News
Grenell emails hint at initial steps in Trump effort to decriminalize homosexuality
State Dept. identified 10 countries for int’l efforts

Emails from the State Department — obtained by the Washington Blade from a lawsuit filed under the Freedom of Information Act — reveal the Trump administration had at least laid the preliminary groundwork for a global campaign to decriminalize homosexuality to the extent of identifying 10 countries where it was thought most possible.
The initial seven-page batch of emails, obtained by the FOIA lawsuit seeking communications from former U.S. Ambassador Richard Grenell in his capacity as leader of the initiative to decriminalize homosexuality, was delivered to the Blade last month and hints at initial steps toward a plan shortly after the announcement of the initiative.
It’s unclear from the initial production what further efforts, if any, sprang from the identification of these 10 countries. Critics at the time said the campaign was nothing but window-dressing to cover up for anti-LGBTQ policies during the Trump administration.
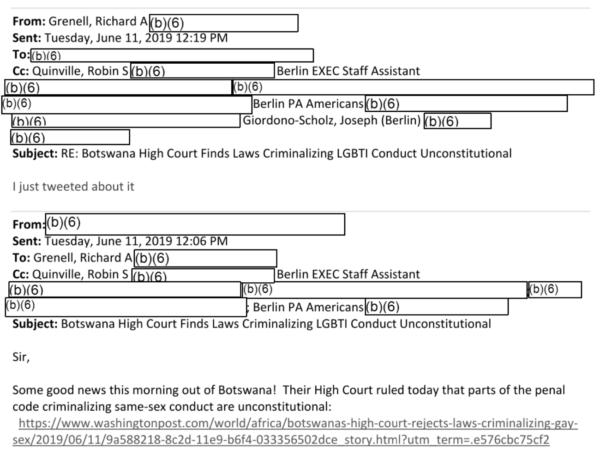
In an exchange dated Aug. 23, 2019, an assistant to Grenell forwards an email from an individual whose identity is redacted on an edited list of 10 countries where “we believe decriminalization is possible.” Copied on the email is Robin Quinville, who was deputy chief of mission in Berlin.
“Per your request, attached and edited below is the list of 10 countries where LGBTI decriminalization is possible — with your and Robin’s edits incorporated,” the email is redacted.
The names of the 10 countries, however, are redacted in the exchange provided to the Blade, as is an apparent Word document attached in the exchange with a short justification for each of the countries. Also redacted are the names of two agencies an assistant in the email identifies as having “cleared” the list.
The assistant tells Grenell the State Department’s Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor hasn’t yet responded, but the embassy “will forward their list when we receive it.”

As a result of the redactions, the identity of the 10 countries is unknown at this time. The early production given the Blade in response to a FOIA request filed in September 2020 offers no indication on the extent to which the State Department conducted further efforts to change the law in these countries, or whether there was any engagement after identifying them.
Grenell didn’t respond to the Blade’s request for comment for this article on how the identification of these 10 countries informed efforts to decriminalize homosexuality. Quinville couldn’t be reached for comment.
The initial FOIA production also includes an earlier exchange between an assistant and Grenell dated June 11, 2019, shortly after Botswana became the latest country to decriminalize homosexuality, forwarding a link to a Washington Post article on that news. The name of the assistant is redacted and may or may not be the same as the one in the other exchange.
“Some good news coming out of Botswana! Their High Court ruled today that parts of the penal code criminalizing same-sex conduct are unconstitutional,” the unidentified assistant writes.
Grenell is short in his reply: “I just tweeted about it.” It’s not clear whether or not Grenell contributed to the decriminalization efforts in Botswana other than the tweet he references. The assistant goes on to share a link from a tweet from the State Department spokesperson congratulating Botswana.
Other countries addressing the criminalization of homosexuality after the Trump administration’s initiative was announced were Gabon, which became one of the few countries in sub-Saharan Africa to decriminalize homosexuality, and Sudan, which eliminated the death penalty as punishment for homosexual conduct (although the punishment remains prison time from five years to life).
There’s no evidence those changes happened as a result of the global initiative Grenell led. One of the aims of the Blade’s FOIA lawsuit is to shed light on any activity from the U.S. government during the Trump administration in assisting with efforts, successful or otherwise, to decriminalize homosexuality.
The redactions on the production in the FOIA lawsuit may not be the last word. FOIA was amended in 2016 to clarify federal agencies cannot redact deliberative language without demonstrating revealing that information would cause “foreseeable harm.” The Blade, represented by attorneys at Davis Wright Tremaine, LLP, will have the opportunity to challenge these redactions once the FOIA production is complete.
At the time the lawsuit was filed, the State Department cited a “sizable universe of potentially responsive records” numbering in the thousands of pages as a reason for being unable to produce the records in a more timely manner. The initial seven pages produced by the State Department are an extremely small percentage of that total.
An unnamed State Department official, in response to an inquiry submitted by the Blade’s attorneys on the reasons for the initial limited production, fell back on the ongoing coronavirus pandemic and overwhelming nature of the work, citing a need to consult “subject matter experts” before disclosing potentially sensitive material.
“That process can take considerable time, particularly given the substantial constraints that have been imposed by the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic,” the State Department response says. “Thus, it’s not necessarily the case that the size of the potentially responsive universe returned by your client’s request should dictate the size of State’s first production. Similarly, a small production set does not necessarily entail that State has not processed a sizeable number of records during the preceding processing cycle.”
The Blade, through its attorneys, has asked the State Department to determine how much of the “sizable universe” has been reviewed and determined to be responsive or non-responsive (“fully processed”) and how long would the process involving subject matter experts take.
Daniel Fiedler, representing the Blade in the FOIA lawsuit as an attorney with Davis Wright Tremaine LLP, said the initial production from the State Department was unsatisfactory.
“In December, the Department of State made its first production in response to the FOIA request submitted by the Washington Blade over a year ago,” Fiedler said. “This nominal production consisted of two email records, both heavily redacted. Such a token response after so much time is truly disheartening, and we will continue to push to ensure that the Department satisfies its obligations under FOIA.”
Fiedler concluded: “The American public is entitled access to the records sought, and every additional day without that access causes further harm.”
District of Columbia
Capital Stonewall Democrats elect new leaders
LGBTQ political group set to celebrate 50th anniversary
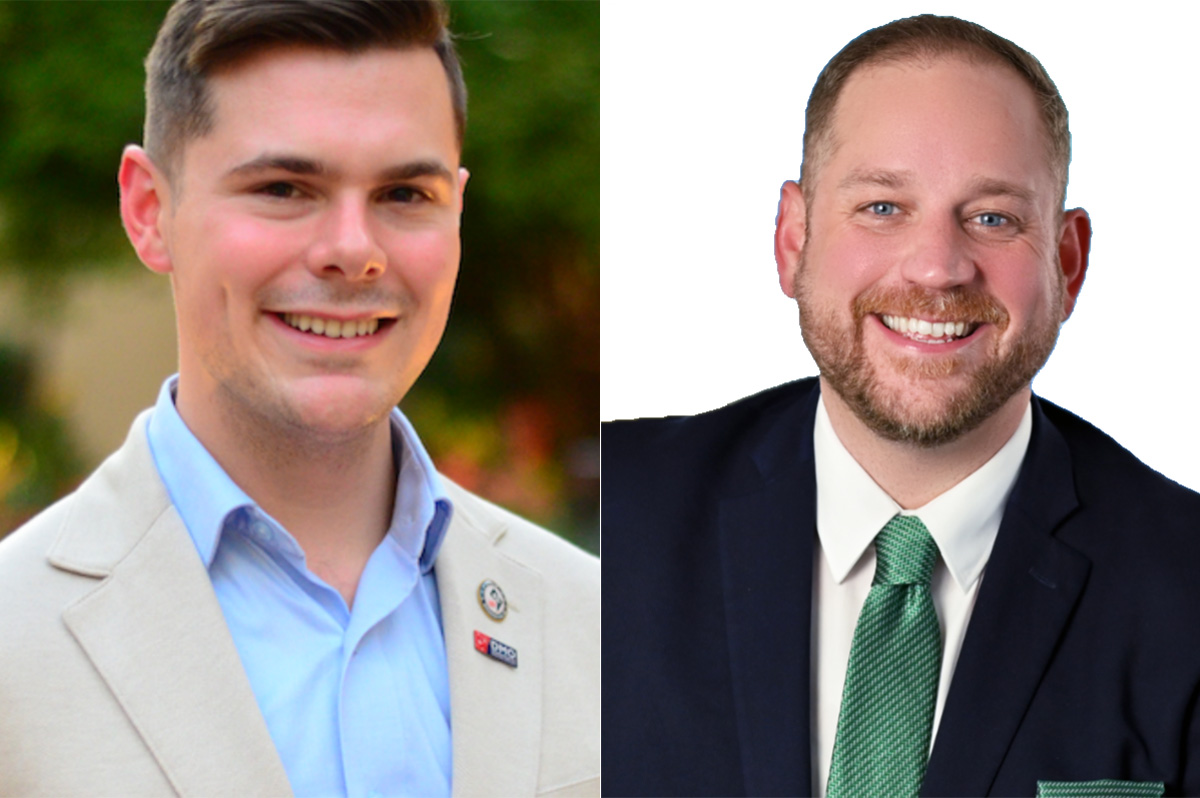

Longtime Democratic Party activists Stevie McCarty and Brad Howard won election last week as president and vice president for administration for the Capital Stonewall Democrats, D.C.’s largest local LGBTQ political organization.
In a Feb. 24 announcement, the group said McCarty and Howard, both of whom are elected DC Advisory Neighborhood Commissioners, ran in a special Capital Stonewall Democrats election to fill the two leadership positions that became vacant when the officers they replaced resigned.
Outgoing President Howard Garrett, who McCarty has replaced, told the Washington Blade he resigned after taking on a new position as chair of the city’s Ward 1 Democratic Committee. The Capital Stonewall Democrats announcement didn’t say who Howard replaced as vice president for administration.
The group’s website shows its other officers include Elizabeth Mitchell as Vice President for Legislative and Political Affairs, and Monica Nemeth as Treasurer. The officer position of secretary is vacant, the website shows.
“As we look toward 2026, the stakes for D.C. and for LGBTQ+ communities have never been clearer,” the group’s statement announcing McCarty and Howard’s election says. “Our 50th anniversary celebration on March 20 and the launch of our D.C. LGBTQ+ Voter’s Guide mark the beginning of a major year for endorsements, organizing, and coalition building,” the statement says.
McCarty said among the organization’s major endeavors will be holding virtual endorsement forums where candidates running for D.C. mayor and the Council will appear and seek the group’s endorsement.
Founded in 1976 as the Gertrude Stein Democratic Club, the organization’s members voted in 2021 to change its name to Capital Stonewall Democrats. McCarty said the 50th anniversary celebration on March 20, in which D.C. Mayor Muriel Bowser and members of the D.C. Council are expected to attend, will be held at the PEPCO Gallery meeting center at 702 8th St., N.W.
Federal Government
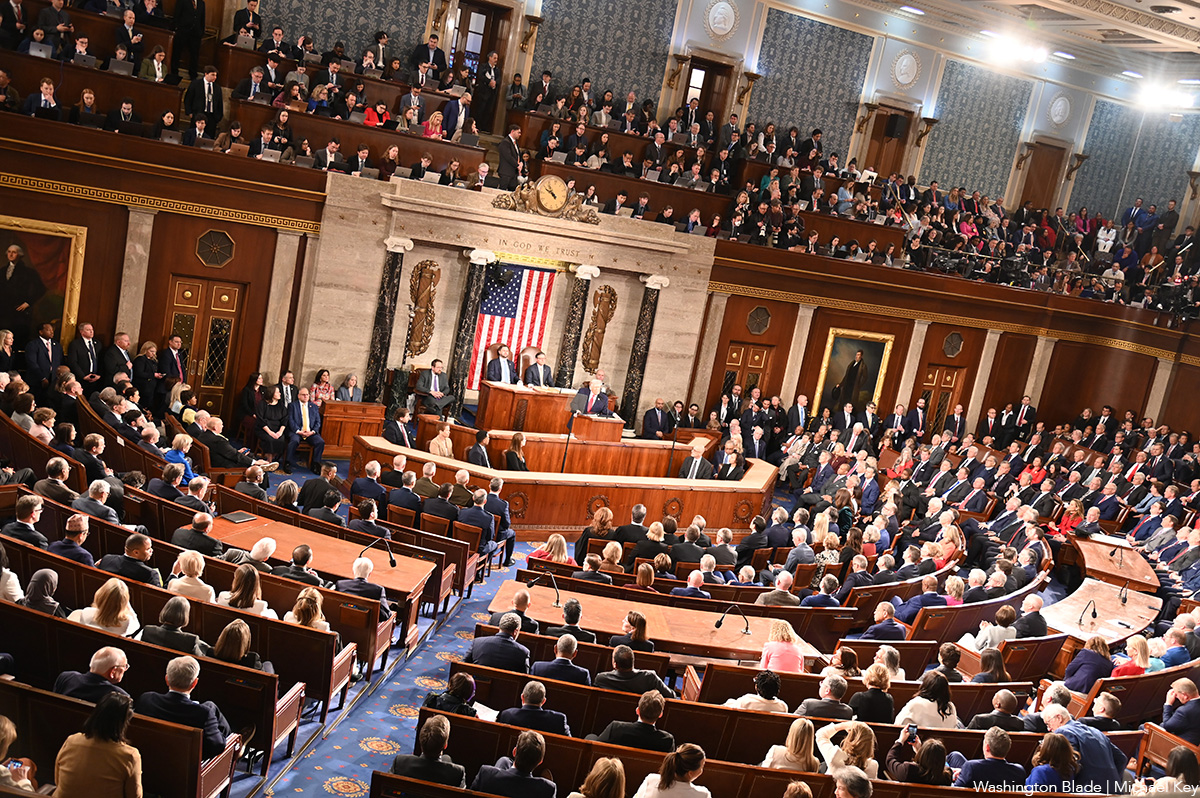
Two very different views of the State of the Union
As Trump delivered his SOTU address inside the Capitol, Democratic lawmakers gathered outside in protest, condemning the administration’s harmful policies.

As President Donald Trump delivered his State of the Union address inside the U.S. Capitol — touting his achievements and targeting political enemies — progressive members of Congress gathered just outside in protest.
Their message was blunt: For many Americans, particularly LGBTQ people, the country is not better off.
Each year, as required by Article II, Section 3 of the Constitution, the president must “give to the Congress Information of the State of the Union.” The annual address is meant to outline accomplishments and preview the year ahead. This year, Trump delivered the longest State of the Union in U.S. history, clocking in at one hour and 48 minutes. He spoke about immigration, his “law and order” domestic agenda, his “peace through strength” foreign policy doctrine, and what he framed as the left’s ‘culture wars’ — especially those involving transgender youth and Christian values.
But one year into what he has called the “Trump 2.0” era, the picture painted outside the Capitol stood in stark contrast to the one described inside.
Transgender youth
In one of the most pointed moments of his speech, Trump spotlighted Sage Blair, using her story to portray gender-affirming care as coercive and dangerous. Framing the issue as one of parental rights and government overreach, he told lawmakers and viewers:
“In the gallery tonight are Sage Blair and her mother, Michelle. In 2021, Sage was 14 when school officials in Virginia sought to socially transition her to a new gender, treating her as a boy and hiding it from her parents. Hard to believe, isn’t it? Before long, a confused Sage ran away from home.
“After she was found in a horrific situation in Maryland, a left-wing judge refused to return Sage to her parents because they did not immediately state that their daughter was their son. Sage was thrown into an all-boys state home and suffered terribly for a long time. But today, all of that is behind them because Sage is a proud and wonderful young woman with a full ride scholarship to Liberty University.
“Sage and Michelle, please stand up. And thank you for your great bravery and who can believe that we’re even speaking about things like this. Fifteen years ago, if somebody was up here and said that, they’d say, what’s wrong with him? But now we have to say it because it’s going on all over, numerous states, without even telling the parents.
“But surely, we can all agree no state can be allowed to rip children from their parents’ arms and transition them to a new gender against the parents’ will. Who would believe that we’ve been talking about that? We must ban it and we must ban it immediately. Look, nobody stands up. These people are crazy. I’m telling you, they’re crazy.”
The story, presented as encapsulation of a national crisis, became the foundation for Trump’s renewed call to ban gender-affirming care. LGBTQ advocates — and those familiar with Blair’s story — argue that the situation was far more complex than described and that using a single anecdote to justify sweeping federal restrictions places transgender people, particularly youth, at greater risk.
Equality Virginia said the president’s remarks were part of a broader effort to strip transgender Americans of access to care. In a statement to the Blade, the group said:
“Tonight, the president is choosing to double down on efforts to disrupt access to evidence-based, lifesaving care.
“Rather than allowing families and doctors to navigate deeply personal medical decisions free from federal interference — or allowing schools to respond with nuance and compassion without putting marginalized children at risk — the president is instead advocating for reckless, one-size-fits-all political control.
“At a time when Virginians are worried about rising costs, economic uncertainty, and aggressive immigration enforcement actions disrupting communities and families, attacking transgender young people is a blatant political distraction from the real challenges facing our nation. Virginia families and health care providers do not need Donald Trump telling them what care they do or do not need.”
For many in the LGBTQ community, the rhetoric inside the chamber echoed actions already taken by the administration.
Earlier this month, the Pride flag was removed from the Stonewall National Monument under a National Park Service directive that came from the top. Community members returned to the site, raised the flag again, and filed suit, arguing the removal violated federal law. To advocates, the move was symbolic — a signal that even the legacy of LGBTQ resistance was not immune.
Immigration and fear
Immigration dominated both events as well.
Inside the chamber, Trump boasted about the hundreds of thousands of immigrants detained in makeshift facilities. Outside, Democratic lawmakers described those same facilities as concentration camps and detailed what they characterized as the human toll of the administration’s enforcement policies.
Sen. Ed Markey (D-Mass.), speaking to the crowd, painted a grim picture of communities living in fear:
“People are vanishing into thin air. Quiet mornings are punctuated by jarring violence. Students are assaulted by ICE agents sitting outside the high school, hard working residents are torn from their vehicles in front of their children. Families, hopelessly search for signs of their loved ones who have stopped answering their phones, stop replying to text… This is un-American, it is illegal, it is unconstitutional, and the people are going to rise up and fight for Gladys Vega and all of those poor people who today need to know that the people’s State of the Union is the beginning of a long fight that is going to result in the end of Republican control of the House of Representatives and the Senate in the United States of America in 2026.”
Speakers emphasized that LGBTQ immigrants are often especially vulnerable — fleeing persecution abroad only to face detention and uncertainty in the United States. For them, the immigration crackdown and the attacks on transgender health care are not separate battles but intertwined fronts in a broader cultural and political war.
Queer leadership

After delivering remarks alongside Robert Garcia, Kelley Robinson, president of the Human Rights Campaign, took the stage and transformed the freezing crowd’s anger into resolve.
Garcia later told the Blade that visibility matters in moments like this — especially when LGBTQ rights are under direct attack.
“We should be crystal clear about right now what is happening in our country,” Garcia said. “We have a president who is leading the single largest government cover up in modern history, we have the single largest sex trafficking ring in modern history right now being covered up by Donald Trump and Pam Bondi In the Department of Justice. Why are we protecting powerful, wealthy men who have abused and raped women and children in this country? Why is our government protecting these men at this very moment? In my place at the Capitol is a woman named Annie farmer. Annie and her sister Maria, both endured horrific abuse by Jeffrey Epstein and Ghislaine Maxwell. As we move forward in this investigation, always center the survivors; we are going to get justice for the survivors. And Donald Trump may call this investigation a hoax. He may try to deflect our work, but our message to him is very clear that our investigation is just getting started, and we will we will get justice for these survivors.”
He told the Blade afterwards that having queer leaders front and center is itself an act of resistance.
“I obviously was very honored to speak with Kelley,” the California representative said. Kelley is doing a great job…it’s important that there are queer voices, trans voices, gay voices, in protest, and I think she’s a great example of that. It’s important to remind the country that the rights of our community continue to be attacked, and then we’ve got to stand up. Got to stand up for this as well.”
Robinson echoed that call, urging LGBTQ Americans — especially young people — not to lose hope despite the administration’s escalating rhetoric.
“There are hundreds of thousands of people that are standing up for you every single day that will not relent and will not give an inch until every member of our community is protected, especially our kids, especially our trans and queer kids. I just hope that the power of millions of voices drowns out that one loud one, because that’s really what I want folks to see at HRC. We’ve got 3.6 million members that are mobilizing to support our community every single day, 75 million equality voters, people that decide who they’re going to vote for based on issues related to our community. Our job is to make sure that all those people stand up so that those kids can see us and hear our voices, because we’re going to be what stands in the way.”
A boycott — and a warning
The list of Democratic lawmakers who boycotted the State of the Union included Sens. Ruben Gallego, Ed Markey, Jeff Merkley, Chris Murphy, Adam Schiff, Tina Smith, and Chris Van Hollen, along with dozens of House members.
For those gathered outside — and for viewers watching the livestream hosted by MoveOn — the counter-programming was not merely symbolic. It was a warning.
While the president spoke of strength and success inside the chamber, LGBTQ Americans — particularly transgender youth — were once again cast as political targets. And outside the Capitol, lawmakers and advocates made clear that the fight over their rights is far from over.

Virginia
Va. activists preparing campaign in support of repealing marriage amendment
Referendum about ‘dignity and equal protection under the law’

Virginia voters in November will vote on whether to repeal their state’s constitutional amendment that defines marriage as between a man and a woman.
Democratic Gov. Abigail Spanberger on Feb. 6 signed House Bill 612 into law. It facilitates a referendum for voters to approve the repeal of the 2006 Marshall-Newman Amendment. Although the U.S. Supreme Court’s Obergefell ruling extended marriage rights to same-sex couples across the country in 2014, codifying marriage equality in Virginia’s constitution would protect it in the state in case the decision is overturned.
Maryland voters in 2012 approved Question 6, which upheld the state’s marriage equality law, by a 52-48 percent margin. Same-sex marriage became legal in Maryland on Jan. 1, 2013.
LGBTQ advocacy groups and organizations that oppose marriage equality mounted political campaigns ahead of the referendum.

Equality Virginia has been involved in advancing LGBTQ rights in Virginia since 1989.
Equality Virginia is working under its 501c3 designation in conjunction with Equality Virginia Advocates, which operates under a 501c4 designation, to plan campaigns in support of repealing the Marshall-Newman Amendment.
The two main campaigns on which Equality Virginia will be focused are education and voter mobilization. Reed Williams, the group’s director of digital engagement and narrative, spoke with the Washington Blade about Equality Virginia’s plans ahead of the referendum.
Williams said an organization for a “statewide public education campaign” is currently underway. Williams told the Blade its goal will be “to ensure voters understand what this amendment does and why updating Virginia’s constitution matters for families across the commonwealth.”
The organization is also working on a “robust media and voter mobilization campaign to identify and turn out voters” to repeal Marshall-Newman Amendment. Equality Virginia plans to work with the community members to guarantee voters are getting clear and accurate information regarding the meaning of this vote and its effect on the Virginia LGBTQ community.
“We believe Virginia voters are ready to bring our constitution in line with both the law and the values of fairness and freedom that define our commonwealth,” said Equality Virginia Executive Director Narissa Rahaman. “This referendum is about ensuring loving, committed couples and their families are treated with dignity and equal protection under the law.”
The Human Rights Campaign has also worked closely with Equality Virginia.
“It’s time to get rid of outdated, unconstitutional language and ensure that same sex couples are protected in Virginia,” HRC President Kelley Robinson told the Blade in a statement.


















