World
Out in the World: LGBTQ news from Europe and Asia
The UK’s general election will take place on July 4

UNITED KINGDOM
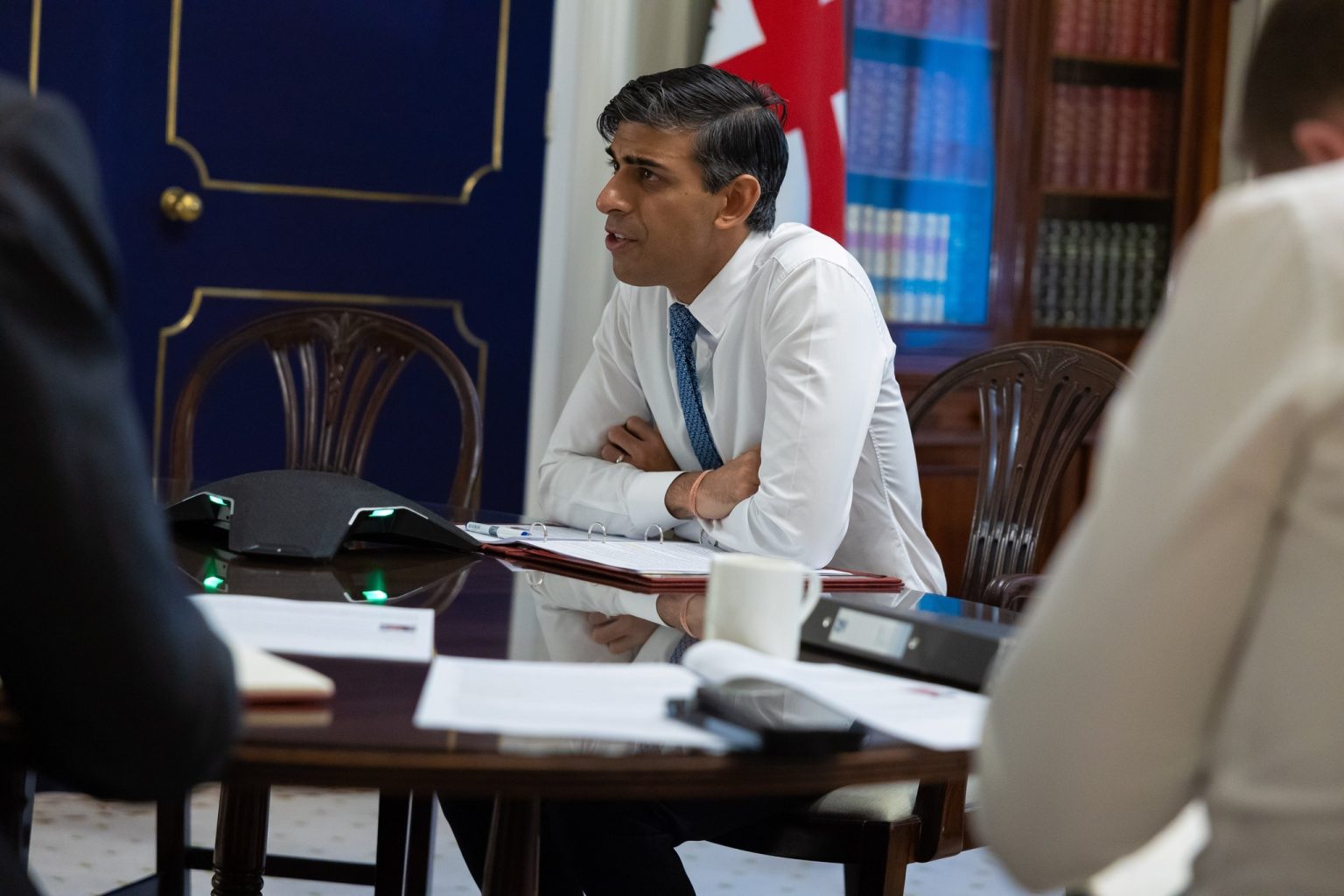

British Prime Minister Rishi Sunak called a long-anticipated election this week, sending UK voters to the polls July 4 and potentially spelling the end of 13 tumultuous years of Conservative Party rule in the UK.
Polls have long indicated that the UK Tories are deeply unpopular, putting them more than twenty points behind the left-leaning UK Labour Party, who are favored to win the election with a sweeping majority.
The last several years of UK politics under a succession of Tory prime ministers — five since 2011 — have been rocky, as the government has tried to manage pulling the UK out of the EU, a growing migrant crisis, and a succession of worsening domestic issues, not least of which has been the government’s handling of LGBTQ and particularly transgender issues.
The Tories have failed to bring in a long-promised conversion therapy ban, amid a growing moral panic around the existence of trans people, driven as much by British celebrities like JK Rowling as by a Tory caucus that’s grown increasingly hostile to LGBTQ issues over its time in power.
In fact, it was Tory Prime Minister David Cameron who introduced same-sex marriage legislation for England and Wales in 2013 — although it only passed parliament with the support of Labour, as the issue split the Conservatives.
Just a few years later, Tory politicians would be racing to declare themselves opposed to even recognizing the existence of trans people. The government has shelved a long-promised conversion therapy ban, and vetoed a law passed by the Scottish government that would have allowed trans people to self-determine their legal gender, as is the emerging norm in many countries.
The UK has even slipped from first to 15th place on ILGA-Europe’s ranking of European countries’ legislated LGBTQ rights during this time.
The Labour Party has not yet released a specific party manifesto as it relates to LGBTQ issues. However, leader Keir Starmer has pledged to introduce a “no loopholes” trans-inclusive ban on conversion therapy and has discussed reforming the UK’s gender recognition system to make it easier for trans people to update their legal gender — although the party no longer supports self-identification.
Starmer’s more recent statements on trans issues have caused concern for some activists. He recently came out in support of the findings of the National Health Service’s Cass Review on gender care for minors, which recommended a more cautious approach to prescribing care for trans youth.
He also recently voiced support for bans on trans women participating in women’s sports or accessing women’s medical centers, and for regulations requiring schools to out trans children to their parents.
“It’s[a] betrayal, a Judas move by Keir Starmer,” trans journalist India Willoughby told PinkNews. They have thrown us under the bus purely because they don’t have the stomach to fight.”
Sunak was required to call the election by the end of the year, but calling it early has put some of the opposition parties in a tight situation — most have not yet recruited a full slate of candidates to stand in all 650 electoral districts or drafted a complete party manifesto.
GERMANY

The Lesbian and Gay Association in Germany has launched a new campaign to amend Germany’s Basic Law to ban discrimination based on sexual orientation or identity.
The German Basic Law was enacted 75 years ago, in the shadow of World War II and was intended to protect freedoms from the evils that had been inflicted by the Nazi regime. Accordingly, Article 3.1 declares that “all persons shall be equal before the law,” while Article 3.3 expands that to list specific criteria that cannot be used to discriminate between individuals.
“No person shall be favored or disfavored because of sex, parentage, race, language, homeland and origin, faith or religious or political opinions. No person shall be disfavored because of disability,” the article says.
LSVD says that the exclusion of sexual orientation and gender identity from that list exposes queer people to discrimination. As an example, they point to Paragraph 175 of the Criminal Code, a Nazi-era law that criminalized same-sex intimacy that remained on the books until 1994.
“In 1949, homosexuals and bisexuals were the only group of victims of the National Socialists who were deliberately not included in Article 3.3. This is because men who loved people of the same sex were also subjected to the often life-destroying persecution under Paragraph 175 of the Criminal Code in democratic post-war Germany,” LSVD says in a press release.
In recent years, the Federal Constitutional Court has begun to read LGBTQ rights into the Basic Law, ruling that “sex” includes “gender identity” and that “sexual orientation” is akin to the other traits listed in Article 3.3. But LSVD says that without explicit inclusion in the Basic Law, discrimination has persisted.
“Many people from the queer community say that they experience discrimination by the police and authorities,” LSVD’s statement says. “Because the Basic Law also applies to state bodies, the extension of Article 3.3 could finally make discrimination against LGBTIQ* by state bodies and their employees legally punishable. Anyone who is not explicitly mentioned there runs the risk of being ignored in political and social reality.”
The LSVD says there are already plenty of examples of constitutions that protect LGBTQ+ rights, including in the German states of Berlin, Brandenberg, Bremen, Saarland, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia, as well as the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union.
LGBTQ activists in Germany have become particularly concerned to secure their rights as the far-right Alternative for Germany party has climbed in the polls and could become part of a future government.
“Making our constitution storm-proof is more urgent than ever. If right-wing extremists in Germany return to a position of power in future elections, we LGBTIQ* people face gradual disenfranchisement, social marginalization and, with it, a massive increase in hate violence and state discrimination,” LSVD says. “Without explicit protection against discrimination in the constitution, we would be largely defenseless against an authoritarian or post-fascist government such as those we are currently experiencing in Hungary or Italy.”
To pass into law, the constitutional amendment would require a 2/3 majority vote in both houses of the German parliament. While the current government has expressed support for the amendment, it would need the support of the Christian Democrats to reach the required majority.
SWITZERLAND

The Swiss canton of Valais passed a law banning conversion therapy by a vote of 106-21 in the cantonal parliament on May 16.
The discredited practice, which seeks to change a person’s sexual orientation or gender identity by exposing them to aversion methods that have been called torture by experts, has also been banned in the canton of Neuchatel since 2023.
The conversion therapy ban was included in a new Health Act that was supported by all parties in the Valais parliament except for the right-wing Swiss People’s Party.
“We are sending out a clear signal that these conversion therapies are unacceptable and have no place in Valais,” says Matthias Reynard, head of the Valais Department of Health.
A nationwide ban on conversion therapy has been under consideration by the federal parliament for several years. The lower house passed a resolution calling for a ban in December 2022, but the motion has stalled in the upper house.
Last month, the federal parliament voted to wait for the government to present its own conversion therapy bill, rather than push ahead with bills that had been submitted by two cantons to ban the practice.
But Switzerland’s cantons aren’t waiting for federal lawmakers. Local bills to ban conversion therapy are also under consideration in the cantons of Geneva, Zurich, Bern, and Vaud.
“Conversion therapy affects a significant part of our community. The latest figures from the Swiss LGBTIQ panel show that 9.5 percent of people who belong to a sexual minority and 15.5 percent of people who belong to a gender minority are affected,” Sandro Niederer, managing director of TGNS, told the news site Mannschaft. “The psychological consequences of such practices are undisputed — the ban is a positive signal for all LGBTIQ people!”
Many of Switzerland’s European neighbors already ban the practice. France, Germany, Belgium, Spain, Malta, Greece, Iceland, Norway, and Cyprus all ban conversion therapy, while neighboring Austria has had a ban under consideration for several years.
ALBANIA
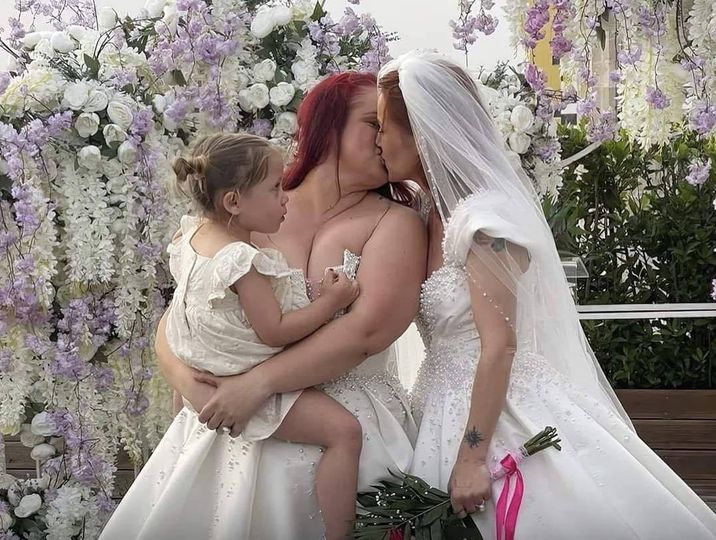

A lesbian couple held a symbolic wedding ceremony at on the roof of city hall overlooking the heart of the Albanian capital city of Tirana on May 19 in a protest against the country’s lack of legal recognition for same-sex couples.
The couple, Alba Ahmetaj and Edlira Mara, applied for a legal marriage at the municipal office on May 17, asserting their right under Article 53 of the Albanian constitution, which states that “everyone has the right to marry and have a family.” However, the current Family Code restricts marriage to opposite-sex couples only.
Mara posted on her Facebook account that the restriction violates the constitution.
“Our request for a declaration of marriage symbolizes the first link in a long and difficult, but above all just, struggle. We are determined to follow the legal path and respect the procedures and institutions of our country, challenging the discriminatory content of the Family Code, to seek the recognition of our right to marry, equally with every other couple in Albania,” she wrote.
The ceremony has caused outrage in Albanian society. The couple have reported receiving death threats for appearing in public both before and after their public wedding.
Mara and Ahmetaj wanted to hold a religious ceremony but could not a find a religious official willing to bless the union in Albania. Instead, they flew in two priests from the U.K. to perform the ceremony.
The Albanian Catholic Church criticized the ceremony and distanced itself from the priests involved.
“Even though he appears as a Catholic clergyman, [he] has no connection with the Catholic Church and represents nothing of us,” Mark Pashkia, a spokesperson for the church, told Balkan Insight.
The couple involved in the suit are also raising twin daughters born through IVF three years ago. They have struggled to legally register the girls as their daughters because Albanian law only recognizes opposite-sex parents. They were forced to register Mara as the girls’ single mother, meaning Ahmetaj would have no rights over the girls if Mara dies or becomes seriously ill.
They sued the government for the right to be recognized as equal parents, but lost at the High Court. The couple are appealing the decision, and say they will fight all the way to the European Court of Human Rights if they have to.
Local LGBTQ activists have filed cases against the government seeking same-sex relationship recognition, but the cases have not progressed in local courts.
Years ago, the government had floated the idea of legalizing same-sex marriage, but the proposal was scrapped amid pushback from religious leaders in the Muslim-majority country.
In neighboring Kosovo, which is also an Albanian-speaking country, Prime Minister Albin Kurti has pledged to reintroduce a new draft Civil Code that would legalize civil unions and open the door to same-sex marriage, but he has faced pushback from Muslim lawmakers in his own party, who voted down the draft code in 2022.
Neighboring Greece legalized same-sex marriage earlier this year.
SOUTH KOREA

(Human Rights Watch) South Korea’s National Health Insurance Service should extend benefits to same-sex partners, Human Rights Watch said in an amicus brief filed before the country’s Supreme Court on May 16, 2024. The agency extends dependent benefits to heterosexual couples who are deemed to be in a de facto marriage, but has refused to extend those benefits to same-sex couples in a similar position.
The Supreme Court is currently considering whether the agency has impermissibly discriminated against a same-sex couple that was refused dependent benefits. In 2023, the Seoul High Court ruled in favor of the couple, concluding that the refusal to extend benefits constituted discrimination based on sexual orientation. The health agency appealed to the Supreme Court.
“The Seoul High Court correctly observed that the health agency’s refusal to recognize same-sex couples is discrimination,” said Lina Yoon, senior Korea researcher at Human Rights Watch. “We hope the Supreme Court will affirm the principle that nobody should be denied benefits solely because of their sexual orientation.”
The couple who brought the case had held a symbolic wedding ceremony in 2019, and one of the men registered his partner with the National Health Insurance Service as his spouse in 2020. The agency later revoked the partner’s dependent benefits following media attention to its effective recognition of a same-sex couple.
Human Rights Watch’s brief examines international and regional precedents for state recognition of same-sex partnerships, the status of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in South Korea, and the growing recognition of same-sex partnerships elsewhere in Asia.
South Korea has not created any framework for recognizing and supporting same-sex couples. The absence of any legal framework or protections for same-sex partners leaves LGBT people with few avenues to protect their relationships with partners and children, to safeguard their shared finances and property, and to access state benefits designed to support couples and families.
The government’s failure to recognize same-sex partnerships falls short of its human rights obligations, Human Rights Watch said. The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights has concluded that UN member states “have a positive obligation to provide legal recognition to couples, regardless of sexual orientation, gender identity and sex characteristics, as well as to their children,” and to extend those benefits offered to heterosexual couples without discrimination.
Among regional human rights bodies, the Inter-American Court of Human Rights has said that states must extend the right to marry to same-sex couples, while the European Court of Human Rights has said that states must create some form of legal recognition and protection for same-sex relationships.
As Human Rights Watch and others have noted, South Korea also lacks comprehensive protections from discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity. Despite strong public support for a comprehensive anti-discrimination law, lawmakers have repeatedly failed to enact basic protections that would prohibit discrimination in employment, education, and other areas.
In failing to protect LGBT rights, South Korea is out of step with trends elsewhere in the region. In 2019, Taiwan became the first jurisdiction in Asia to extend the right to marry to same-sex couples, and Australia and New Zealand have subsequently recognized the right to marry as well.
Courts in Japan and Thailand have expressed concern about the lack of partnership recognition in those contexts, and Nepal’s supreme court has extended interim recognition of the right to marry while it considers a marriage equality case.
A growing number of states in the region also prohibit discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation. Australia, Fiji, Macao, the Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Mongolia, New Zealand, Thailand, and Tuvalu have prohibited sexual orientation discrimination in employment and other fields.
“South Korea’s lawmakers have failed to provide basic protection for same-sex couples by dragging their feet on nondiscrimination and partnership bills,” Yoon said. “South Korea’s courts now have the chance to uphold the state’s human rights obligations by ensuring that the state does not discriminate in the material benefits it does offer to committed couples.”
Iran
Man stuck in Lebanon as Iran war escalates
Mario was traveling to India when conflict began on Feb. 28
The Washington Blade on March 6 spoke with a man who remains stuck in Lebanon because of the escalating Iran war.
Mario, who asked the Blade not to publish his last name, lives in the U.S., but was born in Lebanon. He decided to stop in the country to see his doctor before traveling to India for work.
Mario was about to board a flight at Rafic Hariri International Airport in Beirut, the Lebanese capital, on Feb. 28 when airline personnel announced “we cannot fly anymore” because authorities had closed the country’s airspace.
The U.S. and Israel earlier that day launched airstrikes against Iran.
One of them killed Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. Iran in response launched missiles and drones against Israel and Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Azerbaijan, Cyprus, and other countries.
An Iranian drone that hit a command center in Kuwait on March 1 killed six U.S. soldiers: Sgt. Declan Coady, Sgt. 1st Class Nicole Amor, Capt. Cody Khork, Sgt. 1st Class Noah Tietjens, Chief Warrant Officer 3 Robert Marzan, and Maj. Jeffrey O’Brien. Another American servicemember, Sgt. Benjamin Pennington, died on Sunday, a week after Iranian drones and missiles targeted the Prince Sultan Air Base in Saudi Arabia.
Iranian drones and missiles have also damaged civilian infrastructure, including hotels and airports in Dubai in the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait. An Iranian missile on March 1 killed nine people and injured 27 others in Beit Shemesh, Israel.
The war has left Mario and hundreds of thousands of others stranded in the Middle East.
“I had to come back home,” Mario told the Blade.
“Luckily, I’m with family,” he added.
‘War is between Israel and Hezbollah’
Hezbollah, an Iran-backed Shia militant group the U.S. and Israel have designated a terrorist organization, after Khamenei’s death launched rockets at Israel. The Jewish State in response has carried out airstrikes against Hezbollah targets across Lebanon.
Hamas militants on Oct. 7, 2023, killed upwards of 1,200 people when they launched a surprise attack against Israel from the Gaza Strip. Hezbollah the following day began to launch rockets into Israel.
An Israeli airstrike in Beirut on Sept. 27, 2024, killed Hassan Nasrallah, Hezbollah’s long-time leader. Iran four days later launched upwards of 200 ballistic missiles at Israel.
The U.S. helped broker a ceasefire between Israel and Lebanon that took effect on Nov. 27, 2024. Israel nevertheless continued to carry out airstrikes in Lebanon.
Israel on June 13, 2025, launched airstrikes against Iran that targeted the country’s nuclear and military facilities. The subsequent war, which lasted 12 days, prompted the cancellation of the annual Tel Aviv Pride parade.
Mario noted the Israeli airstrikes have targeted Hezbollah infrastructure in Dahiyah, a Beirut suburb that is predominantly Shia, and in southern Lebanon.
His family’s home is about five miles from downtown Beirut. Mario said there is a mountain “that separates me from the area that is being bombed, so I don’t even hear the sounds.”
“Lebanon is such an interesting juxtaposition, because depending on which area you are in, your quality of life can be different during these times,” he said. “Right now, the war is not between Israel and Lebanon as a government. The war is between Israel and Hezbollah.”
“If you are in the areas where Hezbollah is concentrated, then you are severely impacted,” added Mario. “If you are in other areas, even if they are Shia or … Muslims that usually align themselves with Hezbollah, you’re still relatively in a safe place, in a safe location.”
Israeli evacuation orders have prompted hundreds of thousands of people to flee their homes in Dahiyah and in southern Lebanon.
Mario said many of the evacuees are sleeping in their cars, or on the street. He also noted a video that showed a shepherd with his sheep and goats on a highway in downtown Beirut.
“He took his animals with him because he had to vacate where he was living,” said Mario. “That’s the first time you see in downtown Beirut maybe 100 goats walking the streets with two people sitting on jackasses and herding them.”
“It is very absurd,” he added.
The Lebanese government has opened schools and public shelters for people who have been displaced, but Mario said many of them do not have enough food. He also said gas prices have increased, and people are afraid to drive.
“It really saddens me seeing the kids affected by it,” said Mario. “Hezbollah made this decision, and it was a unilateral decision.”
“I doubt that the Shia people support them,” he added, referring to Hezbollah. “They cannot say it out loud that they do not support them, but I doubt people are happy within less than two years, for the second time in a row, to have to leave their homes and try to find a place to stay.”
Lebanese government urged to develop LGBTQ-inclusive plan for displaced people
Article 534 of Lebanon’s Penal Code states “any sexual intercourse contrary to the order of nature is punishable” by up to a year in prison. Several judges in recent years have opted not to use the statute to prosecute LGBTQ people who have been charged under it.
Helem, a Lebanese LGBTQ and intersex rights group, on March 4 called upon the Lebanese government and international NGOs to develop a response to the Israeli airstrikes that is “comprehensive, fair, and inclusive of all groups, without exception or discrimination.
“The experience of the previous war demonstrated that state response plans were not sufficiently inclusive of displaced LGBTQ+ individuals,” said Helem. “Many faced compounded challenges, including the inability to access state collective shelters, exposure to harassment or violence, difficulty accessing health and psychosocial services, and fear of disclosing their gender identity or sexual orientation due to stigma and discrimination.”
“Any emergency plan that fails to take the most vulnerable groups into account exposes their lives and dignity to additional risks,” added the group.
Helem also made the following requests:
• Integrating a rights-based and nondiscrimination approach in all stages of planning and implementation, ensuring safe and equal access to assistance and services.
• Training staff working in shelters and emergency response on principles of protection from gender-based violence and discrimination, including issues related to gender identity and sexual orientation.
• Reassessment of the currently adopted shelter model, which relies exclusively on the concept of the “traditional family” aligned with a specific social structure. In practice, this leads to the systematic exclusion of non-traditional families and individuals who do not belong to conventional family units, including LGBTQ+ individuals, survivors of domestic violence, migrant workers, and people without supportive family networks.
• Involving civil society organizations specialized in gender issues and LGBTQ+ rights in the design, implementation, and monitoring of the emergency response plan.
• Establishing clear monitoring and accountability standards to ensure that violations or discriminatory practices do not occur during the implementation of the emergency plan.
“Disasters and conflicts do not justify the suspension of rights or the neglect of marginalized groups. On the contrary, the need for a humanitarian approach grounded in dignity and equality becomes even more urgent in times of crisis.”
“Helem places its expertise and experience at the disposal of relevant authorities and affirms its readiness to cooperate to ensure that the emergency plan is more just, effective, and inclusive,” said Helem. “Dignity is indivisible, and protection must include everyone without exception.”
Colombia
Claudia López wins primary in Colombian presidential race
Former Bogotá mayor’s wife lost reelection bid on Sunday

Former Bogotá Mayor Claudia López on Sunday won her primary in the race to succeed Colombian President Gustavo Petro.
López, a centrist who is running as an independent, defeated Leonardo Huerta in the “Consulta de las Soluciones” primary.
López was the Colombian capital’s mayor from 2020-2023. She was a member of the Colombian Senate from 2014-2018.
López is running to succeed Petro, the country’s first leftist president who cannot seek a second consecutive term under Colombia’s constitution. Other presidential candidates who won their respective parties’ primaries on Sunday include Sen. Iván Cepeda, a member of Petro’s Historic Pact party, and Sen. Paloma Valencia of the conservative Democratic Center, the country’s main opposition party that former President Álvaro Uribe leads.
Juan Daniel Oviedo, who finished second in the Democratic Center’s primary, is openly gay.
The first-round of Colombia’s presidential election will take place on May 31.
Polls indicate López is trailing Cepeda and Valencia, who are considered the two frontrunners.
A second round will take place is no candidate receives at least 50 percent of the vote on May 31. López would become Colombia’s first female and first lesbian president if she wins the election.
López’s wife loses Senate seat
Colombia’s congressional elections also took place on Sunday.
Former Congressman Mauricio Toro, a member of the center-left Green Alliance party, in 2018 became the first openly gay man elected to Colombian Congress when he won a seat in the House of Representatives.
He lost his reelection bid in 2022. Voters on Sunday elected Toro for a second term.
Congresswoman María del Mar Pizarro, a bisexual Historic Pact member, won re-election.
Caribe Afirmativo, a Colombian LGBTQ and intersex rights group, notes only two of the 33 openly LGBTQ congressional candidates won their respective races. Among those who lost is Sen. Angélica Lozano, a bisexual woman who in 2018 became the first openly LGBTQ person elected to the Colombian Senate.
Lozano is married to López.
Lozano in a message posted to her Instagram page expressed “heartfelt gratitude to everyone for their support and love.”
“I will end my work in Congress on a high note by ensuring (the) child support and service contractor protection bills will become a reality in June,” she said.
Uganda
Ugandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow
Clare Byarugaba founded PFLAG-Uganda
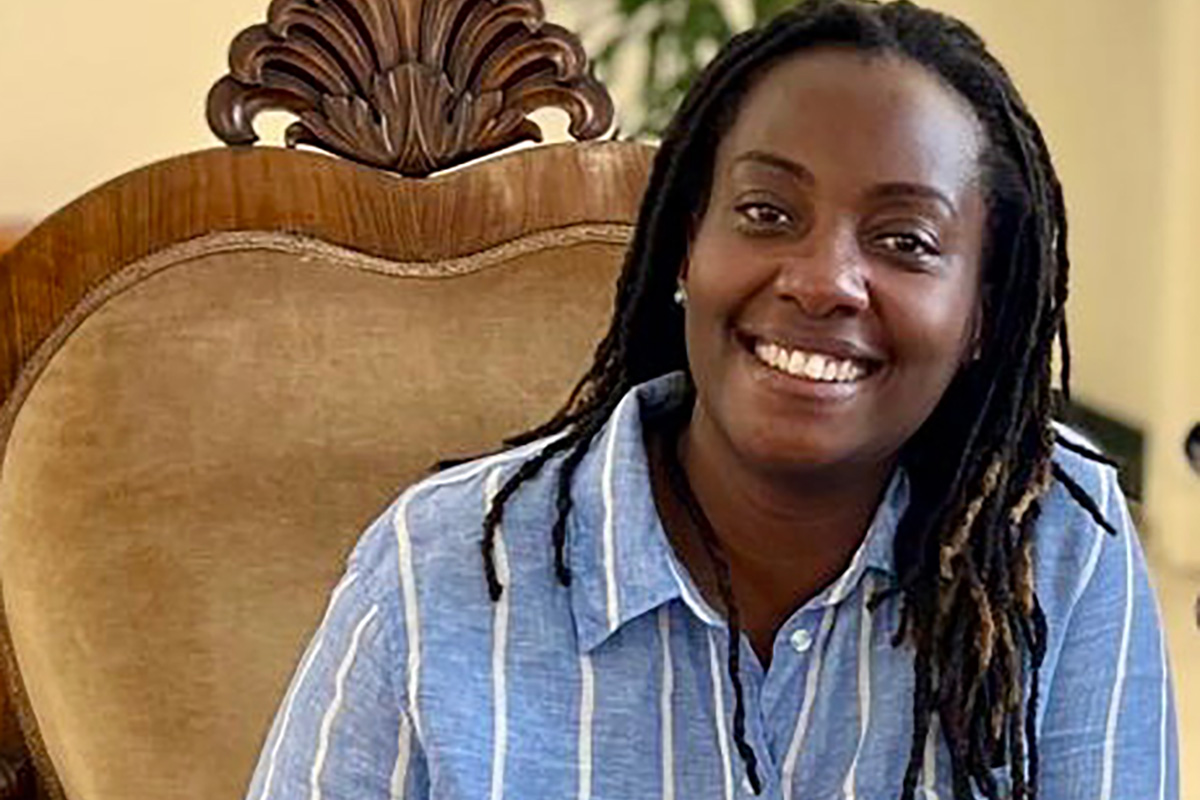

The Charles F. Kettering Foundation has named a prominent Ugandan LGBTQ activist as one of its 2026 fellows.
Clare Byarugaba, founder of PFLAG-Uganda, is one of the foundation’s five 2026 Global Fellows.
Byarugaba, among other things, has been a vocal critic of Uganda’s Anti-Homosexuality Act. Byarugaba in 2024 met with Pope Francis — who criticized criminalization laws during his papacy — at the Vatican.
The foundation on its website says it “is dedicated to bringing research and people together to make the promise of democracy real for everyone, everywhere.”
“Clare is the kind of hero who rushes toward the emergency to help,” said PFLAG CEO Brian K. Bond in a Feb. 27 statement to the Washington Blade. “She founded PFLAG-Uganda as the country pushed to criminalize homosexuality and those who support LGBTQ+ people. Yet, she never hesitated in her courage, telling us that families wanted to organize to keep their LGBTQ+ loved ones safe, and PFLAG was the way to do it. Clare Byarugaba not only deserves this honor, but she will use her compassion and experience to teach the world about LGBTQ+ advocacy as a Kettering Global Fellow.”
-

 National5 days ago
National5 days ago13 HIV/AIDS activists arrested on Capitol Hill
-

 Florida4 days ago
Florida4 days agoFla. Senate passes ‘Anti-Diversity’ bill that could repeal local LGBTQ protections
-

 Uganda4 days ago
Uganda4 days agoUgandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow
-

 Celebrity News4 days ago
Celebrity News4 days agoLiza Minnelli makes surprise appearance at GLAAD Media Awards




















