homepage news
Trans bathroom use next frontier for courts on LGBT rights
A look at the many cases working their way through the system

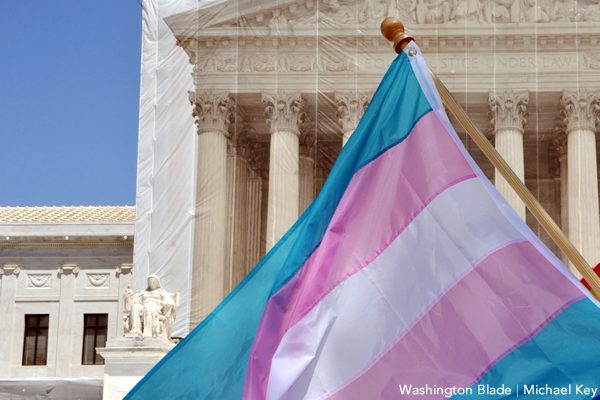
In the aftermath of the historic decision in favor of marriage equality, the next LGBT rights issue the courts will likely settle is the right for transgender people to use the restroom consistent with their gender identity, although legal experts have different predictions on whether the endgame is the Supreme Court or lower courts.
Last week, the U.S. Supreme Court weighed in on the case of a transgender Virginia student whose school is barring him from using the boy’s restroom by issuing a stay blocking a ruling in his favor from the U.S. Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals from taking effect.
The law supporting the case for Gavin Grimm, a student at Gloucester High School, is Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972. The Fourth Circuit determined the prohibition on gender discrimination in schools requires the school to allow Grimm to use the restroom consistent with his gender identity.
Observers have predicted the 5-3 stay in the case indicates the Supreme Court will grant review in the case as part of its upcoming term. After all, issuing a stay requires a vote of five justices on the Supreme Court, but granting a writ of certiorari (or agreeing to take up a case) takes a vote of four.
But legal experts denied that scenario will necessarily unfold of the Supreme Court accepting the Grimm case and settling the transgender restroom issue with that case.
Jon Davidson, legal director for Lambda Legal, said although the Supreme Court may decide to take up the Grimm case, the granting of a stay “doesn’t indicate for sure that they will grant cert.”
“There have been multiple cases where the Supreme Court has granted a stay of a lower court and then denied cert after it’s granted stay pending consideration of a cert petition,” Davidson said.
Ilona Turner, legal director of the San Francisco-based Transgender Law Center, said agreement from the Supreme Court to hear the case is “pretty unlikely” because the Fourth Circuit decision “is so legally sound” and the issue is new in federal courts.
“Usually the Supreme Court will only take up review if the lower courts and specifically the federal courts of appeal are in disagreement with one another, if there’s a real deadlock among the federal courts of appeal, and we are very far from anything like that in terms of Title IX’s protection for transgender students,” Turner said.
The Supreme Court initially granted stays pending review of federal appeals court decisions in favor of marriage equality in the Tenth, Fourth and Seventh Circuits, then ultimately declined to hear the cases. Only after the Sixth Circuit upheld bans on same-sex marriage, creating a split among the circuits, did the Supreme Court decide to adjudicate the marriage issue.
Moreover, U.S. Associate Justice Stephen Breyer, considered one of the four liberal justices on the bench, voted with the conservative justices to grant a stay “as a courtesy.”
Breyer, who has called the death penalty cruel, has been thwarted from considering a case that could potentially ban the punishment, Medellin v. Texas, because justices wouldn’t grant a stay on the execution of a death row inmate before the Supreme Court could consider the issue. Breyer cited the case in his explanation for why he was granting a “courtesy” vote for conservative justices on the bench.
Davidson said the Supreme Court may well decline to hear the Grimm case given Breyer’s apparent disagreement in principle with the stay — as well as the current eight-justice makeup of the bench — because they know the ultimate result would be affirmation of the Fourth Circuit decision.
“Any four justices who may want to hear the case because they disagreed would understand that a 4-4 split by the Supreme Court would summarily confirm the 4th Circuit decision, just as happened recently in the U.S. v. Texas case involving immigration enforcement, and would keep the injunction in place,” Davidson said. “And so, they would need to think about whether they would really want to grant cert under those circumstances.”
The Gloucester School Board has yet to even file a petition of certiorari before the Supreme Court even though the request for a stay was based on Supreme Court consideration of the lawsuit. The deadline for the school board to make the filing is Aug. 29, which is 90 days after the Fourth Circuit’s final decision denying the school board’s motion for en banc review before the full court on May 31.
The Supreme Court would likely docket the petition for consideration during conference after the new term begins in October, although there’s no deadline for the court to consider the request or take action.
Davidson said even if the Supreme Court declines to take up the Grimm case, justices will likely accept review for a lawsuit on whether transgender people can use the restroom consistent with their gender identity at some point in time — perhaps in three to four years.
“I think there’s a good chance that the Supreme Court would grant cert at some point,” Davidson said. “I think there is sort of an issue where I think there’s a good chance there would be a split in the circuits at some point, but one of the issues with respect to the G.G. case is that it is kind of early in the development of the case law here for the Supreme Court to weigh in on this issue.”
If the November election is favorable to transgender advocates, Davidson said the issue could also be resolved through passage of comprehensive LGBT non-discrimination legislation known as the Equality Act, which he said would be a “definitive statement” that gender identity is protected under the law.
Turner, on the other hand, predicted every circuit adjudicating the issue would follow precedent and rule in favor of transgender people using the restroom consistent with their gender identity, eliminating the need for the Supreme Court to take action.
“I’m confident that we won’t see other circuit courts going the other way because the reasoning of the Fourth Circuit is so sound and they were simply applying well-established rules of interpretation to Title IX to conclude that transgender students are entitled to the same protections as everyone else, and it’s pretty hard to disagree with that conclusion legally,” she said.
The Grimm case is but one of multiple cases on the right of transgender people to use the restroom consistent with their gender identity, although his case is the furthest along procedurally.
Five lawsuits are challenging North Carolina’s House Bill 2, which prohibits transgender people from using the restroom in schools and government buildings consistent with their gender identity. Those lawsuits include one filed against the law by U.S. Attorney General Loretta Lynch and another by Lambda, the American Civil Liberties Union and the ACLU of North Carolina as well as countersuits filed by the North Carolina Legislature, the anti-LGBT Alliance Defending Freedom and Gov. Pat McCrory. A trial over HB 2 is set to begin in federal court on Nov. 14.
In response to the Obama administration’s guidance instructing schools to allow transgender students to use the public restroom in accordance with their gender identity, Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton filed a lawsuit representing 12 states and two school districts against the Obama administration. Nebraska Attorney General Doug Peterson is representing 10 states in a separate lawsuit against the guidance. An initial hearing in the Paxton lawsuit is set for Friday.
In Wisconsin, a transgender student has filed a lawsuit against Kenosha Unified School District for barring him from the boys’ restroom and not respecting his gender identity in other ways. A similar lawsuit was filed in federal court by a transgender boy in Talbot County, Md.
In Illinois, the Alliance Defending Freedom has filed a lawsuit representing Palatine School District against the Department of Education after a transgender student was granted access to the girl’s locker room. In Ohio, the Alliance Defending Freedom is representing Highland School District in a similar lawsuit over the federal government’s requirement for accommodation of transgender students.
Also pending is the lawsuit against Mississippi’s recently enacted “religious freedom” law House Bill 1523, which allows businesses to prohibit restroom usage in accordance with gender identity. A federal court has placed an injunction on enforcement of the law, but the litigation isn’t yet resolved.
Joshua Block, a senior staff attorney for the ACLU’s LGBT Project, said the stay in the Grimm case may impact proceedings in these other cases, but they’re unlikely to reach the Supreme Court in time for joint consideration.
“Some judges might hold off on ruling, some judges may not,” Block said. “I’m sure the different parties in the different cases will be arguing to the judges whether they should … move forward, but obviously I don’t think there’s any case that is in a posture of being decided by a district court and being decided by the court of appeals before mid-October.”
A key decision bolstering the case transgender people must be allowed to use the restroom consistent with their gender identity under current law is the 1989 Supreme Court ruling in Price Waterhouse v. Hopkins, which determined gender stereotyping is actionable as sex discrimination under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act. Courts and the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission have drawn on this ruling to determine transgender discrimination is barred under current law.
Although Title VII governs employment, not education, courts look to guidance on Title VII for interpretation of Title IX because both laws prohibit gender discrimination.
Based on this precedent and other rulings under Title IX, Block expressed confidence the Supreme Court would rule in favor of transgender rights if justices granted certiorari to review the case.
“I’ve learned many, many times not to predict how the justices would rule, but I can certainly predict on what the answer should be based on existing precedent on everything the court has said before, which is that the Fourth Circuit’s decision was correct, and under any standard of review or any standard of deference, excluding transgender students from being able to use the same restrooms as their peers violates Title IX,” Block said. “And I think certainly if the court does grant cert now, I am certainly hopeful they will be consistent with what they’ve said before and affirm the Fourth Circuit decision.”
homepage news
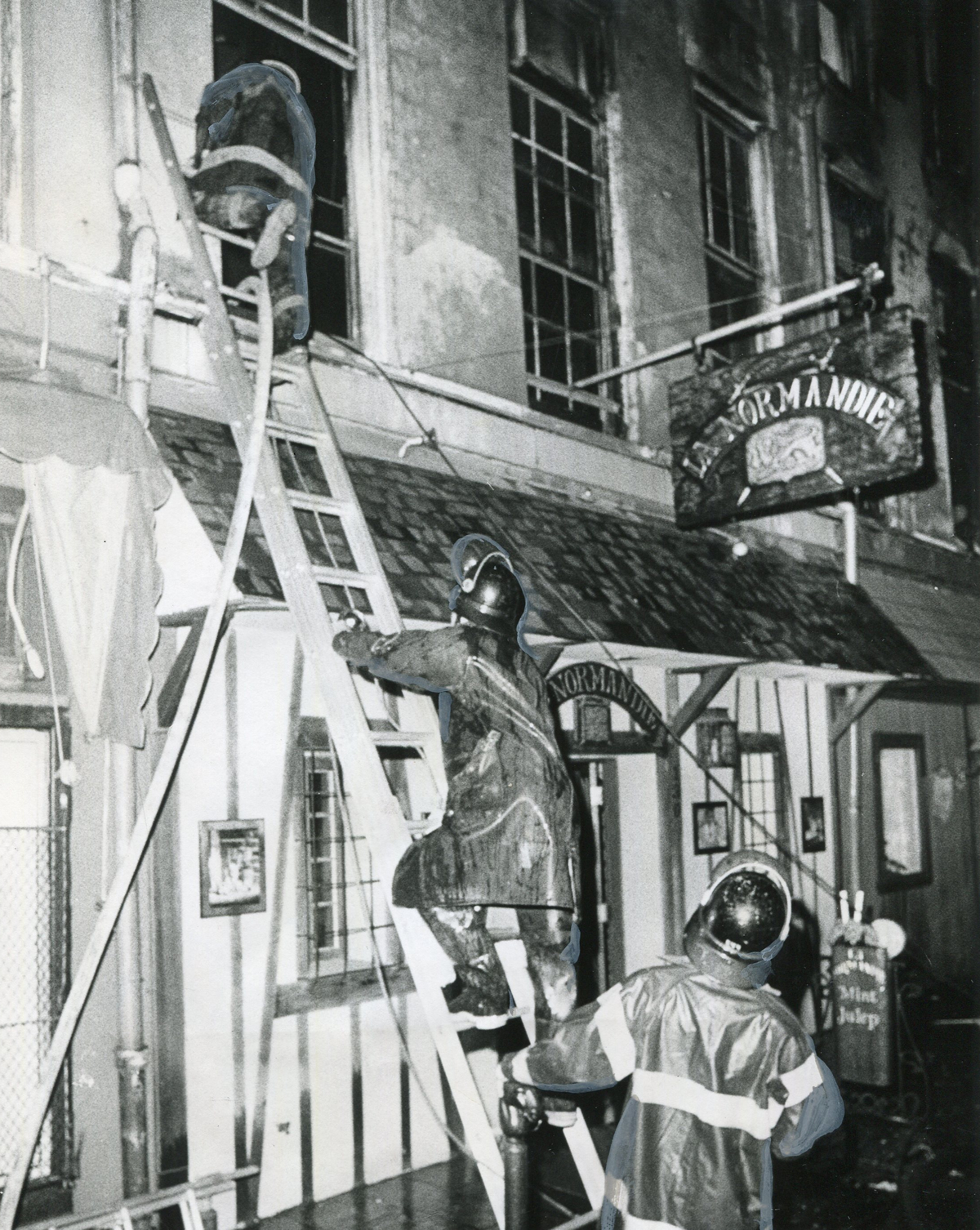
Honoring the legacy of New Orleans’ 1973 UpStairs Lounge fire
Why the arson attack that killed 32 gay men still resonates 50 years later

On June 23 of last year, I held the microphone as a gay man in the New Orleans City Council Chamber and related a lost piece of queer history to the seven council members. I told this story to disabuse all New Orleanians of the notion that silence and accommodation, in the face of institutional and official failures, are a path to healing.
The story I related to them began on a typical Sunday night at a second-story bar on the fringe of New Orleans’ French Quarter in 1973, where working-class men would gather around a white baby grand piano and belt out the lyrics to a song that was the anthem of their hidden community, “United We Stand” by the Brotherhood of Man.
“United we stand,” the men would sing together, “divided we fall” — the words epitomizing the ethos of their beloved UpStairs Lounge bar, an egalitarian free space that served as a forerunner to today’s queer safe havens.
Around that piano in the 1970s Deep South, gays and lesbians, white and Black queens, Christians and non-Christians, and even early gender minorities could cast aside the racism, sexism, and homophobia of the times to find acceptance and companionship for a moment.
For regulars, the UpStairs Lounge was a miracle, a small pocket of acceptance in a broader world where their very identities were illegal.
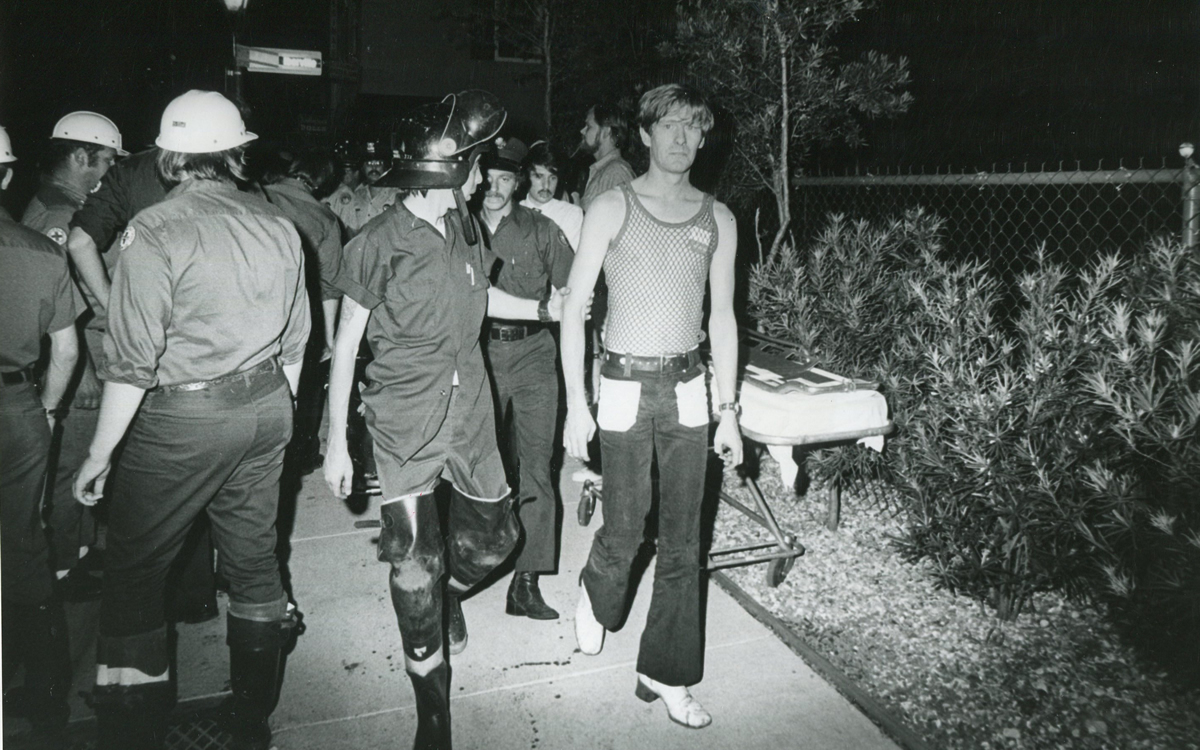
On the Sunday night of June 24, 1973, their voices were silenced in a murderous act of arson that claimed 32 lives and still stands as the deadliest fire in New Orleans history — and the worst mass killing of gays in 20th century America.
As 13 fire companies struggled to douse the inferno, police refused to question the chief suspect, even though gay witnesses identified and brought the soot-covered man to officers idly standing by. This suspect, an internally conflicted gay-for-pay sex worker named Rodger Dale Nunez, had been ejected from the UpStairs Lounge screaming the word “burn” minutes before, but New Orleans police rebuffed the testimony of fire survivors on the street and allowed Nunez to disappear.
As the fire raged, police denigrated the deceased to reporters on the street: “Some thieves hung out there, and you know this was a queer bar.”
For days afterward, the carnage met with official silence. With no local gay political leaders willing to step forward, national Gay Liberation-era figures like Rev. Troy Perry of the Metropolitan Community Church flew in to “help our bereaved brothers and sisters” — and shatter officialdom’s code of silence.
Perry broke local taboos by holding a press conference as an openly gay man. “It’s high time that you people, in New Orleans, Louisiana, got the message and joined the rest of the Union,” Perry said.
Two days later, on June 26, 1973, as families hesitated to step forward to identify their kin in the morgue, UpStairs Lounge owner Phil Esteve stood in his badly charred bar, the air still foul with death. He rebuffed attempts by Perry to turn the fire into a call for visibility and progress for homosexuals.
“This fire had very little to do with the gay movement or with anything gay,” Esteve told a reporter from The Philadelphia Inquirer. “I do not want my bar or this tragedy to be used to further any of their causes.”
Conspicuously, no photos of Esteve appeared in coverage of the UpStairs Lounge fire or its aftermath — and the bar owner also remained silent as he witnessed police looting the ashes of his business.
“Phil said the cash register, juke box, cigarette machine and some wallets had money removed,” recounted Esteve’s friend Bob McAnear, a former U.S. Customs officer. “Phil wouldn’t report it because, if he did, police would never allow him to operate a bar in New Orleans again.”
The next day, gay bar owners, incensed at declining gay bar traffic amid an atmosphere of anxiety, confronted Perry at a clandestine meeting. “How dare you hold your damn news conferences!” one business owner shouted.
Ignoring calls for gay self-censorship, Perry held a 250-person memorial for the fire victims the following Sunday, July 1, culminating in mourners defiantly marching out the front door of a French Quarter church into waiting news cameras. “Reverend Troy Perry awoke several sleeping giants, me being one of them,” recalled Charlene Schneider, a lesbian activist who walked out of that front door with Perry.
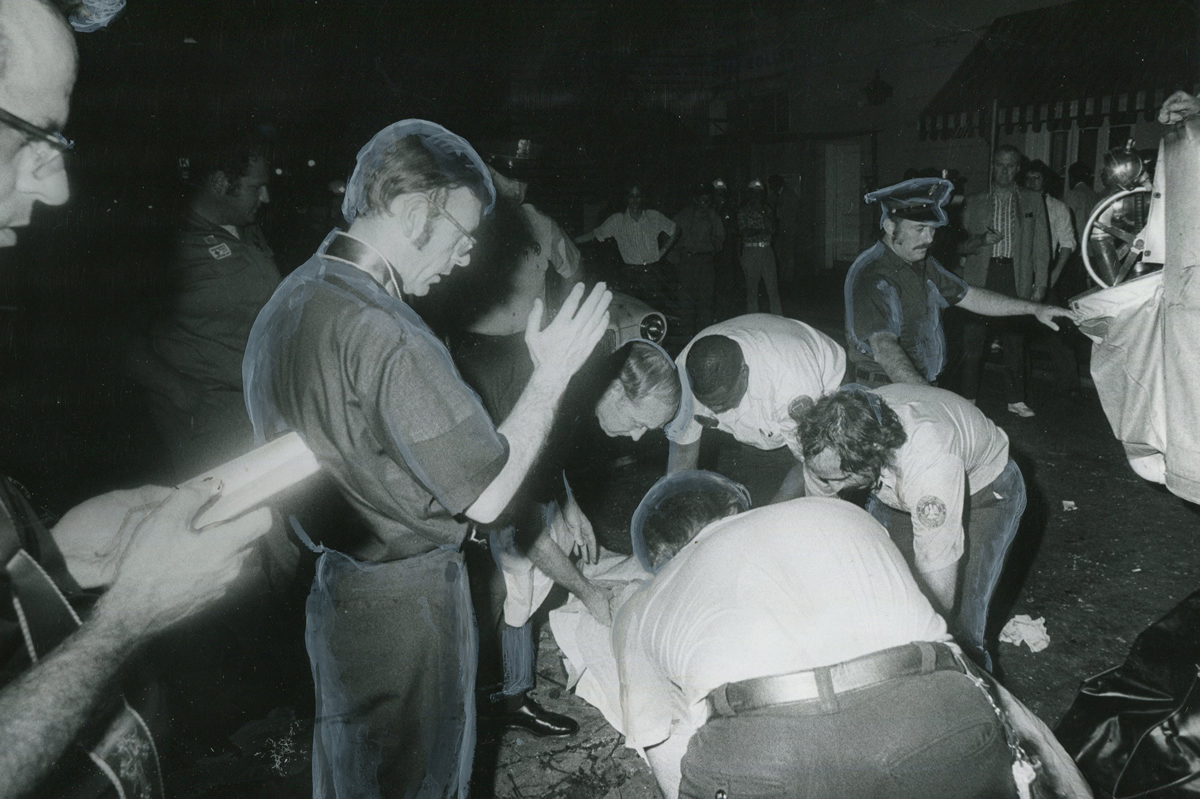

Esteve doubted the UpStairs Lounge story’s capacity to rouse gay political fervor. As the coroner buried four of his former patrons anonymously on the edge of town, Esteve quietly collected at least $25,000 in fire insurance proceeds. Less than a year later, he used the money to open another gay bar called the Post Office, where patrons of the UpStairs Lounge — some with visible burn scars — gathered but were discouraged from singing “United We Stand.”
New Orleans cops neglected to question the chief arson suspect and closed the investigation without answers in late August 1973. Gay elites in the city’s power structure began gaslighting the mourners who marched with Perry into the news cameras, casting suspicion on their memories and re-characterizing their moment of liberation as a stunt.
When a local gay journalist asked in April 1977, “Where are the gay activists in New Orleans?,” Esteve responded that there were none, because none were needed. “We don’t feel we’re discriminated against,” Esteve said. “New Orleans gays are different from gays anywhere else… Perhaps there is some correlation between the amount of gay activism in other cities and the degree of police harassment.”
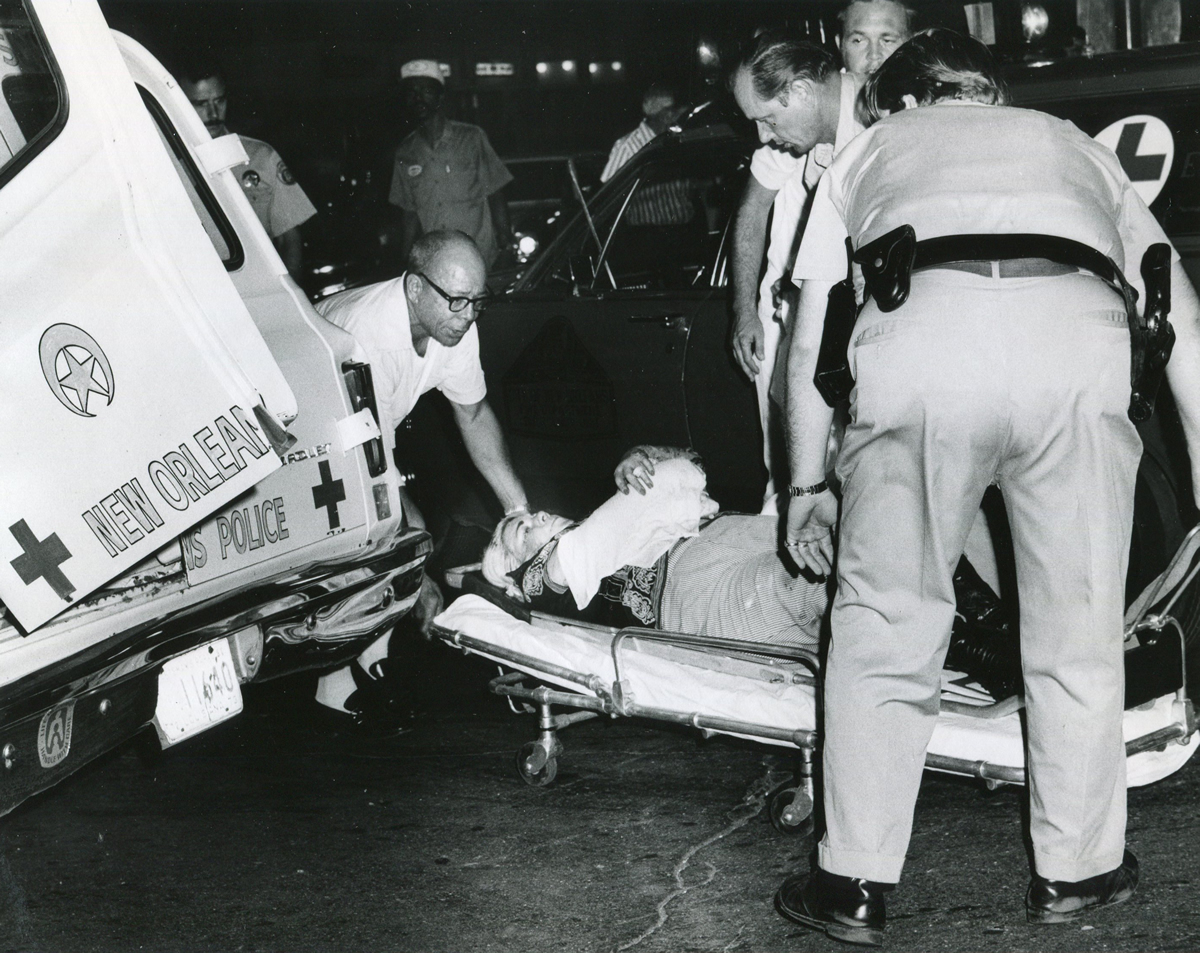
An attitude of nihilism and disavowal descended upon the memory of the UpStairs Lounge victims, goaded by Esteve and fellow gay entrepreneurs who earned their keep via gay patrons drowning their sorrows each night instead of protesting the injustices that kept them drinking.
Into the 1980s, the story of the UpStairs Lounge all but vanished from conversation — with the exception of a few sanctuaries for gay political debate such as the local lesbian bar Charlene’s, run by the activist Charlene Schneider.
By 1988, the 15th anniversary of the fire, the UpStairs Lounge narrative comprised little more than a call for better fire codes and indoor sprinklers. UpStairs Lounge survivor Stewart Butler summed it up: “A tragedy that, as far as I know, no good came of.”
Finally, in 1991, at Stewart Butler and Charlene Schneider’s nudging, the UpStairs Lounge story became aligned with the crusade of liberated gays and lesbians seeking equal rights in Louisiana. The halls of power responded with intermittent progress. The New Orleans City Council, horrified by the story but not yet ready to take its look in the mirror, enacted an anti-discrimination ordinance protecting gays and lesbians in housing, employment, and public accommodations that Dec. 12 — more than 18 years after the fire.
“I believe the fire was the catalyst for the anger to bring us all to the table,” Schneider told The Times-Picayune, a tacit rebuke to Esteve’s strategy of silent accommodation. Even Esteve seemed to change his stance with time, granting a full interview with the first UpStairs Lounge scholar Johnny Townsend sometime around 1989.
Most of the figures in this historic tale are now deceased. What’s left is an enduring story that refused to go gently. The story now echoes around the world — a musical about the UpStairs Lounge fire recently played in Tokyo, translating the gay underworld of the 1973 French Quarter for Japanese audiences.
When I finished my presentation to the City Council last June, I looked up to see the seven council members in tears. Unanimously, they approved a resolution acknowledging the historic failures of city leaders in the wake of the UpStairs Lounge fire.
Council members personally apologized to UpStairs Lounge families and survivors seated in the chamber in a symbolic act that, though it could not bring back those who died, still mattered greatly to those whose pain had been denied, leaving them to grieve alone. At long last, official silence and indifference gave way to heartfelt words of healing.
The way Americans remember the past is an active, ongoing process. Our collective memory is malleable, but it matters because it speaks volumes about our maturity as a people, how we acknowledge the past’s influence in our lives, and how it shapes the examples we set for our youth. Do we grapple with difficult truths, or do we duck accountability by defaulting to nostalgia and bluster? Or worse, do we simply ignore the past until it fades into a black hole of ignorance and indifference?
I believe that a factual retelling of the UpStairs Lounge tragedy — and how, 50 years onward, it became known internationally — resonates beyond our current divides. It reminds queer and non-queer Americans that ignoring the past holds back the present, and that silence is no cure for what ails a participatory nation.
Silence isolates. Silence gaslights and shrouds. It preserves the power structures that scapegoat the disempowered.
Solidarity, on the other hand, unites. Solidarity illuminates a path forward together. Above all, solidarity transforms the downtrodden into a resounding chorus of citizens — in the spirit of voices who once gathered ‘round a white baby grand piano and sang, joyfully and loudly, “United We Stand.”

Robert W. Fieseler is a New Orleans-based journalist and the author of “Tinderbox: the Untold Story of the Up Stairs Lounge Fire and the Rise of Gay Liberation.”
homepage news
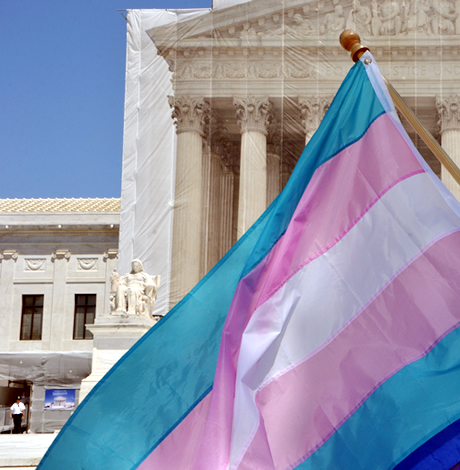
New Supreme Court term includes critical LGBTQ case with ‘terrifying’ consequences
Business owner seeks to decline services for same-sex weddings
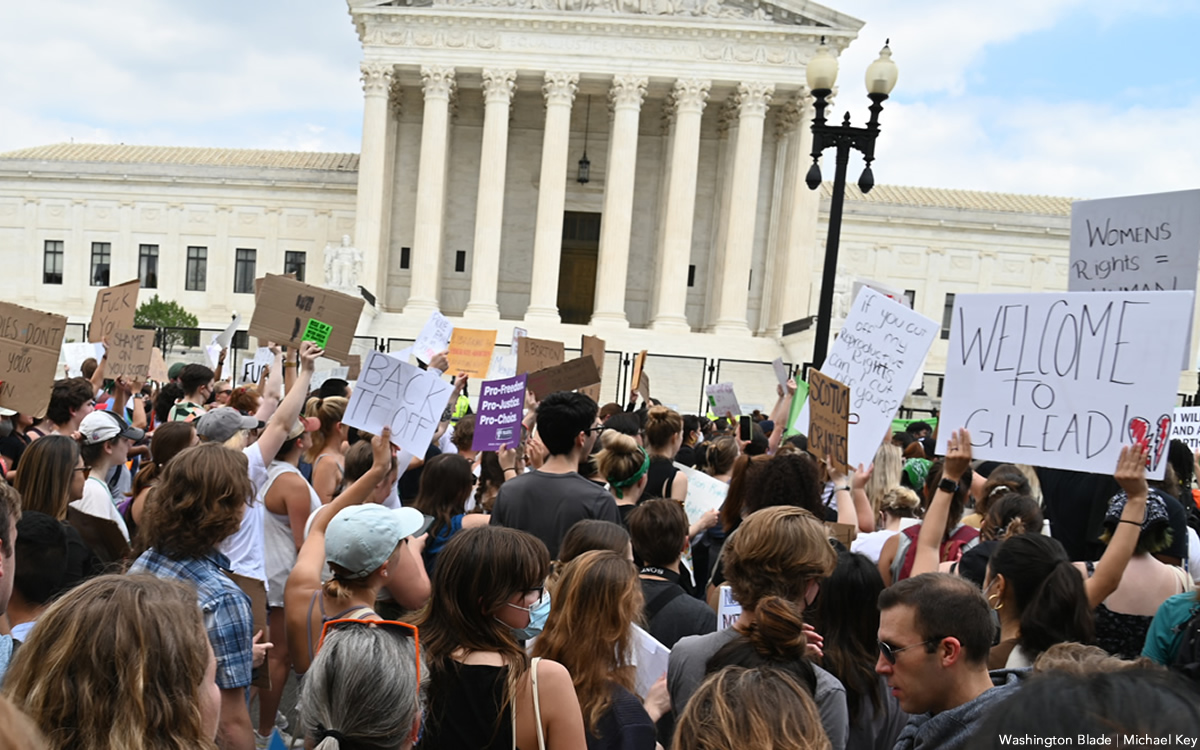

The U.S. Supreme Court, after a decision overturning Roe v. Wade that still leaves many reeling, is starting a new term with justices slated to revisit the issue of LGBTQ rights.
In 303 Creative v. Elenis, the court will return to the issue of whether or not providers of custom-made goods can refuse service to LGBTQ customers on First Amendment grounds. In this case, the business owner is Lorie Smith, a website designer in Colorado who wants to opt out of providing her graphic design services for same-sex weddings despite the civil rights law in her state.
Jennifer Pizer, acting chief legal officer of Lambda Legal, said in an interview with the Blade, “it’s not too much to say an immeasurably huge amount is at stake” for LGBTQ people depending on the outcome of the case.
“This contrived idea that making custom goods, or offering a custom service, somehow tacitly conveys an endorsement of the person — if that were to be accepted, that would be a profound change in the law,” Pizer said. “And the stakes are very high because there are no practical, obvious, principled ways to limit that kind of an exception, and if the law isn’t clear in this regard, then the people who are at risk of experiencing discrimination have no security, no effective protection by having a non-discrimination laws, because at any moment, as one makes their way through the commercial marketplace, you don’t know whether a particular business person is going to refuse to serve you.”
The upcoming arguments and decision in the 303 Creative case mark a return to LGBTQ rights for the Supreme Court, which had no lawsuit to directly address the issue in its previous term, although many argued the Dobbs decision put LGBTQ rights in peril and threatened access to abortion for LGBTQ people.
And yet, the 303 Creative case is similar to other cases the Supreme Court has previously heard on the providers of services seeking the right to deny services based on First Amendment grounds, such as Masterpiece Cakeshop and Fulton v. City of Philadelphia. In both of those cases, however, the court issued narrow rulings on the facts of litigation, declining to issue sweeping rulings either upholding non-discrimination principles or First Amendment exemptions.
Pizer, who signed one of the friend-of-the-court briefs in opposition to 303 Creative, said the case is “similar in the goals” of the Masterpiece Cakeshop litigation on the basis they both seek exemptions to the same non-discrimination law that governs their business, the Colorado Anti-Discrimination Act, or CADA, and seek “to further the social and political argument that they should be free to refuse same-sex couples or LGBTQ people in particular.”
“So there’s the legal goal, and it connects to the social and political goals and in that sense, it’s the same as Masterpiece,” Pizer said. “And so there are multiple problems with it again, as a legal matter, but also as a social matter, because as with the religion argument, it flows from the idea that having something to do with us is endorsing us.”
One difference: the Masterpiece Cakeshop litigation stemmed from an act of refusal of service after owner, Jack Phillips, declined to make a custom-made wedding cake for a same-sex couple for their upcoming wedding. No act of discrimination in the past, however, is present in the 303 Creative case. The owner seeks to put on her website a disclaimer she won’t provide services for same-sex weddings, signaling an intent to discriminate against same-sex couples rather than having done so.
As such, expect issues of standing — whether or not either party is personally aggrieved and able bring to a lawsuit — to be hashed out in arguments as well as whether the litigation is ripe for review as justices consider the case. It’s not hard to see U.S. Chief Justice John Roberts, who has sought to lead the court to reach less sweeping decisions (sometimes successfully, and sometimes in the Dobbs case not successfully) to push for a decision along these lines.
Another key difference: The 303 Creative case hinges on the argument of freedom of speech as opposed to the two-fold argument of freedom of speech and freedom of religious exercise in the Masterpiece Cakeshop litigation. Although 303 Creative requested in its petition to the Supreme Court review of both issues of speech and religion, justices elected only to take up the issue of free speech in granting a writ of certiorari (or agreement to take up a case). Justices also declined to accept another question in the petition request of review of the 1990 precedent in Smith v. Employment Division, which concluded states can enforce neutral generally applicable laws on citizens with religious objections without violating the First Amendment.
Representing 303 Creative in the lawsuit is Alliance Defending Freedom, a law firm that has sought to undermine civil rights laws for LGBTQ people with litigation seeking exemptions based on the First Amendment, such as the Masterpiece Cakeshop case.
Kristen Waggoner, president of Alliance Defending Freedom, wrote in a Sept. 12 legal brief signed by her and other attorneys that a decision in favor of 303 Creative boils down to a clear-cut violation of the First Amendment.
“Colorado and the United States still contend that CADA only regulates sales transactions,” the brief says. “But their cases do not apply because they involve non-expressive activities: selling BBQ, firing employees, restricting school attendance, limiting club memberships, and providing room access. Colorado’s own cases agree that the government may not use public-accommodation laws to affect a commercial actor’s speech.”
Pizer, however, pushed back strongly on the idea a decision in favor of 303 Creative would be as focused as Alliance Defending Freedom purports it would be, arguing it could open the door to widespread discrimination against LGBTQ people.
“One way to put it is art tends to be in the eye of the beholder,” Pizer said. “Is something of a craft, or is it art? I feel like I’m channeling Lily Tomlin. Remember ‘soup and art’? We have had an understanding that whether something is beautiful or not is not the determining factor about whether something is protected as artistic expression. There’s a legal test that recognizes if this is speech, whose speech is it, whose message is it? Would anyone who was hearing the speech or seeing the message understand it to be the message of the customer or of the merchants or craftsmen or business person?”
Despite the implications in the case for LGBTQ rights, 303 Creative may have supporters among LGBTQ people who consider themselves proponents of free speech.
One joint friend-of-the-court brief before the Supreme Court, written by Dale Carpenter, a law professor at Southern Methodist University who’s written in favor of LGBTQ rights, and Eugene Volokh, a First Amendment legal scholar at the University of California, Los Angeles, argues the case is an opportunity to affirm the First Amendment applies to goods and services that are uniquely expressive.
“Distinguishing expressive from non-expressive products in some contexts might be hard, but the Tenth Circuit agreed that Smith’s product does not present a hard case,” the brief says. “Yet that court (and Colorado) declined to recognize any exemption for products constituting speech. The Tenth Circuit has effectively recognized a state interest in subjecting the creation of speech itself to antidiscrimination laws.”
Oral arguments in the case aren’t yet set, but may be announced soon. Set to defend the state of Colorado and enforcement of its non-discrimination law in the case is Colorado Solicitor General Eric Reuel Olson. Just this week, the U.S. Supreme Court announced it would grant the request to the U.S. solicitor general to present arguments before the justices on behalf of the Biden administration.
With a 6-3 conservative majority on the court that has recently scrapped the super-precedent guaranteeing the right to abortion, supporters of LGBTQ rights may think the outcome of the case is all but lost, especially amid widespread fears same-sex marriage would be next on the chopping block. After the U.S. Tenth Circuit Court of Appeals ruled against 303 Creative in the lawsuit, the simple action by the Supreme Court to grant review in the lawsuit suggests they are primed to issue a reversal and rule in favor of the company.
Pizer, acknowledging the call to action issued by LGBTQ groups in the aftermath of the Dobbs decision, conceded the current Supreme Court issuing the ruling in this case is “a terrifying prospect,” but cautioned the issue isn’t so much the makeup of the court but whether or not justices will continue down the path of abolishing case law.
“I think the question that we’re facing with respect to all of the cases or at least many of the cases that are in front of the court right now, is whether this court is going to continue on this radical sort of wrecking ball to the edifice of settled law and seemingly a goal of setting up whole new structures of what our basic legal principles are going to be. Are we going to have another term of that?” Pizer said. “And if so, that’s terrifying.”
homepage news
Kelley Robinson, a Black, queer woman, named president of Human Rights Campaign
Progressive activist a veteran of Planned Parenthood Action Fund
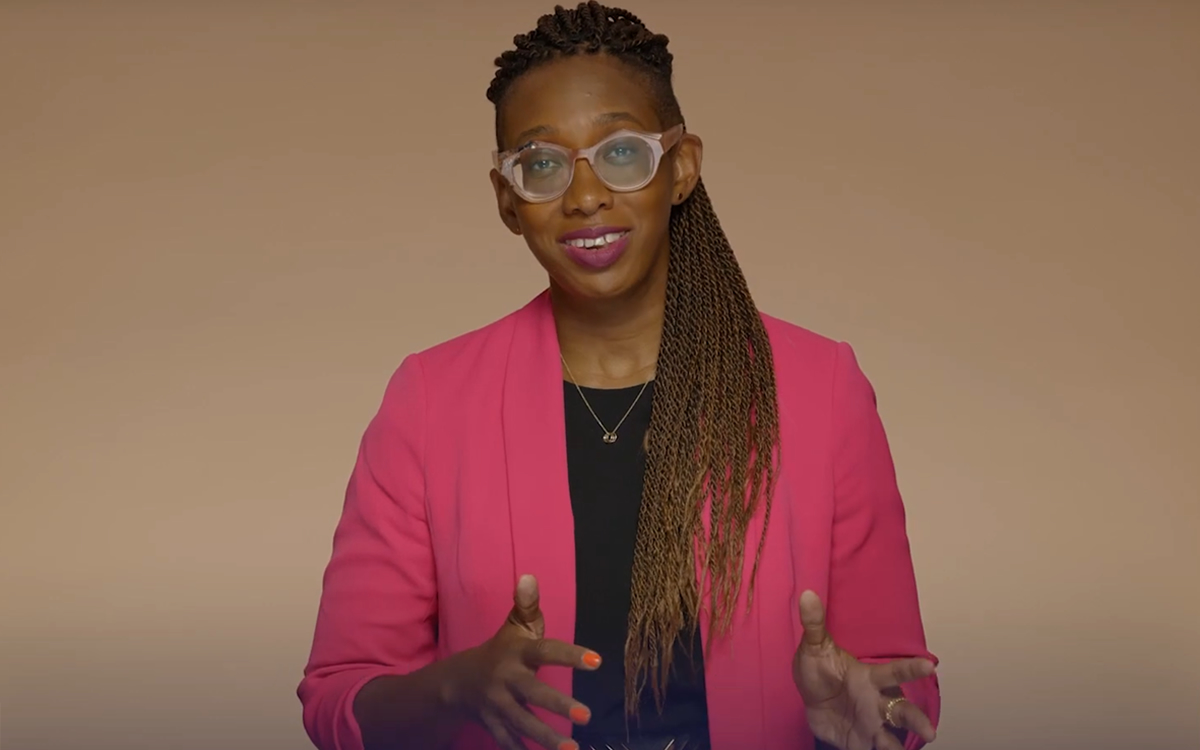

Kelley Robinson, a Black, queer woman and veteran of Planned Parenthood Action Fund, is to become the next president of the Human Rights Campaign, the nation’s leading LGBTQ group announced on Tuesday.
Robinson is set to become the ninth president of the Human Rights Campaign after having served as executive director of Planned Parenthood Action Fund and more than 12 years of experience as a leader in the progressive movement. She’ll be the first Black, queer woman to serve in that role.
“I’m honored and ready to lead HRC — and our more than three million member-advocates — as we continue working to achieve equality and liberation for all Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, and Queer people,” Robinson said. “This is a pivotal moment in our movement for equality for LGBTQ+ people. We, particularly our trans and BIPOC communities, are quite literally in the fight for our lives and facing unprecedented threats that seek to destroy us.”
The next Human Rights Campaign president is named as Democrats are performing well in polls in the mid-term elections after the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade, leaving an opening for the LGBTQ group to play a key role amid fears LGBTQ rights are next on the chopping block.
“The overturning of Roe v. Wade reminds us we are just one Supreme Court decision away from losing fundamental freedoms including the freedom to marry, voting rights, and privacy,” Robinson said. “We are facing a generational opportunity to rise to these challenges and create real, sustainable change. I believe that working together this change is possible right now. This next chapter of the Human Rights Campaign is about getting to freedom and liberation without any exceptions — and today I am making a promise and commitment to carry this work forward.”
The Human Rights Campaign announces its next president after a nearly year-long search process after the board of directors terminated its former president Alphonso David when he was ensnared in the sexual misconduct scandal that led former New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo to resign. David has denied wrongdoing and filed a lawsuit against the LGBTQ group alleging racial discrimination.

-

 Africa4 days ago
Africa4 days agoCongolese lawmaker introduces anti-homosexuality bill
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoOut in the World: LGBTQ news from Europe and Asia
-

 District of Columbia4 days ago
District of Columbia4 days agoReenactment of first gay rights picket at White House set for April 17
-

 Arizona17 hours ago
Arizona17 hours agoAriz. governor vetoes anti-transgender, Ten Commandments bill













