World
Out in the World: LGBTQ news from Europe and Asia
Liechtenstein lawmakers approved a marriage equality bill on May 15

ILGA-Europe

ILGA-Europe released its annual Rainbow Europe Map module ranking countries across the continent on the status of LGBTQ rights, revealing that many countries are falling behind as political pressure from far-right politicians grows.
The report was released May 15, just a day after the EU’s Fundamental Rights Agency released its own report detailing a shocking growth in violence experienced by LGBTQ people across member states over the past year.
“Across Europe, LGBTI people are being targeted by hate speech and violence and their human rights are being actively undermined, yet we still see too many countries across the region stalling in moving legal protection forward and not renewing their commitments through national strategies and action plans,” says ILGA-Europe Advocacy Director Katrin Hugendubel.
“This non-action is dangerous, as without proper legislation in place to protect minorities, including LGBTI people, it will be much too easy for newly elected governments to quickly undermine human rights and democracy.”
Once again, Malta held the lead in the country rankings, as it has for the past nine years, scoring 88 percent across ILGA-Europe’s categories of equality and nondiscrimination law, family recognition, hate crime and hate speech laws, legal gender recognition, intersex bodily integrity, civil society space, and asylum policies.
Iceland jumped to second place with 83 percent after passing new laws banning conversion therapy and facilitating legal gender recognition. Belgium reached third place with 78 percent after banning conversion therapy.
At the other end of the spectrum, Russia (2 percent), Azerbaijan (2 percent), and Turkey (5 percent) hold the bottom rankings amid ongoing crackdowns on LGBTQ rights and expression in all three countries. Last year, Russia banned “the LGBT movement” as an “extremist organization.”
Several countries jumped up the rankings in this year’s report, including Greece and Estonia, which both legalized same-sex marriage. Liechtenstein collected points for extending adoption rights to same-sex couples, although it did not collect points for legalizing same-sex marriage, which happened the day after the report was released.
Germany, Bulgaria, Iceland, and Slovenia all collected points for passing legislation on hate crimes and hate speech, while Belgium, Cyprus, Iceland, Norway, and Portugal all collected points for banning conversion therapy.
But the changes haven’t all been positive. Several countries tumbled down the rankings as progress stalled on LGBTQ rights. Montenegro, Finland, Spain, Sweden, and Slovenia all lost points because their governments failed to renew action plans to promote LGBTQ rights. The report also noted the looming threat of right-wing governments across Europe, including in Italy where the national government has restricted the recognition of same-sex parents, and in several countries which are eying restrictions on legal gender recognition and trans health care, including France, UK, Slovakia, and Croatia.
The UK once occupied the top spot on ILGA-Europe’s rankings, but has fallen to 15th place as other countries press ahead on LGBTQ rights while the UK’s Conservative government has increasingly come under the sway of an anti-transgender moral panic.
LIECHTENSTEIN

The Alpine microstate Liechtenstein saw its parliament give final approval to legalizing same-sex marriage in a near-unanimous vote on May 15.
By a vote of 24-1, parliament approved a series of bills that would amend marriage law to allow same-sex couples to marry in the country of about 30,000 people nestled between Switzerland and Austria. The only “no” vote came from an MP from the right-wing populist Democrats for Liechtenstein party.
The new law will come into effect on Jan 1, 2025, as long as it is not vetoed by the prince or challenged in a citizen-initiated referendum. The prince is not expected to veto the bill, as he has previously expressed support for same-sex marriage.
Under the new law, no new civil unions will be registered, although same-sex couples already in same-sex unions will be allowed to continue their unions.
Liechtenstein’s parliament had already amended the law to allow same-sex couples to adopt last year, following an order from the Constitutional Court.
The tiny, conservative-leaning and mostly Catholic country has been slow to adopt LGBTQ rights. It lacks any legal protections from employment discrimination or anti-LGBTQ hate crimes.
ILGA-Europe ranked Liechtenstein 33rd out of 48 states in Europe, with a score of 28 percent on its latest Rainbow Europe Map. This decision on marriage will likely see it rise somewhat in the rankings next year.
The Catholic Church has previously strongly rejected same-sex marriage. Last year, the country’s archbishop, Wolfgang Haas had called same-sex marriage a “diabolical attack against the Creator’s will to salvation,” and cancelled a planned service for opening of Parliament in protest of the law. Haas has since retired.
The decision makes Liechtenstein the last German-speaking country to legalize same-sex marriage.
In a state posted to its Facebook group, the Liechtenstein LGBTQ advocacy group FLay thanked the lawmakers and other supporters who helped get same-sex marriage legalized in the country.
“We are looking forward to introducing marriage for all per 1 January 2025 and thank you to all who have fought for it,” the statement said.
Liechtenstein is the 22nd European country to introduce same-sex marriage, bringing the global total to 38 countries. A bill before the Thai Senate is expected to pass before the summer, which would make it the 39th.
GEORGIA
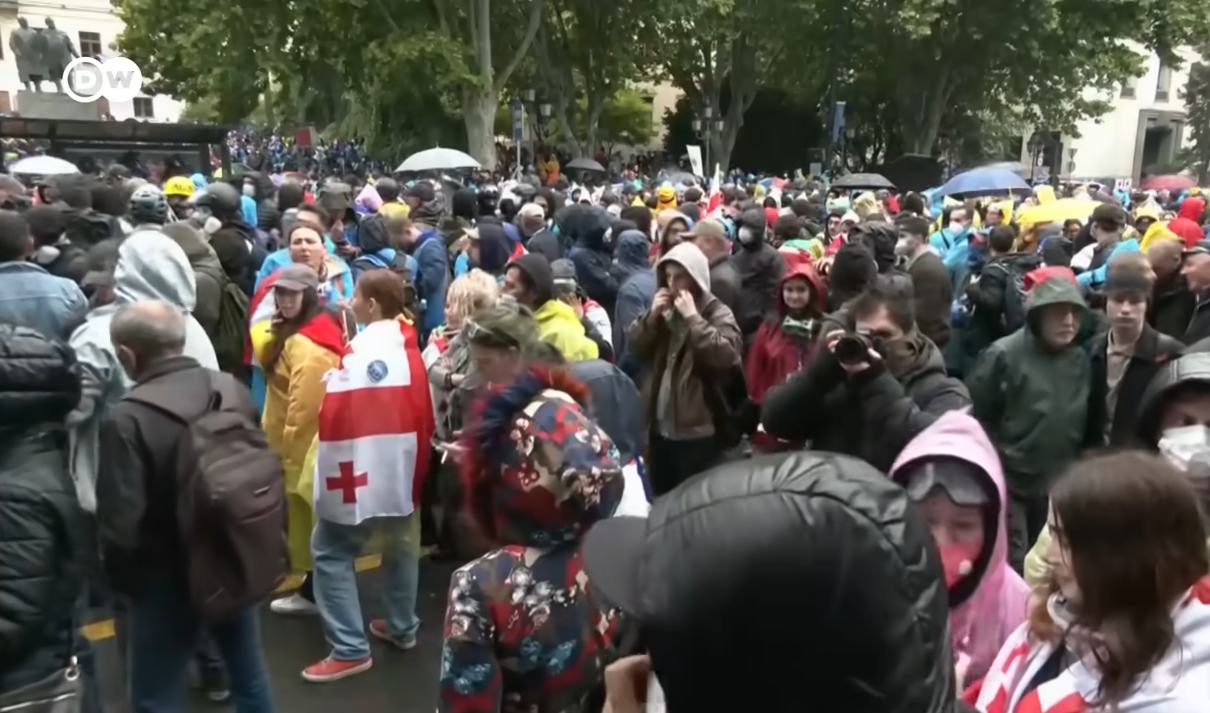

The government of the former Soviet republic of Georgia says it is close to finalizing a new law against so-called LGBTQ propaganda inspired by similar laws passed in Russia and Belarus in recent years, in what critics say is an attempt to maintain power by stoking divisions on a culturally sensitive issue.
The Georgian capital of Tbilisi has been rocked by protests for weeks as the ruling Georgian Dream party reintroduced a controversial “foreign agents” bill inspired by a similar Russian law, which requires any organization that receives funding from out of the country to register with the government as “organizations serving the interests of a foreign power.”
Critics say the bill is intended to silence and discredit media and civil society that is critical of the government.
May 17 saw intense protests marked by anti-government and pro-European demonstrators marking the International Day Against Homophobia, Biphobia, and Transphobia while anti-LGBTQ protesters, including Prime Minister Irakli Kobakhidze and church leaders took to the streets to mark the government’s competing “Family Purity Day,” Reuters reported.
The party had first introduced the foreign agents bill last year, but withdrew it after months of protests and condemnation from EU countries. The government reintroduced the bill this spring, with some observers suggesting it’s an attempt to tip this October’s national elections in their favor. For weeks, protesters have attempted to halt passage of the law, but parliament gave it final approval May 14. It was vetoed by President Salome Zurabishvili on Saturday, but the government has enough votes in parliament to override the veto.
The proposed anti-LGBTQ law would amend article 30 of the Georgian Constitution to include a host of regulations restricting LGBTQ rights. It would ban recognition of same-sex relationships, ban adoption by gay people or same-sex couples, ban medical interventions to facilitate gender change, restrict recognition of gender to that of biological sex, and ban advocacy for recognition of same-sex couples or trans people.
To pass, the bill would require at least a 3/4 vote of parliament (113 votes), or a 2/3 vote (100 votes) in each of two successive parliaments. The government currently controls 84 of the 150 seats in parliament, but likely believes it can pull enough votes from the opposition to pass the constitutional law.
Critics have noted that both laws put Georgia’s application to join the EU in jeopardy as they clearly attack the fundamental rights at the heart of the union. But while the EU has been sharply critical of the foreign agents law, its criticism of the anti-LGBTQ law has been far more muted.
Local activists say that the EU’s silence has been strategic, as any criticism would play into the hands of Georgian Dream, who claim that LGBTQ rights are a “pseudo-liberal ideology” advanced by a decadent West.
The timing of the bill is likely meant to further divide the opposition as protests mount against the foreign agents law. Georgian Dream has been sliding in the polls since it was returned to power in 2020, but still commands a plurality of support compared to the highly fractured opposition according to most polls.
Georgian Dream politicians have deep ties to Russia, and have increasingly sided with Russia in international and cultural disputes, including by refusing to impose sanction against Russia for the invasion of Ukraine. The support is ironic, considering that Russian forces invaded Georgia in 2008 and continues to support two unrecognized breakaway republics that resulted from that war.
On May 17, U.S. Rep. Joe Wilson (R-S.C.) of the House Foreign Affairs Committee announced that he plans to introduce legislation to sanction Georgian leaders over their assault on democracy and introduce incentives for the government to reverse course.
ILGA-Europe ranked Georgia 36th out of 48 countries, with a score of just 25 percent on its most recent Rainbow Europe Map this week.
UNITED KINGDOM

The Conservative government of the UK has directed schools in England to ban discussion of gender identity in schools and restrict sex education for children under age nine, in an update to statutory guidance issued to schools that is currently under review.
Although the guidance has not yet been released or put into effect, LGBTQ activists and government critics are already comparing the guidance to the notorious Thatcher-era Section 28, which banned discussion of homosexuality in all schools across the UK from 1988 until it was repealed in England and Wales in 2003 and in Scotland in 2000.
The UK has long been in the grip of an anti-trans moral panic, fostered by segments of the ruling Conservative Party that are hostile to trans people and influential British celebrities like “Harry Potter” creator JK Rowling who has long campaigned against trans people’s rights.
Last week, Prime Minister Rishi Sunak appeared on ITV’s daytime talk show “Loose Women,” where he complained that “gender ideology” was infiltrating UK schools.
“Children were being exposed to lots of different things,” Sunak said. “You know, we’ve got lots of people talking to kids, they were talking about [how] you can have 72 different gender identities.”
There is no evidence that children in UK schools are being taught that there are 72 different gender identities or are being taught to engage in inappropriate behavior.
London Mayor Sadiq Khan, who was recently reelected to a third term, blasted the government’s new policy as being harmful to the children the government claims to want to protect.
“We’ve just got to be a bit aware when we have these conversations that we’re conscious about the impact that this has on trans young people,” he said.
“Many of these people — young people — learn about these things through social media. You know, the proliferation of porn, and also the proliferation of misogynists like Andrew Tate. If we’re delaying proper, responsible teaching until later on, I worry about who’s going to be rebutting some of the nonsense on social media.”
Education Secretary Gillian Keegan tried to mollify critics by claiming that the new policy will not restrict discussion of adults who have undergone gender reassignment.
“Gender reassignment” is listed as protected characteristic under the 2010 Equality Act, but the act does not list “gender identity” or “gender expression” as protected characteristics.
“Let me be clear on gender ideology in schools,” Keegan said on BBC Radio 4’s “Today.” “The thing that we’re trying to stop is not gender reassignment. Gender reassignment is something that is a protected characteristic — that adults are allowed to reassign their gender, there’s a process that they go through for that. That is a protected characteristic, and that can be taught.
Gender identity and ideology is something different, and this is part of probably similar campaign groups that have been building this set of materials and this ideology,” she said.
Jo Morgan, the chief executive of Engendering Change, an organization that provides sex education workshops in schools, disputed the idea that schools are teaching children to be trans.
“They are concerned that schools are becoming breeding grounds for transgenderism. There’s no evidence to support that. What we are doing as educators is saying, this is in the news, in social media, it’s everywhere — let’s unpack it together and look at what sources of information you are being exposed to, let’s talk about how this relates to the Equality Act,” Morgan told the Guardian.
ILGA-Europe ranked the UK 15th out of 48 countries with a score of just 52 percent on its most recent Rainbow Europe report, citing a lack of legal protections for trans people and outdated procedures for legal gender recognition.
TAIWAN
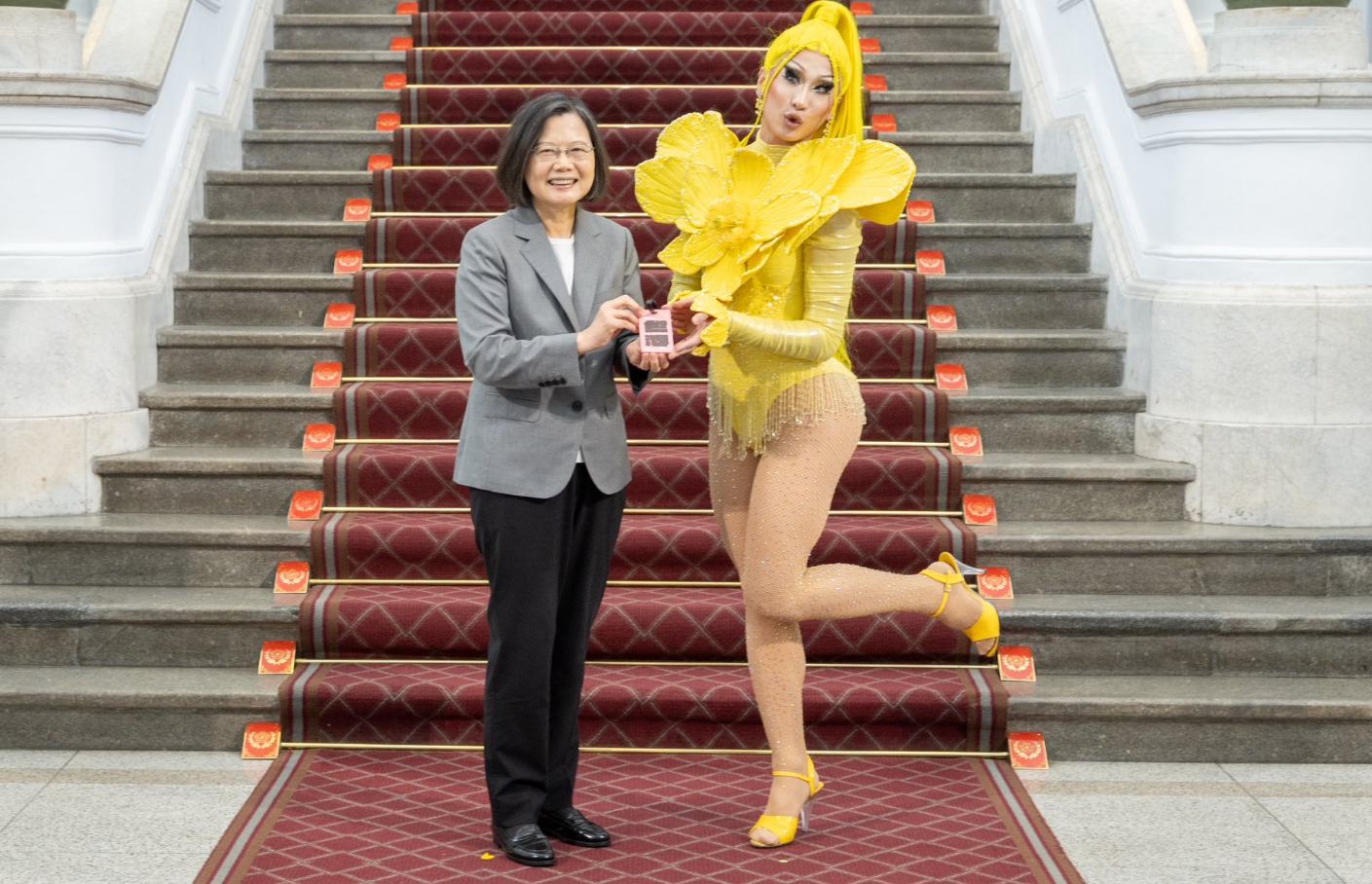

Outgoing Taiwanese President Tsai Ing-Wen hosted “RuPaul’s Drag Race” winner Nymphia Wind at a ceremony at her presidential office May 15, in a sign of the growing acceptance of LGBTQ people in the Asian island nation.
The Taiwanese-American performer Nymphia Wind was crowned the winner of season 16 of “RuPaul’s Drag Race” in an episode that aired April 19, taking home the crown and scepter and a cash prize of $200,000. She is the first person of East Asian descent to win the long-running reality competition series. American drag artist Raja, who is of Dutch-Indonesian ancestry, was the first “Drag Race” winner of Asian descent after taking the crown in season three.
Tsai had been quick to offer her congratulations to Wind, posting a message on Instagram just days after her victory. Less than a month later, Wind was in her office, where she performed a trio of songs in full drag — Lady Gaga’s “Marry the Night,” Taiwanese singer Huang Fei’s “Chase, Chase, Chase,” and Jolin Tsai’s gender equality hit “Womxnly,” which she performed with a quintet of backup dancers in drag.
“I want to thank you for demonstrating your fearless beauty, standing up and breaking down barriers,” Tsai said to Wind after her performance, noting that her win “will bring courage to many young people in Taiwan, so they stay fearless and stay true to their hearts.”
Under Tsai’s leadership, Taiwan has become a bastion of liberal values, including progressive attitudes toward LGBTQ people. Among recent landmarks, Taiwan legalized same-sex marriage and adoption, and it banned conversion therapy, and the capital Taipei hosts East Asia’s largest Pride festival.
“Thank you for your contributions to this country, so that I could grow up to be like this today,” Wind told Tsai after her performance. “Thank you for your eight years of dedication, becoming our Taiwan mother.”
Tsai stepped down May 20. Her successor, Vice President Lai Ching-te, last year became the most senior government official to march in Taipei’s Pride parade.
NEW ZEALAND

Activists are calling for greater access to gender-affirming surgeries after the “New Zealand Medical Journal” published a report of a trans teenager who attempted a self-mastectomy at home and had to be treated at hospital.
The teenager, an 18-year-old high school student, had reportedly watched a “how to” video on YouTube and prepared instruments for the surgery himself. He went to the hospital hours into the surgery after he became concerned that he had damaged a nerve while attempting to remove his left breast.
Surgeons at the hospital then removed both breasts, and he was discharged a day later. The report notes that the boy reported higher confidence and self-esteem at a post-operation interview a month later. The hospital’s mental health team assessed that he did not have a psychiatric disorder and was not suicidal, but that he had attempted the surgery as an act of desperation.
“Due to the long wait times of referral in the public healthcare system, an inability to afford a private consultation and the significant psychological stress of having breasts at an upcoming pool party he planned to complete a bilateral (double) self-mastectomy at home,” wrote the report’s authors, Wellington Regional Hospital doctors Mairarangi Haimona, Sue Hui Ong, and Scott Diamond.
Gender-affirming surgeries are covered by New Zealand’s healthcare system, but wait times for surgeries can be lengthy – 10 years or longer for “bottom surgery” by the only doctor in the country who performs it.
Top surgery can be accessed in the parallel private system for around NZ $15,000 (approximately $9,200) and is generally not covered by private health insurance, putting it out of reach for many.
“Transgender people often need to self-advocate for care in the public health system, but with increasing demand and associated psychological and possible physical harm it’s crucial for public services to be more accessible to an under-served population,” the report’s authors concluded.
Self-surgery is an incredibly risky option for trans people — complications can range from scarring to infection to death. And the surgeries may not even work if the patient is taken to the hospital and patched up due to complications.
Te Ahi Wi-Hongi, executive director of the advocacy group Gender Minorities Aotearoa, urges any trans person considering home surgery to avoid it and “hang in there.”
“It might seem right now it’s completely hopeless, but we went from a 40-year waiting list for genital reconstruction surgery to 10 years or less when in 2019 the government made changes [announcing $3 million funding for genital gender-affirming surgery],” Wi-Hongi told the New Zealand Herald.
Iran
Man stuck in Lebanon as Iran war escalates
Mario was traveling to India when conflict began on Feb. 28
The Washington Blade on March 6 spoke with a man who remains stuck in Lebanon because of the escalating Iran war.
Mario, who asked the Blade not to publish his last name, lives in the U.S., but was born in Lebanon. He decided to stop in the country to see his doctor before traveling to India for work.
Mario was about to board a flight at Rafic Hariri International Airport in Beirut, the Lebanese capital, on Feb. 28 when airline personnel announced “we cannot fly anymore” because authorities had closed the country’s airspace.
The U.S. and Israel earlier that day launched airstrikes against Iran.
One of them killed Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. Iran in response launched missiles and drones against Israel and Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Azerbaijan, Cyprus, and other countries.
An Iranian drone that hit a command center in Kuwait on March 1 killed six U.S. soldiers: Sgt. Declan Coady, Sgt. 1st Class Nicole Amor, Capt. Cody Khork, Sgt. 1st Class Noah Tietjens, Chief Warrant Officer 3 Robert Marzan, and Maj. Jeffrey O’Brien. Another American servicemember, Sgt. Benjamin Pennington, died on Sunday, a week after Iranian drones and missiles targeted the Prince Sultan Air Base in Saudi Arabia.
Iranian drones and missiles have also damaged civilian infrastructure, including hotels and airports in Dubai in the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait. An Iranian missile on March 1 killed nine people and injured 27 others in Beit Shemesh, Israel.
The war has left Mario and hundreds of thousands of others stranded in the Middle East.
“I had to come back home,” Mario told the Blade.
“Luckily, I’m with family,” he added.
‘War is between Israel and Hezbollah’
Hezbollah, an Iran-backed Shia militant group the U.S. and Israel have designated a terrorist organization, after Khamenei’s death launched rockets at Israel. The Jewish State in response has carried out airstrikes against Hezbollah targets across Lebanon.
Hamas militants on Oct. 7, 2023, killed upwards of 1,200 people when they launched a surprise attack against Israel from the Gaza Strip. Hezbollah the following day began to launch rockets into Israel.
An Israeli airstrike in Beirut on Sept. 27, 2024, killed Hassan Nasrallah, Hezbollah’s long-time leader. Iran four days later launched upwards of 200 ballistic missiles at Israel.
The U.S. helped broker a ceasefire between Israel and Lebanon that took effect on Nov. 27, 2024. Israel nevertheless continued to carry out airstrikes in Lebanon.
Israel on June 13, 2025, launched airstrikes against Iran that targeted the country’s nuclear and military facilities. The subsequent war, which lasted 12 days, prompted the cancellation of the annual Tel Aviv Pride parade.
Mario noted the Israeli airstrikes have targeted Hezbollah infrastructure in Dahiyah, a Beirut suburb that is predominantly Shia, and in southern Lebanon.
His family’s home is about five miles from downtown Beirut. Mario said there is a mountain “that separates me from the area that is being bombed, so I don’t even hear the sounds.”
“Lebanon is such an interesting juxtaposition, because depending on which area you are in, your quality of life can be different during these times,” he said. “Right now, the war is not between Israel and Lebanon as a government. The war is between Israel and Hezbollah.”
“If you are in the areas where Hezbollah is concentrated, then you are severely impacted,” added Mario. “If you are in other areas, even if they are Shia or … Muslims that usually align themselves with Hezbollah, you’re still relatively in a safe place, in a safe location.”
Israeli evacuation orders have prompted hundreds of thousands of people to flee their homes in Dahiyah and in southern Lebanon.
Mario said many of the evacuees are sleeping in their cars, or on the street. He also noted a video that showed a shepherd with his sheep and goats on a highway in downtown Beirut.
“He took his animals with him because he had to vacate where he was living,” said Mario. “That’s the first time you see in downtown Beirut maybe 100 goats walking the streets with two people sitting on jackasses and herding them.”
“It is very absurd,” he added.
The Lebanese government has opened schools and public shelters for people who have been displaced, but Mario said many of them do not have enough food. He also said gas prices have increased, and people are afraid to drive.
“It really saddens me seeing the kids affected by it,” said Mario. “Hezbollah made this decision, and it was a unilateral decision.”
“I doubt that the Shia people support them,” he added, referring to Hezbollah. “They cannot say it out loud that they do not support them, but I doubt people are happy within less than two years, for the second time in a row, to have to leave their homes and try to find a place to stay.”
Lebanese government urged to develop LGBTQ-inclusive plan for displaced people
Article 534 of Lebanon’s Penal Code states “any sexual intercourse contrary to the order of nature is punishable” by up to a year in prison. Several judges in recent years have opted not to use the statute to prosecute LGBTQ people who have been charged under it.
Helem, a Lebanese LGBTQ and intersex rights group, on March 4 called upon the Lebanese government and international NGOs to develop a response to the Israeli airstrikes that is “comprehensive, fair, and inclusive of all groups, without exception or discrimination.
“The experience of the previous war demonstrated that state response plans were not sufficiently inclusive of displaced LGBTQ+ individuals,” said Helem. “Many faced compounded challenges, including the inability to access state collective shelters, exposure to harassment or violence, difficulty accessing health and psychosocial services, and fear of disclosing their gender identity or sexual orientation due to stigma and discrimination.”
“Any emergency plan that fails to take the most vulnerable groups into account exposes their lives and dignity to additional risks,” added the group.
Helem also made the following requests:
• Integrating a rights-based and nondiscrimination approach in all stages of planning and implementation, ensuring safe and equal access to assistance and services.
• Training staff working in shelters and emergency response on principles of protection from gender-based violence and discrimination, including issues related to gender identity and sexual orientation.
• Reassessment of the currently adopted shelter model, which relies exclusively on the concept of the “traditional family” aligned with a specific social structure. In practice, this leads to the systematic exclusion of non-traditional families and individuals who do not belong to conventional family units, including LGBTQ+ individuals, survivors of domestic violence, migrant workers, and people without supportive family networks.
• Involving civil society organizations specialized in gender issues and LGBTQ+ rights in the design, implementation, and monitoring of the emergency response plan.
• Establishing clear monitoring and accountability standards to ensure that violations or discriminatory practices do not occur during the implementation of the emergency plan.
“Disasters and conflicts do not justify the suspension of rights or the neglect of marginalized groups. On the contrary, the need for a humanitarian approach grounded in dignity and equality becomes even more urgent in times of crisis.”
“Helem places its expertise and experience at the disposal of relevant authorities and affirms its readiness to cooperate to ensure that the emergency plan is more just, effective, and inclusive,” said Helem. “Dignity is indivisible, and protection must include everyone without exception.”
Colombia
Claudia López wins primary in Colombian presidential race
Former Bogotá mayor’s wife lost reelection bid on Sunday

Former Bogotá Mayor Claudia López on Sunday won her primary in the race to succeed Colombian President Gustavo Petro.
López, a centrist who is running as an independent, defeated Leonardo Huerta in the “Consulta de las Soluciones” primary.
López was the Colombian capital’s mayor from 2020-2023. She was a member of the Colombian Senate from 2014-2018.
López is running to succeed Petro, the country’s first leftist president who cannot seek a second consecutive term under Colombia’s constitution. Other presidential candidates who won their respective parties’ primaries on Sunday include Sen. Iván Cepeda, a member of Petro’s Historic Pact party, and Sen. Paloma Valencia of the conservative Democratic Center, the country’s main opposition party that former President Álvaro Uribe leads.
Juan Daniel Oviedo, who finished second in the Democratic Center’s primary, is openly gay.
The first-round of Colombia’s presidential election will take place on May 31.
Polls indicate López is trailing Cepeda and Valencia, who are considered the two frontrunners.
A second round will take place is no candidate receives at least 50 percent of the vote on May 31. López would become Colombia’s first female and first lesbian president if she wins the election.
López’s wife loses Senate seat
Colombia’s congressional elections also took place on Sunday.
Former Congressman Mauricio Toro, a member of the center-left Green Alliance party, in 2018 became the first openly gay man elected to Colombian Congress when he won a seat in the House of Representatives.
He lost his reelection bid in 2022. Voters on Sunday elected Toro for a second term.
Congresswoman María del Mar Pizarro, a bisexual Historic Pact member, won re-election.
Caribe Afirmativo, a Colombian LGBTQ and intersex rights group, notes only two of the 33 openly LGBTQ congressional candidates won their respective races. Among those who lost is Sen. Angélica Lozano, a bisexual woman who in 2018 became the first openly LGBTQ person elected to the Colombian Senate.
Lozano is married to López.
Lozano in a message posted to her Instagram page expressed “heartfelt gratitude to everyone for their support and love.”
“I will end my work in Congress on a high note by ensuring (the) child support and service contractor protection bills will become a reality in June,” she said.
Uganda
Ugandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow
Clare Byarugaba founded PFLAG-Uganda
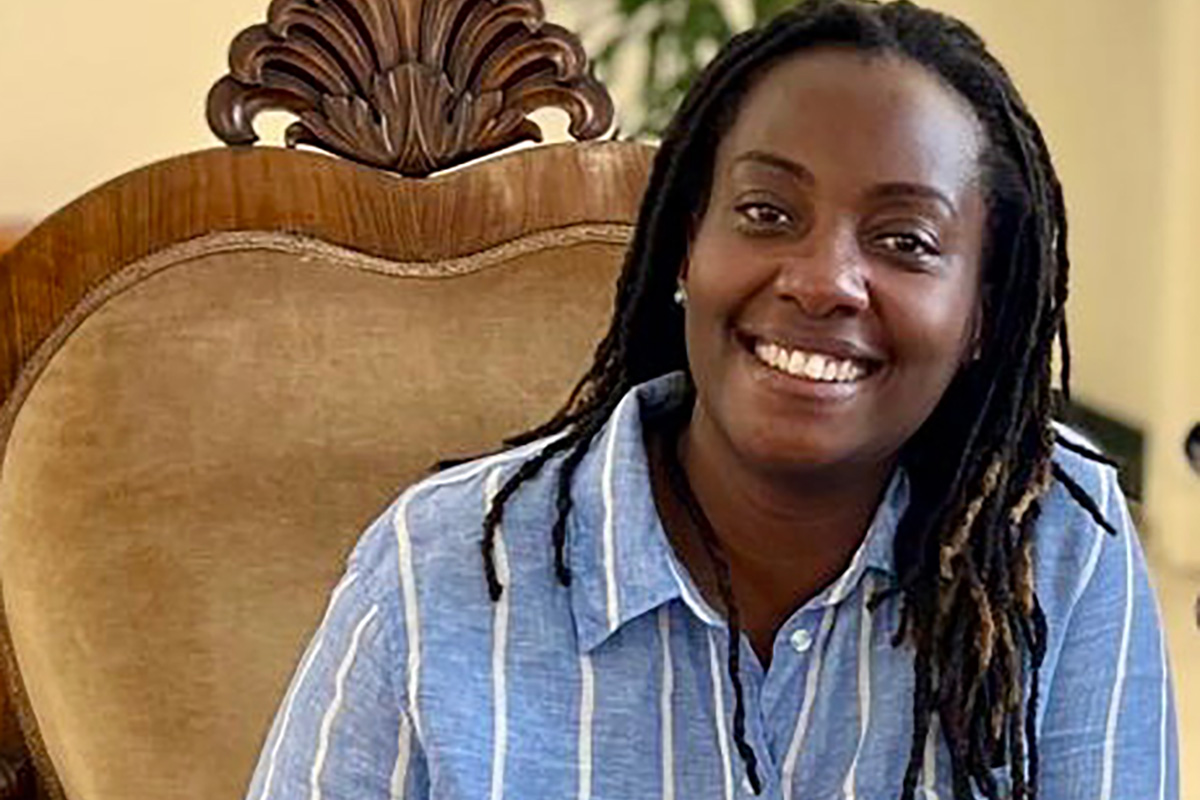

The Charles F. Kettering Foundation has named a prominent Ugandan LGBTQ activist as one of its 2026 fellows.
Clare Byarugaba, founder of PFLAG-Uganda, is one of the foundation’s five 2026 Global Fellows.
Byarugaba, among other things, has been a vocal critic of Uganda’s Anti-Homosexuality Act. Byarugaba in 2024 met with Pope Francis — who criticized criminalization laws during his papacy — at the Vatican.
The foundation on its website says it “is dedicated to bringing research and people together to make the promise of democracy real for everyone, everywhere.”
“Clare is the kind of hero who rushes toward the emergency to help,” said PFLAG CEO Brian K. Bond in a Feb. 27 statement to the Washington Blade. “She founded PFLAG-Uganda as the country pushed to criminalize homosexuality and those who support LGBTQ+ people. Yet, she never hesitated in her courage, telling us that families wanted to organize to keep their LGBTQ+ loved ones safe, and PFLAG was the way to do it. Clare Byarugaba not only deserves this honor, but she will use her compassion and experience to teach the world about LGBTQ+ advocacy as a Kettering Global Fellow.”




















