National
In first, fed’l appeals court rules anti-gay bias barred under current law
Panel finds sexual orientation bias barred under Title VII


For the first tine, a federal appeals court has ruled anti-gay bias is illegal under current law.
For the first time, a federal appeals court has determined discrimination based on sexual orientation amounts to sex discrimination and is unlawful under current civil rights law.
In a 69-page decision, the U.S. 7th Circuit Court of Appeals in Chicago ruled Tuesday in the case of Hively v. Ivy Tech Community College anti-gay workplace bias is unlawful under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, reversing an earlier decision from a three-judge panel finding precedent precludes the court from making that determination.
Writing for the majority in the 8-3 decision, U.S. Chief Judge Diane Wood, a Clinton appointee, finds discrimination based on sexual orientation constitutes discrimination based on one’s perception of gender stereotypes, which the U.S. Supreme Court has determined is unlawful under Title VII.
“Any discomfort, disapproval, or job decision based on the fact that the complainant—woman or man— dresses differently, speaks differently, or dates or marries a same-sex partner, is a reaction purely and simply based on sex,” Wood writes. “That means that it falls within Title VII’s prohibition against sex discrimination, if it affects employment in one of the specified ways.”
Wood also relies heavily on the reasoning in the 1967 U.S. Supreme Court decision in the case of Loving v. Virginia, which struck down bans on interracial marriage and served as a basis for the court’s ruling in favor of marriage equality in 2015.
“Changing the race of one partner made a difference in determining the legality of the conduct, and so the law rested on distinctions drawn according to race, which were unjustifiable and racially discriminatory,” Wood writes. “So too, here. If we were to change the sex of one partner in a lesbian relationship, the outcome would be different. This reveals that the discrimination rests on distinctions drawn according to sex.”
Wood cautions the ruling “decided only the issue put before us” and not, for example, whether Ivy Tech is a religious institution and therefore entitled to the religious exemption under Title VII, nor the legality of anti-gay discrimination “in the context of the provision of social or public services.”
“We hold only that a person who alleges that she experienced employment dis- crimination on the basis of her sexual orientation has put forth a case of sex discrimination for Title VII purposes,” Wood concludes. “It was therefore wrong to dismiss Hively’s complaint for failure to state a claim.”
In a new trend, a number of district courts have begun to rule anti-gay discrimination violates federal laws against sex discrimination, but federal appeals courts — including the 11th Circuit and the 2nd Circuit — had continued to reject that interpretation of Title VII until now. The 7th Circuit ruling marks the first time a federal court has reached that conclusion after decades of gay, lesbian and bisexual plaintiffs filing complaints before federal courts under that law.
The ruling reverses and remands the lower court ruling in the case, which was filed in 2014 by Kimberly Hively against her former employer, the Indiana-based Ivy Tech Community College, where she worked as a part-time professor. The lawsuit alleged the school violated Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 by denying Hively full-time employment and promotions because she’s a lesbian.
Echoing Wood in a concurring decision is U.S. Circuit Judge Richard Posner, who was responsible for the 7th Circuit’s decision in favor of marriage equality in 2015 and opined in this case changing attitudes toward sex and gender call for a new interpretation of Title VII.
“The position of a woman discriminated against on account of being a lesbian is thus analogous to a woman’s being discriminated against on account of being a woman,” Posner writes. “That woman didn’t choose to be a woman; the lesbian didn’t choose to be a lesbian. I don’t see why firing a lesbian because she is in the subset of women who are lesbian should be thought any less a form of sex discrimination than firing a woman because she’s a woman.”
But Posner cautioned against basing the decision on Supreme Court precedent prohibiting gender stereotyping in Oncale, which he wrote is “rather evasive,” or Loving, which he said was a constitutional case based on race and “had nothing to do with the recently enacted Title VII.”
Despite criticism of the judiciary for allegedly interpreting the law in ways inconsistent with the intentions of Congress, Posner writes that’s not a problem because he says courts do it “fairly frequently to avoid statutory obsolescence and concomitantly to avoid placing the entire burden of updating old statutes on the legislative branch.”
Also writing a concurring opinion was U.S. Circuit Judge Joel Flaum, a Reagan-appointed judge who writes that sexual orientation discrimination constitutes sex discrimination under Title VII without any need to reinterpret the law.
“So if discriminating against an employee because she is homosexual is equivalent to discriminating against her because she is (A) a woman who is (B) sexually attracted to women, then it is motivated, in part, by an enumerated trait: The employee’s sex,” Flaum writes. “That is all an employee must show to successfully allege a Title VII claim.”
Writing the dissent in the case was U.S. Circuit Judge Diane Sykes, a George W. Bush-appointed judge who writes the majority “deploys a judge-empowering, common-law decision method that leaves a great deal of room for judicial discretion.”
“Respect for the constraints imposed on the judiciary by a system of written law must begin with fidelity to the traditional first principle of statutory interpretation: When a statute supplies the rule of decision, our role is to give effect to the enacted text, interpreting the statutory language as a reasonable person would have understood it at the time of enactment,” Sykes writes. “We are not authorized to infuse the text with a new or unconventional meaning or to update it to respond to changed social, economic, or political conditions.”
Sykes was on the list of judges from which President Trump said during his campaign he’d make appointments to the U.S. Supreme Court and reportedly was one of the three picks on the short list for the late U.S. Associate Justice Antonin Scalia’s seat before Trump nominated U.S. Circuit Judge Neil Gorsuch.
The decision was a source of joy for LGBT rights supporters, who for decades have made a priority of protecting LGBT workers from discrimination.
Greg Nevins, employment fairness program director for Lambda Legal and attorney for the plaintiff, said in a statement the decision is a “gamechanger” for gay people facing workplace discrimination and “sends a clear message to employers: It is against the law to discriminate on the basis of sexual orientation.”
“In many cities and states across the country, lesbian and gay workers are being fired because of who they love,” Nevins said. “But, with this decision, federal law is catching up to public opinion: ninety-percent of Americans already believe that LGBT employees should be valued for how well they do their jobs—not who they love or who they are. Now, through this case and others, that principle is backed up by the courts.”
The U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, the U.S. agency charged with enforcing federal employment civil rights law, determined in its 2015 decision in the case of Baldwin v. Foxx that discrimination against workers for being gay, lesbian or bisexual violates Title VII.
Chad Feldblum, a lesbian and commissioner of the EEOC, said in reaction to the Hively ruling she hopes the decision will serve as model for outside the 7th Circuit in sexual-orientation discrimination cases.
“I am gratified to see that the Seventh Circuit has adopted the simple logic that sexual orientation discrimination is a form of sex discrimination and I hope its reasoning can serve as a model for other courts,” Feldblum said.
The 7th Circuit is composed of Wisconsin, Illinois and Indiana. Wisconsin and Illinois already had state laws against sexual-orientation discrimination in employment, but the ruling assures for the first-time gay, lesbian and bisexual workers have recourse if they face discrimination in Indiana.
Shannon Minter, legal director for the National Center for Lesbian Rights, said the decision “opens the door to a new era for LGBTQ plaintiffs under federal sex discrimination law.”
“With this historic decision, the 7th Circuit is the first federal appellate court to acknowledge that discrimination because a person is gay, lesbian or bisexual can only reasonably be understood as discrimination based on sex,” Minter said. “The court deserves credit for rejecting the tortured rationales of older decisions and undertaking a principled analysis, based on the Supreme Court’s affirmation in Price Waterhouse and other cases, that Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 must be broadly construed to prohibit the full range of sex-based discrimination.”
Although Ivy Tech Community College could file a petition for certiorari to urge the U.S. Supreme Court to reverse the 7th Circuit decision, the school has indicated it won’t pursue that route.
“Ivy Tech Community College rejects discrimination of all types, sexual-orientation discrimination is specifically barred by our policies,” said Jeff Fanter, an Ivy Tech spokesperson. “Ivy Tech respects and appreciates the opinions rendered by the judges of the Seventh Circuit Court of Appeals and does not intend to seek Supreme Court review. The college denies that it discriminated against the plaintiff on the basis of her sex or sexual orientation and will defend the plaintiff’s claims on the merits in the trial court.”
With the 7th Circuit decision, workplace protections for gay, lesbian and bisexual people are catching up to those of transgender people. For years, federal appeals courts have determined discrimination against workers for being transgender amounts to sex discrimination under Title VII, but haven’t done so for sexual orientation discrimination. In 2012, the U.S. EEOC affirmed anti-trans discrimination is unlawful under Title VII in the case of Macy v. Holder.
Federal Government
4th Circuit rules gender identity is a protected characteristic
Ruling a response to N.C., W.Va. legal challenges

BY ERIN REED | The 4th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals ruled Monday that transgender people are a protected class and that Medicaid bans on trans care are unconstitutional.
Furthermore, the court ruled that discriminating based on a diagnosis of gender dysphoria is discrimination based on gender identity and sex. The ruling is in response to lower court challenges against state laws and policies in North Carolina and West Virginia that prevent trans people on state plans or Medicaid from obtaining coverage for gender-affirming care; those lower courts found such exclusions unconstitutional.
In issuing the final ruling, the 4th Circuit declared that trans exclusions were “obviously discriminatory” and were “in violation of the equal protection clause” of the Constitution, upholding lower court rulings that barred the discriminatory exclusions.
The 4th Circuit ruling focused on two cases in states within its jurisdiction: North Carolina and West Virginia. In North Carolina, trans state employees who rely on the State Health Plan were unable to use it to obtain gender-affirming care for gender dysphoria diagnoses.
In West Virginia, a similar exclusion applied to those on the state’s Medicaid plan for surgeries related to a diagnosis of gender dysphoria. Both exclusions were overturned by lower courts, and both states appealed to the 4th Circuit.
Attorneys for the states had argued that the policies were not discriminatory because the exclusions for gender affirming care “apply to everyone, not just transgender people.” The majority of the court, however, struck down such a claim, pointing to several other cases where such arguments break down, such as same-sex marriage bans “applying to straight, gay, lesbian, and bisexual people equally,” even though straight people would be entirely unaffected by such bans.
Other cases cited included literacy tests, a tax on wearing kippot for Jewish people, and interracial marriage in Loving v. Virginia.
See this portion of the court analysis here:

Of particular note in the majority opinion was a section on Geduldig v. Aiello that seemed laser-targeted toward an eventual U.S. Supreme Court decision on discriminatory policies targeting trans people. Geduldig v. Aiello, a 1974 ruling, determined that pregnancy discrimination is not inherently sex discrimination because it does not “classify on sex,” but rather, on pregnancy status.
Using similar arguments, the states claimed that gender affirming care exclusions did not classify or discriminate based on trans status or sex, but rather, on a diagnosis of gender dysphoria and treatments to alleviate that dysphoria.
The majority was unconvinced, ruling, “gender dysphoria is so intimately related to transgender status as to be virtually indistinguishable from it. The excluded treatments aim at addressing incongruity between sex assigned at birth and gender identity, the very heart of transgender status.” In doing so, the majority cited several cases, many from after Geduldig was decided.
Notably, Geduldig was cited in both the 6th and 11th Circuit decisions upholding gender affirming care bans in a handful of states.
The court also pointed to the potentially ridiculous conclusions that strict readings of what counts as proxy discrimination could lead to, such as if legislators attempted to use “XX chromosomes” and “XY chromosomes” to get around sex discrimination policies:
Importantly, the court also rebutted recent arguments that Bostock applies only to “limited Title VII claims involving employers who fired” LGBTQ employees, and not to Title IX, which the Affordable Care Act’s anti-discrimination mandate references. The majority stated that this is not the case, and that there is “nothing in Bostock to suggest the holding was that narrow.”
Ultimately, the court ruled that the exclusions on trans care violate the Equal Protection Clause of the Constitution. The court also ruled that the West Virginia Medicaid Program violates the Medicaid Act and the anti-discrimination provisions of the Affordable Care Act.
Additionally, the court upheld the dismissal of anti-trans expert testimony for lacking relevant expertise. West Virginia and North Carolina must end trans care exclusions in line with earlier district court decisions.
The decision will likely have nationwide impacts on court cases in other districts. The case had become a major battleground for trans rights, with dozens of states filing amicus briefs in favor or against the protection of the equal process rights of trans people. Twenty-one Republican states filed an amicus brief in favor of denying trans people anti-discrimination protections in healthcare, and 17 Democratic states joined an amicus brief in support of the healthcare rights of trans individuals.
Many Republican states are defending anti-trans laws that discriminate against trans people by banning or limiting gender-affirming care. These laws could come under threat if the legal rationale used in this decision is adopted by other circuits. In the 4th Circuit’s jurisdiction, West Virginia and North Carolina already have gender-affirming care bans for trans youth in place, and South Carolina may consider a similar bill this week.
The decision could potentially be used as precedent to challenge all of those laws in the near future and to deter South Carolina’s bill from passing into law.
The decision is the latest in a web of legal battles concerning trans people. Earlier this month, the 4th Circuit also reversed a sports ban in West Virginia, ruling that Title IX protects trans student athletes. However, the Supreme Court recently narrowed a victory for trans healthcare from the 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals and allowed Idaho to continue enforcing its ban on gender-affirming care for everyone except the two plaintiffs in the case.
Importantly, that decision was not about the constitutionality of gender-affirming care, but the limits of temporary injunctions in the early stages of a constitutional challenge to discriminatory state laws. It is likely that the Supreme Court will ultimately hear cases on this topic in the near future.
Celebrating the victory, Lambda Legal Counsel and Health Care Strategist Omar Gonzalez-Pagan said in a posted statement, “The court’s decision sends a clear message that gender-affirming care is critical medical care for transgender people and that denying it is harmful and unlawful … We hope this decision makes it clear to policy makers across the country that health care decisions belong to patients, their families, and their doctors, not to politicians.”
****************************************************************************

Erin Reed is a transgender woman (she/her pronouns) and researcher who tracks anti-LGBTQ+ legislation around the world and helps people become better advocates for their queer family, friends, colleagues, and community. Reed also is a social media consultant and public speaker.
******************************************************************************************
The preceding article was first published at Erin In The Morning and is republished with permission.
National
GLSEN hosts Respect Awards with Billy Porter, Peppermint
Annual event aims to ‘inspire a lot of people to get active’

GLSEN will host its annual Respect Awards April 29 in New York, with guests including Miss Peppermint and Billy Porter.
Respect Awards director Michael Chavez said that the event will be moving.
“It will inspire a lot of people to get active and take action in their own communities and see how much more work there is to do, especially with all of the harmful things happening,” he said.
At the event, they will recognize the Student Advocate of the Year, Sophia T. Annually, GLSEN recognizes a student from around the country who is impacting their community.
“Sophia is doing incredible work advocating for inclusive sex education that is LGBTQ+ affirming, working with Johns Hopkins University to implement curriculum.” Chavez said.
Chavez calls the students that attend the Respect Awards the “biggest celebrities” of the evening.
“It is really important for the adults, both the allies and the queer folks, to hear directly from these queer youth about what it’s like to be in school today as a queer person,” he said.
GLSEN is a queer youth advocacy organization that has been working for more than 30 years to protect LGBTQ youth.
“GLSEN is all hands on deck right now, because our kids are under direct attack and have been for years now,” said actor Wilson Cruz.
Cruz is the chair of GLSEN’s National Board, which works to fundraise and strategize for the organization.
“I think we are fundamental to the education of LGBTQ students in school,” he said. “We advocate for more comprehensive support at the local, national, and federal levels so our students are supported.”
Chavez is one of the students that was impacted by this work. He led his school’s GSA organization and worked with GLSEN throughout his youth.
Cruz said Chavez is doing what he hopes today’s GLSEN students do in the future, which is pay the work forward.
“There’s nothing more powerful than people who have experienced the work that GLSEN does and then coming back and allowing us to expand on that work with each generation that comes forward,” he said.
Florida
Homeless transgender woman murdered in Miami Beach
Andrea Doria Dos Passos attacked while she slept

Gregory Fitzgerald Gibert, 53, who was out on probation, is charged with the second-degree murder of 37-year-old Andrea Doria Dos Passos, a transgender Latina woman who was found deceased in front of the Miami Ballet company facility by a security guard this past week.
According to a Miami Beach Police spokesperson the security guard thought Dos Passos was sleeping in the entranceway around 6:45 a.m. on April 23 and when he went to wake her he discovered the blood and her injuries and alerted 911.
She was deceased from massive trauma to her face and head. According to Miami Beach police when video surveillance footage was reviewed, it showed Dos Passos lying down in the entranceway apparently asleep. WFOR reported: In the early morning hours, a man arrived, looked around, and spotted her. Police said the man was dressed in a black shirt, red shorts, and red shoes.
At one point, he walked away, picked up a metal pipe from the ground, and then returned. After looking around, he sat on a bench near Dos Passos. After a while, he got up and repeatedly hit her in the head and face while she was sleeping, according to police.
“The male is then seen standing over her, striking her, and then manipulating her body. The male then walks away and places the pipe inside a nearby trash can (the pipe was found and recovered in the same trash can),” according to the arrest report.
Police noted that in addition to trauma on her face and head, two wooden sticks were lodged in her nostrils and there was a puncture wound in her chest.
Victor Van Gilst, Dos Passos’s stepfather confirmed she was trans and experiencing homelessness.
“She had no chance to defend herself whatsoever. I don’t know if this was a hate crime since she was transgender or if she had some sort of interaction with this person because he might have been homeless as well. The detective could not say if she was attacked because she was transgender,” said Van Gilst.
“She has been struggling with mental health issues for a long time, going back to when she was in her early 20s. We did everything we could to help her. My wife is devastated. For her, this is like a nightmare that turned into reality. Andrea moved around a lot and even lived in California for a while. She was sadly homeless. I feel the system let her down. She was a good person,” he added.
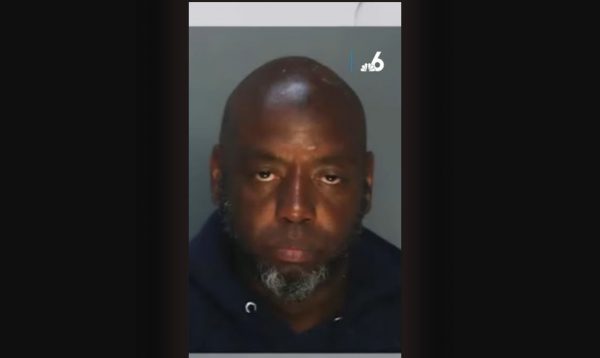
The Miami Police Department arrested Gibert, collected his clothing, noting the red shorts were the same type in the video and had blood on them. Blood was also found on his shoes, according to police. He was taken into custody and charged.
“The suspect has an extensive criminal record and reportedly was recently released from custody on probation for prior criminal charges. Police apprehended the suspect in the city of Miami and the investigation is currently ongoing. This case is further evidence that individuals need to be held accountable for prior violent crimes for the protection of the public. We offer our sincere condolences to the family and friends of the victim,” Miami Beach Mayor Steve Meiner said in a statement.
Joe Saunders, senior political director with LGBTQ rights group Equality Florida, told the Miami Herald that “whenever a transgender person is murdered, especially when it is with such brutality, the question should be asked about whether or not this was a hate-motivated crime.”
-

 South America5 days ago
South America5 days agoArgentina government dismisses transgender public sector employees
-

 Mexico4 days ago
Mexico4 days agoMexican Senate approves bill to ban conversion therapy
-

 Advice4 days ago
Advice4 days agoShould I divorce my husband for the hot new guy in our building?
-

 Maryland3 days ago
Maryland3 days agoMd. governor signs Freedom to Read Act









