World
Out in the World: LGBTQ news from Europe and Asia
The Polish government has moved forward with a civil unions bill

UNITED KINGDOM
The UK’s new Labour government is defending the previous Conservative government’s ban on the use of puberty blockers for transgender children and moving to make the ban permanent, the new health minister announced this weekend.
Wes Streeting, who was appointed Secretary of State for Health and Social Care on July 5, one day after Labour’s landslide election victory, posted a thread on X over the weekend defending the new government’s policy.
Streeting said the Cass Review — the previous government’s official review of gender care, which has been derided by trans activists as misleading and one-sided — found there was a lack of evidence that puberty blockers were safe and effective for use in gender questioning youth.
“We don’t yet know the risks of stopping pubertal hormones at this critical life stage. That is the basis upon which I am making decisions. I am treading cautiously in this area because the safety of children must come first,” Streeting wrote.
The Labour government is continuing to defend the previous government’s emergency ban on puberty blockers in court. This week, the court was told by counsel for trans groups challenging the ban that the policy stems only from the previous minister’s personal views about trans people, rather than medical expertise.
“The evidence shows that the impetus and only disclosed rationale for the making of the order was the personal view of [former Health Secretary Victoria Atkins] that the Cass report required immediate action,” Jason Coppel said.
“Officials were then tasked with working up arguments in favor of a banning order to fit that personal view. No clinical or other scientific advice was taken on whether the statutory criteria were, or were capable of being, satisfied. This was a wholly insufficient basis for invocation of the emergency process.”
While Streeting has previously supported trans rights, more recently he’s walked back that support, saying he no longer stands by the belief that “trans women are women.”
POLAND

Poland’s government has finally agreed to a draft civil union bill, long after Prime Minister Donald Tusk’s initial promise to pass the bill within 100 days of taking office.
The government plans to debate the bill during the fall session of parliament, beginning in September, and have it passed by the end of the year, but recent cracks in the governing coalition have put some doubt on that timetable.
Since December, Poland has been governed by a rocky coalition of left and center-right parties who united to oppose and increasingly anti-democratic right-wing party that had governed Poland since 2014. But the coalition partners don’t see eye-to-eye on a number of social issues, including LGBTQ and reproductive rights.
The center-right Polish People’s Party had threatened not to support the civil union bill if the bill provided unions that were too similar to marriage, which would effectively kill its chances of passing. As a compromise, the center and left-leaning coalition partners agreed to amendments that would block same-sex couples from being able to adopt their partner’s children.
But a similar compromise on a landmark abortion bill failed in parliament last week.
Poland is one of only two European Union countries in which abortion is not legal – the other is Malta. Tusk had promised to decriminalize abortion up to 12 weeks, a position broadly agreed to by the left and center wings of his coalition government. But the Polish People’s Party voted against the bill, and it failed by three votes, killing it in parliament.
The Left Party in the coalition has vowed to reintroduce the bill over and over until it is passed.
An additional hurdle to both the abortion and civil union bills is President Andrzej Duda from the far-right Law and Justice Party, who has vowed to veto any abortion bill and has not committed to signing the civil union bill.
The next presidential election is in May 2024. Duda is termed out.
JAPAN
A court in Japan has allowed a trans woman to change her legal gender without undergoing gender-affirming surgery for the first time last week.
The ruling by the Hiroshima High Court handed down on July 10 overturns a lower court decision that had denied her the gender change because she hadn’t undergone surgery.
Under Japanese law, in order to legally change gender, a trans person must have a diagnosis of “gender identity disorder” and must have had surgery. The law also used to require that the person seeking a gender change has no ability to reproduce, forcing them to be sterilized, but that provision was struck down as unconstitutional by the Supreme Court of Japan last October.
The claimant, a trans woman in her late 40s argued to the court that the surgical requirement would be an unfair financial and physical burden.
One of her lawyers has said that when she was told of the ruling, she cried in relief, the Associated Press reports.
The ruling still requires trans people who want to change their legal gender to have received a “gender identity disorder” diagnosis and to have undergone hormone therapy.
LGBTQ rights have become a growing political issue in Japan. Last year, the national parliament failed to pass a nondiscrimination bill, instead passing a bill it hoped would “promote understanding” of the LGBTQ community. A majority of Japan’s prefectures have instituted recognition and registration of same-sex couples, while a series of court cases have been pressing for full equal marriage rights nationwide.
PHILIPPINES
Mandaue City on the island of Cebu is the latest city in the Philippines to pass a comprehensive anti-discrimination ordinance to protect is LGBTQ community, with the publication of implementing rules and regulations July 10.
The regulations prohibit discrimination based on sexual orientation, gender identity, and gender expression in health care, education, and public accommodations, and from impediments to free association and organization.
Mandaue Mayor Jonas Cortes says the aim of the ordinance is to make everyone feel welcome.
“The [regulations] provide the detailed guidelines on how we will implement and enforce this ordinance, ensuring that our commitment to equality is not just words but real actionable steps,” Cortes said.
More than 30 cities across the island nation have passed anti-discrimination ordinances to protect the LGBTQ community, but a bill to ban SOGIE (sexual orientation and gender identity and expression) discrimination nationwide has been stuck in the Philippine Congress for more than 20 years, having been first introduced in 2001.
A lawmaker has also attempted to get a bill to recognize same-sex civil unions passed, but it has stalled in committees.
Greenland
The Greenland lesson for LGBTQ people
Playbook is the same for our community and Europeans

I understand my own geopolitical limits and don’t pretend to know how Europeans should respond to U.S. threats to seize Greenland or retaliate against anyone who opposes them. However, as I mentioned in March, it’s clear that for Europeans and LGBTQ+ people alike, hug-and-kiss diplomacy is over.
In practice, that means responding to the U.S. administration’s provocations with dialogue, human‑rights rhetoric, and reasoning may now be counterproductive. It looks weak. At some point, Europeans will have to draw a line and show how bullying allies and breaking international agreements carry a cost — and that the cost is unpredictable. On the surface, they have few options; like LGBTQ+ communities, they are very behind in raw power and took too long to wake up. But they still have leverage, and they can still inflict harm.
Maybe it is time for them to call the bluff. America has a great deal to lose, not least its reputation and credibility on the world stage. Stephen Miller and Pete Hegseth, with all their bravado, obviously underestimate both the short‑ and long‑term geopolitical price of ridicule. Force the United States to contemplate sending troops into an ally’s territory, and let the consequences play out in international opinion, institutions, and markets.
In the United States, LGBTQ+ communities have already endured a cascade of humiliations and live under constant threat of more. In 2025 our symbols and heroes were systematically erased or defaced: the USNS Harvey Milk was quietly renamed after a straight war hero, Admiral Rachel Levine’s title and image were scrubbed from official materials, Pride flags were banned from public buildings, World AIDS Day events were defunded or stripped of queer content, the Orlando memorial and other sites of mourning were targeted, the U.S. lead a campaign against LGBTQ+ language at the U.N., and rainbow crosswalks were literally ripped up or painted over. We cannot simply register our distress; we must articulate a response.
In practice, that means being intentional and focused. We should select a few unmistakable examples: a company that visibly broke faith with us, a vulnerable political figure whose actions demand consequences, and an institution that depends on constituencies that still need us. The tools matter less than the concentration of force — boycotts, shaming, targeted campaigning all qualify — so long as crossing certain lines produces visible, memorable costs.
A friend suggested we create what he called a “c***t committee.” I liked the discipline it implies: a deliberate, collective decision to carefully select a few targets and follow through. We need a win badly in 2026.
These thoughts are part of a broader reflection on the character of our movement I’d like to explore in the coming months. My friends know that anger and sarcasm carried me for a long time, but eventually delivered diminishing returns. I am incrementally changing these aspects of my character that stand in the way of my goals. The movement is in a similar place: the tactics that served us best are losing effectiveness because the terrain has shifted. The Greenland moment clarifies that we must have a two-pronged approach: building long-term power and, in the short term, punching a few people in the nose.
Congress
McBride, other US lawmakers travel to Denmark
Trump’s demand for Greenland’s annexation overshadowed trip
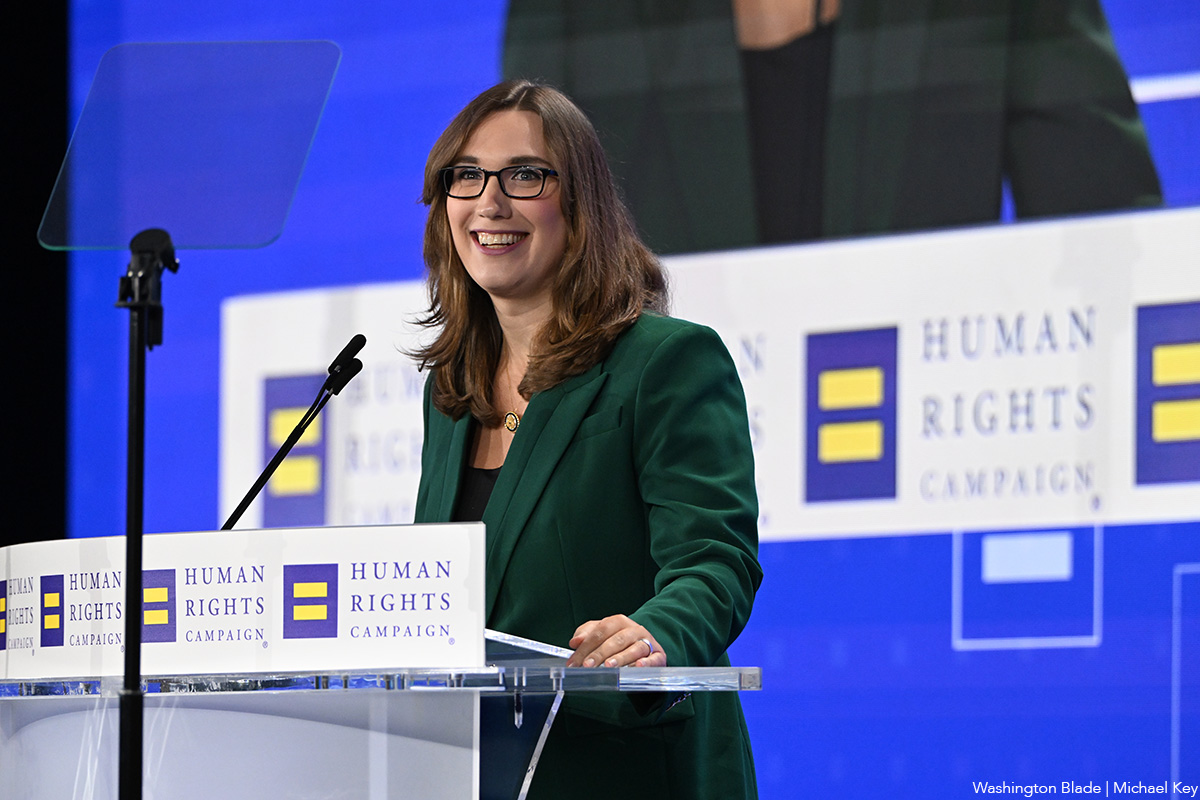

Delaware Congresswoman Sarah McBride is among the 11 members of Congress who traveled to Denmark over the past weekend amid President Donald Trump’s continued calls for the U.S. to take control of Greenland.
McBride, the first openly transgender person elected to Congress, traveled to Copenhagen, the Danish capital, with U.S. Sens. Chris Coons (D-Del.), Thom Tillis (R-N.C.), Jeanne Shaheen (D-N.H.), Dick Durbin (D-Ill.), and Lisa Murkowski (R-Alaska) and U.S. Reps. Steny Hoyer (D-Md.), Gregory Meeks (D-N.Y.), Madeleine Dean (D-Pa.), Don Bacon (R-Neb.), and Sarah Jacobs (D-Calif.). The lawmakers met with Danish Prime Minister Mette Frederiksen and Greenlandic MP Pipaluk Lynge, among others.
“I’m grateful to Sen. Coons for his leadership in bringing together a bipartisan, bicameral delegation to reaffirm our support in Congress for our NATO ally, Denmark,” said McBride in a press release that detailed the trip. “Delaware understands that our security and prosperity depend on strong partnerships rooted in mutual respect, sovereignty, and self-determination. At a time of growing global instability, this trip could not be more poignant.”
Greenland is a self-governing territory of Denmark with a population of less than 60,000 people. Trump maintains the U.S. needs to control the mineral-rich island in the Arctic Ocean between Europe and North America because of national security.
The Associated Press notes thousands of people on Saturday in Nuuk, the Greenlandic capital, protested against Trump. British Prime Minister Keir Starmer is among those who have criticized Trump over his suggestion the U.S. would impose tariffs against countries that do not support U.S. annexation of Greenland.
A poll that Sermitsiaq, a Greenlandic newspaper, and Berlingske, a Danish newspaper, commissioned last January indicates 85 percent do not want Greenland to become part of the U.S. The pro-independence Demokraatit party won parliamentary elections that took place on March 12, 2025.
“At this critical juncture for our countries, our message was clear as members of Congress: we value the U.S.-Denmark partnership, the NATO alliance, and the right of Greenlanders to self-determination,” said McBride on Sunday in a Facebook post that contained pictures of her and her fellow lawmakers meeting with their Danish and Greenlandic counterparts.
Colombia
Gay Venezuelan opposition leader: Country’s future uncertain after Maduro ouster
Yendri Velásquez fled to Colombia in 2024 after authorities ‘arbitrarily detained’ him
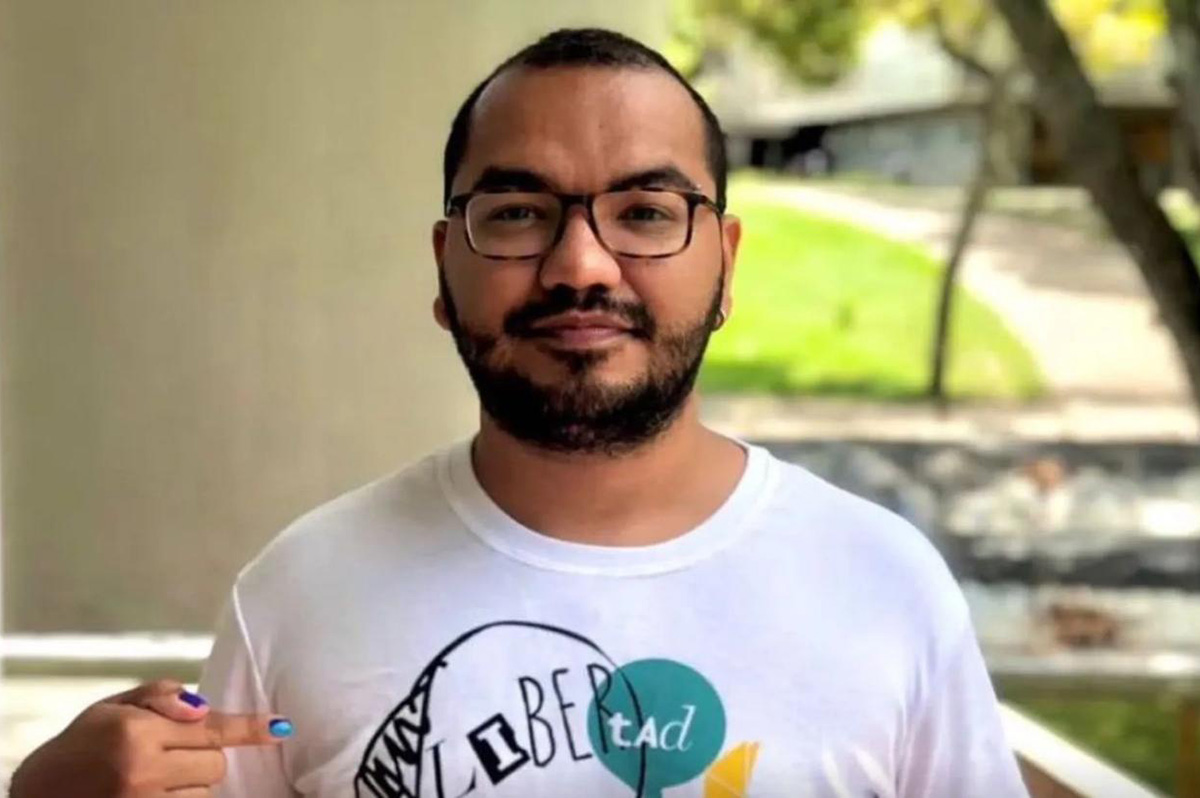

A gay Venezuelan opposition leader who currently lives in Colombia says his country’s future is uncertain in the wake of now former President Nicolás Maduro’s ouster.
The Washington Blade spoke with Yendri Velásquez on Thursday, 12 days after American forces seized Maduro and his wife, Cilia Flores, at their home in Caracas, the Venezuelan capital, during an overnight operation.
Maduro and Flores on Jan. 5 pleaded not guilty to federal drug charges in New York. The Venezuelan National Assembly the day before swore in Delcy Rodríguez, who was Maduro’s vice president, as the country’s acting president.
Velásquez, who lives in the Colombian capital of Bogotá, described the events surrounding Maduro’s ouster as “very confusing.”
“It was a very surprising thing that left me in shock,” Velásquez told the Blade. “We also thought, at least from the perspective of human rights, that the United States was going to respect international law and not go to the extreme of bombing and extracting Maduro.”
“Other questions also arise,” he added. “What could have been done? What else could have been done to avoid reaching this point? That is the biggest question posed to the international community, to other countries, to the human rights mechanisms we established before Trump violated international law, precisely to preserve these mechanisms and protect the human rights of Venezuelan people and those of us who have been forced to flee.”
Velásquez three years ago founded the Venezuelan Observatory of LGBTIQ+ Violence. He also worked with Tamara Adrián, a lawyer who in 2015 became the first openly transgender woman elected to the Venezuelan National Assembly, for more than a decade.
Members of Venezuela’s military counterintelligence agency, known by the Spanish acronym DGCIM, on Aug. 3, 2024, “arbitrarily detained” Velásquez as he was trying to leave the country to attend a U.N. human rights event in Geneva.
Velásquez told the Blade he was “forcibly disappeared” for nearly nine hours and suffered “psychological torture.” He fled to Colombia upon his release.
Two men on Oct. 14, 2025, shot Velásquez and Luis Peche Arteaga, a Venezuelan political consultant, as they left a Bogotá building.
The assailants shot Velásquez eight times, leaving him with a fractured arm and hip. Velásquez told the Blade he has undergone multiple surgeries and has had to learn how to walk again.
“This recovery has been quite fast, better than we expected, but I still need to finish the healing process for a fractured arm and complete the physical therapy for the hip replacement I had to undergo as a result of these gunshots,” he said.
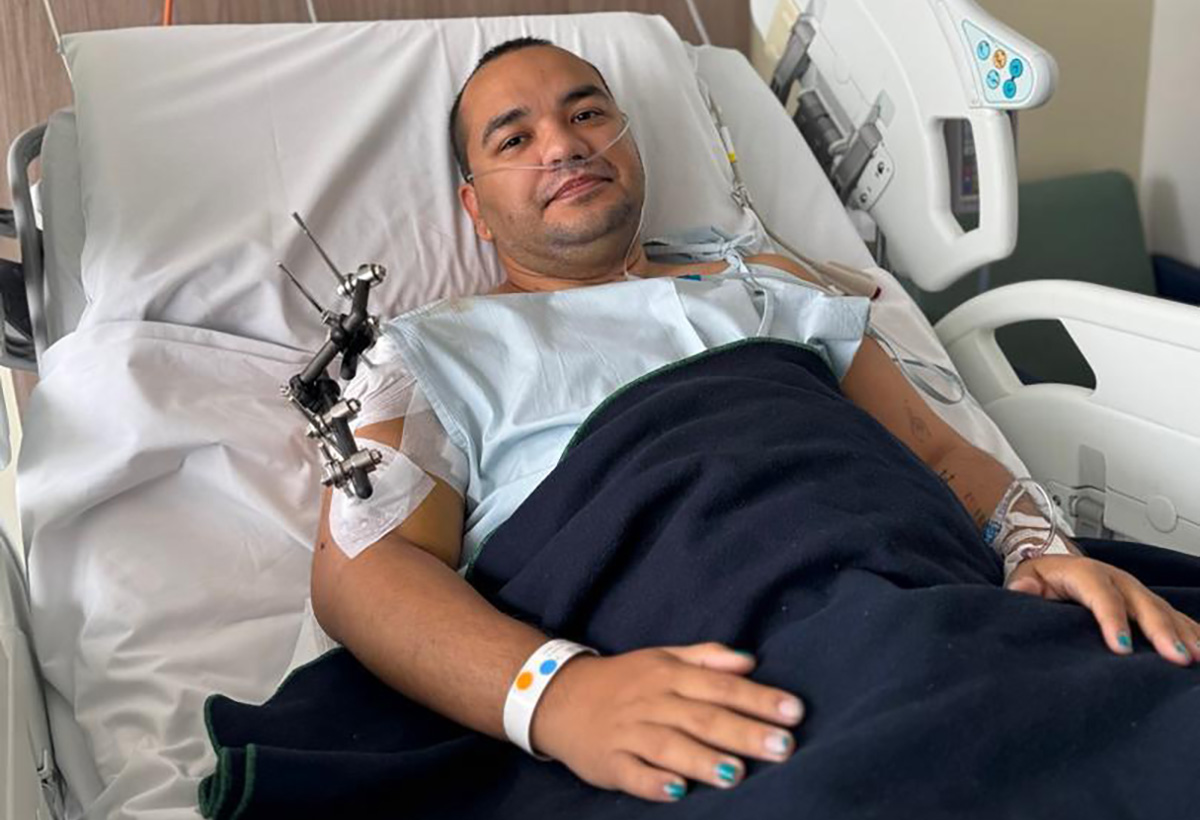
María Corina Machado, who won the 2025 Nobel Peace Prize, and other Venezuelan opposition leaders said Maduro’s government targeted Velásquez and Peche. Colombian President Gustavo Petro and his government also condemned the attack.
Colombian authorities have yet to arrest anyone in connection with the attack.
Velásquez noted to the Blade he couldn’t sleep on Jan. 3 because “of the aches and pains” from the shooting. He said a friend who is “helping me out and looking after my things” was the one who told him about the operation the U.S. carried out to seize Maduro and Flores.
“He said, ‘Look at this! They’re bombing Caracas! And I was like, ‘What is this?'” recalled Velásquez.
White House ‘not necessarily’ promoting human rights agenda
Velásquez noted Rodríguez “is and forms part of the mechanisms of repression” that includes DGCIM and other “repressive state forces that have not only repressed, but also tortured, imprisoned, and disappeared people simply for defending the right to vote in (the) 2024 (election), simply for protesting, simply for accompanying family members.” Velásquez told the Blade that “there isn’t much hope that things will change” in Venezuela with Rodríguez as president.
“Let’s hope that countries and the international community can establish the necessary dialogues, with the necessary intervention and pressure, diplomatically, with this interim government,” said Velásquez, who noted hundreds of political prisoners remain in custody.
He told the Blade the Trump-Vance administration does not “not necessarily” have “an agenda committed to human rights. And we’ve seen this in their actions domestically, but also in their dealings with other countries.”
“Our hope is that the rest of the international community, more than the U.S. government, will take action,” said Velásquez. “This is a crucial moment to preserve democratic institutions worldwide, to preserve human rights.”
Velásquez specifically urged the European Union, Colombia, Brazil, and other Latin American countries “to stop turning a blind eye to what is happening and to establish bridges and channels of communication that guarantee a human rights agenda” and to try “to curb the military advances that the United States may still be considering.”

Velásquez told the Blade he also plans to return to Venezuela when it is safe for him to do so.
“My plan will always be to return to Venezuela, at least when it’s no longer a risk,” he said. “The conditions aren’t right for me to return because this interim government is a continuation of Maduro’s government.”
Editor’s note: International News Editor Michael K. Lavers was on assignment in Bogotá, Colombia, from Jan. 5-10.




















