World
Peru LGBTQ activists express concern over country’s new government
Prime minister has made homophobic, transphobic comments
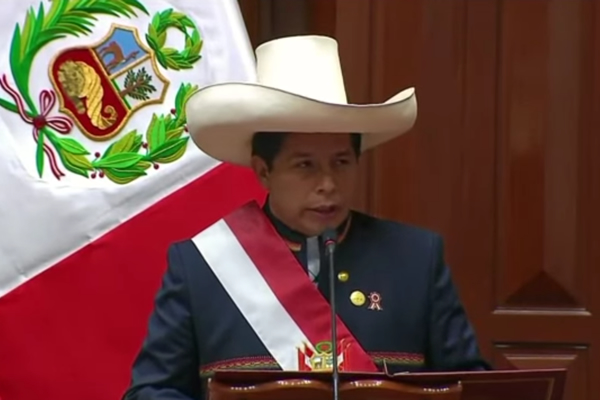

Activists in Peru have expressed concern over their country’s new government and whether it will actively oppose LGBTQ rights.
President Pedro Castillo, a teacher from Cajamarca region of northern Peru who is a member of the leftist and socialist Free Peru party, in June narrowly defeated Keiko Fujimori, his right-wing opponent who is the daughter of former President Alberto Fujimori, in the second round of Peru’s presidential election. Castillo’s inauguration took place in Lima, the Peruvian capital, on July 28.
The Associated Press reported Castillo during his campaign expressed his opposition to marriage rights for same-sex couples, but stressed LGBTQ issues “are not a priority.”
Castillo named Congressman Guido Bellido, an indigenous man who represents Cuzco, as his prime minister.
Bellido in a 2019 Facebook post praised former Cuban President Fidel Castro and specifically his 1963 comments in which he said “the (Cuban) revolution does not need hairdressers and work will make them men. The ‘new man’ cannot be a faggot. The socialist society cannot allow this type of degenerates.”
Media reports indicate Bellido in 2020 made transphobic comments in response to gender-based coronavirus prevention measures that activists said discriminated against trans people. Bellido also reportedly said “the woman is so destructive and ruthless when it comes to mixing her grudges and selfishness” and “I don’t see any lesbian or gay (person) mobilizing” against it.
“Violence is going to intensify every day if things continue as they are,” Bellido said.
Bellido has also been criticized for his previous comments in support of the Shining Path rebel group.
“(Shining Path) has been the biggest violator of human rights in the history of Peru and it concerns me a lot,” Alberto de Belaúnde, an independent congressman from Lima who is openly gay, told the Washington Blade on Monday as he discussed Bellido’s comments. “It is not a good scenario for the human rights agenda in general and specifically for the LGBT agenda.”
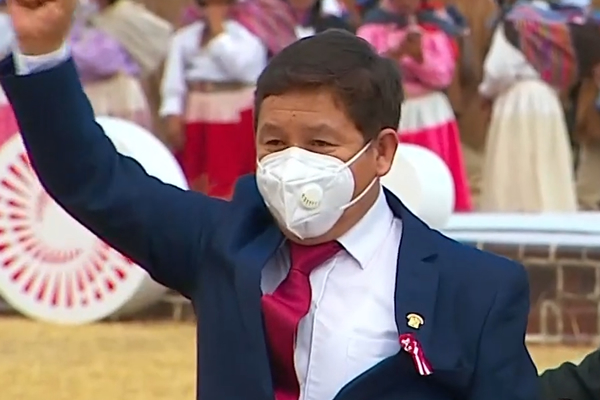

Gabriela Oporto Patroni, a Peruvian human rights lawyer, described Bellido’s comments as “concerning.” George Hale of Centro de Promoción y Defensa de los Derechos Sexuales y Reproductivos (PROMSEX), an LGBTQ and women’s rights group in the South American country, echoed Oporto.
“Prime Minister Bellido’s previous comments that reflect his homophobia, transphobia and misogyny are unfortunate,” Hale told the Blade.
Bellido, for his part, in recent days has said he “categorically rejects all forms of violence and terrorism in all of its extremes.” Hale noted to the Blade that Finance Minister Pedro Francke has publicly said his government will support LGBTQ rights.
“I will fight for equality of opportunities without discrimination based on gender, ethnic identity or sexual orientation,” said Francke on July 31. “I will combat homophobia and I will strongly support the fight against the killer (Shining Path), in line with the public promise that our prime minister has made.”
Asimismo, lucharé por la igualdad de oportunidades sin discriminación de género, identidad étnica u orientación sexual. Combatiré la homofobia y apoyaré una lucha firme contra el senderismo asesino, en línea con el compromiso público hecho por nuestro Primer Ministro. pic.twitter.com/3ycacbrXxM
— Pedro Francke (@pedrofrancke) July 31, 2021
The Latin American and Caribbean Network of Trans People (REDLACTRANS) on Tuesday noted Foreign Affairs Minister Héctor Béjar has said his government supports the Yogyakarta Principles, a set of global LGBTQ rights principles that advocacy groups adopted in 2006.
“We support the 2016 Yogyakarta Principles’ 29 principles about the application of international human rights norms for sexual orientation and gender identity to avoid abuses and to protect the human rights of lesbians, gays, bisexuals and transsexuals,” said Béjar. “The human rights of sex workers will also be part of our agenda.”
#Peru Celebramos las palabras del Ministro de Relaciones Exteriores Sr. Héctor Béjar Rivera. ¡Por los derechos de las personas Trans, la población LGBTI, por los derechos sexuales y reproductivos! Que estas palabras se traduzcan en una política exterior por los #DerechosHumanos pic.twitter.com/jBd1Erjbi4
— RedLacTrans (@REDLACTRANS) August 3, 2021
Miluska Luzquiños is a transgender activist who lives in Lambayeque, a city in northern Peru.
She told the Blade on Monday the situation for LGBTQ Peruvians remains “very complicated and uncertain” because of the pandemic. Luzquiños also noted the country does not have a trans rights law.
“It is necessary for the LGBTIQ movement to keep doing advocacy in government spaces as (part of) civil society,” she said.
Ukraine
Ukrainian Supreme Court recognizes same-sex couple as a family
Zoryan Kis and Tymur Levchuk married in US in 2021
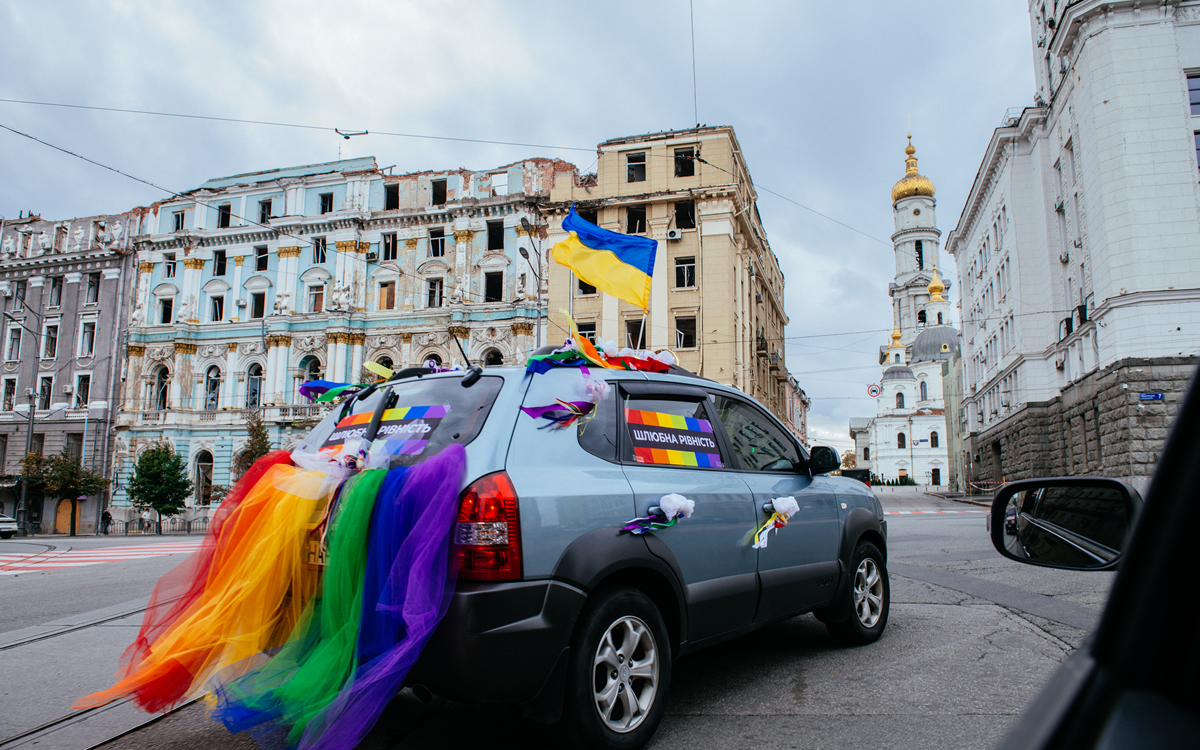

The Ukrainian Supreme Court has recognized a same-sex couple as a family.
The couple — Zoryan Kis and Tymur Levchuk — have lived together since 2013. They legally married in the U.S. in 2021.
The Kyiv Independent notes the couple challenged the Ukrainian Foreign Ministry’s refusal to acknowledge Levchuk as Kis’s family member, therefore denying him spousal rights while Kis was posted at the Ukrainian Embassy in Israel. Kis and Levchuk challenged the decision in court in 2024.
Kyiv’s Desniansky District Court last year in a landmark ruling recognized Kis and Levchuk as a family. Vsi Razom, an anti-LGBTQ organization, appealed the decision.
Insight, the Ukrainian LGBTQ rights group that represented Kis and Levchuk, said the Supreme Court upheld the lower court’s ruling on Feb. 25.
“The Supreme Court of Ukraine has upheld the legality of recognizing a same-sex couple as a family based on their factual relationship, despite the absence of legal recognition of same-sex partnerships in Ukrainian legislation,” Insight Chair Olena Shevchenko noted to the Washington Blade on Tuesday. “The court confirmed the decision, establishing the fact that (the) two men had lived together as a family, affirming that such recognition can be based on proven circumstances of their shared life rather than on political decisions or the existence of formal partnership laws.”
Insight in a Facebook post added the Supreme Court ruling sets “a tremendous precedent.”
“No homophobic or conservative organization will be able to use the courts as a tool to persecute or overturn decisions in favor of LGBT+ people under the guise of ‘social morality,’” said Insight. “The state has protected the boundaries of private life.”
The Supreme Court issued its ruling a day after Ukraine marked four years since Russia began its war against the country.
The Ukrainian constitution defines marriage as between a man and a woman.
President Volodymyr Zelenskyy in 2022 publicly backed civil partnerships for same-sex couples. Shevchenko pointed out Ukrainian law “currently does not provide a mechanism for registering same-sex marriages or partnerships.”
Iran
Man stuck in Lebanon as Iran war escalates
Mario was traveling to India when conflict began on Feb. 28
The Washington Blade on March 6 spoke with a man who remains stuck in Lebanon because of the escalating Iran war.
Mario, who asked the Blade not to publish his last name, lives in the U.S., but was born in Lebanon. He decided to stop in the country to see his doctor before traveling to India for work.
Mario was about to board a flight at Rafic Hariri International Airport in Beirut, the Lebanese capital, on Feb. 28 when airline personnel announced “we cannot fly anymore” because authorities had closed the country’s airspace.
The U.S. and Israel earlier that day launched airstrikes against Iran.
One of them killed Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. Iran in response launched missiles and drones against Israel and Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Azerbaijan, Cyprus, and other countries.
An Iranian drone that hit a command center in Kuwait on March 1 killed six U.S. soldiers: Sgt. Declan Coady, Sgt. 1st Class Nicole Amor, Capt. Cody Khork, Sgt. 1st Class Noah Tietjens, Chief Warrant Officer 3 Robert Marzan, and Maj. Jeffrey O’Brien. Another American servicemember, Sgt. Benjamin Pennington, died on Sunday, a week after Iranian drones and missiles targeted the Prince Sultan Air Base in Saudi Arabia.
Iranian drones and missiles have also damaged civilian infrastructure, including hotels and airports in Dubai in the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait. An Iranian missile on March 1 killed nine people and injured 27 others in Beit Shemesh, Israel.
The war has left Mario and hundreds of thousands of others stranded in the Middle East.
“I had to come back home,” Mario told the Blade.
“Luckily, I’m with family,” he added.
‘War is between Israel and Hezbollah’
Hezbollah, an Iran-backed Shia militant group the U.S. and Israel have designated a terrorist organization, after Khamenei’s death launched rockets at Israel. The Jewish State in response has carried out airstrikes against Hezbollah targets across Lebanon.
Hamas militants on Oct. 7, 2023, killed upwards of 1,200 people when they launched a surprise attack against Israel from the Gaza Strip. Hezbollah the following day began to launch rockets into Israel.
An Israeli airstrike in Beirut on Sept. 27, 2024, killed Hassan Nasrallah, Hezbollah’s long-time leader. Iran four days later launched upwards of 200 ballistic missiles at Israel.
The U.S. helped broker a ceasefire between Israel and Lebanon that took effect on Nov. 27, 2024. Israel nevertheless continued to carry out airstrikes in Lebanon.
Israel on June 13, 2025, launched airstrikes against Iran that targeted the country’s nuclear and military facilities. The subsequent war, which lasted 12 days, prompted the cancellation of the annual Tel Aviv Pride parade.
Mario noted the Israeli airstrikes have targeted Hezbollah infrastructure in Dahiyah, a Beirut suburb that is predominantly Shia, and in southern Lebanon.
His family’s home is about five miles from downtown Beirut. Mario said there is a mountain “that separates me from the area that is being bombed, so I don’t even hear the sounds.”
“Lebanon is such an interesting juxtaposition, because depending on which area you are in, your quality of life can be different during these times,” he said. “Right now, the war is not between Israel and Lebanon as a government. The war is between Israel and Hezbollah.”
“If you are in the areas where Hezbollah is concentrated, then you are severely impacted,” added Mario. “If you are in other areas, even if they are Shia or … Muslims that usually align themselves with Hezbollah, you’re still relatively in a safe place, in a safe location.”
Israeli evacuation orders have prompted hundreds of thousands of people to flee their homes in Dahiyah and in southern Lebanon.
Mario said many of the evacuees are sleeping in their cars, or on the street. He also noted a video that showed a shepherd with his sheep and goats on a highway in downtown Beirut.
“He took his animals with him because he had to vacate where he was living,” said Mario. “That’s the first time you see in downtown Beirut maybe 100 goats walking the streets with two people sitting on jackasses and herding them.”
“It is very absurd,” he added.
The Lebanese government has opened schools and public shelters for people who have been displaced, but Mario said many of them do not have enough food. He also said gas prices have increased, and people are afraid to drive.
“It really saddens me seeing the kids affected by it,” said Mario. “Hezbollah made this decision, and it was a unilateral decision.”
“I doubt that the Shia people support them,” he added, referring to Hezbollah. “They cannot say it out loud that they do not support them, but I doubt people are happy within less than two years, for the second time in a row, to have to leave their homes and try to find a place to stay.”
Lebanese government urged to develop LGBTQ-inclusive plan for displaced people
Article 534 of Lebanon’s Penal Code states “any sexual intercourse contrary to the order of nature is punishable” by up to a year in prison. Several judges in recent years have opted not to use the statute to prosecute LGBTQ people who have been charged under it.
Helem, a Lebanese LGBTQ and intersex rights group, on March 4 called upon the Lebanese government and international NGOs to develop a response to the Israeli airstrikes that is “comprehensive, fair, and inclusive of all groups, without exception or discrimination.
“The experience of the previous war demonstrated that state response plans were not sufficiently inclusive of displaced LGBTQ+ individuals,” said Helem. “Many faced compounded challenges, including the inability to access state collective shelters, exposure to harassment or violence, difficulty accessing health and psychosocial services, and fear of disclosing their gender identity or sexual orientation due to stigma and discrimination.”
“Any emergency plan that fails to take the most vulnerable groups into account exposes their lives and dignity to additional risks,” added the group.
Helem also made the following requests:
• Integrating a rights-based and nondiscrimination approach in all stages of planning and implementation, ensuring safe and equal access to assistance and services.
• Training staff working in shelters and emergency response on principles of protection from gender-based violence and discrimination, including issues related to gender identity and sexual orientation.
• Reassessment of the currently adopted shelter model, which relies exclusively on the concept of the “traditional family” aligned with a specific social structure. In practice, this leads to the systematic exclusion of non-traditional families and individuals who do not belong to conventional family units, including LGBTQ+ individuals, survivors of domestic violence, migrant workers, and people without supportive family networks.
• Involving civil society organizations specialized in gender issues and LGBTQ+ rights in the design, implementation, and monitoring of the emergency response plan.
• Establishing clear monitoring and accountability standards to ensure that violations or discriminatory practices do not occur during the implementation of the emergency plan.
“Disasters and conflicts do not justify the suspension of rights or the neglect of marginalized groups. On the contrary, the need for a humanitarian approach grounded in dignity and equality becomes even more urgent in times of crisis.”
“Helem places its expertise and experience at the disposal of relevant authorities and affirms its readiness to cooperate to ensure that the emergency plan is more just, effective, and inclusive,” said Helem. “Dignity is indivisible, and protection must include everyone without exception.”
Colombia
Claudia López wins primary in Colombian presidential race
Former Bogotá mayor’s wife lost reelection bid on Sunday

Former Bogotá Mayor Claudia López on Sunday won her primary in the race to succeed Colombian President Gustavo Petro.
López, a centrist who is running as an independent, defeated Leonardo Huerta in the “Consulta de las Soluciones” primary.
López was the Colombian capital’s mayor from 2020-2023. She was a member of the Colombian Senate from 2014-2018.
López is running to succeed Petro, the country’s first leftist president who cannot seek a second consecutive term under Colombia’s constitution. Other presidential candidates who won their respective parties’ primaries on Sunday include Sen. Iván Cepeda, a member of Petro’s Historic Pact party, and Sen. Paloma Valencia of the conservative Democratic Center, the country’s main opposition party that former President Álvaro Uribe leads.
Juan Daniel Oviedo, who finished second in the Democratic Center’s primary, is openly gay.
The first-round of Colombia’s presidential election will take place on May 31.
Polls indicate López is trailing Cepeda and Valencia, who are considered the two frontrunners.
A second round will take place is no candidate receives at least 50 percent of the vote on May 31. López would become Colombia’s first female and first lesbian president if she wins the election.
López’s wife loses Senate seat
Colombia’s congressional elections also took place on Sunday.
Former Congressman Mauricio Toro, a member of the center-left Green Alliance party, in 2018 became the first openly gay man elected to Colombian Congress when he won a seat in the House of Representatives.
He lost his reelection bid in 2022. Voters on Sunday elected Toro for a second term.
Congresswoman María del Mar Pizarro, a bisexual Historic Pact member, won re-election.
Caribe Afirmativo, a Colombian LGBTQ and intersex rights group, notes only two of the 33 openly LGBTQ congressional candidates won their respective races. Among those who lost is Sen. Angélica Lozano, a bisexual woman who in 2018 became the first openly LGBTQ person elected to the Colombian Senate.
Lozano is married to López.
Lozano in a message posted to her Instagram page expressed “heartfelt gratitude to everyone for their support and love.”
“I will end my work in Congress on a high note by ensuring (the) child support and service contractor protection bills will become a reality in June,” she said.
-

 Florida5 days ago
Florida5 days agoFla. Senate passes ‘Anti-Diversity’ bill that could repeal local LGBTQ protections
-

 Celebrity News5 days ago
Celebrity News5 days agoLiza Minnelli makes surprise appearance at GLAAD Media Awards
-

 Opinions5 days ago
Opinions5 days agoCapital Pride must be transparent about sexual misconduct investigation
-

 Nightlife4 days ago
Nightlife4 days agoIn D.C. comedy, be sure to shop local




















