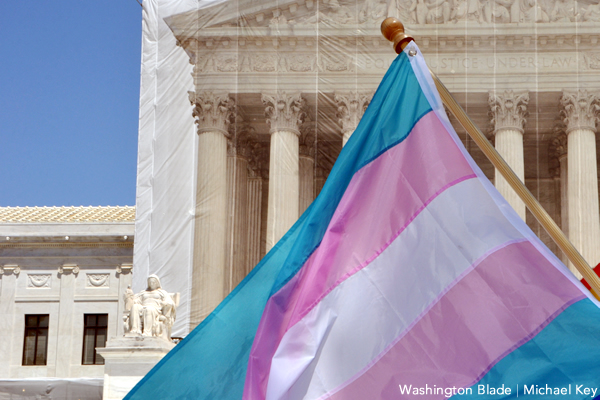
National
Couples make history testifying against DOMA
Senate hears from spouses, activists about burdens of marriage ban; hearing first-ever in Congress on repeal of anti-gay law
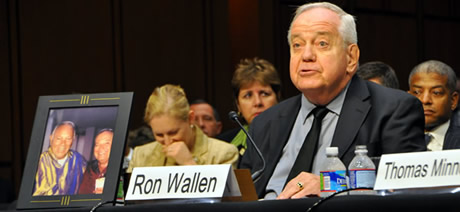

‘The time has come for the federal government to recognize that these married couples deserve the same legal protections afforded to opposite-sex married couples,’ said Sen. Patrick Leahy (D-Vt.) (Washington Blade photo by Michael Key)
A Senate hearing Wednesday on repealing the Defense of Marriage Act featured poignant testimony from couples in same-sex marriages, who described how the anti-gay law has harmed them.
The hearing, which took place before the Senate Judiciary Committee, was the first ever before Congress on repeal of DOMA, the 1996 law prohibiting federal recognition of same-sex marriage. The hearing was intended to highlight the Respect for Marriage Act, legislation pending before Congress that would repeal DOMA.
Ron Wallen, an Indio. Calif., resident, who married his partner of 55 years in 2008, said he’s unable to make payments on his home following the death of his spouse, Tom Carrollo, four months ago. Had he been in an opposite-sex marriage, he would have been able to receive Social Security benefits to help pay for the cost of living.
“I am selling the last house I shared with my husband in a panic sale because I can’t afford the mortgage and expenses,” Wallen said. “I am spending my days and nights sorting through our possessions, packing boxes to move — even while I am still answering the condolence cards that come in the mail.”
Susan Murray, who lives in Ferrisburgh, Vt., with her spouse, Karen Murray, said she also faces financial inequities as a result of DOMA. Murray was the co-counsel in the lawsuit Baker v. Vermont, which established civil unions in Vermont in 2000.
One issue Murray cited was the additional tax that she and her spouse have to pay on employer-based insurance coverage provided to them through her spouse’s employer, Fletcher Allen Health Care.
“Because of DOMA, I am not considered Karen’s spouse, so the value of that health insurance coverage for me ($6,200 a year) is considered taxable income to Karen,” Murray said. “She therefore has to pay income tax, as well as FICA and Medicare tax, on that ‘phantom’ income — unlike her other married colleagues.”
Andrew Sorbo, a Cheshire, Conn., resident and retired history teacher, also testified about financial troubles he faced after his spouse, Colin Atterbury, died of pancreatic cancer in 2009. Among other things, Sorbo said he was denied the right to be included in his deceased spouse’s medical insurance plan through the federal government.
“When I retired as a teacher in 2005, I had no alternative except to pay for my insurance coverage in full through my former school district, at a much higher cost than if I could have been covered under Colin’s plan as a spouse,” Sorbo said. “Last year, my insurance payments consumed almost a third of my $24,000 teacher pension.”
Sen. Patrick Leahy (D-Vt.), chair of the committee, spoke out in his opening statement for passage of the Respect for Marriage Act and said it would allow same-sex couples married under state law to receive federal benefits.
“Nothing in this bill would obligate any person, religious organization, state, or locality to perform a marriage between two persons of the same sex,” Leahy said. “What would change, and what must change, is the federal government’s treatment of state-sanctioned marriage. The time has come for the federal government to recognize that these married couples deserve the same legal protections afforded to opposite-sex married couples.”
Sen. Dianne Feinstein (D-Calif.), sponsor of the DOMA repeal legislation, maintained that the anti-gay law should be off the books because marriage, as well as other issues related to family such as adoption and divorce, have been under the jurisdiction of state law.
“Family law has traditionally been the preserve of state law,” Feinstein said. “The single exception is DOMA. Chief Justice [William] Rehnquist once wrote that family law ‘has been left to the states from time immemorial, and not without good reason.’ He was right.”
Passed by Congress in 1996, DOMA was signed into law by President Clinton. Both Clinton and the bill’s sponsor at the time, former Republican Rep. Bob Barr, have come out for repeal of the law.
DOMA has two components: one that prohibits the federal government from recognizing same-sex marriage and another that allows states not to recognize such marriages performed in other jurisdictions.
As a result of the component of DOMA known as Section 3, married same-sex couples cannot participate in federal programs. For instance, they can’t file joint federal income taxes, receive spousal benefits under Social Security or obtain exemptions of the estate tax law upon the death of one of the spouses.
Sen. Chuck Schumer (D-N.Y.), who represents a state where same-sex marriage will be available next week, emphasized the fiscal reasons for repealing DOMA and predicted that lifting the anti-gay law from the books “would, on balance, likely increase federal revenue.”
According to Schumer, in 2004 the Congressional Budget Office found that DOMA repeal at the time would have increased revenues by less than $400 million a year from 2005 through 2010, and by $500 million to $700 million annually from 2011 through 2014.
“I think that there are three fundamental principles at stake here,” Schumer continued. “Repealing DOMA makes good fiscal sense, it respects states’ rights to make their own determinations about marriage, and it treats all married people the same. It’s fair, it makes sense, and it’s time.”
The sole committee member to speak out against DOMA repeal during the hearing was Sen. Charles Grassley (R-Iowa), ranking Republican on the committee.
Grassley, who represents a state where same-sex marriage is legal, said he opposes the Respect for Marriage Act because he believes marriage should be reserved for one man and one woman.
“The bill before us today is entitled the Respect for Marriage Act,” Grassley said. “George Orwell would have marveled at the time. A bill to restore marriage would restore marriage as it has been known — one man, one woman. That is the view of marriage that I support. This bill would undermine, not restore marriage by repealing it.”
Grassley and Sen. Orrin Hatch (R-Utah) were the only Republican senators who made an appearance at the DOMA hearing. Grassley was the only GOP committee member who asked questions of the witnesses.
Witnesses who married someone of the same-sex testified about how DOMA negatively affected their relationship or their ability to receive benefits after the death of their spouse.
The hearing took place on the heels of an announcement from White House Press Secretary Jay Carney on Tuesday that President Obama supports the Respect for Marriage Act.
“I can tell you that the president has long called for legislative repeal of the so-called Defense of Marriage Act, which continues to have a real impact on the lives of real people families, friends and neighbors,” Carney said. “He is proud to support the Respect for Marriage Act introduced by Sen. Feinstein and Congressman Nadler, which would take DOMA off the books once and for all. This legislation would uphold the principle that the federal government should not deny gay and lesbian the same rights and legal protections as straight couples.”
President Obama has previously said he supports legislative repeal of the Defense of Marriage Act, but has yet to come out in support of the Respect for Marriage Act, which is the specific measure pending before Congress that would repeal the law.
During the hearing, Grassley erroneously said that Obama until Tuesday “was a supporter of DOMA.” During the 2008 campaign, Obama made full repeal of DOMA one of his campaign promises.
Experts testify before Senate
House members also testified on both sides of the Respect for Marriage Act. Two Democratic members — Reps. Jerrold Nadler (D-N.Y.), the sponsor of the bill, and John Lewis (D-Ga.) — favored DOMA repeal, while Rep. Steve King (R-Iowa), a lawmaker known for his anti-gay views, opposed it.
Nadler maintained that not just same-sex couples — but children being raised by LGBT parents — are among those who are affected by the discrimination of DOMA.
“No legitimate federal interest in the welfare of children is ever advanced by withholding protection for some children based on the desire to express mild disapproval of their parents,” Nadler said. “It defies common sense to claim that it’s necessary to harm or exclude the children of married same-sex couples in order to somehow protect the children of opposite-sex couples.”
Similarly, Lewis expressed disbelief that Congress has yet to act on something as fundamental as allowing Americans the right to marry the person they choose.
“I find it hard to believe that in the year 2011, there’s still the need to hold hearings and debate on whether or not to allow people to marry the one they love,” Lewis said.
Lewis said DOMA imposes similar discrimination that blacks endured in the South under segregation and recalled the discrimination he faced as a child growing up in Southern Alabama.
“As a child, I tasted the bitter fruits and racism and discrimination, and I did not like it,” Lewis said. “And in 1996, when Congress passed the Defense of Marriage Act, the taste of that old bitter fruit filled my mouth once again.”
King, countering those arguments, based his testimony against repeal of DOMA on the basis that marriage is intended for procreation and thus should be reserved for one man and one woman because the union can produce children.
“The other side argues that you can’t choose who you love and that the union between two men and two women is equal to that of one man and one woman,” King said. “These are the same arguments that are used to promote marriage between fathers and daughters, mothers and sons or even polygamous relationships.”
Expert witnesses on both sides of DOMA testified before lawmakers. LGBT advocates maintained DOMA should be repealed to lift the burden of discrimination against same-sex couples, while supporters of DOMA said the anti-gay law is necessary to keep marriage as between one man and one woman.
Joe Solmonese, president of the Human Rights Campaign, was among the LGBT advocates who testified during the hearing. He addressed the financial burdens DOMA imposes on same-sex couples.
“DOMA means that the many protections the federal government provides for the health and financial security of American families remain out of reach for same-sex couples and their children,” Solmonese said. “Same-sex spouses of federal employees and active members of the military are denied access to health insurance coverage and a host of other benefits. Even when private sector companies voluntarily provide spousal health benefits, they are taxed, making it financially burdensome if not impossible for gay and lesbian couples to make use of these fair-minded policies.”
Evan Wolfson, president of Freedom to Marry, said DOMA “carves out a gay exception” in the way the U.S. government traditionally and currently treats married couples.
“DOMA divides those married at the state level into first-class marriages for those the federal government prefers and second-class marriages for those the federal government doesn’t like,” Wolfson said. “But in America, we don’t have second-class citizens, and we shouldn’t have second-class marriages either.”
Arguing in favor of DOMA, anti-gay advocates maintained the importance of keeping marriage between one man and one woman.
Austin Nimrocks, senior legal counsel for the Alliance Defense Fund, said the purpose of family and relationships is to procreate and raise children.
“Accordingly, from the lexicographers who have defined marriage, to the eminent scholars in every relevant academic discipline who have explained marriage, to the legislatures and courts that have given legal recognition and effect to marriage, they all demonstrate that an animating purpose of marriage in every society is to increase the likelihood that procreative relationships benefit society,” Nimrocks said. “Marriage between a man and a woman is a long standing, world-wide idea that is a building block of society.”
Edward Whelan, president of the Ethics & Public Policy Center, warned that DOMA repeal could require the federal government to recognize not only same-sex marriages — but also polygamous relationships.
“If the male-female nature of traditional marriage can be dismissed as an artifact and its inherent link to procreation denied, then surely the distinction between a marriage of two persons and a marriage of three or more is all the more arbitrary and irrational,” Whelan said. “It’s doubtful that any further sliding down the slippery slope would be necessary to get to polyamory: unlike the novelty of same-sex marriage, the polygamous version of polyamory has been widely practiced throughout history — and is therefore arguably up the slope from same-sex marriage.”
Whelan previously testified in April against same-sex marriage before the Republican-controlled House Judiciary Subcommittee on the Constitution hearing on “Defending Marriage.”
The assertion that DOMA would institute same-sex marriage is places where it didn’t exist before didn’t go without criticism from LGBT advocates after the hearing.
Rick Jacobs, chair and co-founder of the Courage Campaign, rebuked the assertion during that DOMA repeal would expand the places where gay couples can marry and maintained the Defense of Marriage Act would simply remove the federal government from the marriage issue.
“They don’t seem to understand what DOMA is,” Jacobs said. “They just keep missing the point that all DOMA is give the states the ability to decide what marriage is.”
Mary Bonauto, civil rights projects director for Gay & Lesbian Advocates & Defenders, also chided anti-gay advocates’ emphasis on marriage as between one man, one woman during the hearing as she said DOMA only affects those who are already married.
“I think it’s important to talk about marriage, but I wish there had been that much more delineation between what marriage is about one hand and what DOMA does, which is simply discriminate against people who are already married,” Bonauto said. “But there’s still, particularly in the opposition witnesses, this complete conflation between DOMA and marriage.”
Tom Minnery, vice president of public policy for Focus on the Family, bore the brunt of the tough questioning from the committee undermining his credibility for his position that children reared by opposite-sex parents are better off than those raised by same-sex parents.

Tom Minnery, vice president of public policy for Focus on the Family (Washington Blade photo by Michael Key)
“It is a strong and dramatically consistent finding in the social science, psychological and medical literature that children do best when living with their own married mother and father,” Minnery said.
In his testimony, Minnery cites a December 2010 study from the Department of Health & Human Services which he said found “children living with their own married biological or adoptive mothers and fathers were generally healthier and happier, had better access to health care, less likely to suffer mild or severe emotional problems, did better in school, were protected from physical, emotional and sexual abuse and almost never life in poverty, compared with children in any other family form.”
Sen. Al Franken (D-Minn.) challenged Minnery’s assertion, saying the HHS report “actually doesn’t say what you said it says.”
“It says that nuclear families — not opposite-sex married families — are associated with those positive outcomes,” Franken said. “Isn’t it true, Mr. Minnery, that married same-sex couple that has or had adopted kids would fall under the definition of the nuclear family in the study that you cite?”
Minnery replied that he would believe the study means nuclear families are families with opposite-sex parents, but Franken denied this speculation, saying, “It doesn’t,” eliciting laugher from those attending the hearing.
“The study defines nuclear family as one or more children living with two parents who are married to one another and each biological or adoptive parents of all the children in the family,” Franken said. “And I, frankly, don’t really know how we can trust the rest of your testimony if you are reading studies these ways.”
Rea Carey, executive director of the National Gay & Lesbian Task Force, said following the hearing the testimony of those affected by DOMA compared to apparently misleading testimony of the anti-gay law’s proponents shows why “we’re winning on this issue.”
“The families who spoke — they talked from their human experience,” Carey said. “The other side talked from technical matters, from research that actually didn’t reveal the true, full research. We’re actually — children are doing quite well in our families, thank you very much.”
Time for a markup?
Now that the Respect for Marriage Act has had a hearing in the Senate, one option to move the legislation would be to hold a markup to bring the legislation to the floor. All 10 Democrats on the committee have signaled support for the legislation, so the bill already has sufficient support to move forward.
A Senate Democratic aide, who spoke on condition of anonymity, said the committee has yet to set a date to report out the legislation to the Senate floor.
“This hearing began to build the record for repealing DOMA, and this is the beginning of the process,” the aide said. “Sen. Leahy will continue to work with Sen. Feinstein and other supporters, and hopes there will be support from both sides of the aisle for this repeal, but I have no announcements to make today concerning any kind of timeline.”
Jacobs said he wants to see more co-sponsors for the Respect for Marriage Act — and maintained he wants “all Democrats on board” — but said the time may be right for a markup on the bill.
“I think that we should move to that pretty quickly,” Jacobs said. “I’d like to see it. I know some people don’t, but I think we need to keep the momentum going.”
Following the hearing, Solmonese expressed caution about moving to a markup and deferred the decision to the Senate Judiciary Committee leadership.
“If we are genuinely committed to a clare path to victory, to ensuring that DOMA is repealed, then I would defer to the chairman in terms of the degree to which he thinks the time is appropriate for a markup — and how that relates to a full Senate vote and the prospects in the House,” Solmonese said. “As was the case with ‘Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell,’ as was the case with any legislative victory that we have seen through to the end, we never want to evaluate it on the merits of one action.”
Bonauto, who’s leading several lawsuits against DOMA in the federal courts, said she isn’t sure if a committee vote on DOMA repeal — or a floor vote in the Senate without action in the House — would have any effect on how the courts would evaluate the constitutionality of the anti-gay law. She cautioned that a symbolic victory in the Senate may not have the desired impact on the courts.
“It’s hard to predict,” Bonauto said. “In the 1970’s, when the Congress had approved of the Equal Rights Amendment and sent it up for ratification to the states, the Supreme Court stayed its hand and didn’t declare that gender was a suspect classification because it thought the issue was moving through the political process. I think we’ve all learned through of the failure of ratification of the ERA that because something has been approved by the Congress of even is a constitutional amendment is set forth for ratification, it doesn’t predict future results.”
Florida
Fla. Senate passes ‘Anti-Diversity’ bill that could repeal local LGBTQ protections
Bipartisan coalition urges Florida House to reject ‘extremism’ measure

The Florida Senate on March 4 voted 25-11 to approve an “Anti-Diversity in Local Government” bill that critics have called a sweeping and extreme measure that, among other things, could repeal local LGBTQ rights protections.
According to Equality Florida, a statewide LGBTQ advocacy organization, if approved by the Florida House of Representatives and signed by Republican Gov. Ron DeSantis, the bill “would ban, repeal, and defund any local government programming, policy, or activity that provides ‘preferential treatment or special benefits’ or is designed or implemented’ with respect to race, color, sex, ethnicity, sexual orientation, or gender identity.”
In a March 4 statement, Equality Florda added that the bill would also threaten city and county officials with removal from office “for activities vaguely labeled as DEI,” with only limited exceptions.
The Florida House was scheduled to vote on the bill on Monday, March 9, with opponents hopeful that a broad coalition of both Democratic and Republican lawmakers would secure enough votes to defeat the bill.
“Once again, Gov. DeSantis and Florida lawmakers are advancing one of the most sweeping and extreme bills in the country — this time threatening decades of local progress supporting diverse communities, including the LGBTQ community,” said Equality Florida Senior Political Director Joe Saunders. “This legislation is a sledgehammer aimed at cities and counties that recognize and address the diversity of the people they serve,” he said.
Among the LGBTQ organizations that could be adversely impacted by the bill is the highly acclaimed Stonewall National Museum, Archives and Library located in Fort Lauderdale.
Robert Kesten, the Stonewall organization’s president and CEO, told the Washington Blade the organization receives some funding from Broward County, in which Fort Lauderdale is located, and the city of Fort Lauderdale has provided support by purchasing tables at some of the museum’s fundraising events.
“Based on this legislation, hose things would be gone,” he said. “We also are based in a government building. So, we don’t know what potential side effects that could have.” He noted that the building in question is owned by Broward County and leased by Fort Lauderdale, with the bill’s vaguely worded provision making it unclear whether Stonewall would be forced to leave its building.
“It’s unknown, and we’re really in unchartered waters,” he said.
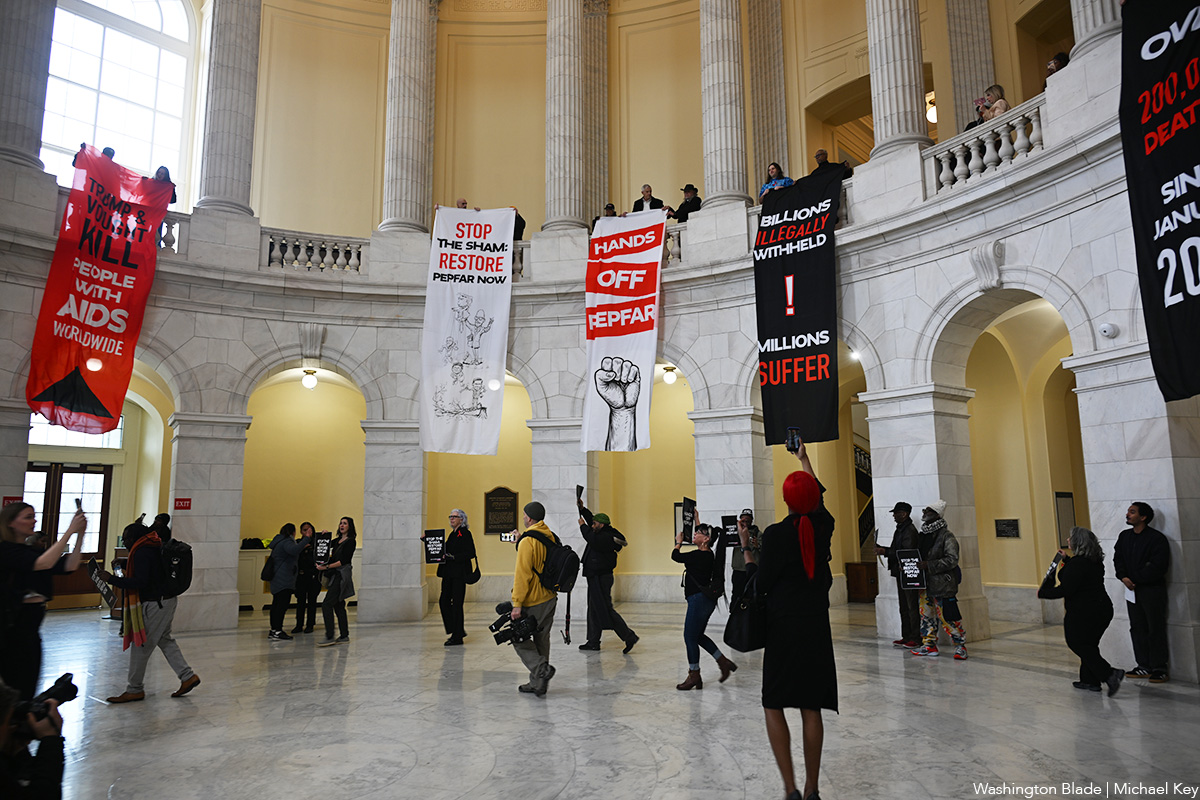

U.S. Capitol Police on Thursday arrested 13 HIV/AIDS activists in the Cannon House Office Building Rotunda.
The activists — members of Housing Works, Health GAP, and the Treatment Action Group — joined former PEPFAR staffers in demanding full funding of the program that President George W. Bush created in 2003. They chanted “AIDS cuts kill, PEPFAR now!” and unfurled banners from the Rotunda’s second floor that read “Trump and (Office of Management and Budget Director Russell) Vought kill people with AIDS worldwide,” “Over 200,000 deaths since January 2025,” and “Hands off PEPFAR” before their arrest.
(Washington Blade video by Michael K. Lavers)
This protest is the latest against the Trump-Vance administration’s HIV/AIDS policies since it took office.
Secretary of State Marco Rubio on Jan. 28, 2025, issued a waiver that allowed PEPFAR and other “life-saving humanitarian assistance” programs to continue to operate during a freeze on nearly all U.S. foreign aid spending. HIV/AIDS service providers around the world with whom the Washington Blade has spoken say PEPFAR cuts and the loss of funding from the U.S. Agency for International Development, which officially closed on July 1, 2025, has severely impacted their work.
The State Department last September announced PEPFAR will distribute lenacapavir in countries with high prevalence rates. Zambia is among the nations in which the breakthrough HIV prevention drug has arrived.
The New York Times last summer reported Vought “apportioned” only $2.9 billion of $6 billion that Congress set aside for PEPFAR for fiscal year 2025. (PEPFAR in the coming fiscal year will use funds allocated in fiscal year 2024.)
Bipartisan opposition in the U.S. Senate prompted the Trump-Vance administration last July withdraw a proposal to cut $400 million from PEPFAR’s budget. Vought on Aug. 29, 2025, said he would use a “pocket rescission” to cancel $4.9 billion for HIV/AIDS prevention and global health programs and other foreign aid assistance initiatives that Congress had already approved.
The White House in January announced an expansion of the global gag rule to ban U.S. foreign aid for groups that promote “gender ideology.” President Ronald Reagan in 1985 implemented the original regulation, also known as the “Mexico City” policy, which bans U.S. foreign aid for groups that support abortion and/or offer abortion-related services. The Council for Global Equality and other groups say the expanded rule will adversely impact HIV prevention efforts around the world.
A press release that Housing Works and Health GAP issued on Thursday notes more than $977 million “in appropriated PEPFAR funding for HIV prevention and treatment was unspent by the end of fiscal year (FY) 2025 — triple amount unspent at the end of FY 2024.”
“Activists predict this backlog will worsen rapidly in FY 2026 unless Congress immediately reasserts its Constitutionally-mandated oversight authority,” notes the press release.
The press release also indicates funding for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s PEPFAR programs “will run out” by April 1 because “only 45 percent of their FY26 funding has been transferred from the State Department.
“Unless funding is transferred immediately, CDC’s global HIV programs across sub-Saharan Africa, Asia and the Caribbean will grind to a halt,” notes the press release.
The activists demanded Trump, Vought, Rubio, and Congress do the following:
- Activists are calling for full obligation of appropriated PEPFAR funds and rejection of growing political interference in global and domestic HIV programs
- Immediately release already-appropriated, unobligated PEPFAR funds
- Break the blackout on PEPFAR data, so Congress and people with HIV know how funding is being spent and can program based on data
- Activists are calling for full obligation of appropriated PEPFAR funds and rejection of growing political interference in global and domestic HIV programs.
“PEPFAR has saved more than 26 million lives and changed the trajectory of an epidemic,” said Housing Works CEO Charles King. “However, the Trump administration’s decision, over the objection of Republicans in Congress, to freeze PEPFAR funding has caused decades of progress to come undone and has been a death sentence for people with HIV relying on life-saving treatment. The U.S. must immediately restore PEPFAR funding and regain our standing in the global fight against HIV.”
King is among the activists who were arrested.
(Washington Blade video by Michael K. Lavers)
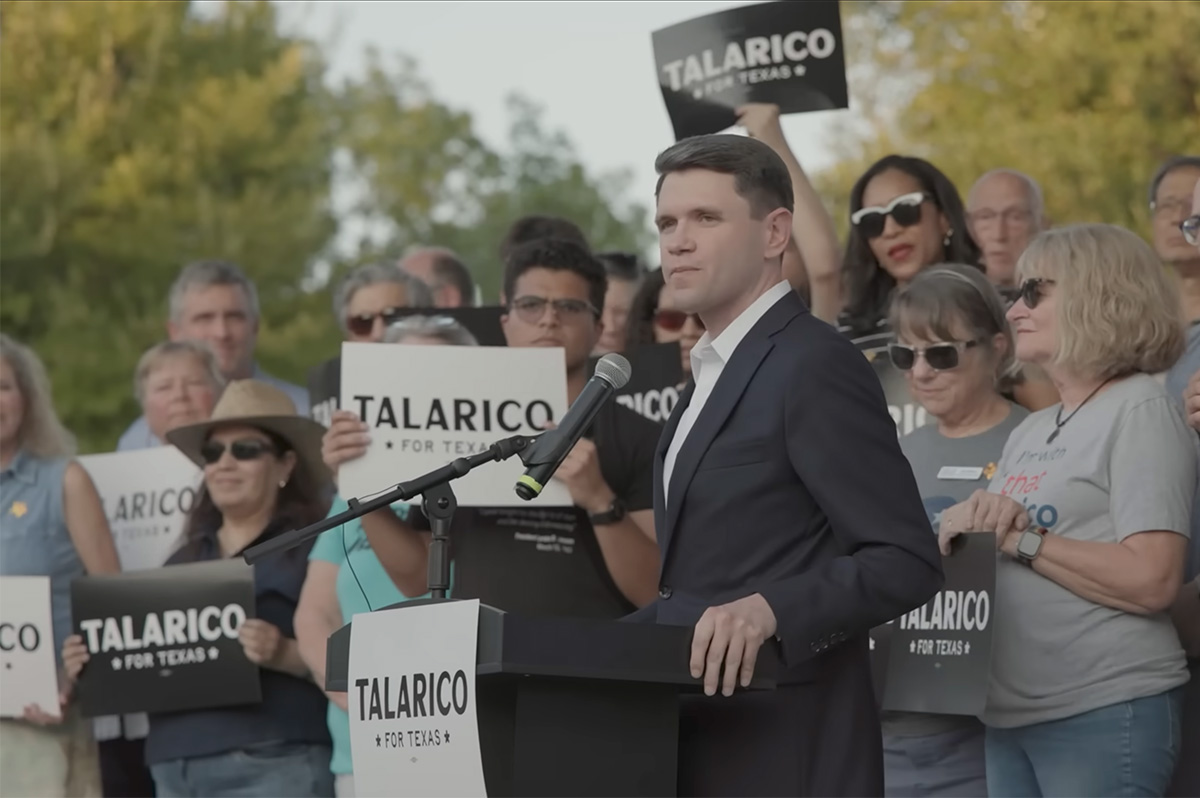

Texas state Rep. James Talarico won a hard-fought primary Tuesday to become the state’s Democratic nominee for U.S. Senate, defeating U.S. Rep. Jasmine Crockett in one of the year’s most closely watched and competitive Democratic contests.
Talarico, a Presbyterian seminarian and three-term lawmaker from Round Rock, was declared the winner by the Associated Press early Wednesday morning after a closely tracked vote count that drew national attention.
“Tonight, the people of our state gave this country a little bit of hope,” Talarico told the AP. “And a little bit of hope is a dangerous thing.”
With 52.8% of the vote to Crockett’s 45.9%, Talarico secured the nomination outright, avoiding a runoff and capping months of sharp contrasts between the two candidates over strategy, messaging, and how best to compete statewide in Texas. Democrats hope the competitive primary — and the relatively narrow margin — signals growing momentum in a state that has not elected a Democrat to the U.S. Senate since 1988.
Talarico has long expressed support for the LGBTQ community, a position he highlights prominently on his campaign website. Under the “Issues” section, he directly addresses assumptions that might arise from his faith and background as a seminarian in a deeply conservative state.
“My faith in Jesus leads me to reject Christian Nationalism and commit myself to the project of democracy,” his website reads. “Because that’s the promise of America: a democracy where every person and every family — regardless of religion, race, gender, sexual orientation, or any other difference between us — can truly be free and live up to their full potential.”
Crockett struck a conciliatory tone following her defeat, emphasizing party unity ahead of November.
“This morning I called James and congratulated him on becoming the Senate nominee,” Crockett told Politico. “Texas is primed to turn blue and we must remain united because this is bigger than any one person. This is about the future of all 30 million Texans and getting America back on track.”
Talarico also drew national attention earlier in the race when “Late Show” host Stephen Colbert said he was initially unable to air an interview with the state legislator due to potential FCC concerns involving CBS. The episode sparked a broader political debate.
Brendan Carr, chair of the Federal Communications Commission, appointed by President Donald Trump, told reporters the controversy was a “hoax,” though he also acknowledged Talarico’s ability to harness the moment to build support as an underdog candidate. The interview was later released online and garnered millions of views, boosting Talarico’s national profile.
In November, Talarico will face the winner of the Republican primary between incumbent Sen. John Cornyn and Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton, who have been locked in a bruising GOP contest. Rep. Wesley Hunt was also in the Republican primary field. The GOP race is expected to head to a May runoff.
In a joint statement, Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer and Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee Chair Kirsten Gillibrand praised Talarico’s victory and framed him as a candidate capable of broad appeal.
“As an eighth-generation Texan, former middle school teacher, and Presbyterian seminarian, James will be a fighter for Texans from all walks of life and of all political stripes,” they said. “In November, Texans will elect a champion for working people: James Talarico.”
-

 National5 days ago
National5 days agoPeter Thiel’s expanding power — and his overlap with Jeffrey Epstein
-

 National3 days ago
National3 days ago13 HIV/AIDS activists arrested on Capitol Hill
-

 Maryland5 days ago
Maryland5 days agoMd. Commission on LGBTQIA+ Affairs released updated student recommendations
-

 Virginia5 days ago
Virginia5 days agoVa. lawmakers consider partial restoration of Ryan White funds






















