National
Sodomy laws remain on books in 17 states, including Md. and Va.
Trans women, gay men prosecuted under ‘loophole’ in Supreme Court ruling
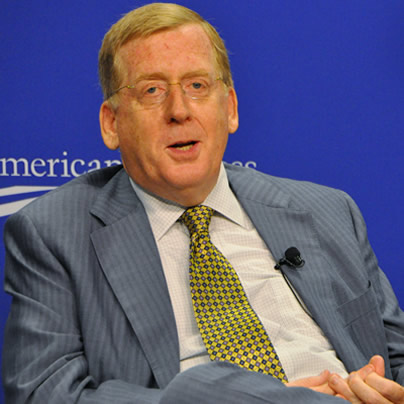


Some gay rights attorneys, including Paul Smith, who successfully argued the Lawrence case before the Supreme Court, have expressed concern that prosecutors and lower court judges are misinterpreting language in the Lawrence decision. (Washington Blade photo by Michael Key)
Laws that make it a crime for consenting adults to engage in sodomy remain on the books in 17 states and continue to be enforced in several of those states 10 years after the U.S. Supreme Court declared such laws unconstitutional.
Last week, the Montana Legislature gave final approval of a bill to repeal that state’s sodomy law. (A spokesperson for the state’s Democratic governor, Steve Bullock, said Bullock was scheduled to sign the bill on Thursday, which would lower the number of states with sodomy laws from 18 to 17.)
According to LGBT activists and gay rights attorneys, most of the cases in which police and prosecutors enforce sodomy or “crime against nature” statutes involve marginalized groups such as transgender sex workers or gay men arrested by undercover police officers for engaging in or soliciting sex in parks or other public places.
But the author of a comprehensive report on the continued enforcement of state sodomy laws released in 2011 by the national LGBT advocacy group Equality Matters said many of the cases involve arrests of men who merely seek to invite another willing male partner to their home for a sexual encounter where prostitution is not involved.
Equality Matters researcher Carlos Maza, author of the report “State Sodomy Laws Continue to Target LGBT Americans,” told the Blade that although sodomy laws apply to straights as well as LGBT people in all but four of the states that have them, LGBT people are targeted far more often than straights.
“LGBT people in Michigan continue to be charged with crimes for public speech, in which they let another person know they are interested in private, unpaid sex with another adult,” the report quotes Michigan gay rights attorney Rudy Serra as saying in the Michigan publication Pride Source.
“Bag-A-Fag (undercover decoy cop) operations, where police officers pretend to be gay men cruising for unpaid, consensual sex continue in Michigan,” the report quotes Serra as saying. “LGBT people are still at risk of spending 15 years in state prison for acts that are perfectly legal in most other states.”
Serra told the Blade in an interview that someone convicted under Michigan’s sodomy law, called the Abominable and Detestable Crime Against Nature statute, and a separate “Gross Indecency” law, also must register with the state as sex offenders.
He said despite the fact that the Lawrence v. Texas decision renders these laws unconstitutional, the Michigan State Bar, which every lawyer is required to join, has retained written instructions about how juries should deliberate over cases in which a person is charged and brought to trial under the sodomy and Gross Indecency laws.
Gary Buseck, legal director of the New England-based litigation group Gay & Lesbian Advocates & Defenders, said he is not aware of any cases in which the Massachusetts sodomy law has been enforced against people for private, consensual, non-commercial sex since the 2003 Lawrence decision.
But he said the Massachusetts law continues to be used, although rarely, by police against gays in cases of “public” sex.
“We have always understood that in straight ‘lovers’ lanes,’ the police traditionally just shoo couples away and that’s that,” he told the Blade. “With gay men there has traditionally been the ebb and flow of sting efforts or entrapment efforts or enhanced enforcement efforts at what become identified as gay cruising areas.”
Buseck added, “Occasionally, men will still be charged with a felony sodomy [in Massachusetts]. But we have not been aware in recent years of any district attorneys who will go forward with such a case.”
In at least one case in North Carolina in 2008, police arrested two gay men under that state’s sodomy statute for allegedly engaging in consenting sex in the privacy of one of their homes. The case outraged gay activists in the state, who noted it was similar to the Lawrence v. Texas case in which the Supreme Court supposedly overturned state sodomy laws.
A prosecutor eventually dropped the charges against the men after determining that the arrest by officers of the Raleigh Police Department violated the Lawrence v. Texas ruling.
The Raleigh News and Observer and other news media outlets reported that police got involved in the case after the men became involved in an incident of domestic violence and one of them called police.
In the course of a police investigation, one of the men said the other sexually assaulted him, according to media accounts. But a police official told media outlets the incident appeared to be “a case of a consensual act that may have gotten out of hand.” Instead of charging one of the men with sexual assault, police charged both men with violating the sodomy statute.
The News and Observer reported at the time that the man who claimed he was sexually assaulted said he was grateful that the sodomy charge was dropped but said he had been humiliated over being accused of a crime listed as a Class 1 felony — sodomy — punishable by up to two years in prison.
“The reality is the process of being arrested for these laws is extremely damaging to the people who get caught up in the system,” Maza told the Blade. “And the only real solution is to have those laws taken off the books.”
Added Maza, “Unfortunately a lot of people don’t have the motivation to get that done when things like marriage and employment discrimination are being discussed in state legislatures.”
Maza and gay rights attorneys familiar with Maryland said they were not aware of Maryland’s sodomy law being enforced since the late 1990s. [See separate Blade story on Maryland’s sodomy law.]
The Virginia sodomy law, which also remains on the books, has been enforced against gays and straights charged with offenses related to public sex or sex with minors, attorneys familiar with the Virginia Crimes Against Nature law have said. A federal appeals court ruled last month that the Virginia statute was “facially” or completely unconstitutional and could no longer be enforced under any circumstances.
The Equality Matters report notes, however, that police and prosecutors in some states, including Michigan and Texas, have continued to enforce sodomy laws despite the fact that state courts have joined the U.S. Supreme Court in invalidating those laws.
“Even in states where these statutes are never enforced, anti-LGBT animosity is fanned by government recognition that LGBT people are viewed as criminals in the eyes of the law,” Maza states in the Equality Matters report. “This animosity helps create the conditions for anti-LGBT hate crimes as well as disproportionate rates of suicide among non-heterosexual youth,” the report says.
Lawrence loophole?
Some gay rights attorneys, including Washington, D.C. attorney Paul Smith, who successfully argued the Lawrence case before the Supreme Court, have expressed concern that prosecutors and lower court judges are misinterpreting language in the Lawrence decision.
According to these attorneys, certain prosecutors and judges are claiming a passage in the Lawrence decision penned by Justice Anthony Kennedy, who wrote the majority opinion in the case, provides a broad loophole that gives them authority to continue enforcing their state sodomy laws in cases involving public sex, sex with minors, or prostitution-related sex.
The passage in question states, “The present case does not involve minors. It does not involve persons who might be injured or coerced or who are situated in relationships where consent might not easily be refused. It does not involve public conduct or prostitution. It does not involve whether the government must give formal recognition to any relationship that homosexual persons seek to enter. The case does involve two adults who, with full and mutual consent from each other, engaged in sexual practices common to a homosexual lifestyle.”
Virginia Attorney General Ken Cuccinelli, who defended Virginia’s sodomy law against a court challenge this year, has cited the so-called loophole in his arguments urging the Fourth Circuit U.S. Court of Appeals in Richmond to uphold the statute. The court instead declared the law unconstitutional based on the Lawrence decision and refused Cuccinelli’s request that the full 15-judge court reconsider the decision handed down by a three-judge panel.
Cuccinelli has yet to disclose whether he plans to ask the U.S. Supreme Court to consider the case as a final appeal.
Gay rights attorneys say that Kennedy’s passage appearing to limit the scope of the Lawrence decision to non-commercial, consenting sex among adults in private appears reasonable on its face. Smith, for example, told the Blade he and the other attorneys who helped him prepare the Lawrence case before the high court did not call for a ruling that went beyond invalidating state sodomy laws for private, consenting, non-commercial sex between adults.
But gay rights attorneys say they do not think Justice Kennedy and the justices who ruled with him intended that gays be singled out for harsher treatment than straights for identical infractions through the enforcement of state sodomy laws.
In the Equality Matters report, Maza points out that prosecutors in some states, especially Louisiana, have used sodomy laws to push for harsher penalties against LGBT suspects using sodomy laws than they would for heterosexual suspects accused of engaging in the exact same behavior, such as prostitution or public sex.
In Louisiana, the report says, people accused of engaging in prostitution could be charged either under the state’s anti-prostitution law or under the solicitation provision of the Louisiana “Crime Against Nature” law, which criminalizes oral and anal sex.
The Crime Against Nature statute carries a longer prison term than the prostitution law, the report says, and unlike the prostitution statute, people convicted under the Crime Against Nature law must register as sex offenders, even if the sex is between consenting adults.
Activists say some of Louisiana’s transgender women and young gay men who have been rejected by their families for being gay or transgender engage in prostitution as a means of survival. Activists say members of these two groups have been among those most frequently charged under the Crime Against Nature law in Louisiana.
The Center for Constitutional Rights, which has provided legal assistance to people charged under Louisiana’s crime against nature law, has criticized law enforcement officials for seeking to enforce the law up until last year, when a state court ruled it could no longer be enforced based on the Lawrence decision.
“[T]he only reason our clients are registered sex offenders is that they were convicted under the provisions of a 200-year-old statute that condemns non-procreative sex acts and sex acts traditionally associated with homosexuality, solely on grounds of moral disapproval,” the group said in a statement.
The Equality Matters report says one of the most dramatic examples of how a state sodomy law can inflict a harsher penalty on LGBT people surfaced in Kansas in 2004. In a case known as State v. Limon, a Kansas state appellate court cited the so-called Lawrence loophole or “exemption” for minors in a ruling upholding a trial court conviction of an 18-year-old male charged with engaging in consensual oral sex with a 14-year-old boy. Both had been living in the same residential school facility for mentally challenged youth.
If the 14-year-old had been a girl rather than a boy, the 18-year-old would have been charged under a Kansas “Romeo & Juliet” law. That law calls for a young adult charged with having sex with a minor whose age is within four years of the young adult to receive a far more lenient sentence under the state’s statutory rape law if the sex is consensual. The 18-year-old, who was charged and convicted under the Kansas criminal sodomy law, was sentenced to 17 years in prison.
His conviction was later overturned by the U.S. Supreme Court on grounds that the Kansas sodomy law was unconstitutional based on the Lawrence decision.
“The reality is that, in many states, enforcement occurs sporadically, typically at the discretion of particular police officers,” said Maza in discussing the rationale for enforcing sodomy laws.
“Even though the laws are clearly unconstitutional, their existence in the legal code gives officers the cover they need to arrest and prosecute gay people,” he said. “Sometimes officers simply choose to ignore Lawrence altogether in an attempt to enforce state sodomy laws as if the decision never occurred.”
Although the majority of sodomy cases are eventually dismissed, Maza said, the fact that people are still charged under the laws, and few people until recently were aware of this taking place, demonstrates that LGBT organizations should take a far more aggressive approach in addressing the issue.
“Only fully repealing these measures ensures that LGBT Americans will be protected from arbitrary and discriminatory legal treatment,” Maza said.
Following is a list of the states that had sodomy laws on the books as of early this week.
Montana’s governor was expected to sign a bill this week to repeal that state’s sodomy law, making Montana the first state to repeal its sodomy statute through legislation in many years.
An asterisk indicates the state sodomy law only applies to gay sex.
- Alabama
- Florida
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Kansas*
- Louisiana
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Montana*
- North Carolina
- Oklahoma*
- South Carolina
- Texas*
- Utah
- Virginia
National
Four bisexual women on stereotypes, erasure, representation, and joy
Panel talks coming out, pop culture, and why dating men doesn’t erase queerness
Uncloseted Media published this article on Feb. 7.
By SPENCER MACNAUGHTON, TAYA STRAUSS, and SAM DONNDELINGER | The number of openly LGBTQ American adults has skyrocketed in the past few years, but there’s one group that’s been leading the way: Gen Z women, 20.7 percent of whom are bisexual.
Despite this increase, many bi women still feel deeply misunderstood. To understand this, Uncloseted Media put together a panel of four bisexual women who spoke candidly about coming out, bi erasure and why bisexuality is often treated as a phase or something that disappears the moment a woman dates a man.
Watch the full interview above or read the transcript here:
Spencer Macnaughton: Hi everyone, I’m Spencer Macnaughton and today I am here with a panel of four bisexual women from across the United States. Thank you all so much for speaking with me and Uncloseted today.
Sophie Sandberg: Thanks so much for having us.
SM: So I always like to start with people’s coming out stories. So yeah, does somebody want to tell me their coming out story a little bit, or when you realized you were bi?
SS: I think part of being bisexual was that it was a long coming out story and kind of a long period of coming out. I always dated cis men when I was in middle school and high school. I started having boyfriends really early and was kind of even boy crazy, I would say. But I did always notice these crushes on my friends, on girls, on more queer and androgynous people I was seeing in the media. So, I would say I started noticing it myself in high school and definitely in college, but I didn’t have to come out because I was in serious relationships with cis men and very straight-passing. So I didn’t officially come out to everyone in my life until I was about 23.
SM: And was that like, I know when I was closeted, I’d hook up with girls, but I didn’t want to be hooking up with girls, right? And it stressed me out. But was there a stressor on that? I always wonder if the stress levels are the same or different as somebody who’s bisexual because you can date people you’re still genuinely interested in.
SS: Yeah, that’s a good point, and I think this is something that differs between me and my lesbian friends. They’ll be like, “yeah, I never enjoyed it, I was so unhappy, and then suddenly everything made sense when I came out.” And for me, I did genuinely have love and connection with cis men who I was in relationships with and slept with, but I also did always have this kind of knowledge or curiosity or interest in sleeping with people who weren’t cis men. So I think I was able to kind of have something genuine there, but also was always aware that there was more than just that for me. If that makes sense.
SM: Yeah. Kelly, how about you?
Kellie Wilson: Yeah, so I actually really only realized that I was bi about a year and a half ago, and so I feel a little bit of imposter syndrome being on a bi panel because I’m pretty new to this actually, and it was an interesting realization of learning that one of my friends that I had been growing closer with actually had feelings for myself and my husband. And at the time it was kind of like a, “whoa, I don’t know what to do with this information.” But over the course of the next few weeks and a bit of identity crisis and thinking about my past and my life and things like that, I realized “oh, I have a crush on her too.” And that I’ve probably had crushes on many women because there have been so many people in my life where I’d see them and like, “oh my gosh, they’re just, they are so cool. I love their vibe, they’re so pretty. I really want to be friends with them.” But then most of the time I wouldn’t actually become friends with them because I’d be too nervous when I was around them. There were absolutely signs and it just never clicked because I think, kind of like what you were saying Sophie, I had been in a long-term relationship with a cis man since my freshman year in college, which, he was my first boyfriend, my first everything. We got engaged, we got married, we had kids. And so there was never necessarily … I don’t know, there was no drive or reason for me to be questioning it, and I think part of that was some internalized biphobia from growing up in a very Christian, not fundamentalist, but gayness was of course a sin in the eyes of the church and all these things. It was something that I think I had internalized enough that it never really crossed my mind because I had feelings for cis men, and so it was like, “okay, yeah, I like men, I must be straight.”
Abby Stein: I think it’s a bit more complicated for me just because I’m also trans, and to add more to it, I grew up in a very gender-segregated community. So that played a very big role in this whole conversation. But the first, I guess, let’s call him a boyfriend for now, was in this very religious school. I was in upstate New York, kind of in the middle of nowhere. I guess in some ways it was a coming out but in other ways in my mind I made sense of it by being like “I’m actually a girl.” Then when, I guess when I was 18, I got married, arranged marriage, very much part of my community, to a woman, and I was very into that as well. So it’s hard for me to be like “okay at what point did I realize both of these people have been very interesting and therefore it says something about my sexuality.” I don’t know, I actually am having a hard time to be like the exact moment or even date or year.
SM: Yeah. And how does, obviously coming out as trans, especially in a gender-segregated community is a very tall task that I’m sure is an entirely different conversation, right? Was coming out as bi, did it feel like even a thing after having come out as trans or how did that play into it all?
AS: I think I struggled with it a lot more than with gender. People tell me a lot, “oh, you must have been struggling with your gender.” And I’m like, “no, I don’t know.” I think my gender, I was very comfortable with who I was and knew who I was since I was a child. Sexuality, I think, I’m still figuring out every day exactly what I do and don’t like. And it’s a constant struggle and journey. Not necessarily a struggle, sometimes a struggle. Sometimes a really great adventure. But it’s definitely something that has been, I think, more complicated to me than gender.
Katie Marie: I thought that I was straight for a very long time, thought that I was just an ally. I was married to a man for about 10 years. I had the house, the picket fence, the master’s degree, the job, and I was still very, very unhappy at the end of every day. I am Indigenous. I started leaning back into my spirituality and started to really dig deep into understanding who I am. It was at that moment in time, I had a really beautiful dream. And in that dream, I saw myself with a woman. I didn’t know that she was a woman, funnily enough, I just felt the energy. And I awoke from that dream and immediately turned to the man who was my husband at that moment in time and said, “I think I am interested in women.” Of course, whenever you first come out as bisexual in a situation like that — I was from the South — there are some negative implications that come with saying that you’re bisexual, especially even from the gay community, right? It’s that implication that you can’t choose a side or that you must choose a side or some version of that?
SM: Tell me a little bit about the biggest misconceptions about bisexual women in society specifically. What are the stereotypes, the misconceptions that are perhaps most frustrating for you guys?
KM: For me, I can speak to one. And this was just one that I experienced very quickly was this idea that for some, because I was bisexual, I was going to now have sex with everybody, right? This idea that I can’t choose a side, so I’m just gonna have relations with everyone and I just can’t make up my mind.
SM: A stereotype of promiscuity.
KM: Yes, exactly. That was a big one. And it came through in my marriage, actually, that was one of the initial problems is my husband started assuming that I was going to have sexual relationships with all of my girlfriends. And that became a big barrier for me to have to overcome.
SS: I feel like there’s a misconception, well, one, that bisexual women just want to be with men. I feel like there’s this misogynistic misconception that anyone who’s bisexual actually wants to be with a cis man, whether it’s a bisexual man or a bisexual woman.
SM: Interesting, I didn’t know that.
SS: If you’re a bisexual man you must really want to be with a man and if you are a bisexual woman you probably also just really want to be with a man. But I think in general just, yeah, people not fully understanding that bisexuality is more fluid and open than that.
KW: I think one of the things that I most often see would be on this idea of fluidity in levels of attraction and the bi cycle, right? And this idea that, “oh, it’s just a phase,” if you start off being more attracted to one gender and then it’s shifting over time, that it’s not gonna shift back. Existing in the middle space is not something that can happen. So I’m also biracial. I’m half black, half white, and I think that it’s this consistent theme in society, like, you can’t be both. And I think that’s really pervasive in the idea of stereotypes about bisexual women. You just have to pick one or you’re never gonna be enough of the other to fully fit. And so it’s sometimes easier to just exist in one space or the other. But then the internal experience of that is where it gets more uncomfortable. Like, no, it’s both. It’s absolutely both.
AS: So I’ve definitely had people saying, “oh, your sexuality” — by people I mean, literally my brother just a few weeks ago — “your sexuality is just part of your entire personality that’s just very confused.” And I don’t see it as that. I just don’t think that everything needs to fit in a very neat box. So it all ties into this idea, for me it all makes sense, which is that I like to look at things and constantly explore them and never decide that something has to be a specific way. And it’s like that with my sexuality, it’s that with the way I see my cultural and spiritual practices. And I think that’s beautiful.
SM: Well, I think it’s really interesting what you said. And I think it takes me back to what Kellie was mentioning about the bi cycle, right? Where people can be more interested in men one day, women the next day, anything in between, right? But I also think, Kellie, what you were mentioning is that there’s people who won’t accept that people can live in this gray zone. I could imagine that’s really frustrating.
KW: I don’t understand why people are so caught up on this need to check one box, right? And that you have to fit into one box. Because, I mean, to me, it’s just the most natural thing in the world to exist in this space of both and all the time and to understand that they — and I think everyone else is confused. I don’t understand why there’s this need to think you can only have one thing.
SS: And people wanna snap us back into a heteronormative space. So I think that’s something I experienced a lot early on coming out as bisexual. People saying, “you’re probably really straight, you’re probably gonna end up in a straight relationship, but this is kind of a phase or something you’re just trying out.” So, I think it comes from this heteronormative society that we live in. People just wanting to force us back into that box. And I think that’s what’s so beautiful about bisexuality. It’s constantly moving into the gray space, getting uncomfortable, having to explore and figure ourselves out. Yeah, I love that about bisexuality.
SM: I think I’ve heard before, “not queer enough.” I’ve heard that from bisexual folks as well. And is the reverse sometimes true as well? Can there be biphobia from gay people?
SS: Yes, absolutely, “not queer enough, not actually gay, just a little bit gay, half gay.” I feel like, yeah, this idea of bisexual as one half gay, one half straight has never made any sense to me ‘cause we’re all fully bisexual, that’s who we are. So yeah, that’s always a really frustrating stereotype too.
KW: I have been pretty nervous in terms of coming out to people who I know who are lesbian because of this stigma or this idea that can exist in the lesbian community, this idea of the gold standard, or if you’ve been with men, then you’re somehow tainted, or you’re not actually fully invested in other women and things like that. Or that if you’re with a woman, then you’re just gonna leave them for a man because of these heteronormative biases and things like that. And so I’ve found myself, I think more nervous to come out to people who I know who are lesbian than people who I know are straight.
AS: Just gonna add, and I think it’s very similar to what you’re saying, Kellie, which is this idea that people constantly assume that you’re never gonna be satisfied, whether from gay people, from straight people, from your own partners. Which is very weird to me, because I think even if you’re a straight person, if you have more than one very specific type, which I think a lot of people do, no one assumes, “oh, you’re never gonna be satisfied because this is not all your types in one person.” It’s not how it works.
SM: Again, frustrating too. I wanted to ask specifically, obviously in many societies in the U.S. right now, it’s still dominated, especially in religious areas, of patriarchal governance structures, right? There’s obviously still a lot of misogyny in society at large. How do you find men treat bisexual women differently than straight women, lesbian women, other women?
KW: Women are already so hypersexualized, and then when they find out that you’re bi it’s like this new level you didn’t even know existed of hypersexualization, of like, oh, they’re thinking, threesomes are always the first thought, and “this would be so hot,” and the idea of … what’s the word I’m looking for? Watching people …
SM: Voyeurism?
KW: There we go. Wanting to watch women be with women but then they’re also with you. And so then there’s this heightened level of fantasization that can happen when they find out that you’re bisexual. I noticed it at bars when I was with my husband and my girlfriend at the time and people trying to figure out the nature of your relationship and then, “oh, there’s these two bi women here, this is so hot.”
SM: Do people feel like they have more free rein to say things like that to you, perhaps because you’re bi?
KW: Not even, I think it’s not even saying things to me, but about me to the man, right? So then they’re directing their comments to my husband, like, “oh, you’re so lucky. How did you manage this?” And one, then that strips me of my own autonomy. And so then it’s weird because you’re objectified as this thing that this other man has somehow managed to collect, achieve. Yes, and then they’re not even directed at me. It’s just like I’m there as this object that exists for the satisfaction of the men in this interaction.
SM: It sounds like these men almost characterize it as though you don’t have agency to come out and say, “I am a proud bisexual woman,” but rather it’s your partner, your male partner who activated the bisexuality, which is obviously crazy. All very interesting. I want to talk quickly about pop culture and the media in 2026. Obviously I think — I’m a geriatric millennial here — and I think we’ve come a long way since Katie Perry’s “I kissed a girl and I liked it.” So we have celebrities now coming out as bi, Jojo Siwa, Billie Eilish. It feels like there’s more of a normalization, but I don’t know, I’m curious about the state of media representation of bi women in 2026. Go for it.
KM: For me, I feel like everybody’s gay. And I think that it is beautiful that more celebrities are coming out. It’s showing the natural progression of understanding who we are as beings, as people. Because I think as children, whenever we don’t get the chance to figure out who we are and who we love, and we’re told instead who we are and who we love, then we have a whole group of geriatric millennials figuring out just now, “wait a minute, maybe I’m somebody else.”
AS: There definitely seems to have been a very intentional, which has to do with the moment we’re in and with funding from federal grants and the attack on DEI and so on, that there’s definitely been. Shows that have been filmed over the past year, if that makes sense, seem to be less queer than, I think, what we had five, six years ago. Specifically traditional media, like network TV and the big name studios, are trying to dial back a bit, a lot of queer representation.
KW: I see that too, Abby. And I think that they’re, especially when it comes to bi representation in the media, I feel like it’s still much lower. When I was first realizing that I was bi, I was like, I couldn’t think of hardly anyone that I had seen in a movie or books that I knew that were about bisexuality. I couldn’t think of any. I had to really go and research and go on reddit and do all this googling to find things to watch to see representation.
SM: I do think what’s fascinating is that the Gallup poll came out this year, and it reported that 23 percent of Gen Z respondents self-identified as bisexual. That’s versus a 9 percent average of the population at large, and that’s a 146 percent rise. Why do you guys think young people are coming out so much more as bi?*1
AS: I think a lot of people, at least in religious communities, and I know some people who I grew up [with] who are like this, who are bi, and they would tell me directly, “if I was gay, I would leave this community and just go do my thing. But I’m bi, I made it work, it’s fine, I will be in this straight-passing relationship and it’s fine.” And the more we give people permission to be themselves, the more people are gonna come out. I don’t think suddenly there are more queer people, I think there’s just more people who are not afraid to literally be shunned from their families and societies for coming out as queer. So I think that is a big part of it. But I definitely think the bi part of this specifically is that even though it has been easier — it’s still not easy, but it has gotten easier over the past few decades. And I think that impacts bi people perhaps even more than — it gets harder for lesbians and gay people to choose not to be that, and to choose to be in a straight-passing relationship. If it’s hard to come out, it can be easier for bi people. So as we are making it easier for people to come out, the numbers go up by a lot.
SS: Abby I really agree with you there, I think that’s really interesting. But I also wonder if Gen Z is more flexible with gender identity and just fluidity in general, and I wonder if that creates more space for a bi identity, ‘cause we’re all talking about how bi-ness is fluidity and it has created this space for a gray area. And I think of Gen Z as being very open also with gender identity and being very fluid and accepting. So I wonder if that in turn creates more space for the bisexual identity. Because there’s fluidity in that too, if that makes sense.
SM: No, it definitely does. And I think a lot of what we’ve talked about today has been around, especially in years past, the idea of bi erasure, right? That’s a concept that’s discussed a lot. And I’m curious what you think we can do as a society to make bi erasure less of a problem and something that feels very prevalent still in 2026.
KW: I think the more that we deconstruct the idea that sexuality is a choice, I think the less bi erasure there will be. The idea of sexuality as a choice has been so harmful for the gay community, right? When people who are bi have been like, “oh, I’ve had the gay erased out of me or prayed the gay away” and things like that. This idea that you can have gayness removed has been so harmful. And so there’s that side of it. And then from the straight side of things, there’s no threat of “oh, well, now someone might see me as gay because there’s these people who are both,” you can never prove that you’re just straight or just lesbian. If you take away the need to prove this and take away this idea that it is a choice at all, then that’s where people can have this more accepting perspective of existence.
AS: I just wanna say we need to focus also on joy, bi joy and queer joy and our joy generally, because at the end of the day, it is really cool. I mean, we get to experience so much of the world. I’m not gonna say that people who are not open to all kinds of genders don’t have that, but I definitely think we are experiencing a very fun and very unique part of the world and that’s amazing.
SM: That is a great thing that I absolutely should have asked more about. What are the best parts about being bisexual?
KM: Freedom for me, freedom to love. It gave me a deeper understanding of self. And at the end of the day, I think that that’s what everybody deserves.
SS: I think that bisexuality has allowed me to understand my gender and my queerness differently because of my attractions to different types of people, and I think that’s a beautiful way that bisexuality allows for freedom and yeah, just like feeling more yourself. Also, I was just gonna say we need more representation. This conversation made me realize wow, yeah, I can’t think of a bi character who I found and looked up to, except for like Alice in The L Word, but she was basically within the lesbian community. So, if anyone’s out there listening and is like, “I wanna create an amazing, joyful bi character,” I feel like that would also be very helpful.
KW: I was just gonna echo the freedom piece, and having the freedom to explore and learn so much about myself has been so freeing, and this feeling of wholeness, I think, has been the most joyful thing of realizing there was a whole piece of me that I didn’t even know existed. It’s just been incredible.
SM: Sophie, Kellie, Katie and Abby, I’m so grateful for your time and for sharing all of this with me and Uncloseted Media today. It’s been a really fantastic conversation, so thank you.
KW: Thanks so much for having us.
SS: Thank you.
New York
Pride flag raised at Stonewall after National Park Service took it down
‘Our flag represents dignity and human rights’
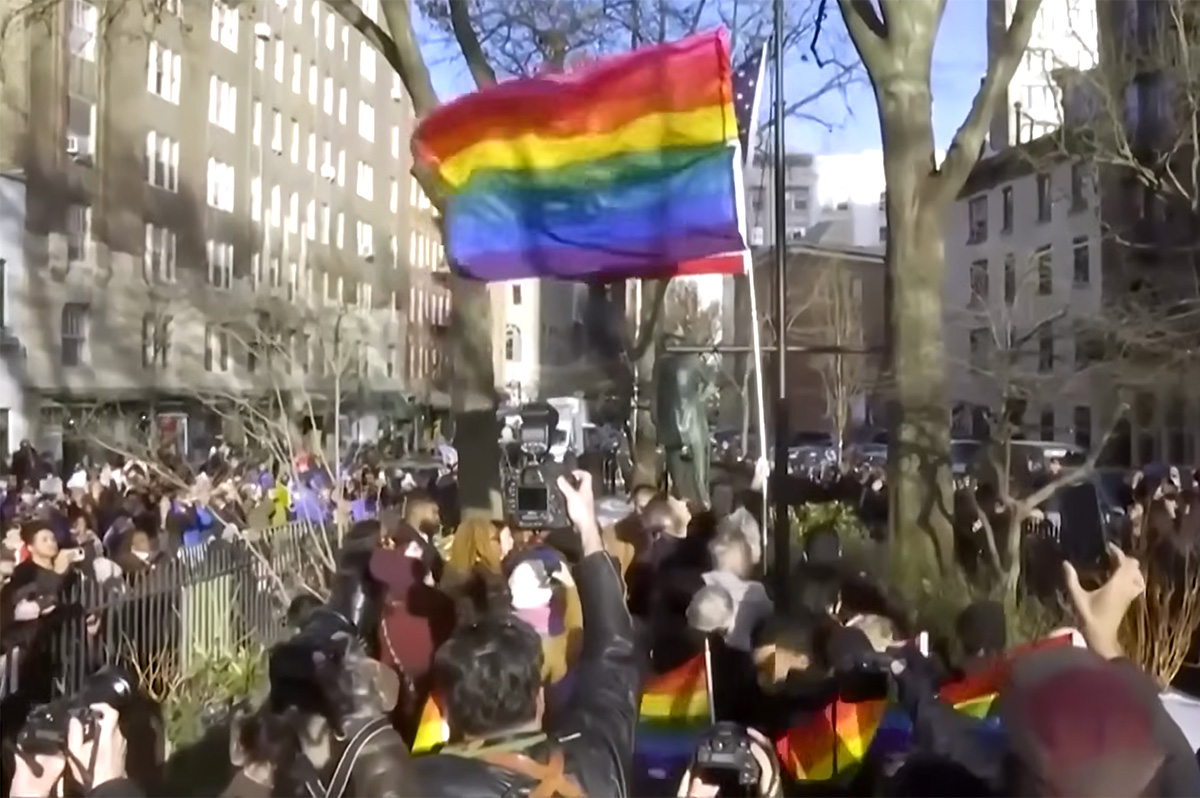
A Pride flag was raised at the site of the Stonewall National Monument days after a National Park Service directive banned flying the flag at the birthplace of the LGBTQ rights movement in the U.S.
The flag-raising was led by Manhattan Borough President Brad Hoylman-Sigal and supported by other elected officials.
“The community should rejoice. We have prevailed,” Hoylman-Sigal said shortly after the flag was hoisted. “Our flag represents dignity and human rights.”
The flag now sits in Christopher Street Park, feet away from the Stonewall Inn, where in 1969 a police raid of the gay bar sparked outrage and led to a rising of LGBTQ people pushing back on NYPD brutality and unjust treatment.
Elected officials brought a new flagpole with them, using plastic zip ties to attach it to the existing pole.
In 2016, President Barack Obama declared the site a national monument.
One day before the planned re-raising of the Pride flag, the National Park Service installed only an American flag on the flagpole, which days prior had flown a rainbow flag bearing the NPS logo.
The directive removing the flag was put forward by Trump-appointed National Park Service Acting Director Jessica Bowron.
This comes one day after more than 20 LGBTQ organizations from across the country co-signed a letter to Interior Secretary Doug Burgum and General Services Administrator Ed Forst, demanding the flag be restored to the monument.
“It is our understanding that the policy provides limited exceptions for non-agency flags that provide historical context or play a role in historic reenactments. Simply put, we urge you to grant this flag an exception and raise it once again, immediately,” the letter read. “It also serves as an important reminder to the 30+ million LGBTQ+ Americans, who continue to face disproportionate threats to our lives and our liberty, that the sites and symbols that tell our stories are worth honoring … However, given recent removals of the site’s references to transgender and bisexual people — people who irrefutably played a pivotal role in this history — it is clear that this is not about the preservation of the historical record.”
The letter finished with a message of resilience the LGBTQ community is known for: “The history and the legacy of Stonewall must live on. Our community cannot simply be erased with the removal of a flag. We will continue to stand up and fight to ensure that LGBTQ+ history should not only be protected — it should be celebrated as a milestone in American resilience and progress.”
When asked about the directive, the NPS responded with this statement:
“Current Department of the Interior policy provides that the National Park Service may only fly the U.S. flag, Department of the Interior flags, and the Prisoner of War/Missing in Action flag on flagpoles and public display points. The policy allows limited exceptions, permitting non-agency flags when they serve an official purpose. These include historical context or reenactments, current military branch flags, flags of federally recognized tribal nations affiliated with a park, flags at sites co-managed with other federal, state, or municipal partners, flags required for international park designations, and flags displayed under agreements with U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services for Naturalization ceremonies.”
An Interior Department spokesperson on Thursday called the move to return the flag to the monument a “political stunt.”
“Today’s political pageantry shows how utterly incompetent and misaligned the New York City officials are with the problems their city is facing,” a department spokesperson said when reached for comment.
The clash comes amid broader efforts by the Trump-Vance administration to minimize LGBTQ history and political power. The White House has spent much of President Donald Trump’s second presidency restricting transgender rights — stopping gender-affirming care for transgender youth, issuing an executive order stating the federal government will recognize only two sexes, male and female, and blocking Medicaid and Medicare from being used for gender-affirming care.
State Department
FOIA lawsuit filed against State Department for PEPFAR records
Council for Global Equality, Physicians for Human Rights seeking data, documents

The Council for Global Equality and Physicians for Human Rights have filed a Freedom of Information Act lawsuit against the State Department for PEPFAR-related data and documents.
The groups, which Democracy Forward represents, filed the lawsuit in U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York on Wednesday.
Then-President George W. Bush in 2003 signed legislation that created PEPFAR. UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima last March said PEPFAR has saved 26 million lives around the world.
The Trump-Vance administration in January 2025 froze nearly all U.S. foreign aid spending for at least 90 days. Secretary of State Marco Rubio later issued a waiver that allowed PEPFAR and other “life-saving humanitarian assistance” programs to continue to operate during the freeze.
The Washington Blade has previously reported PEPFAR-funded programs in Kenya and other African countries have been forced to suspend services and even shut down because of gaps in U.S. funding. HIV/AIDS activists have also sharply criticized the Trump-Vance administration over reported plans it will not fully fund PEPFAR in the current fiscal year.
The lawsuit notes the Council for Global Equality and Physicians for Human Rights have “filed several FOIA requests” with the State Department for PEPFAR-related data and documents. The groups filed their most recent request on Jan. 30.
“On Jan. 30, 2026, plaintiffs, through counsel, sent State a letter asking it to commit to prompt production of the requested records,” reads the lawsuit. “State responded that the request was being processed but did not commit to any timeline for production.”
“Plaintiffs have received no subsequent communication from State regarding this FOIA request,” it notes.
“Transparency and inclusion have been hallmarks of PEPFAR’s success in the last decade,” said Beirne Roose-Snyder, a senior policy fellow at the Council for Global Equality, in a press release that announced the lawsuit. “This unprecedented withholding of data, and concurrent ideological misdirection of foreign assistance to exclude LGBTQI+ people and others who need inclusive programming, has potentially devastating and asymmetrical impacts on already marginalized communities.”
“This data is vital to understanding who’s getting access to care and who’s being left behind,” added Roose-Snyder.
“We filed this lawsuit to seek transparency: the administration’s PEPFAR data blackout withholds information the public, health providers, and affected communities need to track the HIV epidemic and prevent avoidable illness and death, obscuring the true human cost of these policy decisions,” said Physicians for Human Rights Research, Legal, and Advocacy Director Payal Shah.
The State Department has yet to respond to the Blade’s request for comment on the lawsuit.



















