Africa
Ugandan activists travel to D.C.
MPs last month passed Anti-Homosexuality Act
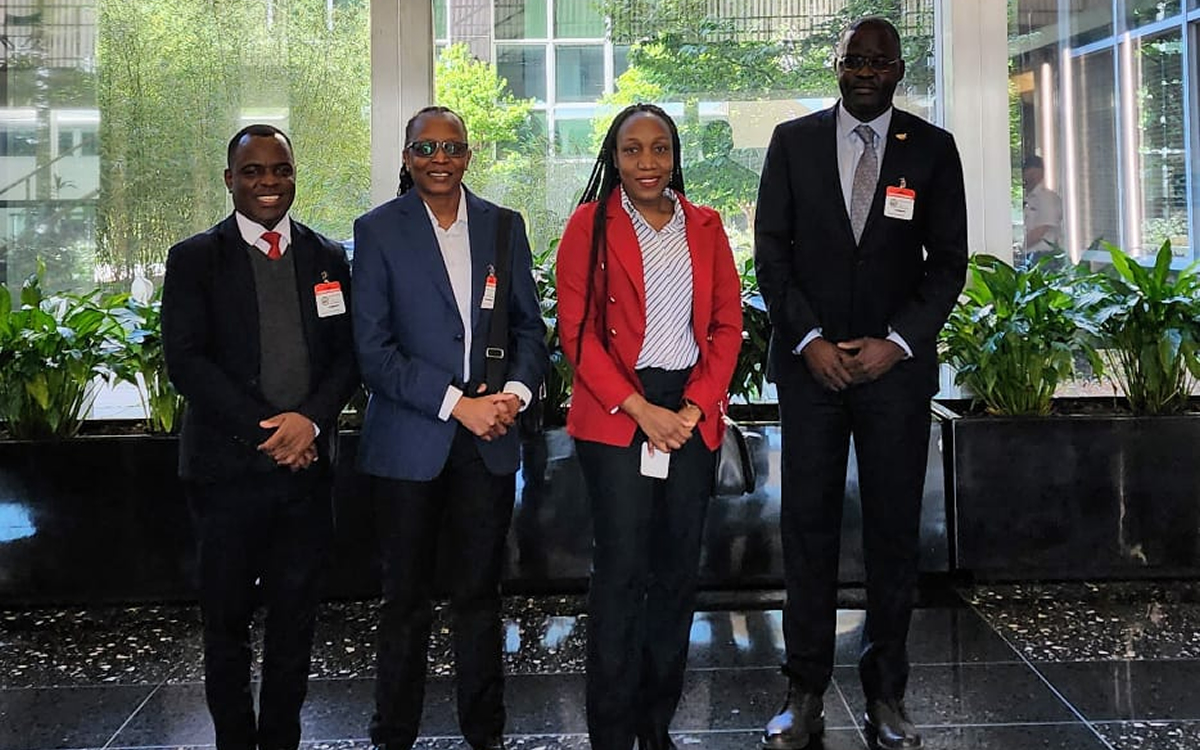

A group of LGBTQ and intersex activists from Uganda traveled to D.C. this week.
Sexual Minorities Uganda Executive Director Frank Mugisha, GLBTQ Legal Advocates and Defenders Senior Manager of Organizational Culture and Community Partnerships Quin Mbabazi and Chapter Four Uganda Executive Director Nicholas Opiyo on Monday spoke about the country’s Anti-Homosexuality Act 2023 at the Center for Strategic and International Studies in D.C. Maria Burnett, senior associate of CSIS’ Africa Program, moderated the panel discussion in which Jessica Stern, the special U.S. envoy for the promotion of LGBTQ and intersex rights rights, also participated.
Mugisha, Mbabazi, Opiyo and Jacqueline Kasha Nabagesara while in D.C. met officials from the White House, the State Department and the U.S. Agency for International Development and representatives from the Council for Global Equality. The activists also briefed the Congressional Equality Caucus.
D.C pic.twitter.com/aOgGeGpImq
— Dr. Frank Mugisha (@frankmugisha) April 11, 2023
Assistant Health Secretary Rachel Levine, a four-star admiral in the U.S. Public Health Service who is the first openly transgender person confirmed by the U.S. Senate, on Thursday tweeted a picture of her with Mugisha.
“It was such an honor to meet (Frank Mugisha.) His courage gives me strength, but no one should have to be brave just to be their authentic self,” tweeted Levine. “Progress is not real unless it means progress for all.”
It was such an honor to meet @frankmugisha. His courage gives me strength, but no one should have to be brave just to be their authentic self. Progress is not real unless it means progress for all. #GlobalHealth #HealthEquity @HHS_Global pic.twitter.com/ughU80xjY7
— ADM Rachel Levine (@HHS_ASH) April 13, 2023
The activists came to D.C. less than a month after Ugandan MPs passed the Anti-Homosexuality Act.
Opiyo notes the measure would impose a “mandatory” death penalty for “aggravated homosexuality” and “anybody who is convicted of being engaged in same-sex relations” would face life in prison.
The bill would also punish the “promotion, recruitment and funding” of LGBTQ-specific activities in Uganda with up to 10 years in prison. Any “person who ‘holds out as a lesbian, gay, transgender, a queer or any other sexual or gender identity that is contrary to the binary categories of male and female'” would also face up to 10 years in prison. Opiyo also noted the measure’s provision that would require Ugandans to report LGBTQ-specific activities to authorities would create “a moral police force.”
Uganda is among the dozens of countries in which consensual same-sex sexual relations are criminalized.
President Yoweri Museveni in 2014 signed that year’s Anti-Homosexuality Act, which imposed a life sentence upon anyone found guilty of repeated same-sex sexual acts. The law was known as the “Kill the Gays” bill because it previously contained a death penalty provision.
The U.S. subsequently cut aid to Uganda and imposed a travel ban against officials who carried out human rights abuses. Uganda’s Constitutional Court later struck down the 2014 Anti-Homosexuality Act on a technicality.
Museveni has said he supports the current bill for which MPs with close ties to anti-LGBTQ American evangelical groups have championed.
“Anti-gay groups and anti-gender groups (are) radicalizing the Ugandan society against the LGBTQ community,” said Mugisha during the CSIS panel. “We’re seeing a lot of hatred. We’re seeing a lot of fear of LGBTQ persons.”
Mugisha noted there has been an increase in violence against LGBTQ and intersex Ugandans over the last year. Uganda’s National Bureau for Non-Government Organizations last August forced Sexual Minorities Uganda to shut down.
“We’re seeing a very systematic, targeted, group that is targeting the LGBTQ community and we’ve seen that Ugandans have sort of been prepared for this legislation,” said Mugisha.
US ‘has significant concerns about the Anti-Homosexuality Act’
Stern during the CSIS panel reiterated the Biden-Harris administration’s criticisms of the Anti-Homosexuality Act.
“The U.S. has significant concerns about the Anti-Homosexuality Act that the Parliament of Uganda passed on March 21,” said Stern. “If the Anti-Homosexuality Act is signed into law and enacted, it would threaten the human rights of Ugandan citizens, jeopardize progress in the fight against HIV/AIDS, deter tourism and investment in Uganda and damage Uganda’s international reputation.”
White House Press Secretary Karine Jean-Pierre during her March 22 press briefing reiterated many of the same points that Stern did. National Security Council spokesperson John Kirby that day also noted the U.S. provides substantial aid to Uganda through the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief and other programs.
“If this bill passes as it is now, the work that PEPFAR currently funds would be criminalized,” said Burnett. “We’re talking about people who are implementing U.S.-funded programs who could not do their jobs without potentially running afoul of the law and losing their liberty.”
Stern said the U.S. “continues to raise issues around the Anti-Homosexuality Act with the government of Uganda at all levels” and is “coordinating with diplomatic partners, with the private sector and with human rights organizations directly.” Stern also noted she and her colleagues are in “daily communication” with Mugisha and the other activists who were on the CSIS panel.
“We’re in constant contact with the community because they know how severe this issue is, how high the stakes are, how to push, what messages to use and what consequences the threat of the bill is already having on the community,” said Stern. “LGBTQI human rights defenders and human rights defenders of all stripes in Uganda are some of our greatest partners in this work. We are working with partners to engage at the multilateral level to address this issue.”
Stern also warned the U.S. would reconsider foreign assistance to Uganda if Museveni signs the Anti-Homosexuality Act.
“We are investing the potential impact of the Anti-Homosexuality Act on U.S. foreign assistance,” said Stern. “If this bill is signed into law, it will be an action-forcing event.”
Uganda
Ugandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow
Clare Byarugaba founded PFLAG-Uganda
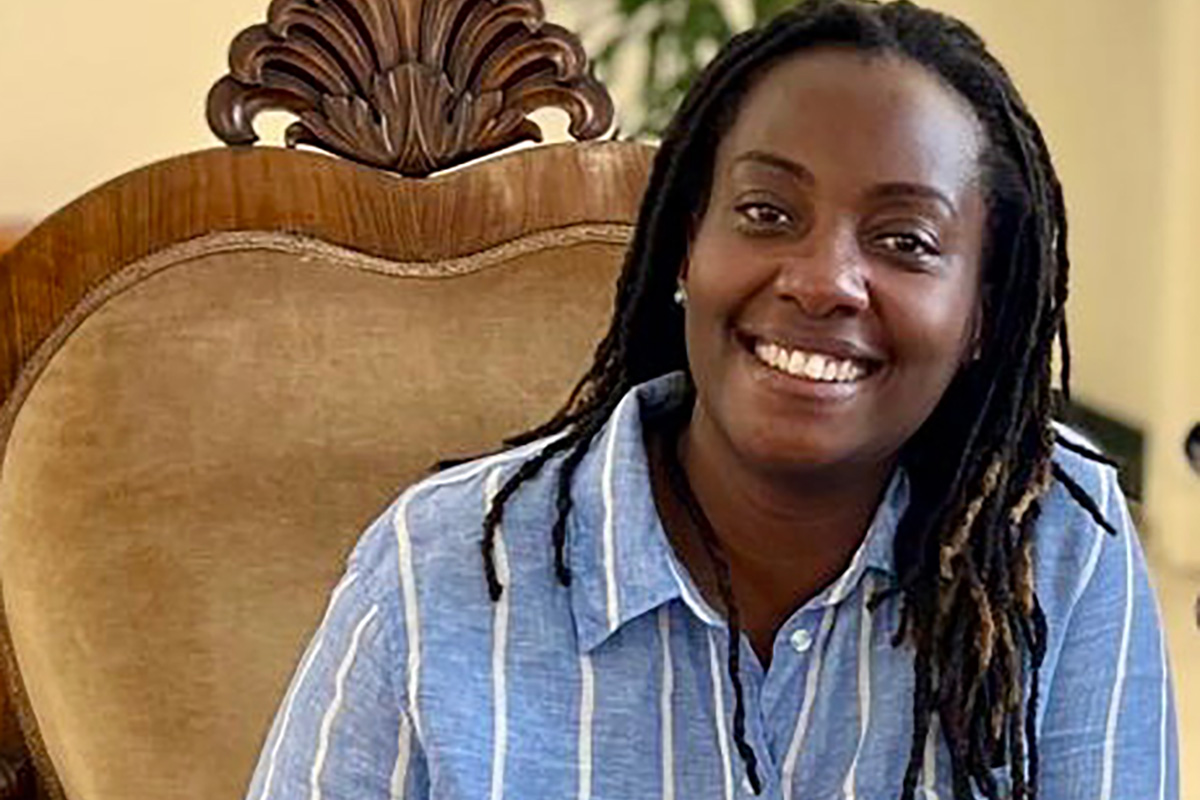

The Charles F. Kettering Foundation has named a prominent Ugandan LGBTQ activist as one of its 2026 fellows.
Clare Byarugaba, founder of PFLAG-Uganda, is one of the foundation’s five 2026 Global Fellows.
Byarugaba, among other things, has been a vocal critic of Uganda’s Anti-Homosexuality Act. Byarugaba in 2024 met with Pope Francis — who criticized criminalization laws during his papacy — at the Vatican.
The foundation on its website says it “is dedicated to bringing research and people together to make the promise of democracy real for everyone, everywhere.”
“Clare is the kind of hero who rushes toward the emergency to help,” said PFLAG CEO Brian K. Bond in a Feb. 27 statement to the Washington Blade. “She founded PFLAG-Uganda as the country pushed to criminalize homosexuality and those who support LGBTQ+ people. Yet, she never hesitated in her courage, telling us that families wanted to organize to keep their LGBTQ+ loved ones safe, and PFLAG was the way to do it. Clare Byarugaba not only deserves this honor, but she will use her compassion and experience to teach the world about LGBTQ+ advocacy as a Kettering Global Fellow.”
Africa
LGBTQ groups question US health agreements with African countries
Community could face further exclusion, government-sanctioned discrimination

Some queer rights organizations have expressed concern that health agreements between the U.S. and more than a dozen African countries will open the door to further exclusion and government-sanctioned discrimination.
The Trump-Vance administration since December has signed five-year agreements with Kenya, Uganda, and other nations that are worth a total of $1.6 billion.
Kenyan and Ugandan advocacy groups note the U.S. funding shift from NGO-led to a government-to-government model poses serious risks to LGBTQ people and other vulnerable populations in accessing healthcare due to existing discrimination based on sexual orientation.
Uganda Minority Shelters Consortium, Let’s Walk Uganda, the Kenya Human Rights Commission, and the Center for Minority Rights and Strategic Litigation note the agreements’ silence on vulnerable populations in accessing health care threatens their safety, privacy, and confidentiality.
“Many LGBTQ persons previously accessed HIV prevention and treatment, sexual and reproductive health services, mental health support, and psychosocial care through specialized clinics supported by NGOs and partners such as USAID (the U.S. Agency for International Development) or PEPFAR,” Let’s Walk Uganda Executive Director Edward Mutebi told Washington Blade.
He noted such specialized clinics, including the Let’s Walk Medical Center, are trusted facilities for providing stigma-free services by health workers who are sensitized to queer issues.
“Under this new model that sidelines NGOs and Drop-in Centers (DICs), there is a high-risk of these populations being forced into public health facilities where stigma, discrimination, and fear of exposure are prevalent to discourage our community members from seeking care altogether, leading to late testing and treatment,” Mutebi said. “For LGBTQ persons already living under criminalization and heightened surveillance, the loss of community-based service delivery is not just an access issue; it is a full-blown safety issue.”
Uganda Minority Shelters Consortium Coordinator John Grace said it is “deeply troubling” for the Trump-Vance administration to sideline NGOs, which he maintains have been “critical lifelines” for marginalized communities through their specialized clinics funded by donors like the Global Fund and USAID.
USAID officially shut down on July 1, 2025, after the White House dismantled it.
Grace notes the government-to-government funding framework will impact clinics that specifically serve the LGBTQ community, noting their patients will have to turn to public systems that remain inaccessible or hostile to them.
“UMSC is concerned that the Ugandan government, under this new arrangement, may lack both the political will and institutional safeguards to equitably serve these populations,” Grace said. “Without civil society participation, there is a real danger of invisibility and neglect.”
Grace also said the absence of accountability mechanisms or civil society oversight in the U.S. agreement, which Uganda signed on Dec. 10, would increase state-led discrimination in allocating health resources.
Center for Minority Rights and Strategic Litigation Legal Manager Michael Kioko notes the U.S. agreement with Kenya, signed on Dec. 4, will help sustain the country’s health sector, but it has a non-binding provision that allows Washington to withdraw or withhold the funding at any time without legal consequences. He said it could affect key health institutions’ long-term planning for specialized facilities for targeted populations whose independent operations are at stake from NGOS the new agreement sidelines.
“The agreement does not provide any assurance that so-called non-core services, such as PrEP, PEP, condoms, lubricants, targeted HIV testing, and STI prevention will be funded, especially given the Trump administration’s known opposition to funding these services for key populations,” Kioko said.
He adds the agreement’s exclusionary structure could further impact NGO-run clinics for key populations that have already closed or scaled down due to loss of the U.S. funding last year, thus reversing hard-won gains in HIV prevention and treatment.
“The socio-political implications are also dire,” Kioko said. “The agreement could be weaponized to incite discrimination and other LGBTQ-related health issues by anti-LGBTQ voices in the parliament who had called for the re-authorization of the U.S. funding (PEPFAR) funding in 2024, as a political mileage in the campaign trail.”
Even as the agreement fails to safeguard specialized facilities for key populations, the Kenya Human Rights Commission states continued access to healthcare services in public facilities will depend on the government’s commitment to maintain confidentiality, stigma-sensitive care, and targeted outreach mechanisms.
“The agreement requires compliance with applicable U.S. laws and foreign assistance policies, including restrictions such as the Helms Amendment on abortion funding,” the Kenya Human Rights Commission said in response to the Blade. “More broadly, funded activities must align with U.S. executive policy directives in force at the time. In the current U.S. context, where executive actions have narrowed gender recognition and reduced certain transgender protections, there is a foreseeable risk that funding priorities may shift.”
Just seven days after Kenya and the U.S. signed the agreement, the country’s High Court on Dec. 11 suspended its implementation after two petitioners challenged its legality on grounds that it was negotiated in secrecy, lacks proper parliamentary approval, and violates Kenyans’ data privacy when their medical information is shared with America.
The agreement the U.S. and Uganda signed has not been challenged.
Senegal
A dozen Senegalese men arrested for ‘unnatural acts’
Popular journalist and musician among those taken into custody
Senegalese police have charged a dozen men with committing “unnatural acts.”
The New York Times reported Pape Cheikh Diallo, a popular television reporter, and Djiby Dramé, a musician, are among the men who authorities arrested. They appeared in court in Dakar, the Senegalese capital, on Monday.
Le Soleil, a Senegalese newspaper, reported authorities arrested the men on Feb. 6 “for intentional transmission of HIV, unnatural acts, criminal conspiracy, and endangering others.” The newspaper further notes the men have been placed in “pre-trial detention.”
Senegal is among the countries in which consensual same-sex sexual relations remain criminalized.
Police in Kaolack, a town that is roughly 135 miles southeast of Dakar, in 2015 arrested 11 people who allegedly engaged in same-sex sexual acts during “a celebration of a gay marriage.” The National Assembly in 2021 rejected a bill that would have further criminalized homosexuality in the country.
-

 National4 days ago
National4 days agoSupreme Court deals blow to trans student privacy protections
-

 District of Columbia4 days ago
District of Columbia4 days agoD.C. Black Pride theme, performers announced at ‘Speakeasy’
-

 Opinions4 days ago
Opinions4 days agoWhy innovation matters for Black health
-

 National3 days ago
National3 days agoPeter Thiel’s expanding power — and his overlap with Jeffrey Epstein




















