World
Report documents anti-LGBT discrimination, violence in Africa
Amnesty International highlights abuses ahead of Obama’s trip to continent

Protesters gather outside the Ugandan embassy in Northwest D.C. in December 2012 to protest the country’s “Kill the Gays” bill. (Washington Blade photo by Michael Key)
The report — “Making Love a Crime: Criminalization of Same-Sex Conduct in Sub-Saharan Africa — notes 38 African countries continue to criminalize consensual same-sex conduct. These include South Sudan, Liberia and Burundi.
The Nigeria House of Representatives late last month passed a measure that would criminalize what Reuters described as same-sex “amorous relationships” and marriages and memberships in a gay rights group. Those convicted under the proposal that President Goodluck Jonathan has yet to sign into law would face up to 14 years in prison.
Mauritania, Sudan and portions of northern Nigeria and Sudan impose the death penalty upon anyone found guilty of consensual same-sex sexual acts. Ugandan lawmakers have faced criticism over the so-called “Kill the Gays” bill that would impose the death penalty upon anyone convicted of repeated same-sex sexual acts.
The Amnesty International report further notes at least seven LGBT South Africans were murdered between June-Nov. 2012 because of their sexual orientation or gender identity and expression.
It also documents police officers in Cameroon who subjected those they detained under the country’s anti-homosexuality law to forced anal exams. Michel Togué, a lawyer who advocates on behalf of gay Cameroonians, discussed these and other human rights abuses during an interview with the Washington Blade earlier this year in D.C.
“Gay people are not seeking everyone to approve of their behavior,” he said. “They are seeking freedom.”
Widney Brown, director of law and policy for Amnesty International, stressed African governments have a responsibility to protect the rights of their LGBT citizens.
“These attacks — sometimes deadly — must be stopped,” Brown said. “No one should be beaten or killed because of who they are attracted to or intimately involved with.”
Amnesty International released its report less than two days before President Obama is scheduled to leave D.C. for a week-long trip to Africa that will include stops in Senegal, South Africa and Tanzania.
The White House and the State Department have repeatedly spoken out against Uganda’s anti-homosexuality bill.
Secretary of State John Kerry last week responded to a question during Gays and Lesbians in Foreign Affairs Agencies (GLIFAA)’s annual Pride event in Foggy Bottom about “a marked increase in anti-gay legislation and homophobic statements” by government officials and religious leaders in Nigeria, Uganda and other countries. The State Department in August 2012 criticized the Zimbabwean government after police arrested dozens of activists inside the offices of Gays and Lesbians of Zimbabwe (GALZ,) an LGBT rights organization, in Harare, the country’s capital.
“When they raid our offices they think they are going to find pornographic materials,” a GALZ member told the Blade during an exclusive interview earlier this year in D.C. “When they come in there, they find it is a resource center. People are busy working.”
The Obama administration and British Prime Minister David Cameron have both suggested the allocation of international aid should hinge upon a country’s record on LGBT rights.
Amnesty International cites progress on LGBT issues in Africa
In spite of the continued human rights abuses against LGBT Africans, Amnesty International’s report notes progress in many countries across the continent.
Cape Verde, Mauritius, São Tomé and Príncipe and the Seychelles have decriminalized homosexuality over the last decade. Botswana and Mozambique are among the African countries that have banned anti-gay employment discrimination in recent years.
Same-sex couples have been able to marry in South Africa since 2006.
African countries have responsibility to ‘protect, not prosecute’
The Amnesty International report contains a number of recommendations on how it feels African governments can eliminate discrimination and violence against their LGBT citizens. These include repealing laws that criminalize or “otherwise impose punitive sanctions on consensual same-sex conduct,” abolishing the death penalty and eliminating anti-LGBT discrimination in the judicial system.
“As the chorus for recognition grows stronger and stronger, African states have to stop denying that homophobia is a human rights issue and recognize that LGBTI rights are an integral part of the human rights struggle,” Brown said. “It is their responsibility to protect, not persecute.”
India
Anaya Bangar challenges ban on trans women in female cricket teams
Former Indian cricketer Sanjay Bangar’s daughter has received support
Anaya Bangar, the daughter of former Indian cricketer Sanjay Bangar, has partnered with the Manchester Metropolitan University Institute of Sport in the U.K. to assess her physiological profile following her gender-affirming surgery and undergoing hormone replacement therapy.
From January to March 2025, the 23-year-old underwent an eight-week research project that measured her glucose levels, oxygen uptake, muscle mass, strength, and endurance after extensive training.
The results, shared via Instagram, revealed her metrics align with those of cisgender female athletes, positioning her as eligible for women’s cricket under current scientific standards. Bangar’s findings challenge the International Cricket Council’s 2023 ban on transgender athletes in women’s cricket, prompting her to call for a science-based dialogue with the Board of Control for Cricket in India and the ICC to reform policies for transgender inclusion.
“I am talking with scientific evidence in my hand,” Bangar said in an interview posted to her Instagram page. “So, I hope, this makes an impact and I will be hoping to BCCI and ICC talking with me and discussing this further.”
On Nov. 21, 2023, the ICC enacted a controversial policy barring trans women from international women’s cricket. Finalized after a board meeting in Ahmedabad, India, the regulation prohibits any trans player who has experienced male puberty from competing, irrespective of gender-affirming surgery or hormone therapy. Developed through a 9-month consultation led by the ICC’s Medical Advisory Committee, the rule aims to safeguard the “integrity, safety, and fairness” of women’s cricket but has drawn criticism for excluding athletes like Canada’s Danielle McGahey, the first trans woman to play internationally. The policy, which allows domestic boards to set their own rules, is slated for review by November 2025.
Bangar shared a document on social media verifying her participation in a physiological study at the Manchester Metropolitan University Institute of Sport, conducted from Jan. 20 to March 3, 2025, focused on cricket performance. The report confirmed that her vital metrics — including haemoglobin, blood glucose, peak power, and mean power — aligned with those of cisgender female athletes. Initially, her fasting blood glucose measured 6.1 mmol/L, slightly above the typical non-diabetic range of 4.0–5.9 mmol/L, but subsequent tests showed it normalized, reinforcing the study’s findings that her physical profile meets female athletic standards.
“I am submitting this to the BCCI and ICC, with full transparency and hope,” said Bangar. “My only intention is to start a conversation based on facts not fear. To build space, not divide it.”
In a letter to the BCCI and the ICC, Bangar emphasized her test results from the Manchester Metropolitan University study. She explained that the research aimed to assess how hormone therapy had influenced her strength, stamina, haemoglobin, glucose levels, and overall performance, benchmarked directly against cisgender female athletic standards.
Bangar’s letter to the BCCI and the ICC clarified the Manchester study was not intended as a political statement but as a catalyst for a science-driven dialogue on fairness and inclusion in cricket. She emphasized the importance of prioritizing empirical data over assumptions to shape equitable policies for trans athletes in the sport.
Bangar urged the BCCI, the world’s most influential cricket authority, to initiate a formal dialogue on trans women’s inclusion in women’s cricket, rooted in medical science, performance metrics, and ethical fairness. She called for the exploration of eligibility pathways based on sport-specific criteria, such as haemoglobin thresholds, testosterone suppression timelines, and standardized performance testing. Additionally, she advocated for collaboration with experts, athletes, and legal advisors to develop policies that balance inclusivity with competitive integrity.
“I am releasing my report and story publicly not for sympathy, but for truth. Because inclusion does not mean ignoring fairness, it means measuring it, transparently and responsibly,” said Bangar in a letter to the BCCI. “I would deeply appreciate the opportunity to meet with you or a representative of the BCCI or ICC to present my findings, discuss possible policy pathways, and work towards a future where every athlete is evaluated based on real data, not outdated perceptions.”
Before her transition, Bangar competed for Islam Gymkhana in Mumbai and Hinckley Cricket Club in the U.K., showcasing her talent in domestic cricket circuits. Her father, Sanjay Bangar, was a dependable all-rounder for the Indian national cricket team from 2001 to 2004, playing 12 test matches and 15 One Day Internationals. He later served as a batting coach for the Indian team from 2014 to 2019, contributing to its strategic development.
Cricket in India is a cultural phenomenon, commanding a fanbase of more than 1 billion, with more than 80 percent of global cricket viewership originating from the country.
The International Cricket Council, the sport’s governing body, oversees 12 full member nations and more than 90 associate members, with the U.S. recently gaining associate member status in 2019 and co-hosting the 2024 ICC Men’s T20 World Cup. The BCCI generated approximately $2.25 billion in revenue in the 2023–24 financial year, primarily from the Indian Premier League, bilateral series, and ICC revenue sharing. The ICC earns over $3 billion from media rights in India alone for the 2024–27 cycle, contributing nearly 90 percent of its global media rights revenue, with the BCCI receiving 38.5 percent of the ICC’s annual earnings, approximately $231 million per year.
Women’s cricket in India enjoys a growing fanbase, with over 300 million viewers for the Women’s Premier League in 2024, making it a significant driver of the sport’s global popularity. The International Cricket Council oversees women’s cricket in 12 full member nations and over 90 associate members, with the U.S. fielding a women’s team since gaining associate status in 2019 and competing in ICC events like the 2024 Women’s T20 World Cup qualifiers. The BCCI invests heavily in women’s cricket, allocating approximately $60 million annually to the WPL and domestic programs in 2024–25, while contributing to the ICC’s $20 million budget for women’s cricket development globally. India’s media market for women’s cricket, including WPL broadcasting rights, generated $120 million in 2024, accounting for over 50 percent of the ICC’s women’s cricket media revenue.
“As a woman, I feel when someone says that they are women, then they are, be trans or cis. A trans woman is definitely the same as a cis woman emotionally and in vitals, and specially, when someone is on hormone replacement therapy. Stopping Anaya Bangar from playing is discrimination and violation of her rights. It is really sad and painful that every transwoman need to fight and prove their identity everywhere,” said Indrani Chakraborty, an LGBTQ rights activist and a mother of a trans woman. “If ICC and BCCI is stopping her from playing for being transgender, then I will say this to be their lack of awareness and of course the social mindsets which deny acceptance.”
Chakraborty told the Blade that Bangar is an asset, no matter what. She said that the women’s cricket team will only benefit by participation, but the discriminating policies are the hindrance.
“Actually the transgender community face such discrimination in every sphere. In spite of being potent, they face rejection. This is highly inhuman. These attitudes is regressive and will never let to prosper. Are we really in 2025?,” said Chakraborty. “We, our mindset and the society are the issues. We, as a whole, need to get aware and have to come together for getting justice for Anaya. If today, we remain silent, the entire community will be oppressed. Proper knowledge of gender issues need to be understood.”
The BCCI and the International Cricket Council have not responded to the Blade’s repeated requests for comment.
El Salvador
La marcha LGBTQ desafía el silencio en El Salvador
Se realizó el evento en San Salvador bajo la lluvia, pero con orgullo
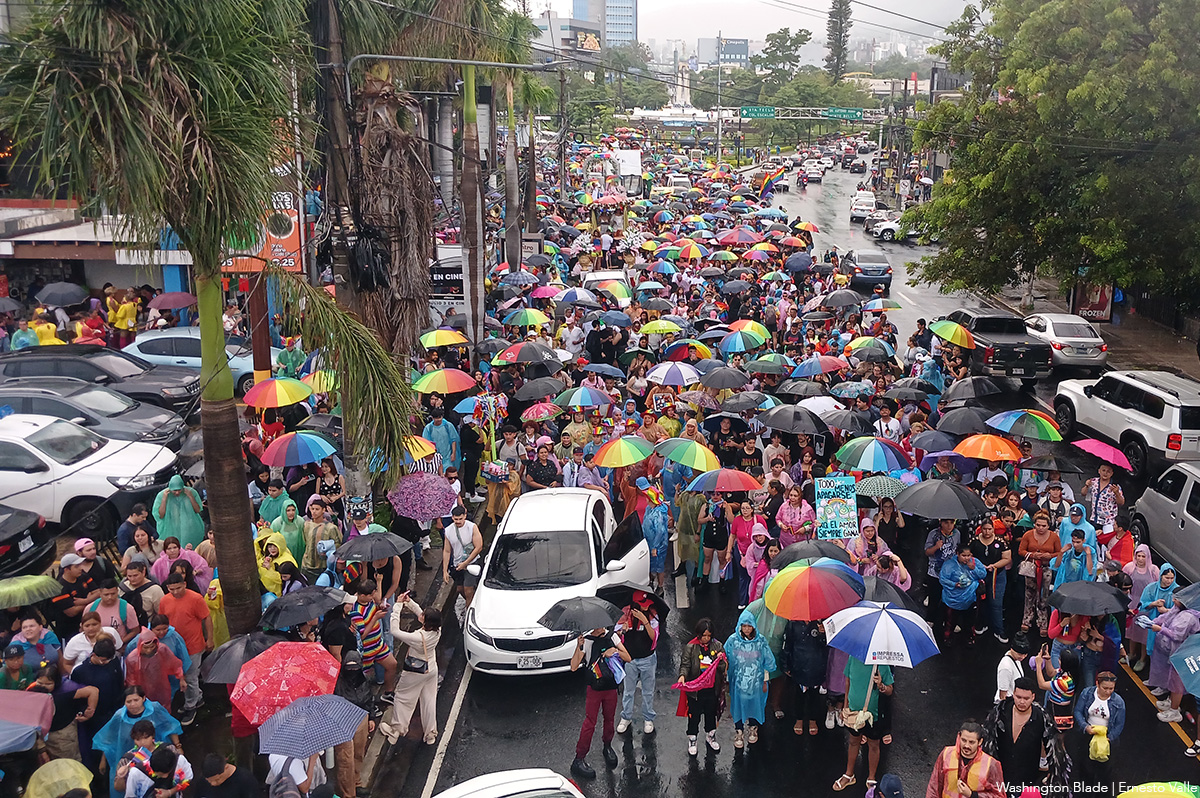

SAN SALVADOR, El Salvador — El reloj marcaba el mediodía cuando los primeros colores del arcoíris comenzaron a ondear frente a la emblemática Plaza del Divino Salvador del Mundo. A pesar de la incertidumbre generada en redes sociales, donde abundaban los rumores sobre una posible cancelación de la marcha por la diversidad sexual, la ciudad capital comenzaba a llenarse de esperanza, de resistencia y de orgullo.
Este año, la Marcha del Orgullo LGBTQ+ en El Salvador se desarrolló en un contexto tenso, en medio de un clima político que reprime y silencia a las voces disidentes.
“Aunque las estadísticas digan que no existimos, viviendo en El Salvador, un país donde hoy, después de décadas de avances, defender los derechos humanos es de nuevo una causa perseguida, criminalizada y silenciada”, afirmaron representantes de la Federación Salvadoreña LGBTQ+.
A pesar de la cancelación del festival cultural que usualmente acompaña la marcha, los colectivos decidieron seguir adelante con la movilización, priorizando el sentido original de la actividad: salir a las calles para visibilizarse, exigir respeto a sus derechos y recordar a quienes ya no están.
A la 1:30 p.m., una fuerte lluvia comenzó a caer sobre la ciudad. Algunas de las personas presentes corrieron a refugiarse, mientras otras, debajo de sombrillas y de los escasos árboles en la plaza, decidieron mantenerse firmes. Los comentarios pesimistas no se hicieron esperar: “a lo mejor la cancelan por el clima”, “no se ve tanta gente como otros años”. Sin embargo, lo que siguió fue una muestra de resistencia: a las 2:05 p.m. las voces comenzaron a llamar a tomar las calles.
Visibilidad como resistencia
La marcha arrancó bajo una llovizna persistente. La Avenida Roosevelt y la Alameda Juan Pablo II se tiñeron de colores con banderas arcoíris, trans, lésbicas, bisexuales y otras que representan a los diversos sectores de la población LGBTQ. Cada bandera alzada fue un acto político, cada paso una declaración de existencia.
Desde la Plaza del Divino Salvador del Mundo hasta la Plaza Gerardo Barrios, frente a Catedral Metropolitana y el Palacio Nacional, la marcha se convirtió en un carnaval de dignidad. Carteles con frases como “El amor no se reprime”, “Mi existencia no es delito” o “Marcho por quien ya no puede hacerlo” se alzaron entre las multitudes.
La movilización fue también un espacio para recordar a quienes han perdido la vida por la discriminación y el rechazo. Familias que marcharon por hijos, hijas o amigues que se suicidaron a causa del estigma. Personas que caminaron por quienes aún viven en el miedo, por quienes no pudieron salir del clóset, por quienes se han ido del país huyendo de la violencia.
Arte, fe y rebeldía
Una de las escenas más llamativas fue protagonizada por Nelson Valle, un joven gay que marchó vestido como sacerdote.
“Hay muchas personas que secretamente asisten a ritos religiosos como en Semana Santa, y les gusta vivir en lo oculto. Pero la fe debe ser algo libre porque Dios es amor y es para todos”, dijo.
Valle utilizó su vestimenta como una forma de protesta contra las estructuras religiosas que aún condenan la diversidad sexual.
“Un ejemplo de persona que abrió el diálogo del respeto fue el papa Francisco, abrió la mente y muy adelantado a su tiempo, porque dejó claro que hay que escuchar a toda persona que quiere encontrar a Dios”, agregó.
La marcha también incluyó bandas musicales, grupos de cachiporristas, carrozas artísticas, colectivos provenientes de distintos puntos del país, y manifestaciones de orgullo en todas sus formas. Fue un mosaico cultural que mostró la riqueza y diversidad de la población LGBTQ en El Salvador.
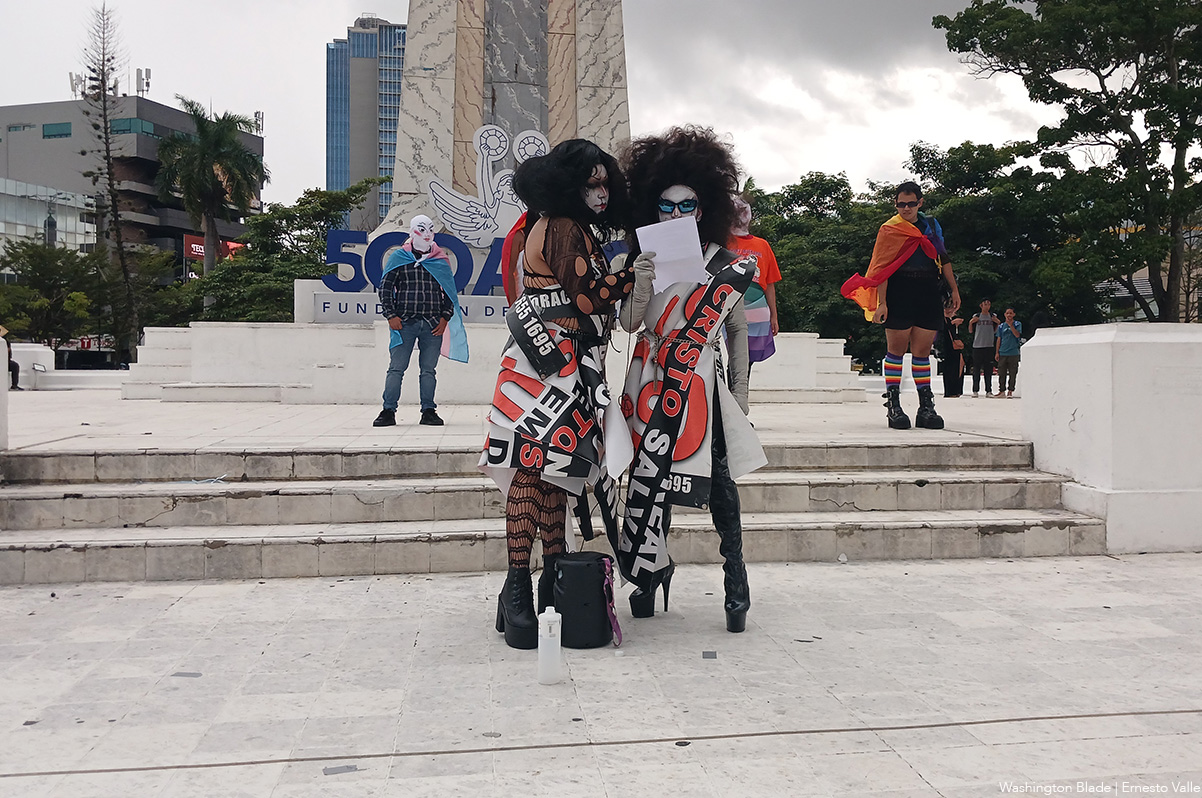

Una lucha que persiste
Las organizaciones presentes coincidieron en su mensaje: la lucha por la igualdad y el reconocimiento no se detiene, a pesar de los intentos del Estado por invisibilizarlos.
“Nuestros cuerpos se niegan a ser borrados y a morir en la invisibilidad de registros que no guardan nuestros nombres ni nuestros géneros”, declararon representantes de la Federación.
Además, agregaron: “Desde este país que nos quiere callar, levantamos nuestras voces: ¡La comunidad LGBTIQ+ no se borra! ¡El Salvador también es nuestro! Construyamos, entre todes, un país donde podamos vivir con Orgullo.”
El ambiente fue de respeto, pero también de desconfianza. La presencia de agentes policiales no pasó desapercibida. Aunque no hubo reportes oficiales de violencia, varias personas expresaron su temor por posibles represalias.
“Marchar hoy es también un acto de valentía”, comentó Alejandra, una joven lesbiana que viajó desde Santa Ana para participar. “Pero tenemos derecho a vivir, a amar, a soñar. Y si nos detenemos, les damos la razón a quienes nos quieren ver en silencio.”
Rumbo al futuro
Concluida la marcha frente a Catedral y el Palacio Nacional, muchas personas permanecieron en la plaza compartiendo abrazos, fotos y palabras de aliento. No hubo festival, no hubo escenario, pero hubo algo más valioso: una comunidad que sigue viva, que sigue resistiendo.
Los retos son muchos: falta de leyes de protección y que apoye las identidades de las personas trans, discriminación laboral, violencia por prejuicio, rechazo familiar, y una narrativa estatal que pretende que no existen. Pero la marcha del 28 de junio demostró que, aunque el camino sea cuesta arriba, la dignidad y el orgullo no se borran.
La lucha por un El Salvador más justo, más plural y más inclusivo continúa. En palabras de uno de los carteles más llamativos de ese día: “No estamos aquí para pedir permiso, estamos aquí para recordar que también somos parte de este país”.
Hungary
Upwards of 100K people march in Budapest Pride
Participants defined Hungarian government’s ban on public LGBTQ events
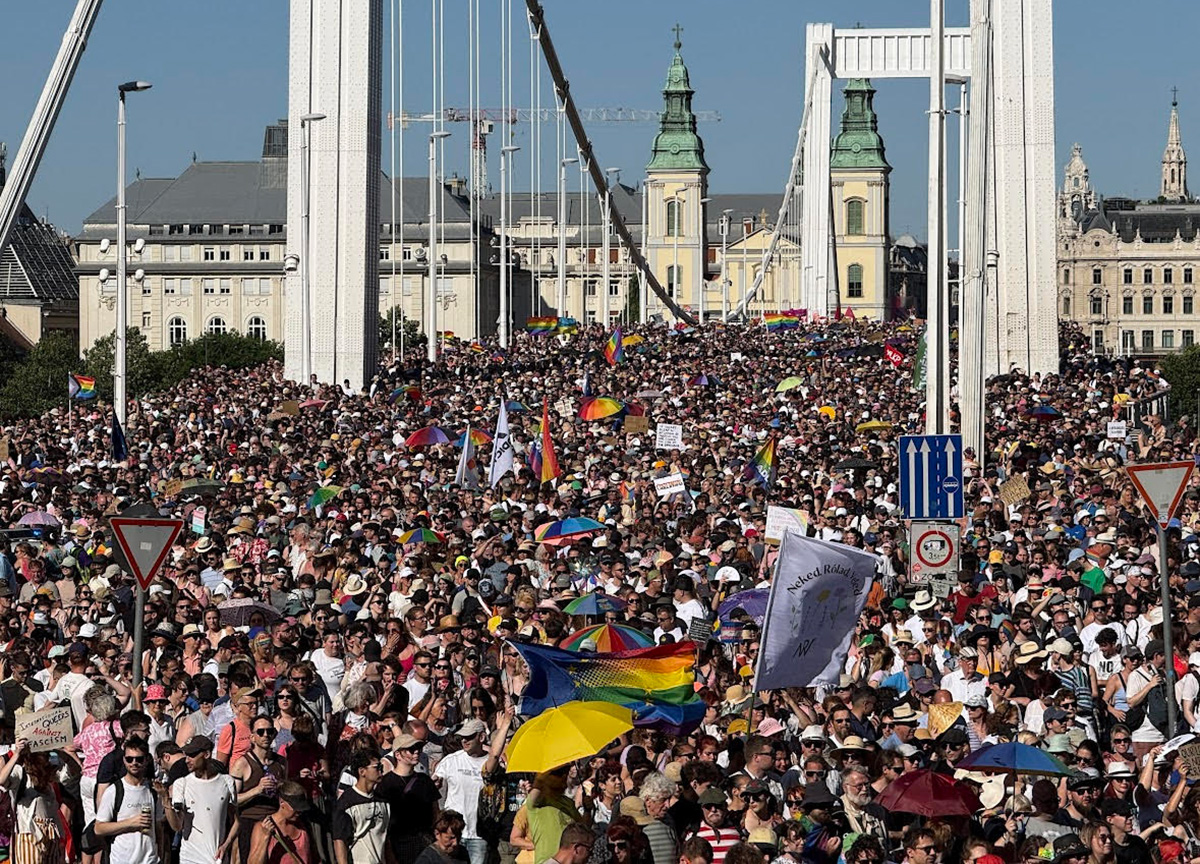

More than 100,000 people on Saturday defied the Hungarian government’s ban on public LGBTQ events and participated in the 30th annual Budapest Pride parade.
The New York Times published a picture that shows throngs of people marching on Budapest’s Erzsébet Bridge over the Danube River. Openly gay MEP Krzysztof Śmiszek, who was previously Poland’s deputy justice minister, is among the dozens of European lawmakers who participated in the march that began at Budapest City Hall.
The New York Times reported Hungarian police officers stood along the march, but they did not try to stop it. Śmiszek described the march to the Washington Blade as “beautiful and huge.”
“[It was] very peaceful and political,” he said.
Prime Minister Viktor Orbán and his Fidesz-KDNP coalition government have faced widespread criticism over its anti-LGBTQ crackdown.
Hungarian lawmakers in March passed a bill that bans Pride events and allow authorities to use facial recognition technology to identify those who participate in them. MPs in April amended the Hungarian constitution to ban public LGBTQ events.
Budapest Mayor Gergely Karácsony endorsed the march, even though Orbán’s government threatened to arrest him and fine participants.
“Today a country shows that no ruling party can tell it on what topic, for what cause it is allowed to march and why not,” said Budapest Pride President Viktória Radványi on Saturday in a Facebook post. “A country demonstrates that whoever will be in government can count on us: dedicated, persistent citizens intolerant to oppression, who will organize themselves and stand against tyranny with their heads held high.”
More than two dozen activists in D.C. who protested outside the Hungarian Embassy on Friday expressed their support for Budapest Pride.
(Washington Blade video by Michael K. Lavers)
-

 U.S. Supreme Court3 days ago
U.S. Supreme Court3 days agoSupreme Court upholds ACA rule that makes PrEP, other preventative care free
-

 U.S. Supreme Court4 days ago
U.S. Supreme Court4 days agoSupreme Court rules parents must have option to opt children out of LGBTQ-specific lessons
-

 National5 days ago
National5 days agoEvan Wolfson on the 10-year legacy of marriage equality
-
 Congress4 days ago
Congress4 days agoSenate parliamentarian orders removal of gender-affirming care ban from GOP reconciliation bill