South America
New Argentinian president eliminates Women, Gender and Diversity Ministry
Javier Milei’s decision has sparked concern among LGBTQ activists
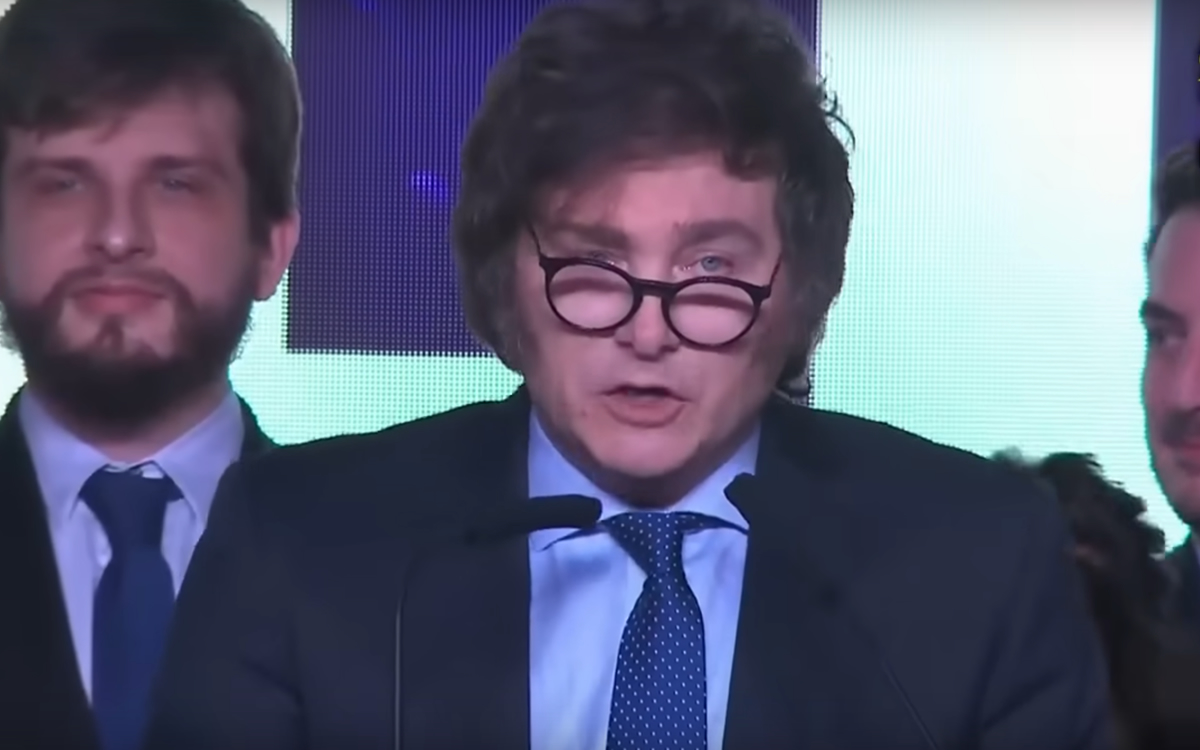

Argentinian President Javier Milei has fulfilled one of his campaign promises, which is to eliminate the Women, Gender and Diversity Ministry.
Milei took office on Dec. 10. He defeated then-Economy Minister Sergio Massa in the second round of the country’s presidential election that took place on Nov. 20.
The president’s controversial decision to eliminate the Women, Gender and Diversity Ministry is intended to reconfigure the government structure, placing the portfolio’s responsibilities under the purview of Human Capital Minister Sandra Viviana Pettovello.
The decree mandates “the commitments and obligations assumed by the Ministry of Women, Gender and Diversity will be under the Ministry of Human Capital,” with the transfer of budgetary credits, organizational units, assets and personnel. This reorganization also eliminates the Education, Culture, Labor and Social Development Ministries amid soaring inflation, increased poverty and political and economic instability.
This radical change comes four years after then-President Alberto Fernández in 2019 created the Women, Diversity and Gender Ministry. The resolution, which Milei signed and has already been published in the Official Gazette, has created a new government structure that has raised concerns, especially among LGBTQ rights activists in the country that has been at the vanguard of expanding rights to sexual and gender minorities.
New Congressman Esteban Paulón, a long-time activist who represents Santa Fe province, criticized Milei’s decision.
“One of the president’s prerogatives is to dictate his own law of ministries to order the government’s management,” Paulón told the Washington Blade. “Out of 18 existing ministries, it is reduced to nine or 10, and obviously one of the ministries that is eliminated is the Ministry of Women, Gender and Diversity.”
Paulón noted this decision reflects Milei’s view of these issues as “superfluous policy expenditures,” sending a clear message that they will not be a priority for his administration.
“The president decided to make his first speech with his back to Congress, ignoring a Congress that is very fragmented and with which he needs to have a dialogue if he wants to pass some of the laws he is pushing,” said Paulón. “This beginning has not been a good omen in the 40th anniversary of democracy.”
Paulón added this situation “adds a lot of uncertainty and concern.”
The congressman also reiterated his concerns about the future of gender and sexual diversity policies in Argentina.
“It is still not clear in the structure of the State where those jobs that exist today, that are created, will remain. It is not resolved,” said Paulón. “We will have to see how the issue evolves, but for now there is silence on the part of the government in relation to this.”
Paulón further stressed the importance of defending policies that benefit LGBTQ people.
He said these policies are not only relevant to LGBTQ people; but also apply to the fight against gender violence, femicides, labor and social inclusion of the transgender community and other inequalities and the implementation of the trans labor quota. Paulón concluded the loss of institutionalism not only implies the lack of resources from the State, but also the absence of a clear message about the importance of these issues in society.
“This is a huge shame because the truth is that these policies are very necessary, first because we know that there are issues linked to gender inequalities and this obviously includes the perspective of dissidence that have a concrete impact on the daily lives of people, care policies, gender violence, the issue of feminist economy, obviously everything that has to do with labor and social inclusion of the LGBTIQ+ collective,” he said.
“These are extremely relevant issues that are lost when losing institutionality because the State stops allocating resources, stops investing and above all stops sending a clear message to society that these are relevant issues,” added Paulón. “They are issues that the State has to deal with and society has to commit to modify, and the truth is that if we do not fight against the structure of patriarchy that is so settled in capitalism, we will not be able to fight against so many other inequalities.”
Ecuador
Justicia reconoce delito de odio en caso de bullying en Instituto Nacional Mejía de Ecuador
Johana B se suicidó el 11 de abril de 2023
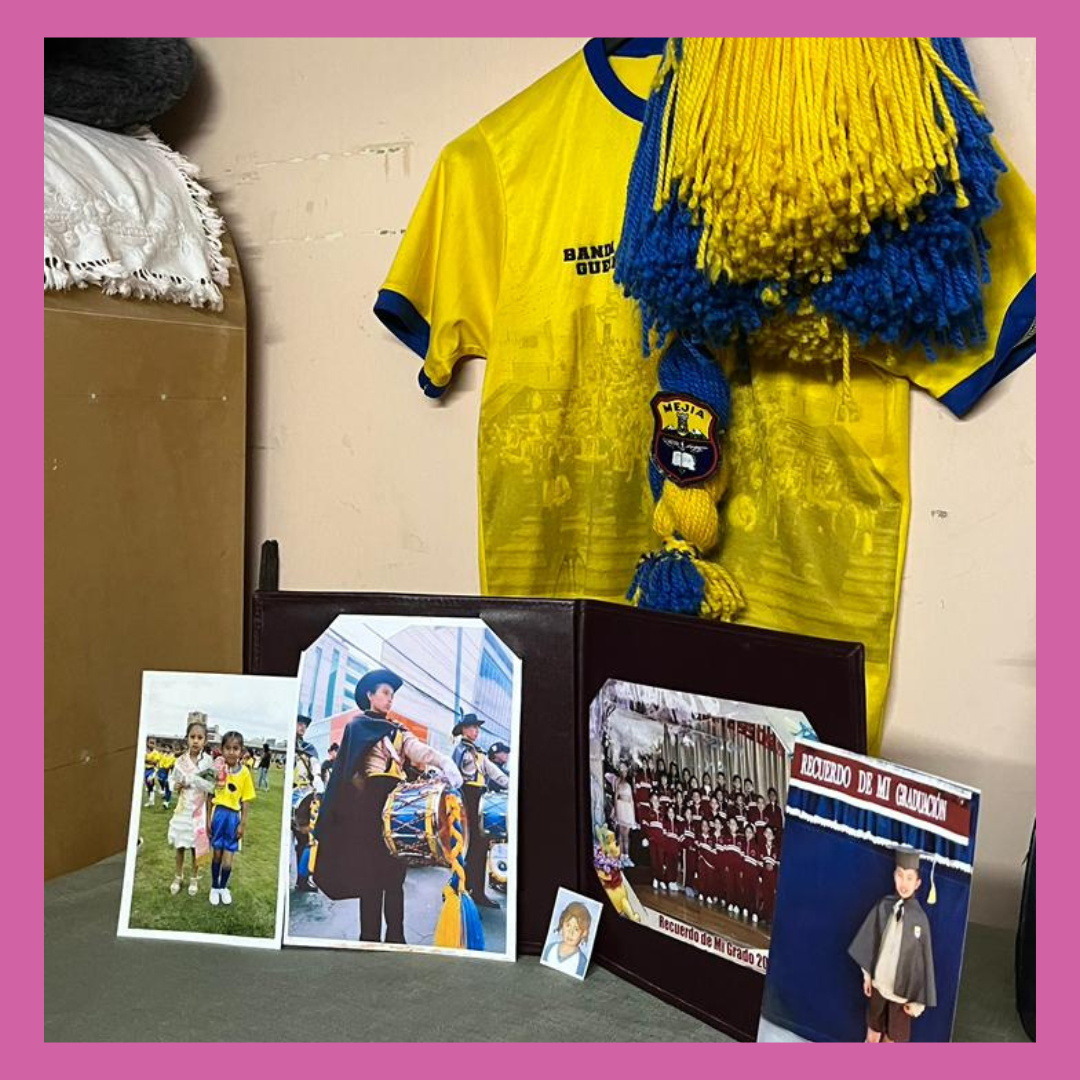

A casi tres años del suicidio de Johana B., quien estudió en el Instituto Nacional Mejía, colegio emblemático de Quito, el Tribunal de la Corte Nacional de Justicia ratificó la condena para el alumno responsable del acoso escolar que la llevó a quitarse la vida.
Según información de la Fiscalía, el fallo de última instancia deja en firme la condena de cuatro años de internamiento en un centro para adolescentes infractores, en una audiencia de casación pedida por la defensa del agresor, tres meses antes de que prescriba el caso.
Con la sentencia, este caso es uno de los primeros en el país en reconocer actos de odio por violencia de género, delito tipificado en el artículo 177 del Código Orgánico Penal Integral (COIP).
El suicidio de Johana B. ocurrió el 11 abril de 2023 y fue consecuencia del acoso escolar por estereotipos de género que enfrentó la estudiante por parte de su agresor, quien constantemente la insultaba y agredía por su forma de vestir, llevar el cabello corto o practicar actividades que hace años se consideraban exclusivamente para hombres, como ser mando de la Banda de Paz en el Instituto Nacional Mejía.
Desde la muerte de Johana, su familia buscaba justicia. Su padre, José, en una entrevista concedida a edición cientonce para la investigación periodística Los suicidios que quedan en el clóset a causa de la omisión estatal afirmó que su hija era acosada por su compañero y otres estudiantes con apodos como “marimacha”, lo que también fue corroborado en los testimonios recogidos por la Unidad de Justicia Juvenil No. 4 de la Fiscalía.
Los resultados de la autopsia psicológica y del examen antropológico realizados tras la muerte de Johana confirmaron las versiones de sus compañeras y docentes: que su agresor la acosó de manera sistemática durante dos años. Los empujones, jalones de cabello o burlas, incluso por su situación económica, eran constantes en el aula de clase.
La violencia que recibió Johana escaló cuando su compañero le dio un codazo en la espalda ocasionándole una lesión que le imposibilitó caminar y asistir a clases.
Días después del hecho, la adolescente se quitó la vida en su casa, tras escuchar que la madre del agresor se negó a pagar la mitad del valor de una tomografía para determinar la lesión en su espalda, tal como lo había acordado previamente con sus padres y frente al personal del DECE (Departamento de Consejería Estudiantil del colegio), según versiones de su familia y la Fiscalía.
#AFONDO | Johana se suicidó el 11 de abril de 2023, tras ser víctima de acoso escolar por no cumplir con estereotipos femeninos 😢.
Dos semanas antes, uno de sus compañeros le dio un codazo en la espalda, ocasionándole una lesión que le imposibilitó caminar 🧵 pic.twitter.com/bXKUs9YYOm
— EdicionCientonce (@EdCientonce) September 3, 2025
“Era una chica linda, fuerte, alegre. Siempre nos llevamos muy bien, hemos compartido todo. Nos dejó muchos recuerdos y todos nos sentimos tristes; siempre estamos pensando en ella. Es un vacío tan grande aquí, en este lugar”, expresó José a Edición Cientonce el año pasado.
Para la fiscal del caso y de la Unidad de Justicia Juvenil de la Fiscalía, Martha Reino, el suicidio de la adolescente fue un agravante que se contempló durante la audiencia de juzgamiento de marzo de 2024, según explicó a este medio el año pasado. Desde entonces, la familia del agresor presentó un recurso de casación en la Corte Nacional de Justicia, que provocó la dilatación del proceso.
En el fallo de última instancia, el Tribunal también dispuso que el agresor pague $3.000 a la familia de Johana B. como reparación integral. Además, el adolescente deberá recibir medidas socioeducativas, de acuerdo al artículo 385 del Código Orgánico de la Niñez y Adolescencia, señala la Fiscalía.
El caso de Johana también destapó las omisiones y negligencias del personal del DECE y docentes del Instituto Nacional Mejía. En la etapa de instrucción fiscal se comprobó que no se aplicaron los protocolos respectivos para proteger a la víctima.
De hecho, la Fiscalía conoció el caso a raíz de la denuncia que presentó su padre, José, y no por el DECE, aseguró la fiscal el año pasado a Edición Cientonce.
Pese a estas omisiones presentadas en el proceso, el fallo de última instancia sólo ratificó la condena para el estudiante.
Colombia
LGBTQ Venezuelans in Colombia uncertain about homeland’s future
US forces seized Nicolás Maduro and his wife on Jan. 3
BOGOTÁ, Colombia — LGBTQ Venezuelans who live in Colombia remain uncertain about their homeland’s future in the wake of now former-President Nicolás Maduro’s ouster.
José Guillén is from Mérida, a city in the Venezuelan Andes that is roughly 150 miles from the country’s border with Colombia. He founded an LGBTQ organization that largely focused on health care before he left Venezuela in 2015.
Guillén, whose mother is Colombian, spoke with the Washington Blade on Jan. 9 at a coffee shop in Bogotá, the Colombian capital. His husband, who left Venezuela in 2016, was with him.
“I would like to think that (Venezuela) will be a country working towards reconstruction in a democracy,” said Guillén, responding to the Blade’s question about what Venezuela will look like in five years.
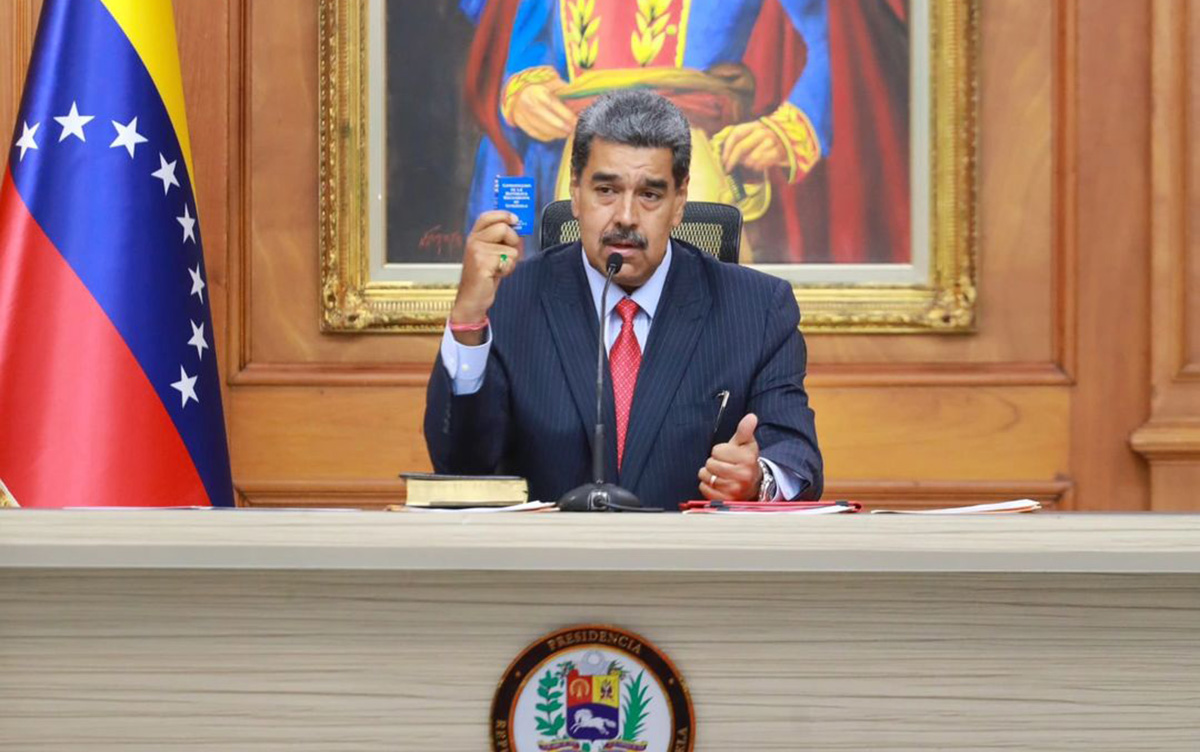
American forces on Jan. 3 seized Maduro and his wife, Cilia Flores, at their home in Caracas, the Venezuelan capital, during an overnight operation.
Maduro and Flores on Jan. 5 pleaded not guilty to federal drug charges in New York. The Venezuelan National Assembly the day before swore in Delcy Rodríguez, who was Maduro’s vice president, as the country’s acting president.
Hugo Chávez died in 2013, and Maduro succeeded him as Venezuela’s president. Subsequent economic and political crises prompted millions of Venezuelans to leave the country.

The Blade in 2021 reported Venezuelan authorities raided HIV/AIDS service organizations, arrested their staffers, and confiscated donated medications for people with HIV/AIDS. Tamara Adrián, a member of the Venezuelan opposition who in 2015 became the first openly transgender person elected to the National Assembly, told the Blade she had to take security precautions during her campaign because government supporters targeted her.
The Blade on Jan. 8 spoke with a Venezuelan AIDS Healthcare Foundation client who said Maduro’s ouster “is truly something we’ve been waiting for for 26 or 27 years.” Another Venezuelan AHF client — a sex worker from Margarita Island in the Caribbean Sea who now lives in Bogotá — echoed this sentiment when she spoke with the Blade two days later.
“I love the situation of what’s happening,” she said during a telephone interview.
Sources in Caracas and elsewhere in Venezuela with whom the Blade spoke after Jan. 3 said armed pro-government groups known as “colectivos” were patrolling the streets. Reports indicate they set up checkpoints, stopped motorists, and searched their cell phones for evidence that they supported Maduro’s ouster.
“In the last few days, it seems there are possibilities for change, but people are also very afraid of the government’s reactions and what might happen,” Guillén said.
“Looking at it from an LGBT perspective, there has never been any recognition of the LGBT community in Venezuela,” he noted. “At some point, when Chávez came to power, we thought that many things could happen because it was a progressive government, but no.”

Luis Gómez is a lawyer from Valencia, a city in Venezuela’s Carabobo state. He and his family since he was a child have worked with autistic children through Fundación Yo Estoy Aquí, a foundation they created.
Gómez was in high school in 2013 when Maduro succeeded Chávez. He graduated from law school in 2018. Gómez in November 2020 fled to Colombia after he became increasingly afraid after his mother’s death that authorities would arrest him because of his criticism of the government.
The Colombian government in December 2025 recognized him as a refugee.
Gómez during a Jan. 9 interview in Bogotá discussed his initial reaction to Maduro’s ouster.
“I’m 28 years old, and 27 of those years have been in dictatorship,” Gómez told the Blade. “I had never experienced anything like this, which is why it had such a strong impact on me.”
Gómez said he initially thought the operation to seize Maduro and Flores was similar to an attempted coup that Chávez led in 1992. Gómez added he quickly realized Jan. 3 was different.
“The last thing we thought would happen was that Maduro would be wearing an orange jumpsuit in prison in New York,” he told the Blade. “It’s also important that those of us outside (of Venezuela) knew about it before those inside, because that’s the level of the lack of communication to which they have subjected all our families inside Venezuela.”
Gómez said Maduro’s ouster left him feeling “a great sense of justice” for his family and for the millions of Venezuelans who he maintains suffered under his government.
“Many Venezuelans, and with every reason, around the world started celebrating euphorically, but given our background and our understanding, we already knew at that moment what was coming,” added Gómez. “Now a new stage is beginning. What will this new stage be like? This has also generated uncertainty in us, which the entire citizenry is now experiencing.”
Trump ‘puts us in a very complex position’
U.S. chargé d’affaires Laura Dogu on Jan. 31 arrived in Caracas to reopen the American embassy that closed in February 2019.
Tens of thousands of people on Jan. 7 gathered in Bogotá and elsewhere in Colombia to protest against President Donald Trump after he threatened Colombian President Gustavo Petro, who was once a member of the now disbanded M-19 guerrilla movement. The two men met at the White House on Tuesday.

Both Gómez and Guillén pointed out Rodríguez remains in power. They also noted her brother, Jorge Rodríguez, is currently president of the National Assembly.
“Delcy has been a key figure in the regime for many years,” said Guillén. “In fact, she was one of the toughest people within the regime.”
Gómez and Guillén also spoke about Trump and his role in a post-Maduro Venezuela.
“Donald Trump, especially in this second term, has played a very particular role in the world, especially for those of us who, genuinely, not falsely or hypocritically, truly defend human rights,” said Gómez. “It puts us in a very complex position.”
Gómez told the Blade the operation to seize Maduro and Flores was “not an invasion for us.”
“It’s not a military intervention,” said Gómez. “It was the beginning, or I would even dare to say the end of the end.”
He acknowledged “there are interests at play, that the United States doesn’t do this for free.” Gómez added U.S. access to Venezuelan oil “for us, at this point, is not something that matters to us.”
“Venezuelans have received nothing, absolutely nothing from the resources generated by oil. We live without it,” he said. “The only ones getting rich from the oil are the top drug traffickers and criminals who remain in power.”
Guillén pointed out the U.S. “has always been one of the biggest buyers of oil from Venezuela, and perhaps we need that closeness to rebuild the country.”
“I also feel that there is a great opportunity with the millions of Venezuelans who left the country and who would like to be part of that reconstruction as well,” he said.
“Logically it’s sad to see the deterioration in the country, the institutions, even the universities in general,” added Guillén. “Those of us who are outside the country have continued to move forward and see other circumstances, and returning to the country with those ideas, with those new approaches, could provide an opportunity for change. That’s what I would like.”
Editor’s note: International News Editor Michael K. Lavers was on assignment in Colombia from Jan. 5-10.
Colombia
Gay Venezuelan opposition leader: Country’s future uncertain after Maduro ouster
Yendri Velásquez fled to Colombia in 2024 after authorities ‘arbitrarily detained’ him

A gay Venezuelan opposition leader who currently lives in Colombia says his country’s future is uncertain in the wake of now former President Nicolás Maduro’s ouster.
The Washington Blade spoke with Yendri Velásquez on Thursday, 12 days after American forces seized Maduro and his wife, Cilia Flores, at their home in Caracas, the Venezuelan capital, during an overnight operation.
Maduro and Flores on Jan. 5 pleaded not guilty to federal drug charges in New York. The Venezuelan National Assembly the day before swore in Delcy Rodríguez, who was Maduro’s vice president, as the country’s acting president.
Velásquez, who lives in the Colombian capital of Bogotá, described the events surrounding Maduro’s ouster as “very confusing.”
“It was a very surprising thing that left me in shock,” Velásquez told the Blade. “We also thought, at least from the perspective of human rights, that the United States was going to respect international law and not go to the extreme of bombing and extracting Maduro.”
“Other questions also arise,” he added. “What could have been done? What else could have been done to avoid reaching this point? That is the biggest question posed to the international community, to other countries, to the human rights mechanisms we established before Trump violated international law, precisely to preserve these mechanisms and protect the human rights of Venezuelan people and those of us who have been forced to flee.”
Velásquez three years ago founded the Venezuelan Observatory of LGBTIQ+ Violence. He also worked with Tamara Adrián, a lawyer who in 2015 became the first openly transgender woman elected to the Venezuelan National Assembly, for more than a decade.
Members of Venezuela’s military counterintelligence agency, known by the Spanish acronym DGCIM, on Aug. 3, 2024, “arbitrarily detained” Velásquez as he was trying to leave the country to attend a U.N. human rights event in Geneva.
Velásquez told the Blade he was “forcibly disappeared” for nearly nine hours and suffered “psychological torture.” He fled to Colombia upon his release.
Two men on Oct. 14, 2025, shot Velásquez and Luis Peche Arteaga, a Venezuelan political consultant, as they left a Bogotá building.
The assailants shot Velásquez eight times, leaving him with a fractured arm and hip. Velásquez told the Blade he has undergone multiple surgeries and has had to learn how to walk again.
“This recovery has been quite fast, better than we expected, but I still need to finish the healing process for a fractured arm and complete the physical therapy for the hip replacement I had to undergo as a result of these gunshots,” he said.
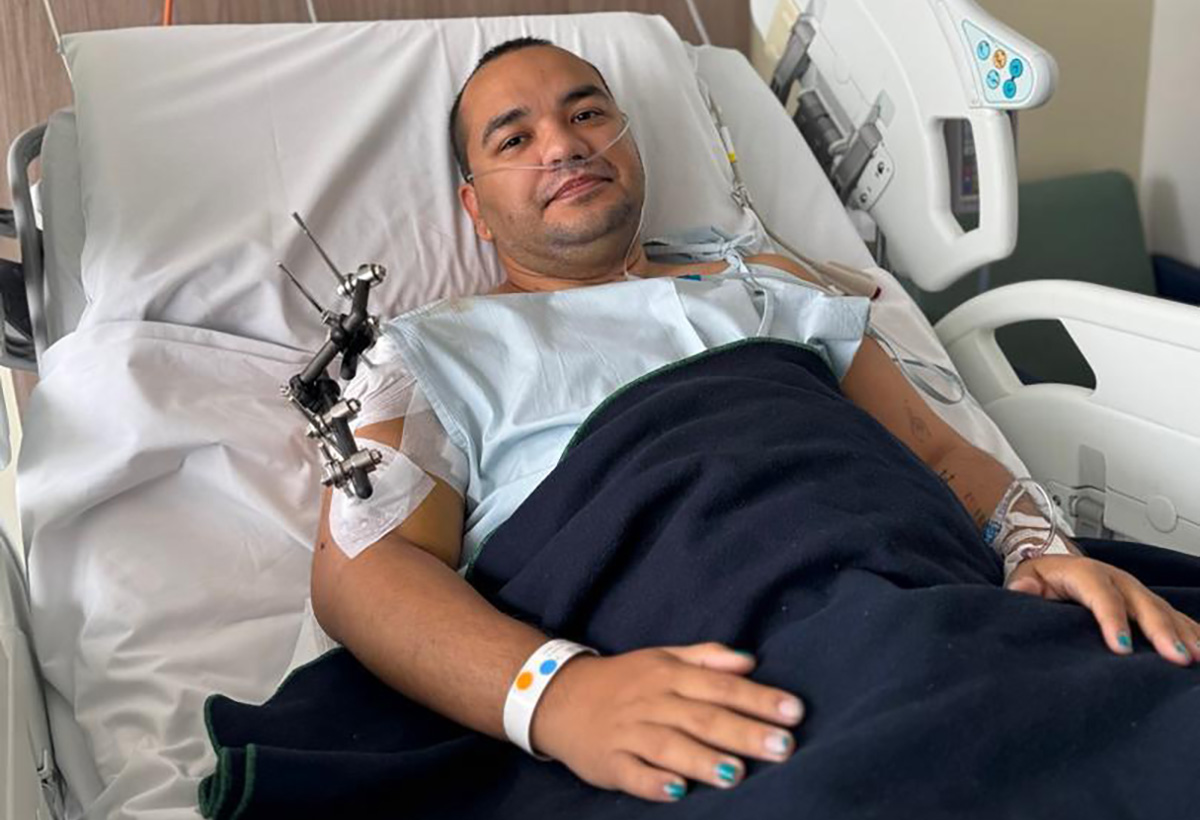
María Corina Machado, who won the 2025 Nobel Peace Prize, and other Venezuelan opposition leaders said Maduro’s government targeted Velásquez and Peche. Colombian President Gustavo Petro and his government also condemned the attack.
Colombian authorities have yet to arrest anyone in connection with the attack.
Velásquez noted to the Blade he couldn’t sleep on Jan. 3 because “of the aches and pains” from the shooting. He said a friend who is “helping me out and looking after my things” was the one who told him about the operation the U.S. carried out to seize Maduro and Flores.
“He said, ‘Look at this! They’re bombing Caracas! And I was like, ‘What is this?'” recalled Velásquez.
White House ‘not necessarily’ promoting human rights agenda
Velásquez noted Rodríguez “is and forms part of the mechanisms of repression” that includes DGCIM and other “repressive state forces that have not only repressed, but also tortured, imprisoned, and disappeared people simply for defending the right to vote in (the) 2024 (election), simply for protesting, simply for accompanying family members.” Velásquez told the Blade that “there isn’t much hope that things will change” in Venezuela with Rodríguez as president.
“Let’s hope that countries and the international community can establish the necessary dialogues, with the necessary intervention and pressure, diplomatically, with this interim government,” said Velásquez, who noted hundreds of political prisoners remain in custody.
He told the Blade the Trump-Vance administration does not “not necessarily” have “an agenda committed to human rights. And we’ve seen this in their actions domestically, but also in their dealings with other countries.”
“Our hope is that the rest of the international community, more than the U.S. government, will take action,” said Velásquez. “This is a crucial moment to preserve democratic institutions worldwide, to preserve human rights.”
Velásquez specifically urged the European Union, Colombia, Brazil, and other Latin American countries “to stop turning a blind eye to what is happening and to establish bridges and channels of communication that guarantee a human rights agenda” and to try “to curb the military advances that the United States may still be considering.”

Velásquez told the Blade he also plans to return to Venezuela when it is safe for him to do so.
“My plan will always be to return to Venezuela, at least when it’s no longer a risk,” he said. “The conditions aren’t right for me to return because this interim government is a continuation of Maduro’s government.”
Editor’s note: International News Editor Michael K. Lavers was on assignment in Bogotá, Colombia, from Jan. 5-10.
-

 Mexico4 days ago
Mexico4 days agoUS Embassy in Mexico issues shelter in place order for Puerto Vallarta
-

 Real Estate5 days ago
Real Estate5 days ago2026: prices, pace, and winter weather
-

 Theater5 days ago
Theater5 days agoJosé Zayas brings ‘The House of Bernarda Alba’ to GALA Hispanic Theatre
-

 Netherlands4 days ago
Netherlands4 days agoRob Jetten becomes first gay Dutch prime minister




















