Opinions
UNHCR must address suffering of LGBTI refugees in Kenya
Broader community remains largely indifferent to camp abuses
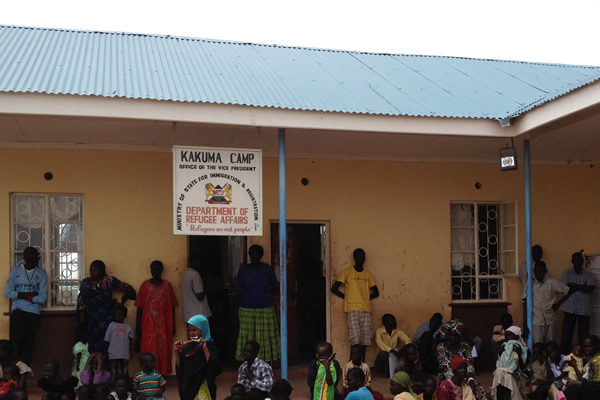


LGBTI activists in the U.S., Belgium, the Netherlands, Germany, the U.K. and other countries are expressing a growing concern about the way in which a considerable group of African LGBTI refugees, or at least part of them, are being treated in Kenya. Whereas they appreciate the efforts of UNHCR (the U.N. Refugee Agency), they also deplore the continuous cries of despair coming out of Kenya, especially from LGBTI refugees in Kakuma Refugee Camp. We urge UNHCR to take these claims and problems more seriously and to open a serious dialogue with the aim of improving the situation considerably. This needs to happen in the short term.
Homosexuality is criminalized in all but a few countries in Africa, which means that LGBTI people live marginalized and often in terror of their lives. Even in the countries that do accept sexual diversity, such as South Africa, which goes as far as to recognize same-sex marriage, the power of disapproval by society is such that LGBTI people live in fear of exposure, loss of jobs, or rejection by their families to the extent of being killed in “honor killings.” Many LGBTI citizens in Africa are being excluded from their families or communities, which explains why many of them flee to other countries hoping to find a decent life there.
The situation has received evermore media attention over the past decade, fomented by the Ugandan government’s particularly hostile stance, which provoked an exodus by LGBTI people, one which is ongoing. The obvious destination for these persons of concern, asylum seekers and refugees is neighboring Kenya, where UNHCR is based in Nairobi. For some years, the resettlement of LGBTI refugees in third countries proceeded at a reasonable pace, but the refusal of the Kenyan government last year to decriminalize homosexuality, plus the obdurate stance of the U.S. administration not to accept more refugees from certain categories, has worsened the situation. We also see that other countries, for example those of the European Union, don’t do enough to accept LGBTI refugees from Kenya, where at least many hundreds of them have fled.
The Kenyan government insists that LGBTI refugees be kept in refugee camps, the largest and most notorious of these being Kakuma in Turkana County in the north of Kenya. There, some two hundred LGBTI refugees from Uganda, Burundi, Rwanda, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Ethiopia, Somalia and South Sudan, women, children and men, are kept without any protection, subject to attack by others living at the camp, mostly Sudanese, and the local Turkana people. Police protection is not provided, since Kenya insists that LGBTI people there are not refugees but “criminals.” A mercenary security company G4S is also complicit in the brutality towards LGBTI refugees. The medical facilities at Kakuma frequently refuse to treat LGBTI refugees.
Advocates from around the world have been lobbying UNHCR to act and remove these LGBTI refugees to a safe place, but these appeals fall on deaf ears. The stance of UNHCR is that the stories by LGBTI refugees of attacks are either fabricated or greatly exaggerated, but eyewitness accounts by the LGBTI refugees themselves provide evidence in videos, photographs and graphic emails. The attacks are extremely violent, involving knife and panga attacks and burning of living quarters, theft of food and mobile phones, and refusal of access to shops and water.
Trust in UNHCR is fast eroding, as no one can understand what the agency’s agenda is; it mostly maintains a deafening silence. The suspicion is that it is under the thumb of the Kenyan authorities, and does not have the moral stamina to confront Kenya on this abuse of human rights. One thing is certain: UNHCR, under High Commissioner Filippo Grandi, does not welcome outsiders’ emails, and other than bland assurances that all is well at the camp, or protestations (amounting to threats) that emails on behalf of individuals put them at further risk, there is no comment from Geneva, Nairobi or the Kakuma Refugee Camp itself. Social media access has been blocked, and the belief among LGBTI people is that this is on the direct orders of UNHCR, in collusion with the Kenyan authorities. Some clearly don’t like the LGBTI refugees to inform the international community about what they are undergoing!
While Black Lives Matter has taken the world by storm, Black LGBTI Lives in Africa do not get a look in, and the LGBTI world outside shows virtually no interest, preferring to concentrate on celebrating Pride month as though the battle has been fought and won. It never will be, but the very least that can be done is to remove all LGBTI refugees from Kakuma, as happened in December 2018, before the Kenyan authorities stepped in and ordered their return to Kakuma, with the evermore gory results that are being seen, harrowing videos and photographs of bodies hacked and bloodied, with minimal medical care and attention.
We would love serious NGOs like Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch and others to step in and get involved. To our satisfaction, we notice a growing willingness within the NGO community to get involved and investigate the claims and worries of many LGBTI refugees in Kenya. The world cannot continue to look away. And we, as serious LGBTI activists, clearly refuse to look away and leave these fellow human beings to their (sad) fate.
Opinions
Capital Pride must be transparent about sexual misconduct investigation
More questions than answers after two board members resign

We are living through some very difficult times in our country. We have a felon in the White House who has surrounded himself with incompetent sycophants and fascists. A Congress that bows down to him, often based on his threats. Things have gotten so bad that his supporters are beginning to wake up to the fact that he cares not a whit for them. They are demanding he stop hiding his involvement with the convicted sex trafficker, Jeffrey Epstein, and come clean. So, to distract them from this, he began a war in the Middle East in which members of the American military have already lost their lives. He says more lives will be lost. He hopes this war of distraction will have Americans forget his failed domestic policies and the Epstein scandal.
But at the same time that all of this is happening, I am forced to look around at organizations I support and ask if they are being open and honest in the way we are demanding of the felon in the White House.
Recently, I have received calls about an organization I have the utmost pride in: Capital Pride. The calls are about Capital Pride’s internal investigation of “a claim” made against a former board chair, who resigned and no longer has any role with the organization. There has been no public proof of any wrongdoing. At the time, Capital Pride announced it had retained an “independent firm” to investigate the complaint. Now, more than four months later, a second board member has resigned sharing her letter of resignation with the Blade.
Taylor Lianne Chandler, a member of the Capital Pride board of directors since 2019 who served as the board’s secretary, submitted a letter of resignation on Feb. 24 that alleges the board has failed to address instances of “sexual misconduct” at Capital Pride.
“This board has made its priorities clear through its actions: protecting a sexual predator matters more than protecting the people who had the courage to come forward. … I have been targeted, bullied, and made to feel like an outsider for doing what any person of integrity would do – telling the truth,” Chandler wrote in her resignation letter.
The Blade reported the organization announced, “As we continue to grow our organization, we’re proactively strengthening the policies and procedures that shape our systems, our infrastructure, and the support we provide to our team and partners.”
Again, it is four months later, and there has been no information from Capital Pride regarding that investigation.
Chandler said a Capital Pride investigation identified one individual implicated in a “pattern” of sexual harassment related behavior over a period of time. She added she was bound by a Non-Disclosure Agreement that applies to all board members and she cannot disclose the name of the person implicated in alleged sexual misconduct or those who came forward to complain about it. She added, “It was one individual, but there was a pattern and a history.”
Again, reading that letter from Chandler and because of the news being full of the Epstein scandal, it makes me want assurances that no organization representing my community will ever think it can cover up issues like this. Capital Pride leadership must be totally transparent.
Capital Pride is a wonderful organization with so many incredible people working and volunteering there. They make our community proud. I never want to see a blemish on the organization. So, I am calling on them to be open and transparent about the investigation they themselves announced, and let the community know what they found, in detail. More important even than the entire community knowing, is for their staff and volunteers to know what they found. No one should be bound by an NDA, which leads to people thinking something really bad is going on.
I thought twice, even three times, before writing this column. I don’t want it to be seen as casting aspersions on all of Capital Pride, or anyone who may have worked there, or volunteered there. But again, because of the focus on the Epstein scandal, and my writing about the felon and his Cabinet officials involved in it, my calling for them to come clean and tell us all they know, I feel compelled to say the same to the organization I have supported over the years, which even honored me as a Capital Pride Hero in 2016. I want them to move forward and be a beacon of light for our community for many years to come. The work they do makes a difference for so many.
I wrote in my memoir that coming to a Pride event helped me to come out, and I am sure it has done the same for so many others in our community. What Capital Pride does is important and it must be as transparent as we demand of any other organization.
Peter Rosenstein is a longtime LGBTQ rights and Democratic Party activist.
Opinions
An undeclared war of distraction by the felon
Will Trump claim a national emergency to undermine midterms?

The president of the United States in his rambling speech about our attack on Iran, recorded during a campaign trip, said, “The Iranian regime seeks to kill. The lives of courageous American heroes may be lost and we may have casualties — that often happens in war — but we’re doing this not for now. We’re doing this for the future, and it is a noble mission.”
Well, the United States has not declared war on Iran, only Congress can do that, not the president. As I write this, the felon has yet to make a live speech to the American people about what he is doing, and Americans have already lost their lives. He is weekending as he usually does at Mar-a-Lago. I wonder if he has the balls to head out to the golf course while American lives continue to be at stake.
This operation is clearly the felon’s way of distracting the people of the United States from his failed domestic policies. From rising food prices, rents, and health insurance. From the loss of manufacturing jobs, as reported in November ”manufacturing shed another 6,000 jobs in September, for a total loss of 58,000 since April.” Had he not acted on Iran now every news outlet in the nation would have reported on the Epstein scandal with the release of the depositions, video and transcripts, of former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton and former President Bill Clinton, in front of the Congressional Oversight Committee.
Even more frightening is this may be his way of preparing to claim a national emergency to undermine the midterm elections, which he is clearly on target to lose, now that his Save America Act has been defeated in Congress.
Americans must ask themselves how long they will put up with this warmonger, racist, sexist, lying, homophobic, SOB, who cares not a whit for them, but only for himself, and his rich colleagues, taking as much grift as they all can, while he is president.
None of this is to say we shouldn’t put constraints on Iran, work to see they never have a nuclear bomb, and limit their production of missiles. We were working toward the goal of stopping them from having a nuclear bomb when the felon, in his first term, pulled us out of the agreement to move forward on that. Today, he has sidelined the State Department, and his Secretary of State, Marco Rubio, in negotiations, and has relied on his son-in-law, Jared Kushner, and Steve Witkoff. The attack was commenced while negotiations were underway. At the end of last week it was reported, Oman’s Foreign Minister Badr Al-Busaidi, who mediated the talks in Geneva, said there had been “significant progress in the negotiation.” Al-Busaidi added, “Technical-level talks would continue next week in Vienna, the home of the International Atomic Energy Agency.” The United Nations’ atomic watchdog likely would be critical in any deal.
So clearly this is all about what the two negotiators, who have sidelined the State Department, Kushner and Witkoff, secretly reported to the felon. My guess is some progress was being made, clearly it was not what the president wanted. So, what ruled was his immediate need for a distraction after the failure of his State of the Union address to make any impact on his sagging poll numbers.
I have written often of the alternate universe Trump has us living in. I am just waiting for his MAGA cult to react to this. Will they still blindly follow everything he says, or will the Laura Loomers of the world finally say, “screw this, take care of us at home, do what you promised to make our lives better”. The first MAGA to say this was Marjorie Taylor Greene. Then Tucker Carlson added his slam against the felon. His PR flack, Karoline Leavitt, is getting confused by all the lies, recently saying “things are better than they were last year.” Clearly forgetting last year was 2025, and the felon was president for all except for 20 days of it, so is responsible for last year.
I am an optimist and believe our democracy will survive him, and his fascist cohorts’ blatant attacks. We won a revolution against one king, and survived a civil war, becoming even stronger as a united nation. We helped Europe defeat Hitler. I believe Sen. Mark Kelly (D-Ariz.) when he says the military will reject illegal orders. Orders that ask them to act against their fellow countrymen and women. I believe the American people will come to their senses before it’s too late. They will finally reject the POS in the White House, and the sycophants, and fascists, surrounding him in time to reclaim our nation for all the people.
Peter Rosenstein is a longtime LGBTQ rights and Democratic Party activist.

I recently lost my dog, Argo.
He was a pit bull, big, sweet, endlessly cuddly, and for 15 years he was my constant. The kind of presence you stop consciously noticing until they’re gone and the quiet hits you all at once. Pit bulls have a reputation. Argo never got the memo. He just loved people, completely and without condition, from the moment he met them until his last day.
I wasn’t prepared for what happened next.
My phone filled up. Instagram lit up. Texts came in from people I hadn’t heard from in months, in some cases years. Hugs from neighbors. Messages from colleagues. Condolences from people I’d lost touch with, some through nothing more than the slow drift of busy lives in a busy city, and some honestly through small tiffs and misunderstandings that neither of us ever bothered to resolve.
And sitting with all of that love pouring in, I found myself asking a question I wasn’t expecting: Why has it taken this long?
We do this in D.C. We get caught in our heads, our calendars, our ambitions. We let weeks turn into months. We let a small misunderstanding calcify into distance because nobody wants to be the first one to reach out, nobody wants to seem like they need something. We perform resilience so well that sometimes the people who care about us most don’t know we need them.
And then something breaks open, a loss, a moment of real vulnerability, and suddenly people show up. And you realize the connection was always there. It just needed permission.
Argo gave people permission. Even in dying, he did what he always did when he was alive. He brought people together.
I’ll be honest with you about where I’ve been lately. As I’ve climbed the entrepreneurial ladder, something quietly shifted. People stopped seeing Gerard. They started seeing a title, a resource, someone who could give them something or who owed them something. A character. Not a person. And when most of your day is spent inside other people’s problems and crises, you can start to feel it, a slow creep of cynicism that you don’t even notice until one day you realize you’ve gone numb.
And I’m not alone in that. Look around. We just watched innocent people die while those in power looked us in the face and called it something else. We watched people erupt over a 10-minute halftime performance like it was the greatest threat to our country. Everywhere you look there is something designed to make you angry, or exhausted, or both. Anger and numbness have become survival strategies. I understand it. I’ve lived it.
But here is what Argo reminded me.
The world is not what the loudest voices say it is. The world is what shows up when something real happens. And what showed up for me, after losing my sweet boy, was people. Caring, loving, present people who put down whatever they were doing to reach out to a friend. Some of them I hadn’t spoken to in too long. Some of them I’d had friction with. All of them showed up anyway.
That is the world. That is what it actually is underneath all the noise.
I think we’ve forgotten that. Or maybe we haven’t forgotten it, maybe we’re just so tired and overstimulated and battle-worn that we’ve stopped letting ourselves feel it. Because feeling it requires vulnerability, and vulnerability feels dangerous right now. It’s easier to scroll. It’s easier to stay mad. It’s easier to keep a wall up and call it wisdom.
Argo spent 15 years showing me a different way. He never met a stranger. He never held a grudge. He never saved his love for people who deserved it on paper. He just gave it, freely, every single time. Not a reward. Not a transaction. Just the most natural thing in the world.
Grief burns off everything that isn’t essential and leaves only what matters. What’s left for me is this: the world is full of good people. You may be surrounded by more of them than you know. And if you’ve gone numb, or angry, or so busy surviving that you’ve stopped connecting, I want you to know that the feeling can come back. It came back for me.
Reach out to someone today. Close a distance you’ve let grow. Tell someone they matter. Not because everything is perfect, but because connection is how we survive when it isn’t. Living disconnected, mad and closed off isn’t living at all. It’s a slower kind of dying.
Death came to teach me how to live. I hope this saves you some time.
Gerard Burley, also known as Coach G, is founder and CEO of Sweat DC.
-

 National4 days ago
National4 days agoSupreme Court deals blow to trans student privacy protections
-

 District of Columbia4 days ago
District of Columbia4 days agoD.C. Black Pride theme, performers announced at ‘Speakeasy’
-

 Opinions4 days ago
Opinions4 days agoWhy innovation matters for Black health
-

 National3 days ago
National3 days agoPeter Thiel’s expanding power — and his overlap with Jeffrey Epstein