World
Out in the World: LGBTQ news from Europe and Asia
Human Rights Watch in new report criticizes Jordanian government

Jordan

The government of Jordanian King Abdullah have systematically targeted lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender rights activists and coordinated an unlawful crackdown on free expression and assembly around gender and sexuality, Human Rights Watch said in a report released earlier this month.
In its Dec. 4 report, HRW documented cases in which Jordan’s General Intelligence Department (GID) and the Preventive Security department of the Public Security Directorate interrogated LGBTQ activists about their work, and intimidated them with threats of violence, arrest and prosecution, forcing several activists to shut down their organizations, discontinue their activities and in some cases, flee the country.
Government officials also smeared LGBTQ rights activists online based on their sexual orientation, and social media users posted photos of LGBTQ rights activists with messages inciting violence against them.
“Jordanian authorities have launched a coordinated attack against LGBT rights activists, aimed at eradicating any discussion around gender and sexuality from the public and private spheres,” said Rasha Younes, senior LGBT rights researcher at Human Rights Watch. “Security forces’ intimidation tactics and unlawful interference in LGBT organizing have driven activism further underground and forced civil society leaders into an impossible reality: severe self-censorship or fleeing Jordan.”
Three activists said the Amman governor interrogated them after they preemptively cancelled the screening of a film depicting gay men. Two LGBTQ organization directors said that because of official intimidation, they were forced to close their offices, discontinue their operations in Jordan and flee the country.
One activist said Preventive Security officers made him sign a pledge that he would report all his venue’s activities to the governor. Another activist reported being targeted online while social media users called for him to be burned alive.
One of the few LGBTQ rights activists who has remained in Jordan described her current reality: “Merely existing in Amman has become terrifying. We cannot continue our work as activists, and we are forced to be hyperaware of our surroundings as individuals.”
More recently, in October 2023, an LGBTQ rights activist said he was summoned for investigation by the intelligence agency. During the interrogation, the activist said intelligence officers searched his phone, intimidated him and threatened him with a travel ban, while asking personal questions about his sexual orientation and sexual relations with other men. After three hours of questioning, the activist said the officers told him he could leave.
“They [Jordanian authorities] invest in intimidation to destroy our minds and isolate us,” the activist said. “Their tactic is to target us mentally, leaving no evidence of our torment behind.”
Jordan’s constitution protects the rights to nondiscrimination (article 6), the right to personal freedom (article 7), and the right to freedom of expression and opinion (article 15).
The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, to which Jordan is a state party, provides that everyone shall have the right to freedom of expression, assembly and association. The ICCPR, in its articles 2 and 26, guarantees fundamental human rights and equal protection of the law without discrimination.
The U.N. Human Rights Committee, which interprets the covenant, has made clear that discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity is prohibited in upholding any of the rights protected by the treaty, including freedom of expression, assembly and association.
France

Legislation that was introduced last month by the openly gay Socialist Senator Hussein Bourgi to acknowledge the French state’s responsibility in the criminalization and persecution of gay men between 1945 and 1982 was adopted.
However, the section of bill that called for compensation of the victims of French homophobic laws, in effect during that period by offering them a lump sum of €10,000 ($10,752.75) was not approved.
Speaking with various French media outlets, Bourgi, who authored the bill, said: “It is high time to bring justice to the living victims of legislation which served as the basis for a politics of repression with brutal and punishing social, professional and familial consequences.”
Agence France-Presse reported:
Bourgi’s text focuses on a 40-year period following the introduction of legislation that specifically targeted homosexuals under the Nazi-allied Vichy regime. The 1942 law, which was not repealed after the liberation of France, introduced a discriminatory distinction in the age of consent for heterosexual and homosexual sex, setting the former at 13 (raised to 15 at the Liberation) and the latter at 21.
Some 10,000 people — almost exclusively men, most of them working-class — were convicted under the law until its repeal in 1982, according to research by sociologists Régis Schlagdenhauffen and Jérémie Gauthier. More than 90 percent were sentenced to jail. An estimated 50,000 more were convicted under a separate “public indecency” law that was amended in 1960 to introduce an aggravating factor for homosexuals and double the penalty.
“People tend to think France was protective of gay people compared to, say, Germany or the UK. But when you look at the figures you get a very different picture,” said Schlagdenhaufen, who teaches at the EHESS institute in Paris.
“France was not this cradle of human rights we like to think of,” he added. “The revolution tried to decriminalise homosexuality, but subsequent regimes found other stratagems to repress gay people. This repression was enshrined in law in 1942 and even more so in 1960.”
The legislation won the backing of Justice Minister Éric Dupond-Moretti in President Emmanuel Macron’s government. However, Dupond-Moretti agreed with the removal of the compensation provision by the right-wing and center senatorial majority. Dupond-Moretti justified this choice noting concerns over “legal difficulties,” telling French magazine Le Monde that “putting into practice” of this compensation measure “appears extremely complex” due to the difficulty of providing proof of an old conviction and its execution.
The Dupond-Moretti added “It was not the law which was responsible for this harm” but “French society, homophobic in all its components at the time” adding, “This is not the fault of the Republic. The law of memory is enough.”
The bill must now be taken up by the lower house, the National Assembly, to be passed and then adopted.
Scotland

The Court of Session in Edinburgh has ruled that Prime Minister Rishi Sunak’s U.K. government acted within the law by invoking Section 35, which blocked the measure passed by the Scottish Parliament, that would have make it easier for transgender people to change their legally-recognized sex on documents.
The actions by Scottish Secretary Alister Jack, with Sunak’s backing kept the act from receiving the signature of King Charles III and becoming law.
The Gender Recognition Reform bill was introduced by the Scottish government in the country’s Parliament in the spring of 2022 was passed in a final 86-39 vote days before last Christmas. The sweeping reform bill modifies the Gender Recognition Act, signed into law in 2004, by allowing trans Scots to gain legal recognition without the need for a medical diagnosis.
The measure further stipulates that age limit for legal recognition is lowered to 16.
In a statement released in January of this year, Jack said:
“After thorough and careful consideration of all the relevant advice and the policy implications, I am concerned that this legislation would have an adverse impact on the operation of Great Britain-wide equalities legislation.
Transgender people who are going through the process to change their legal sex deserve our respect, support and understanding. My decision today is about the legislation’s consequences for the operation of GB-wide equalities protections and other reserved matters.
I have not taken this decision lightly. The bill would have a significant impact on, amongst other things, GB-wide equalities matters in Scotland, England and Wales. I have concluded, therefore, that this is the necessary and correct course of action.”
The Scottish government sued Westminster in the Court of Session, Scotland’s highest civil court, arguing that Jack did not have “reasonable grounds” to block the bill. The BBC reported that in her ruling for the UK governments, Judge Lady Haldane dismissed the Scottish government’s appeal and said the block on the legislation was lawful.
Haldance noted that Jack followed correct legal procedures when he made his decision to invoke section 35 and that the Scottish government had failed to show that he had made legal errors.
The judge wrote: “I cannot conclude that he (Mr. Jack) failed in his duty to take such steps as were reasonable in all the circumstances to acquaint himself with material sufficient to permit him to reach the decision that he did.”
Haldane also said that “Section 35 does not, in and of itself, impact on the separation of powers or other fundamental constitutional principle. Rather it is itself part of the constitutional framework.”
Stonewall UK, the nation’s largest LGBTQ advocacy group, expressed its disappointment with Haldane’s ruling in a statement released this past week:
“We’re disappointed that the Court of Session in Scotland has found in favour of the UK government’s unprecedented decision to use Section 35 to block the Gender Recognition Reform Bill from Royal Assent. This bill was one of the most debated in the Scottish Parliament’s history and was passed by a resounding majority of MSPs drawn from all major Scottish parties.
This unfortunately means more uncertainty for trans people in Scotland, who will now be waiting once again, to see whether they will be able to have their gender legally recognised through a process that is in line with leading nations like Ireland, Canada and New Zealand.
Whatever happens next in discussions with the UK and Scottish governments on this matter, Stonewall will continue to press all administrations to make progress on LGBTQ+ rights in line with leading international practice.”
UNITED KINGDOM

Anti-LGBTQ rhetoric used by British Equalities Minister Kemi Badenoch during her speech on the floor of the House of Commons on Dec. 6, prompted Labor MP Chris Bryant, an openly gay lawmaker, to rise in opposition and declare her speech left him feeling unsafe.
The debate was triggered by Badenoch claiming that the UK does not recognize self-ID from overseas countries for trans people, PinkNewsUK reported. In his retort to her statements, Bryant explained: “I feel, as a gay man, less safe than I did three years or five years ago.”
PinkNewsUK also noted that Bryant said: “Why? Sometimes because of the rhetoric that is used, including by herself [Badenoch] in the public debate.” He added that some MPs had cheered for Badenoch’s statements on the trans community, and for statements against gender-affirming care for trans people, which could lead to LGBTQ people feeling even less safe in the UK.
“Many of us feel less safe today, and when people over there cheer as they just did, it chills me to the bone, it genuinely does,” Bryant said.
She hit back with force, challenging him to identify which words precisely were so problematic. She later criticized the attempts of trans activists to use emotional blackmail to try to shut down debate.
The UK government has updated the list of countries from which gender-certificates will be accepted.
Replying to Bryant, Badenoch said: “He says that my rhetoric chills him to the bone. I would be really keen to hear exactly what it is I have said in this statement or previously that is so chilling.” She added that the current Tory government had done work on “our HIV action plan” and “around trans healthcare,” as well as “establishing five new community-based clinics for adults in the country.”
“There is a lot that we are doing, so it is wrong to characterize us as not caring about LGBT people,” she said.
Bryant’s colleague, Ben Bradshaw, also failed to get the better of Badenoch. He complained the UK had recently fallen in a set of international rankings on LGBTQ rights. She calmly pointed out that those rankings reward states that adopt the Stonewall-supported policy of self-ID and punish those who do not. To cheers from the Tory benches, she declared “Stonewall does not decide the law in this country,” referring to Stonewall UK, the nation’s largest LGBTQ advocacy group.
POLAND
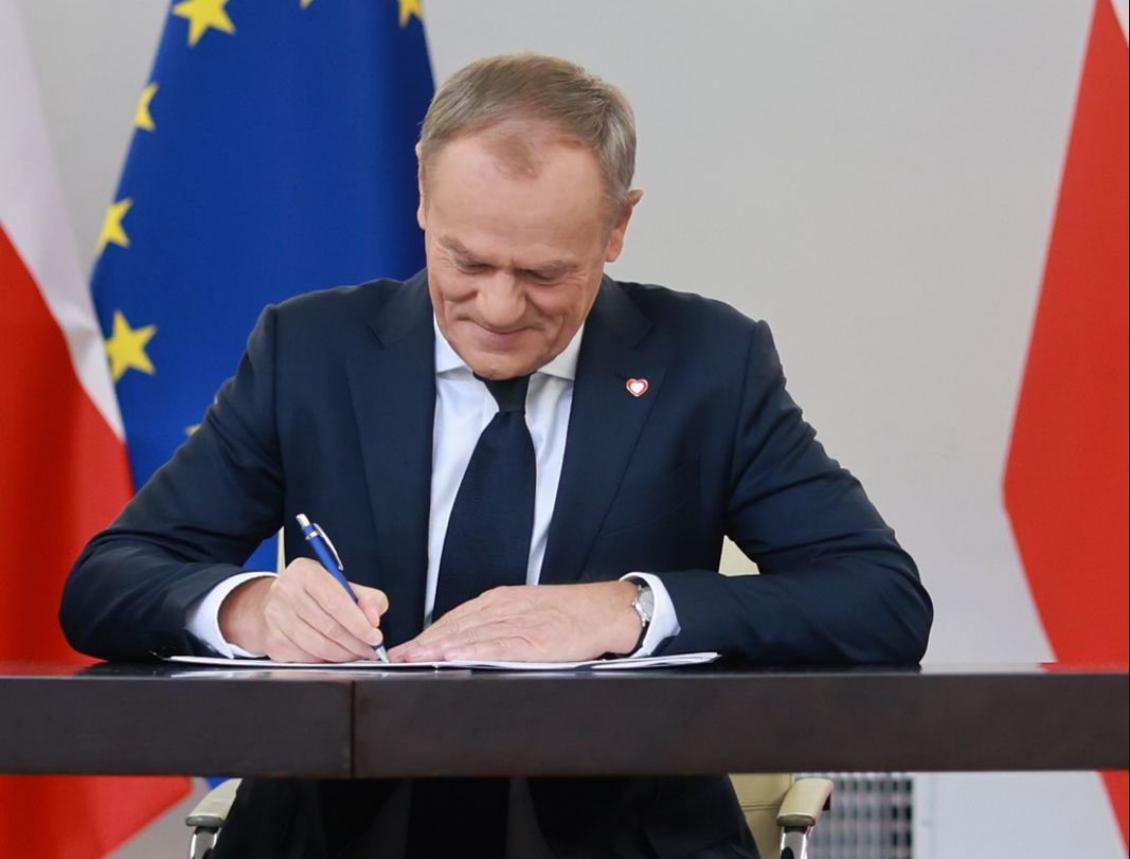

In a turn of events Monday, the lower house of the national legislature of Poland, elected Donald Tusk as the new prime minister after Prime Minister Mateusz Morawiecki failed to win a vote of confidence by lawmakers in his government.
248 MPs voted for the election of Tusk as prime minister, 201 were against and no one abstained in the 460-seat lower house of Parliament.
“This is a truly wonderful day, not only for me, but for all those who have deeply believed for many years that things will get even better, that we will chase away the darkness, that we will chase away evil,” the 66-year-old new prime minister told Parliament after his election.
There had been considerable turmoil in the Polish government, particularly in Parliament, as many accused the ruling conservative right-wing PiS (Law and Justice Party) of Jarosław Kaczyński, who until last month held the post of deputy prime minister, of leading the country backwards into an authoritarian state.
The PiS lost their parliamentary majority in the critical elections this past October after a larger proportion of the country’s 18-29 year-olds had turned out to vote than over-60s and election officials said that turnout was probably 72.9 percent, the highest since the fall of communism in 1989.
Voter anger had steadily risen over erosion of women’s reproductive rights eroded and Polish LGBTQ people who had faced a government hate campaign that drove some to leave the country and caused the European Commission to threatened to pull economic aid and as the BBC reported, the EU is still withholding more than €30 billion ($32 billion) in COVID-19 recovery funds because of its concerns about the politicization of Poland’s courts.
The Polish government has repeatedly clashed with the EU over the rule of law, media freedom, migration and LGBTQ rights since PiS came to power in 2015.
Tusk, who had served as European Council president from 2014-2019 is expected to improve Warsaw’s standing with the EU. Additionally he previously served as Poland’s prime minister from 2007-2014.
“At the invitation of President Andrzej Duda, after the vote in the Sejm, a meeting was held with Prime Minister Donald Tusk. It was agreed that after obtaining a vote of confidence, the swearing-in of the new government would take place on Wednesday, Dec. 13, at 9 a.m. at the Presidential Palace,” a spokesperson for Duda said in a statement released late Monday.
Additional reporting from Human Rights Watch, Agence France-Presse, Le Monde, The BBC and PinkNewsUK.
Iran
Man stuck in Lebanon as Iran war escalates
Mario was traveling to India when conflict began on Feb. 28
The Washington Blade on March 6 spoke with a man who remains stuck in Lebanon because of the escalating Iran war.
Mario, who asked the Blade not to publish his last name, lives in the U.S., but was born in Lebanon. He decided to stop in the country to see his doctor before traveling to India for work.
Mario was about to board a flight at Rafic Hariri International Airport in Beirut, the Lebanese capital, on Feb. 28 when airline personnel announced “we cannot fly anymore” because authorities had closed the country’s airspace.
The U.S. and Israel earlier that day launched airstrikes against Iran.
One of them killed Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. Iran in response launched missiles and drones against Israel and Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Azerbaijan, Cyprus, and other countries.
An Iranian drone that hit a command center in Kuwait on March 1 killed six U.S. soldiers: Sgt. Declan Coady, Sgt. 1st Class Nicole Amor, Capt. Cody Khork, Sgt. 1st Class Noah Tietjens, Chief Warrant Officer 3 Robert Marzan, and Maj. Jeffrey O’Brien. Another American servicemember, Sgt. Benjamin Pennington, died on Sunday, a week after Iranian drones and missiles targeted the Prince Sultan Air Base in Saudi Arabia.
Iranian drones and missiles have also damaged civilian infrastructure, including hotels and airports in Dubai in the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait. An Iranian missile on March 1 killed nine people and injured 27 others in Beit Shemesh, Israel.
The war has left Mario and hundreds of thousands of others stranded in the Middle East.
“I had to come back home,” Mario told the Blade.
“Luckily, I’m with family,” he added.
‘War is between Israel and Hezbollah’
Hezbollah, an Iran-backed Shia militant group the U.S. and Israel have designated a terrorist organization, after Khamenei’s death launched rockets at Israel. The Jewish State in response has carried out airstrikes against Hezbollah targets across Lebanon.
Hamas militants on Oct. 7, 2023, killed upwards of 1,200 people when they launched a surprise attack against Israel from the Gaza Strip. Hezbollah the following day began to launch rockets into Israel.
An Israeli airstrike in Beirut on Sept. 27, 2024, killed Hassan Nasrallah, Hezbollah’s long-time leader. Iran four days later launched upwards of 200 ballistic missiles at Israel.
The U.S. helped broker a ceasefire between Israel and Lebanon that took effect on Nov. 27, 2024. Israel nevertheless continued to carry out airstrikes in Lebanon.
Israel on June 13, 2025, launched airstrikes against Iran that targeted the country’s nuclear and military facilities. The subsequent war, which lasted 12 days, prompted the cancellation of the annual Tel Aviv Pride parade.
Mario noted the Israeli airstrikes have targeted Hezbollah infrastructure in Dahiyah, a Beirut suburb that is predominantly Shia, and in southern Lebanon.
His family’s home is about five miles from downtown Beirut. Mario said there is a mountain “that separates me from the area that is being bombed, so I don’t even hear the sounds.”
“Lebanon is such an interesting juxtaposition, because depending on which area you are in, your quality of life can be different during these times,” he said. “Right now, the war is not between Israel and Lebanon as a government. The war is between Israel and Hezbollah.”
“If you are in the areas where Hezbollah is concentrated, then you are severely impacted,” added Mario. “If you are in other areas, even if they are Shia or … Muslims that usually align themselves with Hezbollah, you’re still relatively in a safe place, in a safe location.”
Israeli evacuation orders have prompted hundreds of thousands of people to flee their homes in Dahiyah and in southern Lebanon.
Mario said many of the evacuees are sleeping in their cars, or on the street. He also noted a video that showed a shepherd with his sheep and goats on a highway in downtown Beirut.
“He took his animals with him because he had to vacate where he was living,” said Mario. “That’s the first time you see in downtown Beirut maybe 100 goats walking the streets with two people sitting on jackasses and herding them.”
“It is very absurd,” he added.
The Lebanese government has opened schools and public shelters for people who have been displaced, but Mario said many of them do not have enough food. He also said gas prices have increased, and people are afraid to drive.
“It really saddens me seeing the kids affected by it,” said Mario. “Hezbollah made this decision, and it was a unilateral decision.”
“I doubt that the Shia people support them,” he added, referring to Hezbollah. “They cannot say it out loud that they do not support them, but I doubt people are happy within less than two years, for the second time in a row, to have to leave their homes and try to find a place to stay.”
Lebanese government urged to develop LGBTQ-inclusive plan for displaced people
Article 534 of Lebanon’s Penal Code states “any sexual intercourse contrary to the order of nature is punishable” by up to a year in prison. Several judges in recent years have opted not to use the statute to prosecute LGBTQ people who have been charged under it.
Helem, a Lebanese LGBTQ and intersex rights group, on March 4 called upon the Lebanese government and international NGOs to develop a response to the Israeli airstrikes that is “comprehensive, fair, and inclusive of all groups, without exception or discrimination.
“The experience of the previous war demonstrated that state response plans were not sufficiently inclusive of displaced LGBTQ+ individuals,” said Helem. “Many faced compounded challenges, including the inability to access state collective shelters, exposure to harassment or violence, difficulty accessing health and psychosocial services, and fear of disclosing their gender identity or sexual orientation due to stigma and discrimination.”
“Any emergency plan that fails to take the most vulnerable groups into account exposes their lives and dignity to additional risks,” added the group.
Helem also made the following requests:
• Integrating a rights-based and nondiscrimination approach in all stages of planning and implementation, ensuring safe and equal access to assistance and services.
• Training staff working in shelters and emergency response on principles of protection from gender-based violence and discrimination, including issues related to gender identity and sexual orientation.
• Reassessment of the currently adopted shelter model, which relies exclusively on the concept of the “traditional family” aligned with a specific social structure. In practice, this leads to the systematic exclusion of non-traditional families and individuals who do not belong to conventional family units, including LGBTQ+ individuals, survivors of domestic violence, migrant workers, and people without supportive family networks.
• Involving civil society organizations specialized in gender issues and LGBTQ+ rights in the design, implementation, and monitoring of the emergency response plan.
• Establishing clear monitoring and accountability standards to ensure that violations or discriminatory practices do not occur during the implementation of the emergency plan.
“Disasters and conflicts do not justify the suspension of rights or the neglect of marginalized groups. On the contrary, the need for a humanitarian approach grounded in dignity and equality becomes even more urgent in times of crisis.”
“Helem places its expertise and experience at the disposal of relevant authorities and affirms its readiness to cooperate to ensure that the emergency plan is more just, effective, and inclusive,” said Helem. “Dignity is indivisible, and protection must include everyone without exception.”
Colombia
Claudia López wins primary in Colombian presidential race
Former Bogotá mayor’s wife lost reelection bid on Sunday

Former Bogotá Mayor Claudia López on Sunday won her primary in the race to succeed Colombian President Gustavo Petro.
López, a centrist who is running as an independent, defeated Leonardo Huerta in the “Consulta de las Soluciones” primary.
López was the Colombian capital’s mayor from 2020-2023. She was a member of the Colombian Senate from 2014-2018.
López is running to succeed Petro, the country’s first leftist president who cannot seek a second consecutive term under Colombia’s constitution. Other presidential candidates who won their respective parties’ primaries on Sunday include Sen. Iván Cepeda, a member of Petro’s Historic Pact party, and Sen. Paloma Valencia of the conservative Democratic Center, the country’s main opposition party that former President Álvaro Uribe leads.
Juan Daniel Oviedo, who finished second in the Democratic Center’s primary, is openly gay.
The first-round of Colombia’s presidential election will take place on May 31.
Polls indicate López is trailing Cepeda and Valencia, who are considered the two frontrunners.
A second round will take place is no candidate receives at least 50 percent of the vote on May 31. López would become Colombia’s first female and first lesbian president if she wins the election.
López’s wife loses Senate seat
Colombia’s congressional elections also took place on Sunday.
Former Congressman Mauricio Toro, a member of the center-left Green Alliance party, in 2018 became the first openly gay man elected to Colombian Congress when he won a seat in the House of Representatives.
He lost his reelection bid in 2022. Voters on Sunday elected Toro for a second term.
Congresswoman María del Mar Pizarro, a bisexual Historic Pact member, won re-election.
Caribe Afirmativo, a Colombian LGBTQ and intersex rights group, notes only two of the 33 openly LGBTQ congressional candidates won their respective races. Among those who lost is Sen. Angélica Lozano, a bisexual woman who in 2018 became the first openly LGBTQ person elected to the Colombian Senate.
Lozano is married to López.
Lozano in a message posted to her Instagram page expressed “heartfelt gratitude to everyone for their support and love.”
“I will end my work in Congress on a high note by ensuring (the) child support and service contractor protection bills will become a reality in June,” she said.
Uganda
Ugandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow
Clare Byarugaba founded PFLAG-Uganda
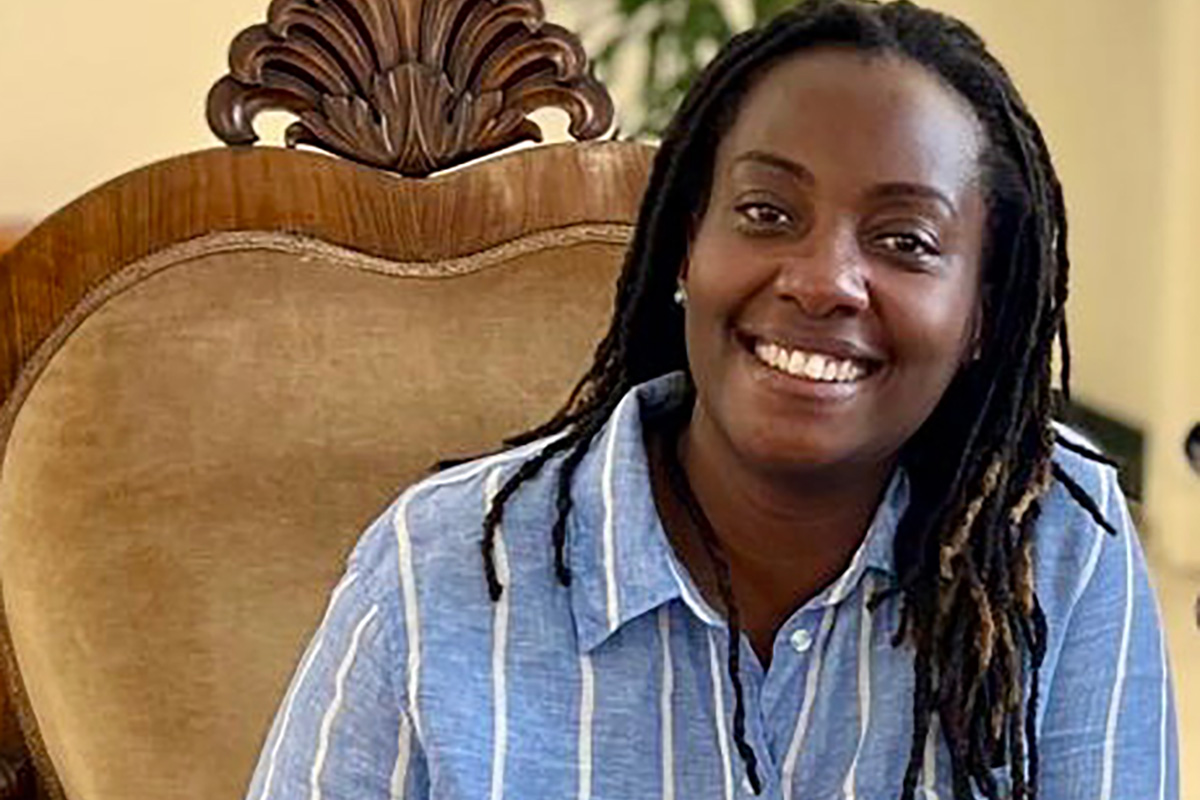

The Charles F. Kettering Foundation has named a prominent Ugandan LGBTQ activist as one of its 2026 fellows.
Clare Byarugaba, founder of PFLAG-Uganda, is one of the foundation’s five 2026 Global Fellows.
Byarugaba, among other things, has been a vocal critic of Uganda’s Anti-Homosexuality Act. Byarugaba in 2024 met with Pope Francis — who criticized criminalization laws during his papacy — at the Vatican.
The foundation on its website says it “is dedicated to bringing research and people together to make the promise of democracy real for everyone, everywhere.”
“Clare is the kind of hero who rushes toward the emergency to help,” said PFLAG CEO Brian K. Bond in a Feb. 27 statement to the Washington Blade. “She founded PFLAG-Uganda as the country pushed to criminalize homosexuality and those who support LGBTQ+ people. Yet, she never hesitated in her courage, telling us that families wanted to organize to keep their LGBTQ+ loved ones safe, and PFLAG was the way to do it. Clare Byarugaba not only deserves this honor, but she will use her compassion and experience to teach the world about LGBTQ+ advocacy as a Kettering Global Fellow.”



















