World
Gay Nigerian priest makes religion serve LGBTQ people
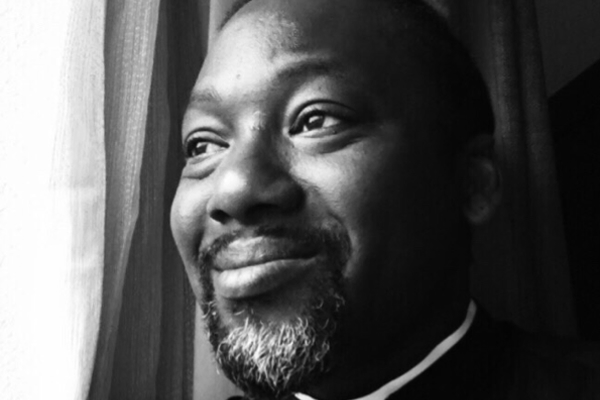
Rev. Jide Macaulay founded House of Rainbow

It is impossible to speak of queer identity and culture without acknowledging the important role religion has played in shaping it throughout history. Whether it’s Pope Francis praising the work an American priest has done to affirm LGBTQ identity, or a Republican legislator rebuking the existence of transgender people by invoking scripture from the Bible, religion and spirituality unquestionably influence conversations about sexual identity in the U.S. and how American society would like for people to manifest their sexuality.
A significant portion of LGBTQ people in the U.S. are religious.
A study the UCLA School of Law’s Williams Institute conducted in 2020 found that 5.3 million LGBTQ adults are religious with almost half of this metric identifying as “highly religious.” Forty percent of those between ages 18 and 35 are religious, and 65 percent percent of those over 65 identify as religious as well. In addition, 71 percent of Black LGBTQ adults in the U.S. are religious.
The Washington Blade recently spoke with Rev. Jide Macaulay, founder and CEO of the London-based House of Rainbow CIC, to talk about his work as a gay Black African Christian priest.
Macaulay was born in London and grew up in Ikeja, the boisterous capital of Nigeria’s Lagos State. He was born into a religious family to parents who he described to the Blade during a 2017 interview as “very dedicated Christians.” His father was one of Nigeria’s leading theologians, so Macaulay’s upbringing was naturally Christian-centric, with him being involved in the church from a young age.
As a budding adult, Macaulay pursued theology as a profession and became an ordained minister in 1998 after training with his father. After a two-year hiatus from the church, he joined the Metropolitan Community Church in London to study theology and later joined its congregation as a minister in 2003. Macaulay says it was there that he became confident in his understanding that “God loves gay people regardless of all these messages of it being a taboo or abomination.”
Sheathed with this conviction, Macaulay moved back to Nigeria to create an environment that mimics that which he had experienced at the Metropolitan Community Church.
“It became important to me to go to Nigeria to create the same space and tell LGBTQ people that ‘God loves you just the way you are,’” says Macaulay. “I embodied a lot of the spirit of the human rights church that came out of the origin of the Metropolitan Community Church.”
Macaulay started House of Rainbow under this ideology on Sept. 2, 2006. This weekly gathering of LGBTQ Christians initially began with 34 congregants, but the congregation grew rapidly to a point where Macaulay “didn’t know what to do with all the people.” He says the growth “perplexed” him as he didn’t realize that House of Rainbow was so popular.
House of Rainbow encountered problems that emanated from operating in a country with virulent homophobic laws, despite its popularity. Many congregants were physically attacked for identifying as queer, and Macaulay recalls individuals emerging to church with broken noses and arms. The media also caught wind of House of Rainbow’s weekly gatherings and chaos ensued.
The culmination of these events forced Macaulay to leave Nigeria after two years. House of Rainbow remained steadfast with its mission to create a community for LGBTQ Christians and soldiered on for a couple of more years before it eventually dissolved.
“It’s unfortunate, now, that as I speak to you we do not have a House of Rainbow community in Nigeria,” says Macaulay. “We still have people connected [to the community], but we don’t have a physical presence or anyone leading it.”
House of Rainbow’s reach has nevertheless now become global, with communities established in 22 countries. The majority of them are in Africa.
‘Homosexuality is not a sin; it is who we are’
The crux of Macaulay’s ideology centers on inclusion and acceptance. He creates a space at House of Rainbow where LGBTQ individuals can not only gather in community, but can also feel seen and recognized as meaningful members and contributors to Christianity
“The important thing [that people need to understand] is that as a minister of the gospel of Christ, I want every LGBTQ person to make [it to] heaven,” says Macaulay. “I want them to be on a path towards salvation and redemption.”
“This whole language that if you are gay, you are destined for hell and eternal damnation is so wrong. That is even abusive in itself,” adds Macaulay.
He further invokes a popular scripture that loosely states, “For all have sinned and fallen short of the glory of God.”
This scripture is a part of what homophobic Christians use to denounce queerness. Macaulay, nevertheless emphasizes that there is a lack of complete understanding of what the scripture truly communicates.
“[The scripture] didn’t say that anyone is going to hell. It said that we have all sinned and fallen short of the glory of God,” says Macaulay. “Having said that, it is important to understand that homosexuality is not a sin; it is who we are.”
Macaulay’s work is therefore enmeshed in the need to fight for social justice causes. He aims to use the church as a platform to bring awareness to and fight for all iterations of LGBTQ rights. Whether it be racism, sexism, or classism, Macaulay aims to “be like Jesus” and emulate his unwavering passion to uplift those at the bottom of society’s hierarchy.
“It’s inconceivable to think that any religious space wouldn’t be a platform for social justice. Jesus Christ was about social justice,” says Macaulay. “Even the Civil Rights Movement in America had the church fighting injustices relating to racism.”
Macaulay stresses that the church needs to “do what is right” and stand up for the rights of LGBTQ people.
“In the Bible in Micah 6:18, it says, ‘What does the Lord require of you but to do justice? To love kindness and work in humility with your God,” says Macaulay. “Therefore, Christian leaders need to have a strong understanding of justice.”
When reflecting on the current state of religion, its diversion from and/or weak approach towards social justice, and also its complicity in oppressing minority groups, Macaulay says, “Jesus Christ would definitely be mad.”
Can you be a gay African and Christian?
Prior to being colonized by European countries, many African cultures had relaxed attitudes towards sexuality and gender. The Shona in Zimbabwe, Pangwe in Cameroon, Igbo in Nigeria and other African tribes all permitted queer existence without any negative repercussions.
The expansion of European global influence brought with it homophobic laws, which were largely enacted under the pretense of “Christian values,” that forced African countries to institutionalize queerphobia, which has now become an undeniable legacy of colonialism on the continent.
That colonialism introduced African populations to Christianity is not an uncommon sentiment among queer Africans and Africans in general. Hence, it is not uncommon to find LGBTQ Africans who denounce Christianity not only because of its association with the racism that fueled European occupation of the continent, but also its functioning as a tool that erased what many of them nostalgically view as a queer-affirming past tainted by the arrival of the white man.
Macaulay both believes and shuns this. He acknowledges that colonialism did participate in the erasure of queer acceptance in African cultures, however, the concept of Christianity being “unAfrican” is fallacious.
He asserts that African and Black African Christians existed before colonialism, and thus, the notion that Christianity is the “white man’s religion” is a false notion.
“Christianity was present in pre-colonial Africa,” says Macaulay. “In the Bible there are numerous references to Africa, including Egypt and Ethiopia where important biblical events happened, [for example], the story of the Israelites leaving Egypt in search of the promised land.”
Macaulay, because of this, spotlights the need for religion to be decolonized.
By reframing how Christians conceive of religion, from unlearning the notion that Jesus is white to acknowledging the existence of Black people in the Bible, one can have a more wholesome and truthful interaction with Christianity.
Also, this will allow for queer African Christians to exist in their queer communities comfortably as Macaulay states that there’s a need for them to occupy space in the community as proudly religious people without bearing the shame that is cast on them by what seems to be an agnostic-leaning landscape.
Lil Nas X and ‘going to hell’
Lil Nas X on March 26 released a single titled “Call Me By Your Name” which garnered massive attention for both its musical mastery through a catchy hook and its depiction of Black queerness. The accompanying video further dramatized the story by drawing from Christian visual imagery of heaven and hell, and God and the Devil.
The song’s video features scenes of Lil Nas X in sensual form, including him giving a caricature of Satan a lap dance. This particularly angered many religious groups, including Christian allies of the LGBTQ community who USA Today reported criticized the video for “going too far to prove a point.’”
Macaulay is a fan of Lil Nas X, who he dubs as his “favorite artist of all time right now, after Michael Jackson,” and for him, Lil Nas X’s discography extends beyond simple displays of queer identity.
Macaulay has one thought at the forefront of his mind when he looks at “Call Me By Your Name”: The concept of hell is abusive and a form of scaremongering.
“The concept of hell is propaganda. It is almost fictional,” says Macaulay. “The idea that if you do something wrong you will go to hell, is wrong in and of itself. Homosexuality was never wrong. Homophobia is wrong.”

He further underlines that God made gay people, and supports this with a scripture from the book of Philippians which loosely points to God’s omnipotent knowledge before, during, and after one’s life on earth.
Macaulay says that people should listen to Lil Nas X’s pain, and not rebuke him, because he speaks for millions of gay people.
“The reality is that when you tell people that they are going to hell, you are excommunicating them from living their own lives appropriately,” says Macaulay.
Macaulay nonetheless has a deep admiration for today’s younger generations, especially because they refuse to align themselves with the bigotry that ravages societal discourse about identity.
“I’m really glad for the young people that have stepped out. They are fighting back. They are the warriors and heroes saying, ‘Enough is enough. I’m proud, queer and African,’” says Macaulay. “I think that the sad reality for the Christian community is that they’re missing out on the gift and talents of the queer community [by being exclusive].”
Macaulay and House of Rainbow have created “GAYMoment,” a weekly online service that centers queer worship. Each Sunday, queer people from around the world gather online for prayer, sermon, and testimonies, all provided by queer people.
Macaulay champions sex positivity
Discussing sex and sexual identity is a topic from which Macaulay does not shy away. In fact, it is one that although he is a religious leader, he also approaches as a person of faith.
Macaulay, who lives with HIV, is a proponent of sex positivity.
“I think it’s important for every adult human being to experience a sexual relationship that is appropriate, suitable, and consensual,” says Macaulay. “It is important that everyone in their lifetime engages positively with sex, particularly adults. I don’t recommend it for minors though.”
Macaulay is also a vocal advocate for having honest and open conversations about sex and sexuality. He gives credence to the fact that society needs to address the lack of comprehensive sex education.
“Countries that have [addressed sex education] are doing better. They have less cases of STIs and teenage pregnancies,” says Macaulay. “Also, students get more opportunities to know more about various sexulities.”
Sex education should be age-appropriate and geared towards protecting children, minors, and vulnerable adults, says Macaulay. He believes that children should know about their bodies and be armed with the confidence to talk to adults when their boundaries are violated.
Thus, by keeping advocacy as the focal point, Macaulay, who is affectionately known as “Mama Jide” functions in a quintessential role in the queer community, one similar to that of house mothers in ballroom culture who outstretch themselves to the limits to ensure that their children not only have their basic needs, but also reach a point of complete self-actualization and realization of their purpose in life.
Uganda
Ugandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow
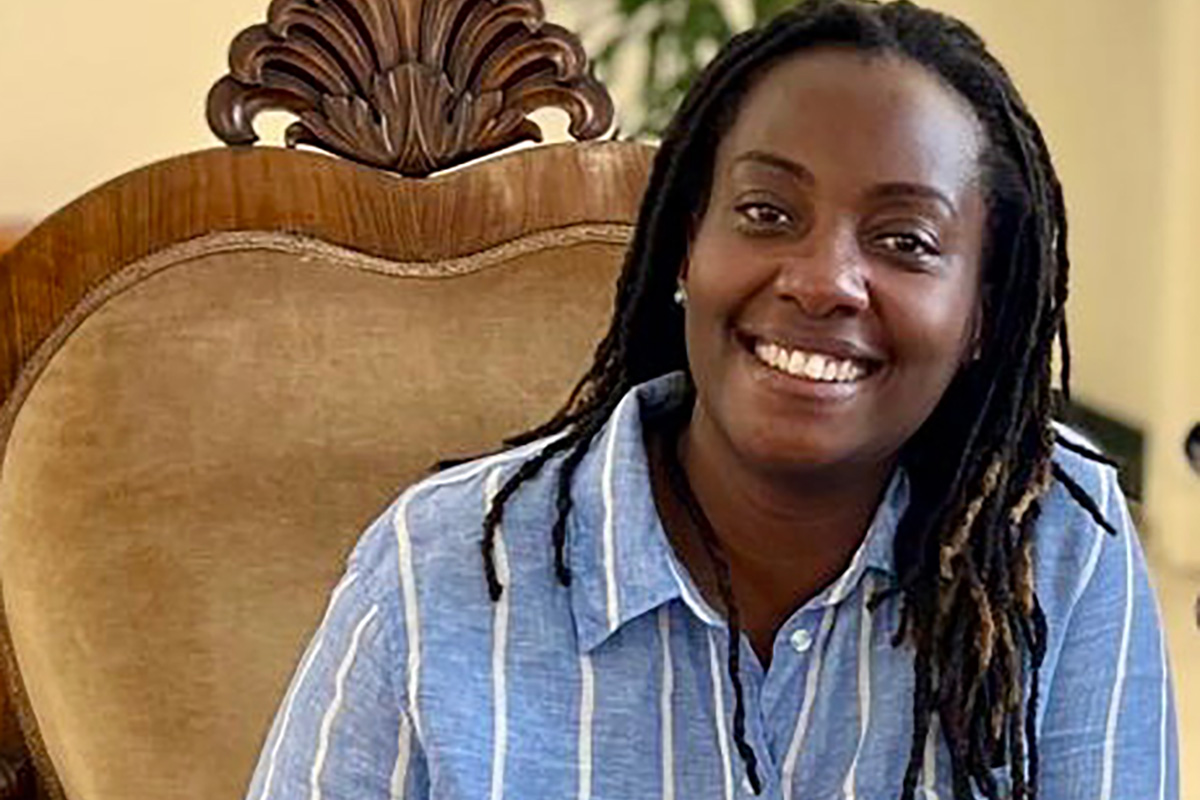
Clare Byarugaba founded PFLAG-Uganda

The Charles F. Kettering Foundation has named a prominent Ugandan LGBTQ activist as one of its 2026 fellows.
Clare Byarugaba, founder of PFLAG-Uganda, is one of the foundation’s five 2026 Global Fellows.
Byarugaba, among other things, has been a vocal critic of Uganda’s Anti-Homosexuality Act. Byarugaba in 2024 met with Pope Francis — who criticized criminalization laws during his papacy — at the Vatican.
The foundation on its website says it “is dedicated to bringing research and people together to make the promise of democracy real for everyone, everywhere.”
“Clare is the kind of hero who rushes toward the emergency to help,” said PFLAG CEO Brian K. Bond in a Feb. 27 statement to the Washington Blade. “She founded PFLAG-Uganda as the country pushed to criminalize homosexuality and those who support LGBTQ+ people. Yet, she never hesitated in her courage, telling us that families wanted to organize to keep their LGBTQ+ loved ones safe, and PFLAG was the way to do it. Clare Byarugaba not only deserves this honor, but she will use her compassion and experience to teach the world about LGBTQ+ advocacy as a Kettering Global Fellow.”
India
Activists push for better counting of transgender Indians in 2026 Census
2011 count noted 488,000 trans people in country

India is preparing to conduct a nationwide Census in April, the first since 2011.
Interim projections based on the previous Census placed India ahead of China as the world’s most populous country. A Technical Group on Population Projections projection in July 2020, chaired by the Registrar General of India, estimated the country’s population in 2023 was 1.388 billion. Transgender Indians are now raising concerns about the data collectors and their sensitization.
Activists have raised concerns about whether data collectors are adequately sensitive to the community ahead of the Census. Government training material emphasizes household engagement, data privacy and sensitivity while asking personal questions, but publicly available flyers do not outline specific guidance or training related to recording trans identity during enumeration.
Concerns around the counting of trans people in India are not new.
The 2011 Census recorded around 488,000 trans people, a figure activists and researchers have described as a likely undercount due to stigma, misclassification, and a reluctance to self-identify. Subsequent surveys and field reports have pointed to inconsistencies in how gender identity is recorded and the absence of uniform sensitivity among Census data collectors. Rights groups and policy researchers have also warned that gaps in official data affect access to welfare schemes, legal recognition, and targeted public policy, making accurate counting central to future Census exercises.
A decade after the 2011 Census formally recorded trans people as a distinct category, multiple studies have continued to document entrenched socio-economic disparities. Research has pointed to lower literacy rates, limited workforce participation and barriers to healthcare access within the community.
A National Human Rights Commission-supported study cited in subsequent reporting found a significant proportion of trans respondents reported employment discrimination, underscoring the gap between formal recognition and lived economic inclusion.
Educational exclusion has remained a persistent concern within the trans community. Studies have documented higher dropout rates, lower literacy levels and barriers to continuing education, often linked to stigma, discrimination and limited institutional support. Policy researchers note that despite formal recognition in official data after 2011, targeted interventions addressing school retention and access for trans people have remained uneven.
Access to housing schemes has reflected similar gaps.
The Washington Blade in December reported only a small number of trans people have benefited from India’s flagship low-income housing program, despite its nationwide rollout and eligibility provisions. The findings underscored continuing barriers to inclusion in welfare delivery systems.
The Social Justice and Empowerment Ministry and the Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner did not respond to the Blade’s multiple requests for comment regarding sensitization measures for Census data collectors and the recording of trans identity in the upcoming Census.
Karnataka state in southern India last September conducted its first statewide baseline survey of gender minorities. The Department of Women and Child Development, in collaboration with the Karnataka State Women’s Development Corporation, launched the initiative to document the lives of trans people across 31 administrative districts.
When the results were released, the survey identified 10,365 trans people. The country’s 2011 Census, by comparison, recorded 20,266 trans people in Karnataka, nearly double the 2025 figure. The discrepancy raised questions about how the state’s recorded trans population appeared to decline over 14 years.
The discrepancy in Karnataka’s survey has intensified scrutiny over how gender minorities are counted. Reports questioned the methodology used in the 2025 exercise, which was conducted over 45 days beginning in mid-September. Instead of door-to-door enumeration, trans people were required to report to designated registration sites — primarily district-level public hospitals and sub-district government health facilities. The approach presented barriers for potential participants, particularly those in rural areas, those without reliable transportation, those wary of institutional settings due to prior discrimination, or those who did not know about the count, raising the possibility of exclusion.
Bihar state in eastern India in January 2023 conducted a caste-based survey that included trans respondents.
The final report identified 825 trans people in the state, compared with 40,827 recorded in the 2011 Census. Activists disputed the figure, calling it inaccurate and pointing to community estimates that suggested higher numbers, including in Patna, the state capital, raising concerns about significant undercounting.
The 2011 Census marked the first attempt to enumerate trans people at the national level, but researchers and activists have described the exercise as limited in scope.
It recorded 487,803 people under the “other” category, a classification used for respondents who did not identify as male or female. Analysts have argued that the figure likely underestimated the community’s size.
The Census questionnaire provided three sex categories — “male,” “female,” and “other” — a framework that critics said did not fully capture the diversity of gender identity and may have affected how some respondents chose to identify.
During the 2011 Census, enumeration practices varied across regions.
In states such as Tamil Nadu, local reporting indicated estimates were at times derived from existing administrative records, including state-issued trans identity cards, rather than solely through door-to-door identification. Such approaches risked excluding individuals who did not possess identity documentation or were not registered with welfare boards, raising concerns about gaps in coverage.
Official data from the Social Justice and Empowerment Ministry shows only a few hundred trans people as of early 2025 have been issued identity cards through the national portal, despite nearly 2,000 applications being submitted. Many are still pending or have been rejected.
Critics of the 2011 Census said many Census data collectors were not adequately trained or sensitized to engage with gender identity beyond traditional binary classifications. Similar, detailed guidelines specific to trans sensitization have not been publicly made available for the 2026 Census, according to an examination of training materials and official circulars.
Akkai Padmashali, a trans rights activist, told the Blade that Census data collectors in earlier exercises were often not sensitized and lacked awareness of intersex people and gender-diverse communities. She said trans people and other gender and sexual minorities continue to face social exclusion and require careful handling during door-to-door data collection. Padmashali called for targeted training of data counting officers and said the government should treat the issue as a priority, adding the trans population is likely to be higher than what was recorded in 2011 and efforts to make officials more sensitive to the community are necessary.
“We will definitely join our hands with this move the government of India has taken,” said Padmashali. “I think there should be proper guidance from the main in-charge people who are conducting this enumeration, and if no such proper information is given to these Census data collectors, it is difficult to gather any sort of information concerned.”
“This whole issue of self-identification — I think India, in its current situation, is not in such a way that it openly accepts people’s identities,” she added. “It will be challenging, it will be difficult, it will be a struggle to offer people the opportunity to express their identities as concerned. But to make sure those who are part of the sexual minority community are counted, I think we also take responsibility for educating people to be part of the enumeration.”
Padmashali said many people are not accustomed to using mobile devices and only a limited number are familiar with them. She said technology should not mislead or misguide the collection of information. Padmashali added she and other trans people plan to engage with Census data collectors and officials who organize the Census.
“Government should have local meetings,” said Padmashali. “Government should hold regional consultations on why the national enumeration is important, because we also know that from 2011 to 2026 is almost 15 years, and now we are here.”
“The government should hold local meetings, especially in their constituencies,” she added. “If the government meets with non-government organizations and civil society groups, this could become a more inclusive exercise across the country. India has a population of more than 1.4 billion, and I think this is the appropriate time to bring accurate statistics to help draft policies in the context of the larger community concerned.”
Books
New book profiles LGBTQ Ukrainians, documents war experiences
Tuesday marks four years since Russia attacked Ukraine

Journalist J. Lester Feder’s new book profiles LGBTQ Ukrainians and their experiences during Russia’s war against their country.
Feder for “The Queer Face of War: Portraits and Stories from Ukraine” interviewed and photographed LGBTQ Ukrainians in Kyiv, the country’s capital, and in other cities. They include Olena Hloba, the co-founder of Tergo, a support group for parents and friends of LGBTQ Ukrainians, who fled her home in the Kyiv suburb of Bucha shortly after Russia launched its war on Feb. 24, 2022.
Russian soldiers killed civilians as they withdrew from Bucha. Videos and photographs that emerged from the Kyiv suburb showed dead bodies with their hands tied behind their back and other signs of torture.
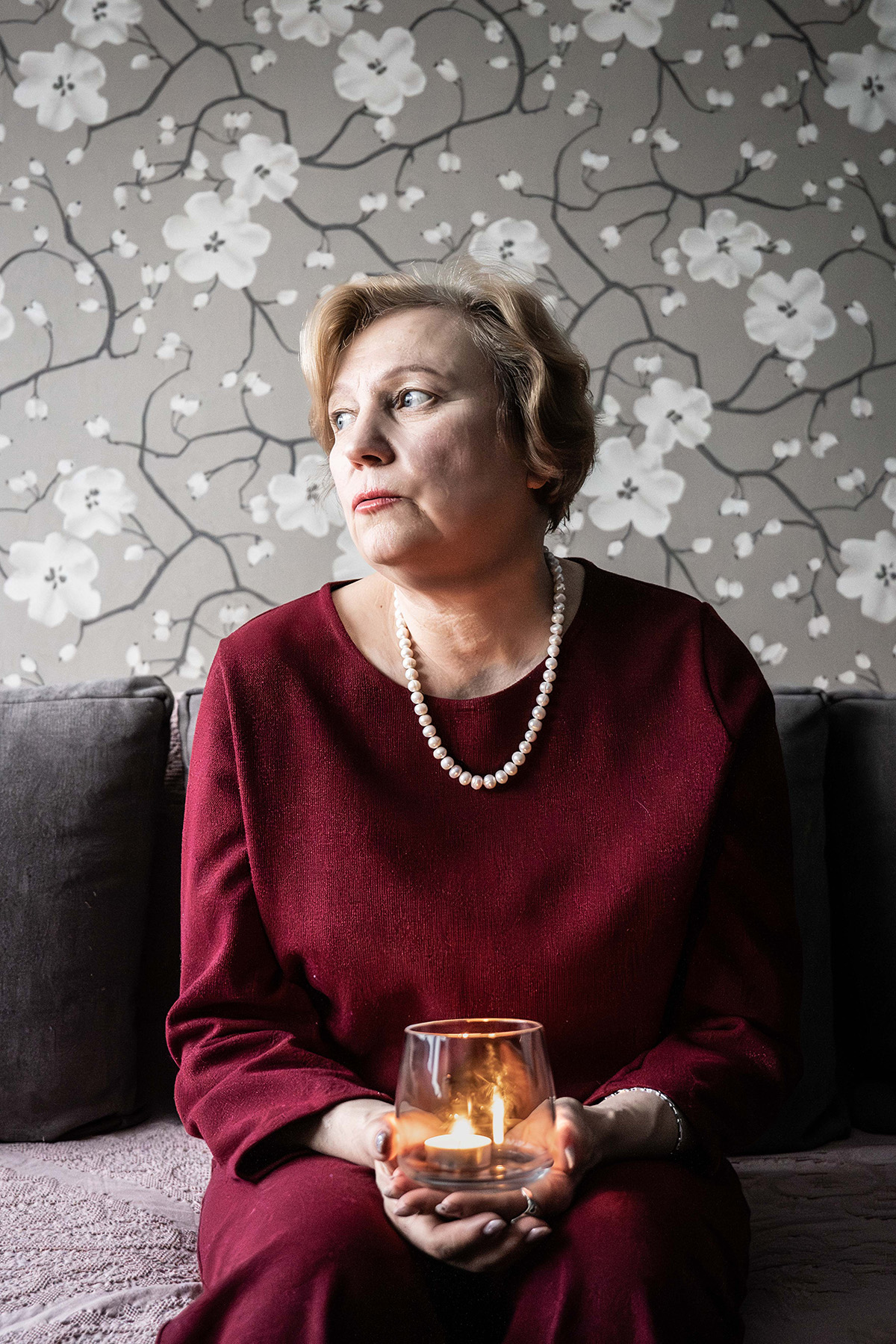

Olena Shevchenko, chair of Insight, a Ukrainian LGBTQ rights group, wrote the book’s forward.
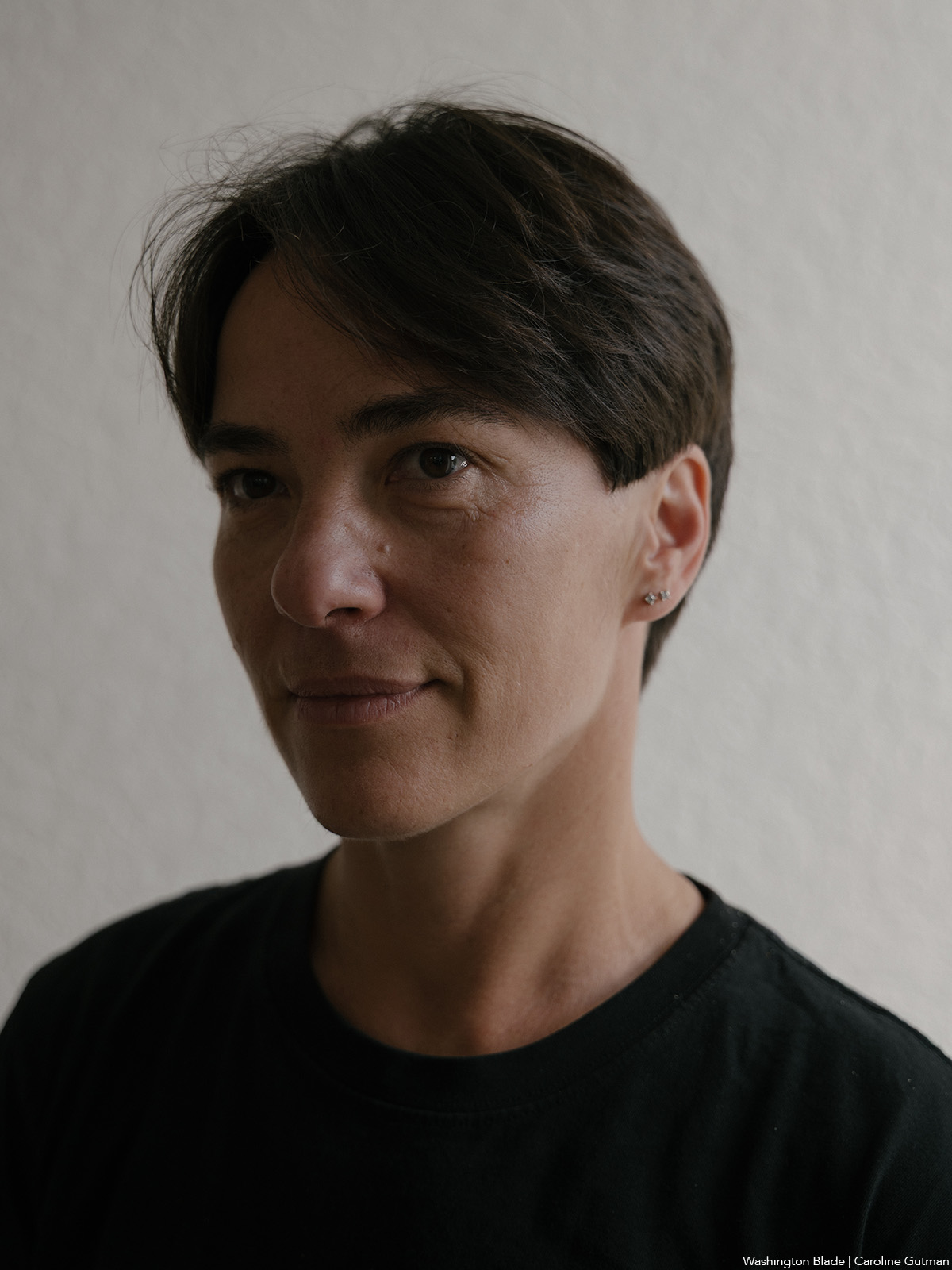

The book also profiles Viktor Pylypenko, a gay man who the Ukrainian military assigned to the 72nd Mechanized Black Cossack Brigade after the war began. Feder writes Pylypenko’s unit “was deployed to some of the fiercest and most important battles of the war.”
“The brigade was pivotal to beating Russian forces back from Kyiv in their initial attempt to take the capital, helping them liberate territory near Kharkiv and defending the front lines in Donbas,” wrote Feder.
Pylypenko spent two years fighting “on Ukraine’s most dangerous battlefields, serving primarily as a medic.”
“At times he felt he was living in a horror movie, watching tank shells tear his fellow soldiers apart before his eyes,” wrote Feder. “He held many men as they took their final breaths. Of the roughly one hundred who entered the unit with him, only six remained when he was discharged in 2024. He didn’t leave by choice: he went home to take care of his father, who had suffered a stroke.”
Feder notes one of Pylypenko’s former commanders attacked him online when he came out. Pylypenko said another commander defended him.
Feder also profiled Diana and Oleksii Polukhin, two residents of Kherson, a port city in southern Ukraine that is near the mouth of the Dnieper River.
Ukrainian forces regained control of Kherson in November 2022, nine months after Russia occupied it.
Diana, a cigarette vender, and Polukhin told Feder that Russian forces demanded they disclose the names of other LGBTQ Ukrainians in Kherson. Russian forces also tortured Diana and Polukhin while in their custody.
Polukhim is the first LGBTQ victim of Russian persecution to report their case to Ukrainian prosecutors.
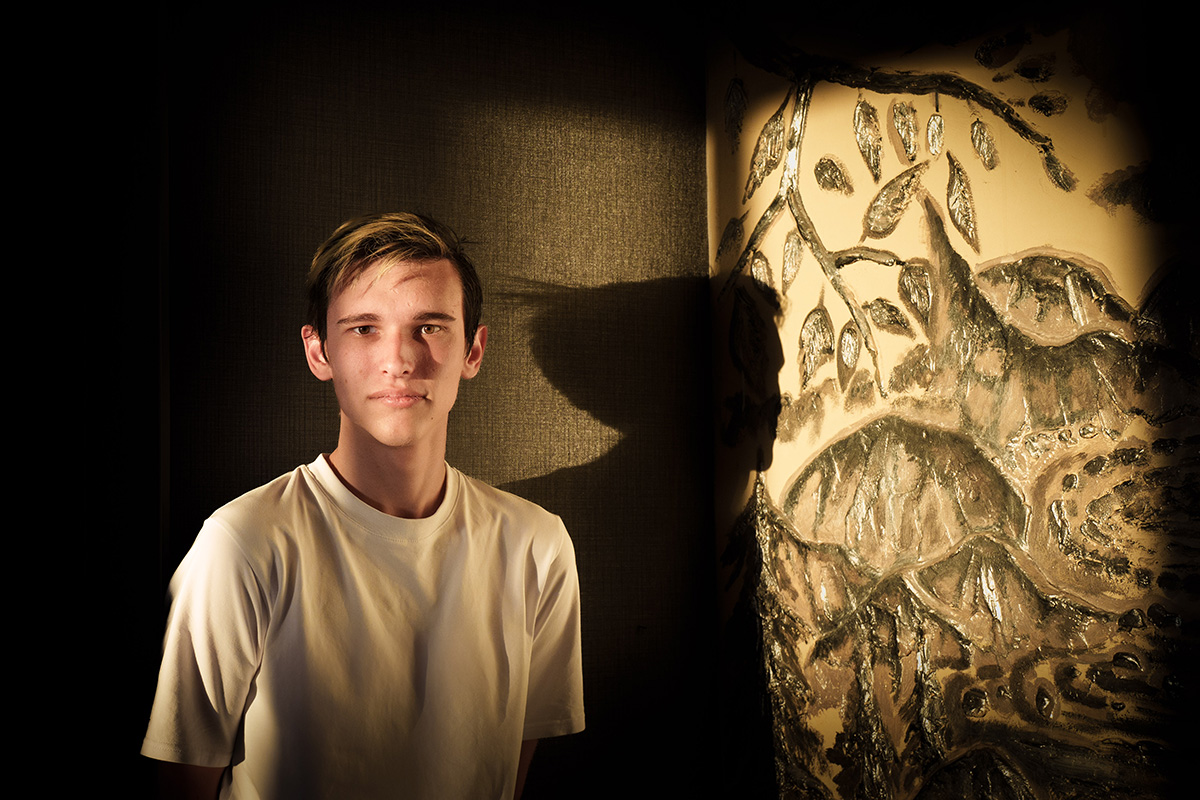

Feder, who is of Ukrainian descent, first visited Ukraine in 2013 when he wrote for BuzzFeed.
He was Outright International’s Senior Fellow for Emergency Research from 2021-2023. Feder last traveled to Ukraine in December 2024.
Feder spoke about his book at Politics and Prose at the Wharf in Southwest D.C. on Feb. 6. The Washington Blade spoke with Feder on Feb. 20.
Feder told the Blade he began to work on the book when he was at Outright International and working with humanitarian groups on how to better serve LGBTQ Ukrainians. Feder said military service requirements, a lack of access to hormone therapy and documents that accurately reflect a person’s gender identity and LGBTQ-friendly shelters are among the myriad challenges that LGBTQ Ukrainians have faced since the war began.
“All of these were components of a queer experience of war that was not well documented, and we had never seen in one place, especially with photos,” he told the Blade. “I felt really called to do that, not only because of what was happening in Ukraine, but also as a way to bring to the surface issues that we’d had seen in Iraq and Syria and Afghanistan.”
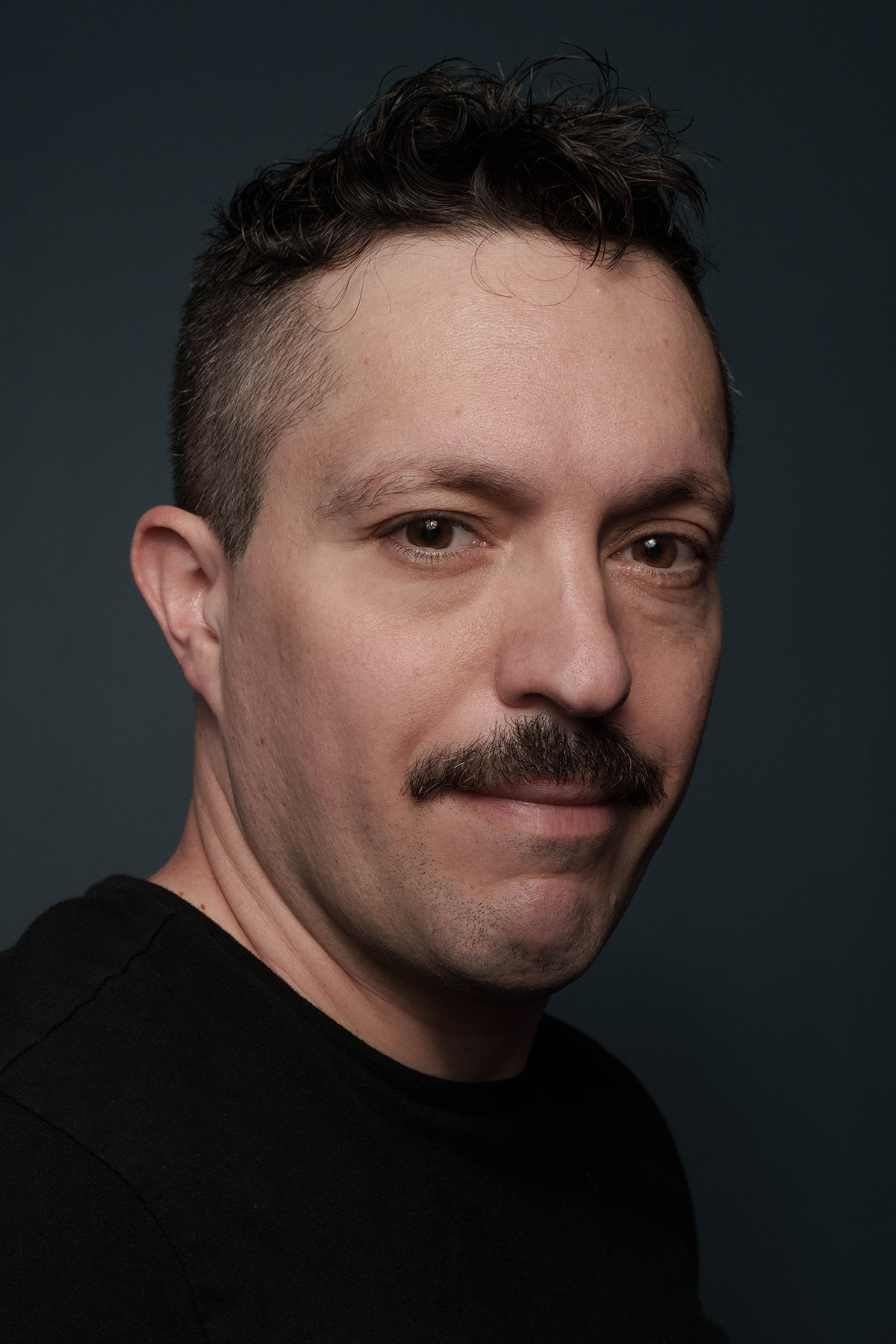

Feder also spoke with the Blade about the war’s geopolitical implications.
Russian President Vladimir Putin in 2013 signed a law that bans the “promotion of homosexuality” to minors.
The 2014 Winter Olympics took place in Sochi, a Russian resort city on the Black Sea. Russia annexed Crimea from Ukraine a few weeks after the games ended.
Russia’s anti-LGBTQ crackdown has continued over the last decade.
The Russian Supreme Court in 2023 ruled the “international LGBT movement” is an extremist organization and banned it. The Russian Justice Ministry last month designated ILGA World, a global LGBTQ and intersex rights group, as an “undesirable” organization.
Ukraine, meanwhile, has sought to align itself with Europe.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy after a 2021 meeting with then-President Joe Biden at the White House said his country would continue to fight discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity. (Zelenskyy’s relationship with the U.S. has grown more tense since the Trump-Vance administration took office.) Zelenskyy in 2022 publicly backed civil partnerships for same-sex couples.
Then-Ukrainian Ambassador to the U.S. Oksana Markarova in 2023 applauded Kyiv Pride and other LGBTQ and intersex rights groups in her country when she spoke at a photo exhibit at Ukraine House in D.C. that highlighted LGBTQ and intersex soldiers. Then-Kyiv Pride Executive Director Lenny Emson, who Feder profiles in his book, was among those who attended the event.
“Thank you for everything you do in Kyiv, and thank you for everything that you do in order to fight the discrimination that still is somewhere in Ukraine,” said Markarova. “Not everything is perfect yet, but you know, I think we are moving in the right direction. And we together will not only fight the external enemy, but also will see equality.”
Feder in response to the Blade’s question about why he decided to write his book said he “didn’t feel” the “significance of Russia’s war against Ukraine” for LGBTQ people around the world “was fully understood.”
“This was an opportunity to tell that big story,” he said.
“The crackdown on LGBT rights inside Russia was essentially a laboratory for a strategy of attacking democratic values by attacking queer rights and it was one as Ukraine was getting closet to Europe back in 2013, 2014,” he added. “It was a strategy they were using as part of their foreign policy, and it was one they were using not only in Ukraine over the past decade, but around the world.”
Feder said Republicans are using “that same strategy to attack queer people, to attack democracy itself.”
“I felt like it was important that Americans understand that history,” he said.
-

 National4 days ago
National4 days agoSupreme Court deals blow to trans student privacy protections
-

 District of Columbia4 days ago
District of Columbia4 days agoD.C. Black Pride theme, performers announced at ‘Speakeasy’
-

 Opinions4 days ago
Opinions4 days agoWhy innovation matters for Black health
-

 National4 days ago
National4 days agoPeter Thiel’s expanding power — and his overlap with Jeffrey Epstein