National
HISTORIC: Oral arguments heard in DOMA challenge
First time appeals court has considered case to overturn anti-gay law
BOSTON — Oral arguments in a landmark legal proceeding challenging the Defense of Marriage Act unfolded Wednesday, marking the first time an appeals court has heard a challenge to the anti-gay federal law.
Lawyers squared off over the constitutionality of DOMA, amid discussion about whether the law fails a rational basis standard of scrutiny or interferes with a state’s rights under the Tenth Amendment.
Stuart Delery, who’s gay and the Justice Department’s acting assistant attorney general for the civil division, surprised many when he said the Obama administration wouldn’t defend DOMA on any basis, including under rational basis review.
Last year, the Obama administration said it would no longer defend DOMA in court, on the basis that President Obama had determined that the anti-gay law fails heightened scrutiny because it discriminates against gay couples.
Asked by Judge Juan Torruella whether the administration has a position on the rational basis test for the law, Delery replied, “We don’t.”
Delery’s position is significant because U.S. District Judge Joseph Tauro in 2010 ruled in favor of plaintiffs on the basis that DOMA didn’t pass the rational basis standard review, or a rational means to a legitimate governmental end. Judges on the First Circuit will have to decide whether to affirm or overrule this decision.
Two cases challenging the constitutionality of DOMA are before the First Circuit: Gill v. Office of Personnel Management, filed by Gay & Lesbian Advocates & Defenders, and Commonwealth of Massachusetts v. Department of Health & Human Services, filed by Massachusetts Attorney General Martha Coakley.
The three-judge panel hearing the cases is made up of Chief Judge Sandra Lynch as well as Torruella and Judge Michael Boudin. Lynch was appointed by a Democrat, former President Bill Clinton, while Torruella was appointed by former President Ronald Reagan and Boudin was appointed by former President George H.W. Bush.
Despite the administration’s position on rational basis review stated during the hearing, Delery said heightened scrutiny, or examining the law on the assumption that it’s discriminatory toward a group of people, is the appropriate way to handle DOMA because Congress passed DOMA in 1996 out of animus toward gay people.
Delery maintained that the name “DOMA” itself indicates that the anti-gay law was intended to discriminate against LGBT families.
“It was a defense against something, and that something was same-sex couples,” Delery said.
But the administration wasn’t willing to accept all arguments against DOMA. Delery said the administration doesn’t share the view that DOMA is unconstitutional on the basis that it interferes with a state’s Tenth Amendment right to regulate marriage, saying “that’s where we disagree” with the lawsuit.
Delery said Congress has the authority to define federal programs — even those related to marriage, where states traditionally have had jurisdiction on who can and cannot marry.
Defending DOMA in court was Paul Clement, a former U.S. solicitor general. After the Obama administration declared it would no longer defend DOMA, House Speaker John Boehner hired Clement to advocate for DOMA on behalf of the Bipartisan Legal Advisory Group, which voted along party lines to take up defense of the law.
Kicking off the arguments, Clement said the Obama administration is free to change its opinion on whether DOMA would pass a rational basis test, but nonetheless the administration has previously argued in a legal brief that DOMA shouldn’t be struck down on this standard.
“It’s certainly open to the president and the attorney general to change their position, and to say that heightened scrutiny should apply, but that doesn’t make their prior submission go away, and it doesn’t make the arguments in their about why there are rational bases — in addition to some that we’ve covered in our brief — to support the statute,” Clement said.
Clement offered many reasons why DOMA should be upheld — among them was an assertion that opposite-sex marriages advance governmental interests because they can produce “unplanned offspring” unlike same-sex couples.
Additionally, Clement said DOMA isn’t an attempt to “override a state’s definition” of marriage, but merely allows the federal government to “preserve the status quo” as states began legalizing same-sex marriages in 1996 to keep benefits from federal programs, like Social Security, flowing only to opposite-sex married couples as they had in the past.
But Delery blasted the notion that procreation is a necessary component for any marriage — whether the union is opposite-sex or same-sex — saying straight couples can marry even if they don’t want and can’t have children.
“On the flip side, there are many children — hundreds of thousands, I think is the best estimate — who are being raised by same-sex parents in this country, and DOMA has the effect of denying those children the stability and protection that many of the federal benefits that we’re talking about in these cases would provide,” Delery said.
Significant discussion related to heightened scrutiny was focused on the case of Cook v. Gates, a challenge to “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” in which the First Circuit ruled that sexual orientation shouldn’t be considered a suspect class. Clement argued that the First Circuit is bound by this precedent not to apply heightened scrutiny to laws affecting gay people. But attorneys opposed to DOMA said this case shouldn’t be applied to the anti-gay law because courts traditionally grant the military a high level of deference.
Mary Bonauto, GLAD’s civil rights project director, represented her organization during the hearing and said the law violates equal protection under the Constitution regardless of whether heightened scrutiny or rational basis review is applied to the anti-gay law.
“To this day, the federal government defers to state marital determinations where marital status is a factor for federal protections,” Bonauto said. “But for DOMA, same-sex couples who began marrying here eight years ago like our plaintiffs would have been included in those federal laws, but DOMA’s precise point was to prevent that conclusion and created an across the board exclusion.”
Massachusetts Assistant Attorney General Maura Healey argued on behalf of Massachusetts, saying that DOMA violates the state’s right under the Tenth Amendment to regulate marriage. She said an end to DOMA would return the federal government to “what it always has done” by recognizing state authority on which couples should be able to marry.
In her conclusion, Healey drew on the lifting of “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” and its implications for gay troops as a reason why the court should overturn DOMA.
“I’ll take you to our state veterans cemeteries because here the operations of DOMA really revives the concept of separate but equal,” Healy said. “In this day and age, when gay people can now go serve in the military, fight for our country and even die, unlike other married service members, they can’t be buried with their spouse on state land in our veterans cemetery. Instead, Massachusetts is essentially required to build on the next hillside over a cemetery for those veterans. We think that’s wrong.”
The panel has no set time to make a ruling in the cases, but advocates are hoping for a speedy decision. Once a decision is reached, it can be appealed either to the full First Circuit or the U.S. Supreme Court.
U.S. Supreme Court
US Supreme Court rules Idaho to enforce gender care ban
House Bill 71 signed in 2023

BY MIA MALDONADO | The U.S. Supreme Court has allowed Idaho to enforce House Bill 71, a law banning Idaho youth from receiving gender-affirming care medications and surgeries.
In an opinion issued Monday, the U.S. Supreme Court granted the state of Idaho’s request to stay the preliminary injunction, which blocked the law from taking effect. This means the preliminary injunction now only applies to the plaintiffs involved in Poe v. Labrador — a lawsuit brought on by the families of two transgender teens in Idaho who seek gender-affirming care.
Monday’s Supreme Court decision enforces the gender-affirming care ban for all other trans youth in Idaho as the lawsuit remains ongoing in the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals.

The American Civil Liberties Union and the ACLU of Idaho, both of whom represent the plaintiffs, said in a press release Monday that the ruling “does not touch upon the constitutionality” of HB 71. The groups called Monday’s ruling an “awful result” for trans Idaho youth and their families.
“Today’s ruling allows the state to shut down the care that thousands of families rely on while sowing further confusion and disruption,” the organizations said in the press release. “Nonetheless, today’s result only leaves us all the more determined to defeat this law in the courts entirely, making Idaho a safer state to raise every family.”
Idaho Attorney General Raúl Labrador in a press release said the state has a duty to protect and support all children, and that he is proud of the state’s legal stance.
“Those suffering from gender dysphoria deserve love, support and medical care rooted in biological reality,” Labrador said. “Denying the basic truth that boys and girls are biologically different hurts our kids. No one has the right to harm children, and I’m grateful that we, as the state, have the power — and duty — to protect them.”
Recap of Idaho’s HB 71, and what led to SCOTUS opinion
Monday’s Supreme Court decision traces back to when HB 71 was signed into law in April 2023.
The law makes it a felony punishable for up to 10 years for doctors to provide surgeries, puberty-blockers and hormones to trans people under the age of 18. However, gender-affirming surgeries are not and were not performed among Idaho adults or youth before the bill was signed into law, the Idaho Capital Sun previously reported.
One month after it was signed into law, the families of two trans teens sued the state in a lawsuit alleging the bill violates the 14th Amendment’s guarantee of equal protection under the law.
In late December, just days before the law was set to take effect in the new year, U.S. District Judge B. Lynn Winmill blocked the law from taking effect under a preliminary injunction. In his decision, he said he found the families likely to succeed in their challenge.
The state of Idaho responded by appealing the district court’s preliminary injunction decision to the Ninth Circuit, to which the Ninth Circuit denied. The state of Idaho argued the court should at least enforce the ban for everyone except for the plaintiffs.
After the Ninth Circuit’s denial, the Idaho Attorney General’s Office in February sent an emergency motion to the U.S. Supreme Court, the Idaho Press reported. Monday’s U.S. Supreme Court decision agrees with the state’s request to enforce its ban on trans health care for minors, except for the two plaintiffs.
******************************************************************************************

Mia Maldonado joined the Idaho Capital Sun after working as a breaking news reporter at the Idaho Statesman covering stories related to crime, education, growth and politics. She previously interned at the Idaho Capital Sun through the Voces Internship of Idaho, an equity-driven program for young Latinos to work in Idaho news. Born and raised in Coeur d’Alene, Mia moved to the Treasure Valley for college where she graduated from the College of Idaho with a bachelor’s degree in Spanish and international political economy.
******************************************************************************************
The preceding piece was previously published by the Idaho Capital Sun and is republished with permission.
The Idaho Capital Sun is the Gem State’s newest nonprofit news organization delivering accountability journalism on state politics, health care, tax policy, the environment and more.
We’re part of States Newsroom, the nation’s largest state-focused nonprofit news organization.
Kansas
Kansas governor vetoes ban on health care for transgender youth
Republican lawmakers have vowed to override veto
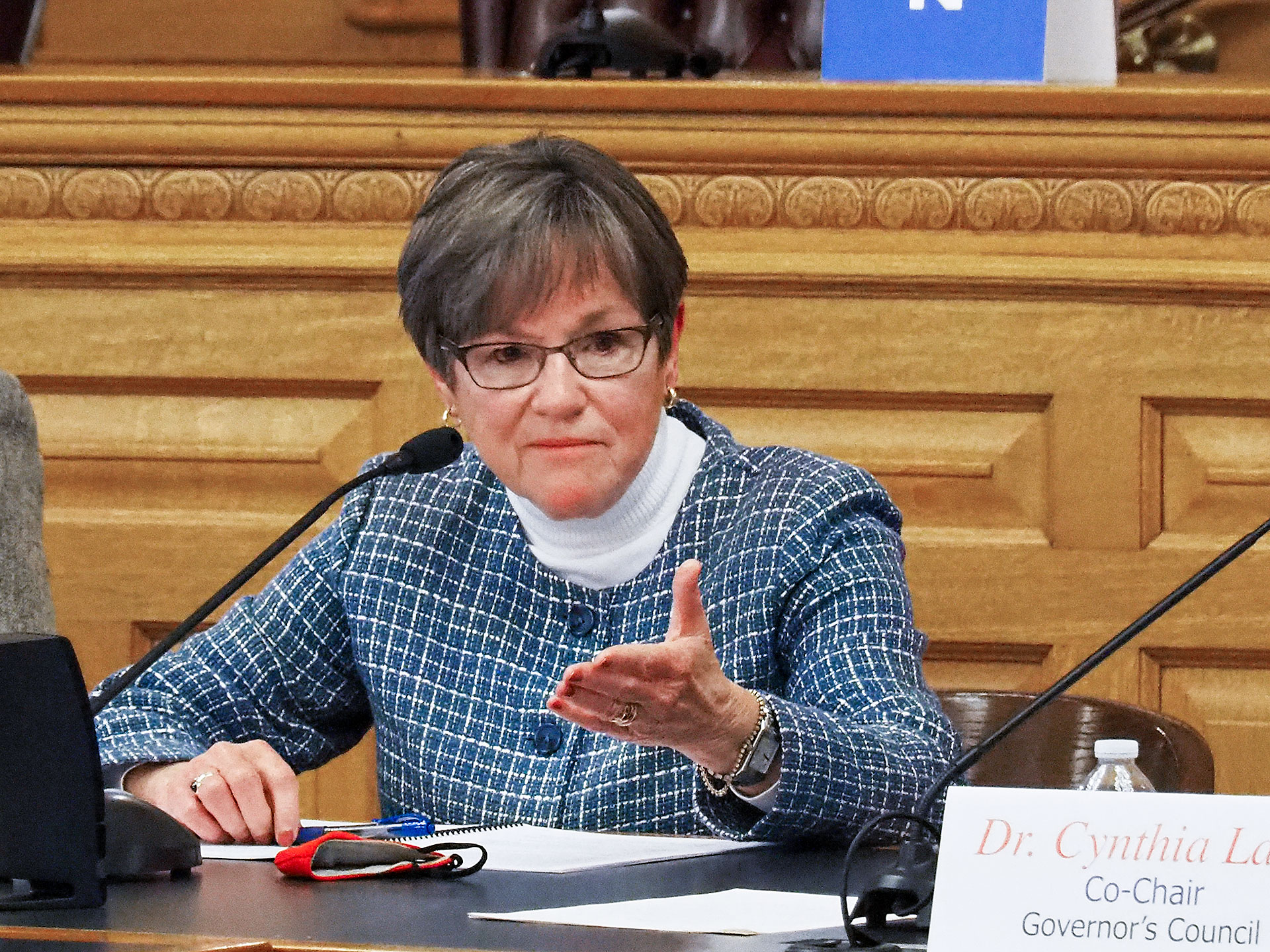


BY TIM CARPENTER | Gov. Laura Kelly flexed a veto pen to reject bills Friday prohibiting gender identity health care for transgender youth, introducing a vague crime of coercing someone to have an abortion and implementing a broader survey of women seeking abortion that was certain to trigger veto override attempts in the Republican-led House and Senate.
The decisions by the Democratic governor to use her authority to reject these health and abortion rights bills didn’t come as a surprise given her previous opposition to lawmakers intervening in personal decisions that she believed ought to remain the domain of families and physicians.
Kelly said Senate Bill 233, which would ban gender-affirming care for trans minors in Kansas, was an unwarranted attack on a small number of Kansans under 18. She said the bill was based on a politically distorted belief the Legislature knew better than parents how to raise their children.
She said it was neither a conservative nor Kansas value to block medical professionals from performing surgery or prescribing puberty blockers for their patients. She said stripping doctors of their licenses for serving health interests of patients was wrong. Under the bill, offending physicians could be face lawsuits and their professional liability insurance couldn’t be relied on to defend themselves in court.
“To be clear, this legislation tramples parental rights,” Kelly said. “The last place that I would want to be as a politician is between a parent and a child who needed medical care of any kind. And, yet, that is exactly what this legislation does.”
Senate President Ty Masterson (R-Andover) and House Speaker Dan Hawkins (R-Wichita) responded to the governor by denouncing the vetoes and pledging to seek overrides when legislators returned to the Capitol on April 26. The trans bill was passed 27-13 in the Senate and 82-39 in the House, suggesting both chambers were in striking distance of a two-thirds majority necessary to thwart the governor.
“The governor has made it clear yet again that the radical left controls her veto pen,” Masterson said. “This devotion to extremism will not stand, and we look forward to overriding her vetoes when we return in two weeks.”
Cathryn Oakley, senior director of the Human Rights Campaign, said the ban on crucial, medically necessary health care for trans youth was discriminatory, designed to spread dangerous misinformation and timed to rile up anti-LGBTQ activists.
“Every credible medical organization — representing over 1.3 million doctors in the United States — calls for age-appropriate, gender-affirming care for transgender and nonbinary people,” Oakley said. “This is why majorities of Americans oppose criminalizing or banning gender-affirming care.”
Abortion coercion
Kelly also vetoed House Bill 2436 that would create the felony crime of engaging in physical, financial or documentary coercion to compel a girl or woman to end a pregnancy despite an expressed desire to carry the fetus to term. It was approved 27-11 in the Senate and 82-37 in the House, again potentially on the cusp of achieving a veto override.
The legislation would establish sentences of one year in jail and $5,000 fine for those guilty of abortion coercion. The fine could be elevated to $10,000 if the adult applying the pressure was the fetuses’ father and the pregnant female was under 18. If the coercion was accompanied by crimes of stalking, domestic battery, kidnapping or about 20 other offenses the prison sentence could be elevated to 25 years behind bars.
Kelly said no one should be forced to undergo a medical procedure against their will. She said threatening violence against another individual was already a crime in Kansas.
“Additionally, I am concerned with the vague language in this bill and its potential to intrude upon private, often difficult, conversations between a person and their family, friends and health care providers,” the governor said. “This overly broad language risks criminalizing Kansans who are being confided in by their loved ones or simply sharing their expertise as a health care provider.”
Hawkins, the House Republican leader, said coercion was wrong regardless of the circumstances and Kelly’s veto of the bill was a step too far to the left.
“It’s a sad day for Kansas when the governor’s uncompromising support for abortion won’t even allow her to advocate for trafficking and abuse victims who are coerced into the procedure,” Hawkins said.
Emily Wales, president and CEO of Planned Parenthood Great Plains Votes, said HB 2436 sought to equate abortion with crime, perpetuate false narratives and erode a fundamental constitutional right to bodily autonomy. The bill did nothing to protect Kansas from reproductive coercion, including forced pregnancy or tampering with birth control.
“Planned Parenthood Great Plains Votes trusts patients and stands firmly against any legislation that seeks to undermine reproductive rights or limit access to essential health care services,” Wales said.
Danielle Underwood, spokeswoman for Kansas for Life, said “Coercion Kelly” demonstrated with this veto a lack of compassion for women pushed into an abortion.
The abortion survey
The House and Senate approved a bill requiring more than a dozen questions be added to surveys of women attempting to terminate a pregnancy in Kansas. Colorful debate in the House included consideration of public health benefits of requiring interviews of men about reasons they sought a vasectomy birth control procedure or why individuals turned to health professionals for treatment of erectile dysfunction.
House Bill 2749 adopted 81-39 in the House and 27-13 in the Senate would require the Kansas Department of Health and Environment to produce twice-a-year reports on responses to the expanded abortion survey. The state of Kansas cannot require women to answer questions on the survey.
Kelly said in her veto message the bill was “invasive and unnecessary” and legislators should have taken into account rejection in August 2022 of a proposed amendment to the Kansas Constitution that would have set the stage for legislation further limiting or ending access to abortion.
“There is no valid medical reason to force a woman to disclose to the Legislature if they have been a victim of abuse, rape or incest prior to obtaining an abortion,” Kelly said. “There is also no valid reason to force a woman to disclose to the Legislature why she is seeking an abortion. I refuse to sign legislation that goes against the will of the majority of Kansans who spoke loudly on Aug. 2, 2022. Kansans don’t want politicians involved in their private medical decisions.”
Wales, of Planned Parenthood Great Plains Votes, said the bill would have compelled health care providers to “interrogate patients seeking abortion care” and to engage in violations of patient privacy while inflicting undue emotional distress.
Hawkins, the Republican House speaker, said the record numbers of Kansas abortions — the increase has been driven by bans or restrictions imposed in other states — was sufficient to warrant scrutiny of KDHE reporting on abortion. He also said the governor had no business suppressing reporting on abortion and criticized her for tapping into “irrational fears of offending the for-profit pro-abortion lobby.”
******************************************************************************************

Tim Carpenter has reported on Kansas for 35 years. He covered the Capitol for 16 years at the Topeka Capital-Journal and previously worked for the Lawrence Journal-World and United Press International.
The preceding story was previously published by the Kansas Reflector and is republished with permission.
******************************************************************************************
The Kansas Reflector is a nonprofit news operation providing in-depth reporting, diverse opinions and daily coverage of state government and politics. This public service is free to readers and other news outlets. We are part of States Newsroom: the nation’s largest state-focused nonprofit news organization, with reporting from every capital.
Colorado
Five transgender, nonbinary ICE detainees allege mistreatment at Colo. detention center
Advocacy groups filed complaint with federal officials on April 9

Five transgender and nonbinary people who are in U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement custody at a privately-run detention center in Colorado say they continue to suffer mistreatment.
The Rocky Mountain Immigrant Advocacy Network, the National Immigration Project and the American Immigration Council on April 9 filed a complaint with the Department of Homeland Security’s Offices for Civil Rights and Civil Liberties, Immigration Detention Ombudsman and Inspector General and ICE’s Office of Professional Responsibility on behalf of the detainees at the Aurora Contract Detention Facility near Denver.
Charlotte, one of the five complainants, says she spends up to 23 hours a day in her room.
She says in the complaint that a psychiatrist has prescribed her medications for anxiety and depression, but “is in the dark about her actual diagnoses because they were not explained to her.” Myriah and Elsa allege they do not have regular access to hormones and other related health care.
Omar, who identifies as trans and nonbinary, in the complaint alleges they would “start hormone replacement therapy if they could be assured that they would not be placed in solitary confinement.” Other detainees in the complaint allege staff have also threatened to place them in isolation.
“They have been told repeatedly that, if they started therapy, they would be placed in ‘protective custody’ (solitary confinement) because the Aurora facility has no nonbinary or men’s transgender housing unit,” reads the complaint. “This is so, despite other trans men having been detained in Aurora in the past, so Omar is very likely receiving misinformation that is preventing them from accessing the treatment they require.”
Omar further alleges staffers told them upon their arrival that “they had to have a ‘boy part’ (meaning a penis) to be assigned to” the housing unit in which other trans people live. Other complainants say staff have also subjected them to degrading comments and other mistreatment because of their gender identity.
“Victoria, Charlotte and Myriah are all apprehensive about a specific female guard who is assigned to the housing unit for transgender women at Aurora,” reads the complaint. “Victoria has experienced this guard peering at her through the glass on the door of her form. Charlotte, Myriah and the other women in her dorm experienced the same guard making fun of them after they complained that she had confiscated all of their personal hygiene products, like their toothbrushes and toothpaste, and replaced them with menstrual pads and tampons, which she knows they do not need.”
“She said something to them like, ‘If you were real women, you would need these things,'” reads the complaint. “The same guard told them that they had to ask her for their personal hygiene products when they wanted to use them, stripping them of their most basic agency.”
Victoria, who has been in ICE custody for more than two years, also says she does not have regular access to hormones. Victoria further claims poor food, lack of access to exercise and stress and anxiety because of her prolonged detention has caused has made her health deteriorate.
The GEO Group, a Florida-based company, operates the Aurora Contract Detention Facility.
Advocates for years have complained about the conditions for trans and nonbinary people in ICE custody and have demanded the agency release all of them.
Roxsana Hernández, a trans Honduran woman with HIV, on May 25, 2018, died in ICE custody in New Mexico. Her family in 2020 sued the federal government and the five private companies who were responsible for her care.
Johana “Joa” Medina Leon, a trans Salvadoran woman, on June 1, 2019, passed away at a Texas hospital four days after her release from ICE custody. Kelly González Aguilar, a trans Honduran woman, had been in ICE custody for more than two years until her release from the Aurora Contract Detention Center on July 14, 2020.
ICE spokesperson Steve Kotecki on Friday told the Blade there were 10 “self-identified transgender detainees” at the Aurora Contract Detention Center on April 11. The facility’s “transgendered units” can accommodate up to 87 trans detainees.
A 2015 memorandum then-ICE Executive Associate Director of Enforcement and Removal Operations Thomas Homan signed requires personnel to allow trans detainees to identify themselves based on their gender identity on data forms. The directive, among other things, also contains guidelines for a “respectful, safe and secure environment” for trans detainees and requires detention facilities to provide them with access to hormone therapy and other trans-specific health care.
“U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) is committed to ensuring that all those in its custody reside in safe, secure and humane environments,” said Kotecki. “ICE regularly reviews each case involving self-identified transgender noncitizens and determines on a case-by-case basis whether detention is warranted.”
The complaint, however, states this memo does not go far enough to protect trans and nonbinary detainees.
“ICE’s 2015 guidance has some significant flaws,” it reads. “It fails to provide meaningful remedies for policy violations. It does not acknowledge the challenges that nonbinary people face when imprisoned by ICE and the lack of such guidance explains why the needs of nonbinary people are largely misunderstood and unmet.”
“Further, the language used to describe people who are TNB is not inclusive and does not reflect terminology adopted by the community it is meant to describe,” adds the complaint. “Although this list is not exhaustive, it addresses some of the primary concerns voiced by the complaints.”
-

 Opinions5 days ago
Opinions5 days agoNetanyahu must go!
-

 LGBTQ Non-Profit Organizations4 days ago
LGBTQ Non-Profit Organizations4 days agoDay of [no] silence, a call to speak out against anti-LGBTQ+ hate
-

 Colorado3 days ago
Colorado3 days agoFive transgender, nonbinary ICE detainees allege mistreatment at Colo. detention center
-

 District of Columbia5 days ago
District of Columbia5 days agoFour LGBTQ candidates running for delegate to Democratic National Convention from D.C.











