s decision to uphold her legal standing as a woman ensures that trans women can access critical protections against domestic abuse, setting a precedent for future cases.
Section 498A’s applicability to trans women, as the court affirmed, extends critical protections against domestic cruelty to marginalized groups. Trans women can now seek legal recourse under this provision for physical, emotional, or economic abuse, including dowry-related harassment, by their husbands or in-laws. This recognition ensures access to police intervention, potential arrest of perpetrators, and penalties under the Indian penal code, aligning trans women’s marital protections with those afforded to cisgender women. By including trans women under Section 498A, the ruling strengthens their ability to combat domestic violence and assert their rights within familial structures.
Shabana and Krishnamurthy lived together in Ongole, a city in Andhra Pradesh, for a short time before Krishnamurthy relocated to Chennai and ceased communication, according to the court document the Washington Blade obtained.
Shabana filed a complaint at the Ongole Women’s Police Station, alleging her in-laws threatened her life and that Krishnamurthy abused her. Based on her accusations, the police registered a case against Krishnamurthy and his parents under Section 498A.
Krishnamurthy and his parents in 2022 petitioned the Andhra Pradesh High Court to dismiss the case, arguing that Shabana, as a trans woman, could not invoke Section 498A, a provision typically applied to cisgender women.
The petitioners’ counsel argued that trans women, due to their inability to conceive, do not meet the legal definition of a woman and thus cannot invoke Section 498A. They also contended Shabana’s cruelty and dowry harassment allegations were baseless and lacked evidentiary support.
The Andhra Pradesh High Court rejected the petitioners’ arguments, ruling that gender identity does not hinge on the ability to bear children and other biological factors. The court affirmed that trans women, like Shabana, have the right to file complaints under Section 498A and are entitled to all constitutional protections afforded to women under the constitution.
While affirming that trans women are legally recognized as women, the Andhra Pradesh High Court dismissed the case against Krishnamurthy and his family, citing insufficient evidence rather than gender-based arguments.
The court noted Shabana’s claims of dowry demands and cruelty lacked supporting material. It ruled that proceeding with the trial without prima facie evidence would constitute a misuse of the judicial process.
“I am relieved, the delighted and thank the Andhra Pradesh High Court and the judge for upholding our basic human right to be identified as what we want. What better reason could that be for celebrating this Pride Month,” said Kalki Subramaniam, a prominent trans activist and artist. “For transgender community, especially trans women this verdict means a lot.”
Subramaniam told the Blade that the verdict is a momentous achievement. She described it as a significant stride toward justice, dignity, and equality for trans people throughout India.
“By affirming their legal status as women, the court has shattered discriminatory barriers and reinforced the fundamental principle that identity is valid and deserving of full legal protection,” said Subramaniam. “This ruling marks a significant moment of progress, sending a clear message that our legal frameworks are evolving to be more inclusive and reflective of the diverse realities of our society. It is a victory of human rights and a beacon of hope for a more equitable future.”
Meera Parida, a prominent trans activist in Odisha, told the Blade the ruling is a significant triumph.
“Only because a trans woman cannot bear a child, she is not a woman — that’s not good,” she said.
“This is a respectful judgement for all of us,” added Parida. “This is restoring equality and somewhere because of this verdict the stigmatization wall will fall and people will respect us. I respect this verdict.”
“This verdict is very progressive and a crucial step forward to the transgender community and gender equality,” Rani Patel, president and founder of Aarohan, an organization that works to address educational disparities among underprivileged communities and advocates for LGBTQ rights, told the Blade. “People said that we should give them separate toilets and classrooms, but that totally excludes them from the community. Many women also cannot give birth to a child, so that is totally different.”
“If someone is carrying themselves as female, they should be honored with their status,” added Patel. “Since the purpose of the verdict is to recognize trans women as women, they will get all the status and rights as cisgender women in dowry and harassment cases.”
India
Madras High Court says families are possible outside marriage
May 22 ruling could set important legal precedent in India

In a significant moment for India’s LGBTQ community ahead of Pride month, the Madras High Court on May 22 affirmed people can form families outside of marriage.
The decision, handed down by Justices G.R. Swaminathan and V. Lakshminarayanan, emphasized “marriage is not the sole mode to found a family,” recognizing the concept of “chosen families” as a well-established principle in LGBTQ jurisprudence.
A two judge Madras High Court panel ordered the release of a 25-year-old lesbian woman who had been forcibly separated from her partner and subjected to harassment by her birth family.
The Madras High Court sharply criticized the local police for their mishandling of the case, condemning their decision to force the woman back to her parents against her will. The two judges denounced the police’s “rank inaction” and insensitivity, emphasizing that government officials, particularly law enforcement, are obligated to respond swiftly and appropriately to complaints from LGBTQ people, ensuring their rights and safety are upheld.
The Madras High Court expressed unease with the term “queer,” noting its dictionary definitions as “strange” or “odd.” The judges questioned the appropriateness of the label in the context of describing LGBTQ identities, urging sensitivity in language to reflect the community’s dignity and rights.
“For a homosexual individual, their sexual orientation is natural and normal,” said the judges. “There is nothing strange about such inclinations. Why then should they be labeled queer?”
The Madras High Court judges observed that not all parents embrace their children’s identities, unfavorably comparing the detained woman’s mother to late-Justice Leila Seth, who publicly supported her son’s sexual orientation. The panel highlighted Seth’s acceptance as a model for familial understanding, underscoring the need for greater societal compassion toward LGBTQ people.
“The mother of the detenue is no Leila Seth,” said the court. “We understand her desire for her daughter to live a conventional heterosexual life, marry, and settle down. However, as an adult, the detenue is entitled to choose her own path.”
The Madras High Court emphasized the concept of “family” must be understood expansively, citing the Supreme Court marriage equality case and other precedents. These international guidelines affirm that all people, regardless of their sexual orientation or gender identity, are entitled to the full spectrum of human rights, reinforcing the court’s stance on recognizing chosen families within the LGBTQ community.
“While the Supriyo case may not have legalized marriage between same-sex couples, they can very well form a family,” the court said in its order. “The concept of ‘chosen family’ is now well settled and acknowledged in LGBTQIA+ jurisprudence. The petitioner and the detenue can very well constitute a family.”
The Madras High Court referenced Supriyo Chakraborty v. Union of India, which is the marriage equality case on which the Supreme Court ruled in 2023.
The Supreme Court in that ruling declined to extend marriage rights to same-sex couples, but recognized the rights of queer people to form families and urged the government to explore civil union protections, bolstering the court’s call for an expanded understanding of family.
The Madras High Court invoked landmark rulings, including NALSA v. Union of India (2014), which affirmed the right to self-identify as one’s gender, Navtej Singh Johar v. Union of India (2018), which decriminalized consensual same-sex sexual relations, and Shakti Vahini v. Union of India (2018), which upheld the right to marry by choice as a fundamental right. The two judges reaffirmed sexual orientation is an individual choice, falling within the ambit of personal liberty protected under Article 21 of the constitution.
Article 21 guarantees the right to life and personal liberty, stating no person shall be deprived of these rights except through lawful procedure. This fundamental right has been expansively interpreted by courts to encompass dignity, privacy, and autonomy, including protections for sexual orientation and other individual identities.
Souvik Saha, an LGBTQ activist and founder of People for Change, a leading Indian advocacy group, described the Madras High Court’s recognition of chosen families as both a relief and a validation of the community’s lived realities.
“As the founder of Jamshedpur Queer Circle and someone who has worked closely with LGBTQ+ individuals navigating rejection, violence, and social isolation, for decades, queer, and trans persons in India have built nurturing ecosystems outside their biological families — often due to rejection, abuse, or lack of acceptance,” said Saha. “This concept of ‘chosen family’ is not new to us; it’s a survival mechanism, a source of healing, and a space where we find dignity, belonging, and love. The fact that the judiciary now formally acknowledges these relationships marks a progressive and humane shift in how family is legally and socially understood.”
Saha shared the story of S, a transgender man from Jamshedpur whose biological family disowned him at 17.
Finding refuge with a queer couple who became his guardians, S received emotional support, celebrated milestones like birthdays, and was guided through education and gender-affirming healthcare. “Isn’t that family?” asked Saha.
Saha told the Washington Blade the Madras High Court’s ruling sparks hope for legal reforms; particularly in securing adoption, inheritance, and caregiving rights for queer people. He said the decision affirms that queer lives are not deviant but diverse, vibrant, and capable of forming loving, responsible families. Most crucially, Saha noted, it sends a powerful message to queer youth in Jamshedpur and other smaller cities that their lives and relationships are valid and valued.
“This ruling is a step forward, but we must be honest. Legal rulings alone won’t change police behavior unless they are followed by systemic structural reforms,” said Saha. “Policing in India is still deeply patriarchal, casteist, and heteronormative. Many officers still view LGBTQ identities as criminal or immoral, even after Section 377 was struck down in 2018.”
Saha said mandatory sensitization programs in every police academy are needed to transform attitudes. He said the inclusion of queer rights in law enforcement curricula — beyond token workshops — are also important. Saha added the recruitment of LGBTQ liaison officers and the formation of compliant mechanisms at the district level is needed.
“This ruling is a strong message from the judiciary, but unless the Ministry of Home Affairs and state police departments institutionalize this into practice, change will remain slow and uneven,” said Saha.