Africa
Report details conversion therapy impact on LGBTQ South Africans
Country’s lawmakers urged to ban discredited practice
So-called conversion therapy is something which is still widely practiced across South Africa, impacting the well-being of the LGBTQ community in the process.
Families, schools, religious sects and peer groups over the years have been used to try and convert those that identify as part of the LGBTQ community to conform to the heterosexual narrative which is promoted as “homogeneous.” Access-Chapter 2, a South African NGO, in a recent study found conversion therapy is proving to be more harmful towards the society and it could pose serious repercussions in the future if nothing is done to address it.
“The LGBTQIA+ community has historically been a site of erasure, silencing and marginalization in many of our communities. This erasure has been normalized over the history of civilization, particularly in the context of Africa, where most countries still criminalize same-sex desiring. Through this study we see a problematic trajectory regarding this erasure even in contemporary South African societies,” reads the study.
The study notes 50 percent respondents “have reported to have been forced to convert by their families, while 43 percent (of respondents) had a session with a religious representative or institution as intervention by parents, families, or communities.”
“Despite the visible efforts to call out the practices of conversion by LGBTQIA+ pressure groups, these practices are still prevalent. The impact is even more detrimental, with most of our participants directly having experienced discrimination, prejudice, homophobia, transphobia or stigma in the hands of their families, churches, psychosocial service providers, schools, and the rest of the community,” it reads.
A total of 303 respondents participated in an online survey, and the study’s findings were shared with a variety of LGBTQ civil society organizations and on social media platforms.
The respondents came from nine provinces: 149 from Gauteng, nine from Mpumalanga, 36 from Free State, 24 from North-West, two from Northern Cape, seven from KwaZulu-Natal, 42 from Eastern Cape, 28 from Western Cape and 14 from Limpopo. Seven respondents identified themselves as White, while five identified as Colored and 209 identified as Black African.
A total of 144 respondents identified as lesbian, while 91 described themselves as gay. Twenty-five respondents identified themselves as bisexual and 31 said they are heterosexual. 183 respondents described themselves as Christian, while 74 said they practice a traditional African religion. Forty respondents said they do not associate with any religion, while one said they are Hindu and one described themselves as Muslim.
“Parents are the main perpetrators of conversion practices and initiators of external sources to fix individuals whose sexual orientation does not align with heterosexuality,” notes the study. “Parents maintain that same-sex sexual and romantic desires is not inborn and therefore engage in efforts to change their child’s sexual orientation or gender identity. Some seek professional therapies or religious interventions for a child’s same-sex sexual orientation or non-heterosexual gender identity while other consider traditional remedies. The study raised distinct ethical concerns concerning appropriate consent because parents and authority figures would exert pressure over minors.”
“Despite parental reliance of religion to fix the non-normative sexual orientation and gender expressions, churches outside the request of the family continue to police gender expressions. Participants reported that they were constantly harassed because of the manner of dressing, expression of identity and attractions that did not align with their gender assigned at birth,” it adds. “They could not be open about their romantic partners and LGBTQIA+ friendships. Community members from the same religious organizations would report members who are seen with LGBTQIA+ individuals, and their religious and spiritual standing would instantly be questioned. Participants who pointed out that they had a particular spiritual gift be it singing in the worship team, praying for others or an usher was recalled from such positions as their lifestyles were deemed demonic.”
The study further notes many respondents experienced “engagement with professional psychological services that subjected them to conversion practices.”
“Those who were subjected to psychological services were forced by parents to attend. They reported that parents claimed that it was normal to experience a phase of confusion about sexual orientation and non-normative gender identity and that therapy could help. Participants also reported how therapist appeared to be under pressure to have them fixed as these services are costly. Those who attended therapeutic interventions were subjected to the confusion narrative and at one stage were desperate to be healed from it,” it says. “Families also sought help from traditional healers.”
The study’s respondents reported “they had to be immersed in rivers and dams to be cleansed while others were fed with potions that would enable the release of the demonic spirit.”
“The traditional practices would continue at home with frequent follow up consultations at traditional practitioners,” it says. “While participants were aware that the focus was to heal them from their abnormal sexual orientation, they were not always aware of what substances they were given. Participants were also subjected to violence such as beatings and slaps while undergoing healing processes with traditional healers. They reported that they were put under spells and were not fully aware of all things they were subjected to.”
“Participants, particularly lesbian-identifying individuals, also reported how they live in fear as they are continuously subjected to threats of rape and even killings. As a result, many Lesbian couples cannot embrace their true self and cannot openly and in a safe way express public affection. Participants mentioned the common practice and spades of LGBTQIA+ murders in South Africa and how it forces them to live a hidden lifestyle.”
The study, which is a notable breakthrough in the research for conceptualizing conversion therapy in the context of South Africa and also the first official evidence of the harmfulness of conversion practices across the country, further highlighted on the impact of the conversion therapies, recommendations and on how to avert the despicable acts.
“Participants in this study showed that there are various psychosocial effects on LGBTQIA+ people who were subjected to conversion practices. Social factors such as discrimination, prejudice, homophobia, transphobia and stigma can create hostile and stressful social environments for LGBTQIA+ people,” it notes. “It left individuals experiencing social rejection and feeling forced to hide their identity. In some instances, individuals also adopted unhealthy coping processes and their mental health negatively impacted. Some of the impacts of conversion practices on mental health include depression, social anxiety, substance abuse, thoughts and attempts of suicide, an altered body image as well as other mental health issues. Individuals also experienced shame, guilt, hopelessness, helplessness, increased self-hatred and social withdrawal. Conversion practices are also known too often lead to severe emotional damage.
Participants who experienced conversion while at school mentioned that learning was affected to the point that some dropped out of school. Others indicated risky behaviors such as unprotected sex to develop a sense of belonging while some indulged in excessive alcohol drinking. These experiences left participants vulnerable even in their young adult developments.”
The study also found those who undergo conversion therapy are at higher risk of depression and anxiety and are more likely to die by suicide.
“This study could not identify a single participant that could confirm that conversion therapy has been effective,” it reads.
The study further notes that despite the fact South Africa has “one of the most progressive Constitutions and LGBTQIA+-inclusive legislation in the world, the social reality depicts the complete opposite.”
“Religious, cultural, professional and social scripts still uphold, produce and perpetuate compulsory heteronormativity hence, conversion practices could pass as normal and acceptable in all domains,” it reads. “Conversion practices emanates directly from privileging heterosexuality as the norm and natural. All other forms of expression are deemed unacceptable, sinful and un-African. This is despite the Constitution that affirms and protects diverse sexual orientations, sex and gender expressions.”
“We therefore, call on legislation that would place an urgent ban on conversion practices in the South African context,” said Access-Chapter 2. “Professional institutions such as the medical and psychological fraternity should be educated about the damaging effects of conversion practices. This form of education should form part of in-service and pre-service training. All civil society organizations should be empowered to support individuals who have been subjected to conversion practices. Supported services for recipients of conversion practices should be widely published to create awareness of interventions, care and support.”
Daniel Itai is the Washington Blade’s Africa Correspondent.
Uganda
Ugandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow
Clare Byarugaba founded PFLAG-Uganda
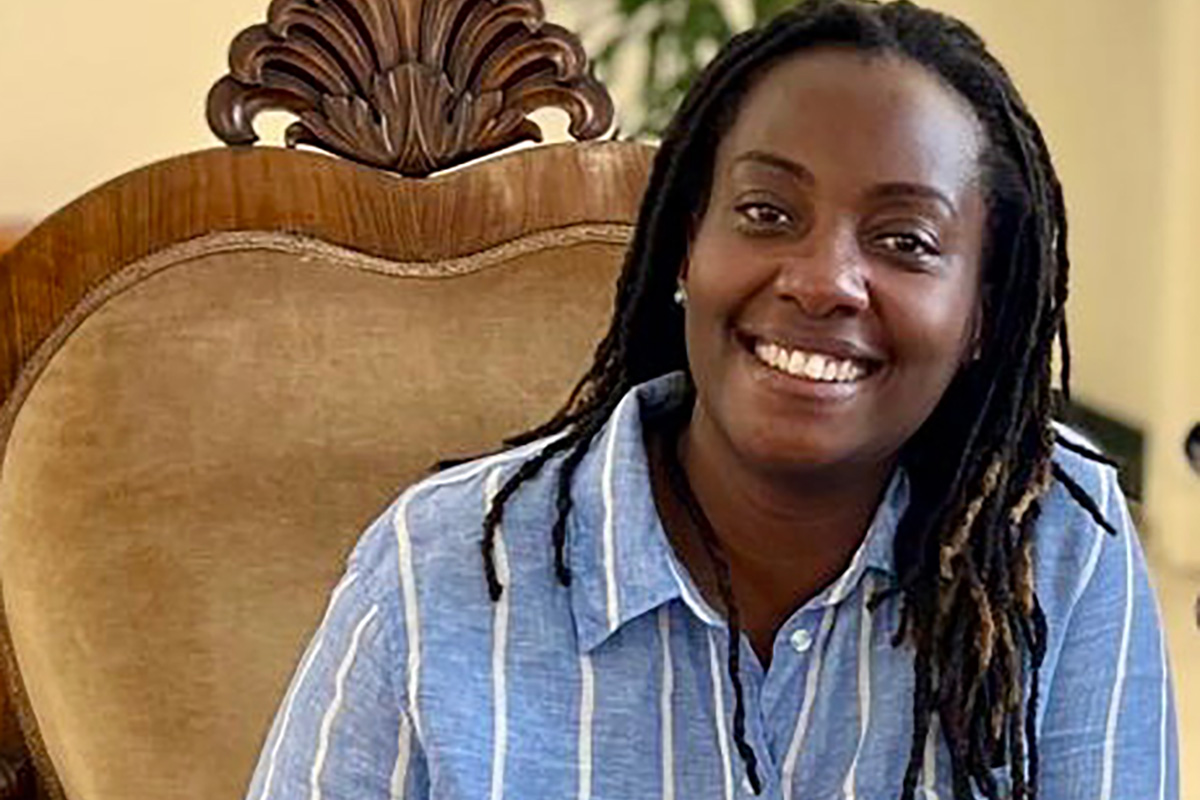

The Charles F. Kettering Foundation has named a prominent Ugandan LGBTQ activist as one of its 2026 fellows.
Clare Byarugaba, founder of PFLAG-Uganda, is one of the foundation’s five 2026 Global Fellows.
Byarugaba, among other things, has been a vocal critic of Uganda’s Anti-Homosexuality Act. Byarugaba in 2024 met with Pope Francis — who criticized criminalization laws during his papacy — at the Vatican.
The foundation on its website says it “is dedicated to bringing research and people together to make the promise of democracy real for everyone, everywhere.”
“Clare is the kind of hero who rushes toward the emergency to help,” said PFLAG CEO Brian K. Bond in a Feb. 27 statement to the Washington Blade. “She founded PFLAG-Uganda as the country pushed to criminalize homosexuality and those who support LGBTQ+ people. Yet, she never hesitated in her courage, telling us that families wanted to organize to keep their LGBTQ+ loved ones safe, and PFLAG was the way to do it. Clare Byarugaba not only deserves this honor, but she will use her compassion and experience to teach the world about LGBTQ+ advocacy as a Kettering Global Fellow.”
Africa
LGBTQ groups question US health agreements with African countries
Community could face further exclusion, government-sanctioned discrimination

Some queer rights organizations have expressed concern that health agreements between the U.S. and more than a dozen African countries will open the door to further exclusion and government-sanctioned discrimination.
The Trump-Vance administration since December has signed five-year agreements with Kenya, Uganda, and other nations that are worth a total of $1.6 billion.
Kenyan and Ugandan advocacy groups note the U.S. funding shift from NGO-led to a government-to-government model poses serious risks to LGBTQ people and other vulnerable populations in accessing healthcare due to existing discrimination based on sexual orientation.
Uganda Minority Shelters Consortium, Let’s Walk Uganda, the Kenya Human Rights Commission, and the Center for Minority Rights and Strategic Litigation note the agreements’ silence on vulnerable populations in accessing health care threatens their safety, privacy, and confidentiality.
“Many LGBTQ persons previously accessed HIV prevention and treatment, sexual and reproductive health services, mental health support, and psychosocial care through specialized clinics supported by NGOs and partners such as USAID (the U.S. Agency for International Development) or PEPFAR,” Let’s Walk Uganda Executive Director Edward Mutebi told Washington Blade.
He noted such specialized clinics, including the Let’s Walk Medical Center, are trusted facilities for providing stigma-free services by health workers who are sensitized to queer issues.
“Under this new model that sidelines NGOs and Drop-in Centers (DICs), there is a high-risk of these populations being forced into public health facilities where stigma, discrimination, and fear of exposure are prevalent to discourage our community members from seeking care altogether, leading to late testing and treatment,” Mutebi said. “For LGBTQ persons already living under criminalization and heightened surveillance, the loss of community-based service delivery is not just an access issue; it is a full-blown safety issue.”
Uganda Minority Shelters Consortium Coordinator John Grace said it is “deeply troubling” for the Trump-Vance administration to sideline NGOs, which he maintains have been “critical lifelines” for marginalized communities through their specialized clinics funded by donors like the Global Fund and USAID.
USAID officially shut down on July 1, 2025, after the White House dismantled it.
Grace notes the government-to-government funding framework will impact clinics that specifically serve the LGBTQ community, noting their patients will have to turn to public systems that remain inaccessible or hostile to them.
“UMSC is concerned that the Ugandan government, under this new arrangement, may lack both the political will and institutional safeguards to equitably serve these populations,” Grace said. “Without civil society participation, there is a real danger of invisibility and neglect.”
Grace also said the absence of accountability mechanisms or civil society oversight in the U.S. agreement, which Uganda signed on Dec. 10, would increase state-led discrimination in allocating health resources.
Center for Minority Rights and Strategic Litigation Legal Manager Michael Kioko notes the U.S. agreement with Kenya, signed on Dec. 4, will help sustain the country’s health sector, but it has a non-binding provision that allows Washington to withdraw or withhold the funding at any time without legal consequences. He said it could affect key health institutions’ long-term planning for specialized facilities for targeted populations whose independent operations are at stake from NGOS the new agreement sidelines.
“The agreement does not provide any assurance that so-called non-core services, such as PrEP, PEP, condoms, lubricants, targeted HIV testing, and STI prevention will be funded, especially given the Trump administration’s known opposition to funding these services for key populations,” Kioko said.
He adds the agreement’s exclusionary structure could further impact NGO-run clinics for key populations that have already closed or scaled down due to loss of the U.S. funding last year, thus reversing hard-won gains in HIV prevention and treatment.
“The socio-political implications are also dire,” Kioko said. “The agreement could be weaponized to incite discrimination and other LGBTQ-related health issues by anti-LGBTQ voices in the parliament who had called for the re-authorization of the U.S. funding (PEPFAR) funding in 2024, as a political mileage in the campaign trail.”
Even as the agreement fails to safeguard specialized facilities for key populations, the Kenya Human Rights Commission states continued access to healthcare services in public facilities will depend on the government’s commitment to maintain confidentiality, stigma-sensitive care, and targeted outreach mechanisms.
“The agreement requires compliance with applicable U.S. laws and foreign assistance policies, including restrictions such as the Helms Amendment on abortion funding,” the Kenya Human Rights Commission said in response to the Blade. “More broadly, funded activities must align with U.S. executive policy directives in force at the time. In the current U.S. context, where executive actions have narrowed gender recognition and reduced certain transgender protections, there is a foreseeable risk that funding priorities may shift.”
Just seven days after Kenya and the U.S. signed the agreement, the country’s High Court on Dec. 11 suspended its implementation after two petitioners challenged its legality on grounds that it was negotiated in secrecy, lacks proper parliamentary approval, and violates Kenyans’ data privacy when their medical information is shared with America.
The agreement the U.S. and Uganda signed has not been challenged.
Senegal
A dozen Senegalese men arrested for ‘unnatural acts’
Popular journalist and musician among those taken into custody
Senegalese police have charged a dozen men with committing “unnatural acts.”
The New York Times reported Pape Cheikh Diallo, a popular television reporter, and Djiby Dramé, a musician, are among the men who authorities arrested. They appeared in court in Dakar, the Senegalese capital, on Monday.
Le Soleil, a Senegalese newspaper, reported authorities arrested the men on Feb. 6 “for intentional transmission of HIV, unnatural acts, criminal conspiracy, and endangering others.” The newspaper further notes the men have been placed in “pre-trial detention.”
Senegal is among the countries in which consensual same-sex sexual relations remain criminalized.
Police in Kaolack, a town that is roughly 135 miles southeast of Dakar, in 2015 arrested 11 people who allegedly engaged in same-sex sexual acts during “a celebration of a gay marriage.” The National Assembly in 2021 rejected a bill that would have further criminalized homosexuality in the country.
-

 Florida5 days ago
Florida5 days agoFla. Senate passes ‘Anti-Diversity’ bill that could repeal local LGBTQ protections
-

 Celebrity News5 days ago
Celebrity News5 days agoLiza Minnelli makes surprise appearance at GLAAD Media Awards
-

 Opinions5 days ago
Opinions5 days agoCapital Pride must be transparent about sexual misconduct investigation
-

 Nightlife4 days ago
Nightlife4 days agoIn D.C. comedy, be sure to shop local



















