World
Cameroon group works to protect, empower LGBTQ community
Working For Our Wellbeing operates throughout country
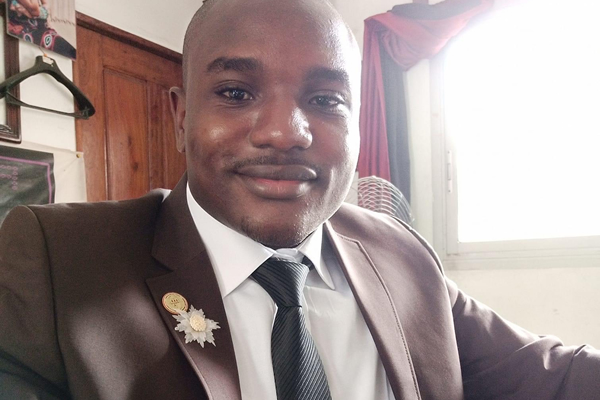

Nkwain Hamlet is the president and executive director of of Working For Our Wellbeing, an LGBTQ advocacy organization in Douala, Cameroon’s bustling economic capital, that works toward providing queer Cameroonians with access to safety and a chance to live confident, fully self-actualized lives in a society that is nothing but vilely queerphobic. Hamlet recently spoke with the Washington Blade about his LGBTQ advocacy and future representation in the country’s government.
“Cameroon, at all stages, is in a transition point. Whether it’s the presidency, ministerial roles, or different members of parliament, or even the Senate. We even have one of the oldest members of parliament in Africa,” he says about the possibility of an LGBTQ politician emerging in the country. “So, I think that in upcoming years, it will be a moment!”
Pushing Cameroon towards acceptance
Cameroon, like many African countries, has a culture of queerphobia that colonialism brought. Before Germany, and later France and the U.K, seized Cameroonian land and resources — wiping away any sense of freedom, agency and culture that existed in opposition to eurocentrism — queerness in what is now Cameroon was the norm.
Native Cameroonians practiced homoeroticism, with men being allowed to have consensual sex with other men. Women could also marry other women and establish same-sex households.
“Among the Pangwe people of present-day Cameroon and Gabon, homosexual intercourse was practiced between males of all ages,” reports Bernadine Evaristo for The Guardian.
Nankiti Nofuru for the Global Press Journal also reports about the Balong ethnic group.
“The Balong tradition allows women to marry to other women in cases where women are barren or have no children. Even women who want additional children but are unable to conceive them may marry other women,” reported Nofaru
So, for Hamlet, whose goal is to advocate for all queer people in Cameroon by affording them the space to confidently inhabit their queerness, one of his organization’s focal points is to participate in politics and make queerness a national conversation that will encourage the government to establish wholly-protected human rights for LGBTQ individuals.
“We currently don’t have any representation at the parliamentary level,” says Hamlet. “And because of this, we want to make sure that [LGBTQ people] are reflected and have role models in [this country’s] political positions.”
Cameroon’s future elections are on Hamlet’s mind, and he has famliarized himself with conversations surrounding the necessity to make sure that queer people are not only acknowledged in politics, but involved in decision-making processes. He emphasizes that there is a need for someone queer to step out, penetrate the politics scene and engage with the government.
Carrying this out, however, does not come without its hindrances. Hamlet recognizes one has to negotiate two realities in order to be a successful out LGBTQ politician in a predominantly queerphobic Cameroon.
“[To be a politician], you have to come out and embrace the political question of who is for you and who isn’t. And also, you have to think about who will support your candidacy and political agenda financially,” says Hamlet.
He notes that financial support can exist through entrepreneurs and other influential figures who support the LGBTQ movement. Attaining it can nevertheless be exacting as many of them fear the public backlash that ensues after standing in favor of what Cameroonian nationals consider controversial identity issues.
“[Entrepreneurs] may not want to give their position regarding identity issues, and because of the backlash, you see them deleting their messages whether on Twitter or Facebook. So, you just have to identify who these people are and know that they’re open-minded and [will work in your favor],” says Hamlet.

Making sure no one is left behind
Cameroon for years has been embroiled in the Anglophone Crisis, a civil war that stems from a conflict between Anglophone and Francophone Cameroonians, and their fight to maintain their respective colonial legacies, especially with regards to law and education.
BBC reports eight out of Cameroon’s 10 semi-autonomous administrative regions are Francophone, while the other two are Anglophone. English-speaking Cameroonians consequently face discrmination because they are excluded from lucrative employment opportunities and a chance at significant political representation as “government documents are often only published in French, even though English is also an official language.” Cameroon’s education system is also Francophone-centric, and it has created disparities because English-speaking areas are subjected to French standards, even though they inherited the British education system.
Reuters reports the Anglophone Crisis as recently as 2020 has killed approximately 3,500 people. The violence has displaced 700,000 people from their homes as English-speaking groups fight to break away from the predominantly French-speaking government.
The crisis has quickly become an LGBTQ human rights issue for Hamlet and Working For Our Wellbeing because a queer population exists in the two Anglophone regions: Northwest and Southwest. Hamlet describes the situation as “catastrophic” when speaking about how the conflict has affected his organization’s work.
“A lot of the work we do involves educating heterosexual people in the Francophone zones on tolerance and acceptance. Now that this conflict exists, our work becomes challenging because we are not able to reach the Anglophone zones as effectively as we are able to reach the Francophone zones,” says Hamlet.
He also notes LGBTQ people in the area are “in a death trap.” It therefore feels to him when he tackles national advocacy work that there is a gap because his organization is unable to reach Anglophone LGBTQ individuals without encountering diffculties.
Working For Our Wellbeing is nevertheless redefining their strategies to better equip themselves to reach out to LGBTQ Cameroonians in the country’s English-speaking areas. Part of this includes the development of a stringent security plan and analyzing the day-to-day situation to ensure that Anglophone LGBTQ individuals can be fiercely advocated for without the organization facing any repercussions. The aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic and Cameroon’s general political crisis have made it imperative to advocate on behalf queer Anglophones with the utmost care and sensitivity.
Imparting hope and joy to the LGBTQ community
As this month nears the end and many countries around the world conclude their Pride celebrations, Working For Our Wellbeing’s festivities are in full force, with preparations for a poetry competition fully underway. There will also be a round-table conversation that will welcome open-minded members of the general public interested in discussing and learning more about LGBTQ issues in Cameroon.
“We’ve been hit hard by the law, and with everything, so we want to celebrate ourselves,” says Hamlet. “We are ready.”
Working For Our Wellbeing after Pride will continue to do what it knows best: Caring for LGBTQ Cameroonians. Whether it’s providing temporary shelter for queer people who have been rejected by their families or empowering them to be financially independent, one thing that is certain is that Hamlet and his organization will put LGBTQ Cameroonians first, normalize queerness and establish a culture akin to that which existed pre-colonialism.
Chile
Far-right Chilean President José Antonio Kast takes office
Former congressman opposes LGBTQ rights
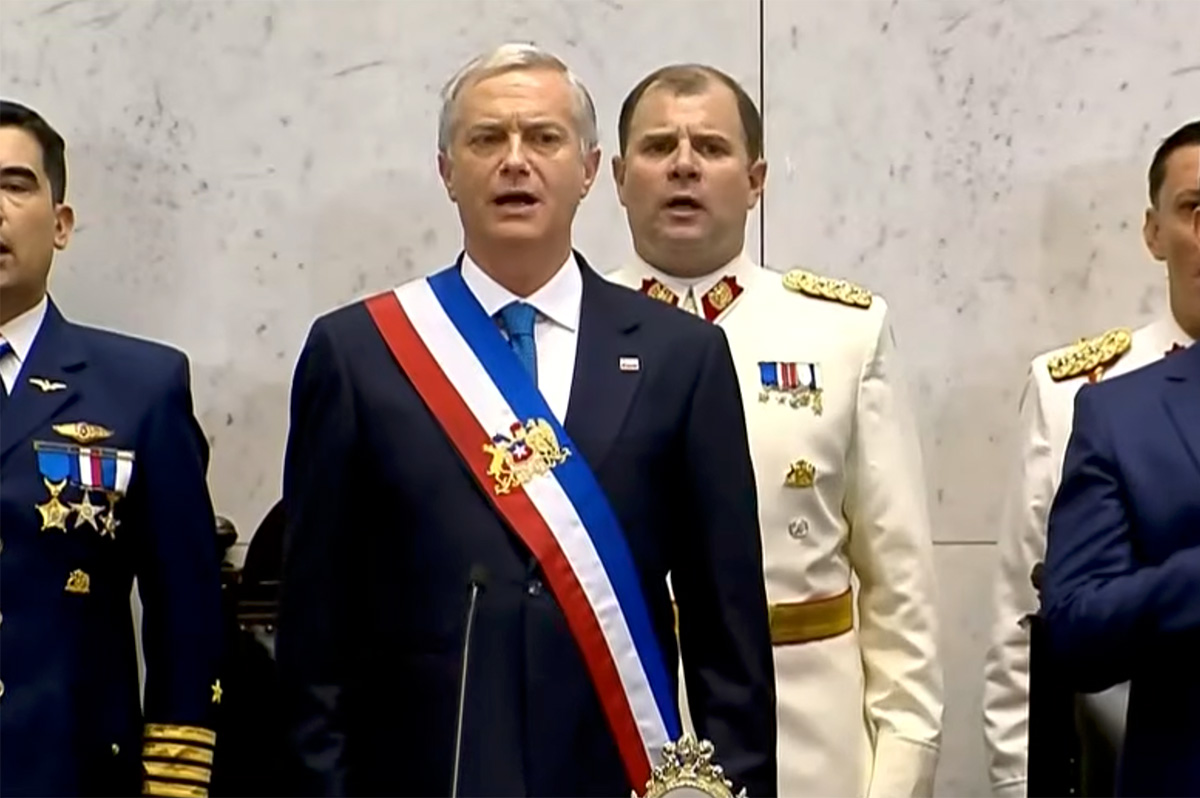

Chilean President José Antonio Kast took office on Wednesday.
Kast — the far-right leader of the Republican Party who was a member of the country’s House of Deputies from 2002-2018 — defeated Jeannette Jara — a member of the Communist Party of Chile who was the former labor and social welfare minister in former President Gabriel Boric’s government — in last year’s presidential election.
The Chilean constitution prevented Boric from running for a second consecutive term.
The Washington Blade has previously reported Kast has expressed his opposition to gender-specific policies, comprehensive sex education, and reforms to Chile’s anti-discrimination laws. Kast has also publicly opposed the country’s marriage equality law that took effect on March 10, 2022, the day before Boric took office.
The Movement for Homosexual Integration and Liberation, a Chilean LGBTQ and intersex rights group known by the acronym Movilh, declared a “state of alert” after Kast’s election, “given this leader’s (Kast’s) public and political trajectory, characterized for decades by systematic opposition to laws and policies aimed at equality and nondiscrimination of LGBTIQ+ individuals.”
Argentine President Javier Milei and Deputy U.S. Secretary of State Christopher Landau are among those who attended Kast’s inauguration that took place in the Chilean Congress in Valparaíso.
Ukraine
Ukrainian Supreme Court recognizes same-sex couple as a family
Zoryan Kis and Tymur Levchuk married in US in 2021

The Ukrainian Supreme Court has recognized a same-sex couple as a family.
The couple — Zoryan Kis and Tymur Levchuk — have lived together since 2013. They legally married in the U.S. in 2021.
The Kyiv Independent notes the couple challenged the Ukrainian Foreign Ministry’s refusal to acknowledge Levchuk as Kis’s family member, therefore denying him spousal rights while Kis was posted at the Ukrainian Embassy in Israel. Kis and Levchuk challenged the decision in court in 2024.
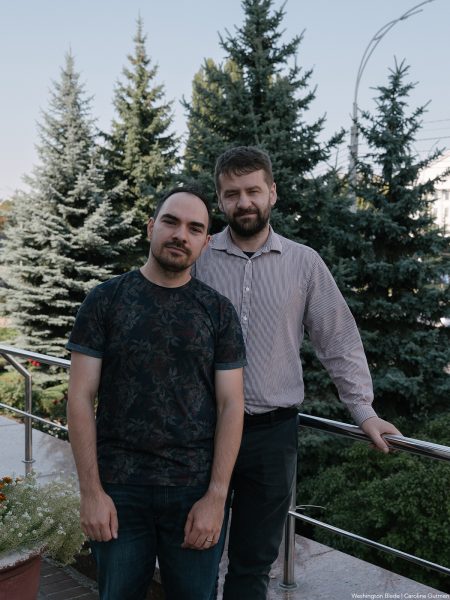

Kyiv’s Desniansky District Court last year in a landmark ruling recognized Kis and Levchuk as a family. Vsi Razom, an anti-LGBTQ organization, appealed the decision.
Insight, the Ukrainian LGBTQ rights group that represented Kis and Levchuk, said the Supreme Court upheld the lower court’s ruling on Feb. 25.
“The Supreme Court of Ukraine has upheld the legality of recognizing a same-sex couple as a family based on their factual relationship, despite the absence of legal recognition of same-sex partnerships in Ukrainian legislation,” Insight Chair Olena Shevchenko noted to the Washington Blade on Tuesday. “The court confirmed the decision, establishing the fact that (the) two men had lived together as a family, affirming that such recognition can be based on proven circumstances of their shared life rather than on political decisions or the existence of formal partnership laws.”
Insight in a Facebook post added the Supreme Court ruling sets “a tremendous precedent.”
“No homophobic or conservative organization will be able to use the courts as a tool to persecute or overturn decisions in favor of LGBT+ people under the guise of ‘social morality,’” said Insight. “The state has protected the boundaries of private life.”
The Supreme Court issued its ruling a day after Ukraine marked four years since Russia began its war against the country.
The Ukrainian constitution defines marriage as between a man and a woman.
President Volodymyr Zelenskyy in 2022 publicly backed civil partnerships for same-sex couples. Shevchenko pointed out Ukrainian law “currently does not provide a mechanism for registering same-sex marriages or partnerships.”
Iran
Man stuck in Lebanon as Iran war escalates
Mario was traveling to India when conflict began on Feb. 28
The Washington Blade on March 6 spoke with a man who remains stuck in Lebanon because of the escalating Iran war.
Mario, who asked the Blade not to publish his last name, lives in the U.S., but was born in Lebanon. He decided to stop in the country to see his doctor before traveling to India for work.
Mario was about to board a flight at Rafic Hariri International Airport in Beirut, the Lebanese capital, on Feb. 28 when airline personnel announced “we cannot fly anymore” because authorities had closed the country’s airspace.
The U.S. and Israel earlier that day launched airstrikes against Iran.
One of them killed Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. Iran in response launched missiles and drones against Israel and Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Azerbaijan, Cyprus, and other countries.
An Iranian drone that hit a command center in Kuwait on March 1 killed six U.S. soldiers: Sgt. Declan Coady, Sgt. 1st Class Nicole Amor, Capt. Cody Khork, Sgt. 1st Class Noah Tietjens, Chief Warrant Officer 3 Robert Marzan, and Maj. Jeffrey O’Brien. Another American servicemember, Sgt. Benjamin Pennington, died on Sunday, a week after Iranian drones and missiles targeted the Prince Sultan Air Base in Saudi Arabia.
Iranian drones and missiles have also damaged civilian infrastructure, including hotels and airports in Dubai in the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait. An Iranian missile on March 1 killed nine people and injured 27 others in Beit Shemesh, Israel.
The war has left Mario and hundreds of thousands of others stranded in the Middle East.
“I had to come back home,” Mario told the Blade.
“Luckily, I’m with family,” he added.
‘War is between Israel and Hezbollah’
Hezbollah, an Iran-backed Shia militant group the U.S. and Israel have designated a terrorist organization, after Khamenei’s death launched rockets at Israel. The Jewish State in response has carried out airstrikes against Hezbollah targets across Lebanon.
Hamas militants on Oct. 7, 2023, killed upwards of 1,200 people when they launched a surprise attack against Israel from the Gaza Strip. Hezbollah the following day began to launch rockets into Israel.
An Israeli airstrike in Beirut on Sept. 27, 2024, killed Hassan Nasrallah, Hezbollah’s long-time leader. Iran four days later launched upwards of 200 ballistic missiles at Israel.
The U.S. helped broker a ceasefire between Israel and Lebanon that took effect on Nov. 27, 2024. Israel nevertheless continued to carry out airstrikes in Lebanon.
Israel on June 13, 2025, launched airstrikes against Iran that targeted the country’s nuclear and military facilities. The subsequent war, which lasted 12 days, prompted the cancellation of the annual Tel Aviv Pride parade.
Mario noted the Israeli airstrikes have targeted Hezbollah infrastructure in Dahiyah, a Beirut suburb that is predominantly Shia, and in southern Lebanon.
His family’s home is about five miles from downtown Beirut. Mario said there is a mountain “that separates me from the area that is being bombed, so I don’t even hear the sounds.”
“Lebanon is such an interesting juxtaposition, because depending on which area you are in, your quality of life can be different during these times,” he said. “Right now, the war is not between Israel and Lebanon as a government. The war is between Israel and Hezbollah.”
“If you are in the areas where Hezbollah is concentrated, then you are severely impacted,” added Mario. “If you are in other areas, even if they are Shia or … Muslims that usually align themselves with Hezbollah, you’re still relatively in a safe place, in a safe location.”
Israeli evacuation orders have prompted hundreds of thousands of people to flee their homes in Dahiyah and in southern Lebanon.
Mario said many of the evacuees are sleeping in their cars, or on the street. He also noted a video that showed a shepherd with his sheep and goats on a highway in downtown Beirut.
“He took his animals with him because he had to vacate where he was living,” said Mario. “That’s the first time you see in downtown Beirut maybe 100 goats walking the streets with two people sitting on jackasses and herding them.”
“It is very absurd,” he added.
The Lebanese government has opened schools and public shelters for people who have been displaced, but Mario said many of them do not have enough food. He also said gas prices have increased, and people are afraid to drive.
“It really saddens me seeing the kids affected by it,” said Mario. “Hezbollah made this decision, and it was a unilateral decision.”
“I doubt that the Shia people support them,” he added, referring to Hezbollah. “They cannot say it out loud that they do not support them, but I doubt people are happy within less than two years, for the second time in a row, to have to leave their homes and try to find a place to stay.”
Lebanese government urged to develop LGBTQ-inclusive plan for displaced people
Article 534 of Lebanon’s Penal Code states “any sexual intercourse contrary to the order of nature is punishable” by up to a year in prison. Several judges in recent years have opted not to use the statute to prosecute LGBTQ people who have been charged under it.
Helem, a Lebanese LGBTQ and intersex rights group, on March 4 called upon the Lebanese government and international NGOs to develop a response to the Israeli airstrikes that is “comprehensive, fair, and inclusive of all groups, without exception or discrimination.
“The experience of the previous war demonstrated that state response plans were not sufficiently inclusive of displaced LGBTQ+ individuals,” said Helem. “Many faced compounded challenges, including the inability to access state collective shelters, exposure to harassment or violence, difficulty accessing health and psychosocial services, and fear of disclosing their gender identity or sexual orientation due to stigma and discrimination.”
“Any emergency plan that fails to take the most vulnerable groups into account exposes their lives and dignity to additional risks,” added the group.
Helem also made the following requests:
• Integrating a rights-based and nondiscrimination approach in all stages of planning and implementation, ensuring safe and equal access to assistance and services.
• Training staff working in shelters and emergency response on principles of protection from gender-based violence and discrimination, including issues related to gender identity and sexual orientation.
• Reassessment of the currently adopted shelter model, which relies exclusively on the concept of the “traditional family” aligned with a specific social structure. In practice, this leads to the systematic exclusion of non-traditional families and individuals who do not belong to conventional family units, including LGBTQ+ individuals, survivors of domestic violence, migrant workers, and people without supportive family networks.
• Involving civil society organizations specialized in gender issues and LGBTQ+ rights in the design, implementation, and monitoring of the emergency response plan.
• Establishing clear monitoring and accountability standards to ensure that violations or discriminatory practices do not occur during the implementation of the emergency plan.
“Disasters and conflicts do not justify the suspension of rights or the neglect of marginalized groups. On the contrary, the need for a humanitarian approach grounded in dignity and equality becomes even more urgent in times of crisis.”
“Helem places its expertise and experience at the disposal of relevant authorities and affirms its readiness to cooperate to ensure that the emergency plan is more just, effective, and inclusive,” said Helem. “Dignity is indivisible, and protection must include everyone without exception.”
-

 Florida5 days ago
Florida5 days agoFla. Senate passes ‘Anti-Diversity’ bill that could repeal local LGBTQ protections
-

 Celebrity News5 days ago
Celebrity News5 days agoLiza Minnelli makes surprise appearance at GLAAD Media Awards
-

 Opinions5 days ago
Opinions5 days agoCapital Pride must be transparent about sexual misconduct investigation
-

 Nightlife4 days ago
Nightlife4 days agoIn D.C. comedy, be sure to shop local




















