World
USAID seeks to bolster LGBTQ rights efforts in Colombia
LGBTQ-inclusive peace agreement took effect in 2016
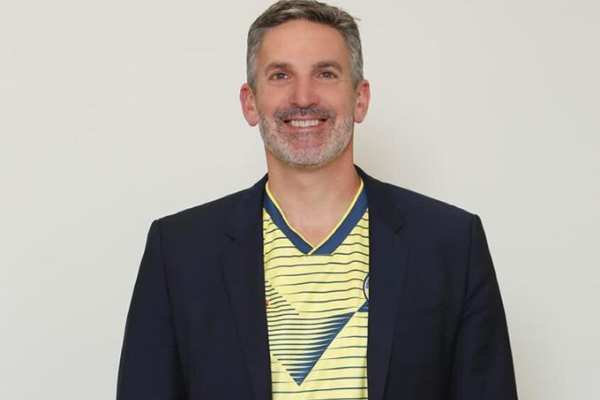

BOGOTÁ, Colombia — The director of the U.S. Agency for International Development’s Colombia mission says he and his colleagues remain committed to the implementation of the country’s LGBTQ-inclusive peace agreement.
“The entire portfolio that we have and all of our work here in Colombia is really to support a durable and an inclusive piece,” Larry Sacks told the Washington Blade on Sept. 21 during an interview in Bogotá, the Colombian capital. “The core principles of what we do are based on equality, inclusion, rights and justice.”
The agreement then-President Juan Manuel Santos and the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia Commander Rodrigo “Timochenko” Londoño signed in Cartagena on Sept. 26, 2016, specifically acknowledged LGBTQ Colombians as victims of the decades-long conflict that killed more than 200,000 people. The accord also called for their participation in the country’s political process.
Wilson Castañeda, director of Caribe Afirmativo, an LGBTQ group in northern Colombia with which USAID works, is one of three activists who participated in the peace talks that took place in Havana.

Colombian voters on Oct. 2, 2016, narrowly rejected the agreement in a referendum that took place against the backdrop of anti-LGBTQ rhetoric from religious and conservative groups. Santos and Londoño less than two months later signed a second peace agreement — which also contains LGBTQ-specific references — in Bogotá.
“That was a very progressive move,” said Sacks in describing the inclusion of LGBTQ Colombians in the agreement.
President Iván Duque, who campaigned against the agreement ahead of his 2018 election, spoke to the U.N. General Assembly hours before the Blade interviewed Sacks. Duque described it as “fragile.”
“Peace accords worldwide tend to be made or broken within the first five years of implementation, and Colombia is right at that point,” Sacks told the Blade when asked about Duque’s comments. “There are certain people deep in the territories and others and high governments who are really helping and making sure that it’s successful, and that there’s continuity, and that the gains that have been made are irreversible. And there’s others who may question, but at the end of the day, I think that from our analysis, it’s on pace with what we’ve seen of the implementation of other peace accords worldwide.”
“At least from USAID’s perspective, we’re doing everything that we can to help support the implementation on multiple chapters of the peace accord,” he added.
USAID specifically supports the implementation of rural development programs through the agreement, efforts to reintegrate former child soldiers into Colombian society and expand the government’s presence into “violence-affected areas.” USAID also works with the Truth Commission, the Unit for the Search of Disappeared Persons, the Special Jurisdiction for Peace, the government’s Victims’ Unit and NGOs that support the conflict’s victims.
USAID’s fiscal year 2021 budget for Colombia is $212.9 million. Upwards of $50 million of this money is earmarked for human rights work that specifically focuses on indigenous Colombians and Colombians of African descent, security, access to the country’s justice system and victims of the conflict.
More than 200 LGBTQ Colombians reported murdered in 2020
Sacks said USAID’s LGBTQ-specific work in Colombia focuses on four specific areas.
“The first is really to kind of shine a light on, raise the visibility, raise the profile on issues of discrimination and violence and stigma and all the issues that this population is facing,” he said.
Colombia Diversa, a Colombian LGBTQ rights group, on Sept. 15 issued a report that notes 226 LGBTQ people were reported murdered in the country in 2020. This figure is more than twice the number of LGBTQ Colombians — 107 — who Colombia Diversa said were known to have been killed in 2019.
Sacks acknowledged anti-LGBTQ violence is increasing in Colombia.
He said the mission works with Ombudsman’s Office of Colombia, an independent agency within the Colombian government that oversees human rights protections in the country, to provide additional support to LGBTQ rights groups. Sacks noted USAID also works with the Interior Ministry to “support the development of their LGBTQI-plus policies” and the country’s attorney general “to hold those accountable.”
Sacks told the Blade that USAID also works to provide “technical and legal support to help” LGBTQ Colombians and other vulnerable groups “access public goods, services and justice.”
USAID-supported groups assist Venezuelan migrants
The Colombian government earlier this year said there were more than 1.7 million Venezuelan migrants in the country, although activists and HIV/AIDS service providers with whom the Blade has spoken say this figure is likely much higher. Duque in February announced it would legally recognize Venezuelan migrants who are registered with the country’s government.
The Coordination Platform for Migrants and Refugees from Venezuela notes upwards of 5.4 million Venezuelans have left the country as of November 2020 as its economic and political crisis grows worse. The majority of them have sought refuge in Colombia, Brazil, Ecuador, Peru and Chile.
Venezuelan migrants are among the upwards of 570,000 people who have benefitted from a USAID program that provides direct cash assistance — between $49-$95 per family — for six months in order to purchase food and other basic needs. USAID also supports Americares, a Connecticut-based NGO that operates several clinics along the Colombia-Venezuelan border and in northern Colombia that specifically serve Venezuelan migrants with the support of the Colombian Health Ministry.


Sacks noted USAID has an “agreement with” Aid for AIDS International, a New York-based group that serves Venezuelans with HIV/AIDS. Aid for AIDS International has used this support to conduct a survey of 300 sex workers in Maicao, Medellín and Cali.
USAID is also working with the Health Ministry to provide health care to Venezuelan migrants with HIV/AIDS, among others, who are now legally recognized in Colombia.
Caribe Afirmativo has opened three “Casas Afirmativos” in Maicao, Barranquilla and Medellín that provide access to health care and other services to Venezuelan migrants who are LGBTQ and/or living with HIV/AIDS. Medellín officials have also invited Caribe Afirmativo staffers to speak with LGBTQ migrants in the city’s public schools.
“Colombia has shown a generosity that you don’t see in many other countries with regard to migrant populations,” Sacks told the Blade. “They really open their borders, their homes, their hearts, to migrants, including the LGBTI community.”
Biden global LGBTQ rights memo is ‘tremendous benefit’
The White House earlier this year released a memorandum that committed the U.S. to promoting LGBTQ rights abroad. State Department spokesperson Ned Price in May told the Blade the protection of LGBTQ migrants and asylum seekers is one of the Biden administration’s priorities on this front.
Sacks said the memo “gives us the political framework with which to operate and obviously sends a message from the highest levels of the U.S. government about LGBTQI-plus rights and equality and inclusion.”
“So for us, it’s a tremendous benefit,” he told the Blade.
USAID Administrator Samantha Power — a vocal champion of LGBTQ rights — has yet to visit Colombia, but Sacks said she has spoken with Vice President Marta Lucía Ramírez.
“We hope to get her down,” said Sacks.
Editor’s note: Michael K. Lavers was on assignment in Colombia from Sept. 11-22.
Iran
Man stuck in Lebanon as Iran war escalates
Mario was traveling to India when conflict began on Feb. 28
The Washington Blade on March 6 spoke with a man who remains stuck in Lebanon because of the escalating Iran war.
Mario, who asked the Blade not to publish his last name, lives in the U.S., but was born in Lebanon. He decided to stop in the country to see his doctor before traveling to India for work.
Mario was about to board a flight at Rafic Hariri International Airport in Beirut, the Lebanese capital, on Feb. 28 when airline personnel announced “we cannot fly anymore” because authorities had closed the country’s airspace.
The U.S. and Israel earlier that day launched airstrikes against Iran.
One of them killed Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. Iran in response launched missiles and drones against Israel and Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Azerbaijan, Cyprus, and other countries.
An Iranian drone that hit a command center in Kuwait on March 1 killed six U.S. soldiers: Sgt. Declan Coady, Sgt. 1st Class Nicole Amor, Capt. Cody Khork, Sgt. 1st Class Noah Tietjens, Chief Warrant Officer 3 Robert Marzan, and Maj. Jeffrey O’Brien. Another American servicemember, Sgt. Benjamin Pennington, died on Sunday, a week after Iranian drones and missiles targeted the Prince Sultan Air Base in Saudi Arabia.
Iranian drones and missiles have also damaged civilian infrastructure, including hotels and airports in Dubai in the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait. An Iranian missile on March 1 killed nine people and injured 27 others in Beit Shemesh, Israel.
The war has left Mario and hundreds of thousands of others stranded in the Middle East.
“I had to come back home,” Mario told the Blade.
“Luckily, I’m with family,” he added.
‘War is between Israel and Hezbollah’
Hezbollah, an Iran-backed Shia militant group the U.S. and Israel have designated a terrorist organization, after Khamenei’s death launched rockets at Israel. The Jewish State in response has carried out airstrikes against Hezbollah targets across Lebanon.
Hamas militants on Oct. 7, 2023, killed upwards of 1,200 people when they launched a surprise attack against Israel from the Gaza Strip. Hezbollah the following day began to launch rockets into Israel.
An Israeli airstrike in Beirut on Sept. 27, 2024, killed Hassan Nasrallah, Hezbollah’s long-time leader. Iran four days later launched upwards of 200 ballistic missiles at Israel.
The U.S. helped broker a ceasefire between Israel and Lebanon that took effect on Nov. 27, 2024. Israel nevertheless continued to carry out airstrikes in Lebanon.
Israel on June 13, 2025, launched airstrikes against Iran that targeted the country’s nuclear and military facilities. The subsequent war, which lasted 12 days, prompted the cancellation of the annual Tel Aviv Pride parade.
Mario noted the Israeli airstrikes have targeted Hezbollah infrastructure in Dahiyah, a Beirut suburb that is predominantly Shia, and in southern Lebanon.
His family’s home is about five miles from downtown Beirut. Mario said there is a mountain “that separates me from the area that is being bombed, so I don’t even hear the sounds.”
“Lebanon is such an interesting juxtaposition, because depending on which area you are in, your quality of life can be different during these times,” he said. “Right now, the war is not between Israel and Lebanon as a government. The war is between Israel and Hezbollah.”
“If you are in the areas where Hezbollah is concentrated, then you are severely impacted,” added Mario. “If you are in other areas, even if they are Shia or … Muslims that usually align themselves with Hezbollah, you’re still relatively in a safe place, in a safe location.”
Israeli evacuation orders have prompted hundreds of thousands of people to flee their homes in Dahiyah and in southern Lebanon.
Mario said many of the evacuees are sleeping in their cars, or on the street. He also noted a video that showed a shepherd with his sheep and goats on a highway in downtown Beirut.
“He took his animals with him because he had to vacate where he was living,” said Mario. “That’s the first time you see in downtown Beirut maybe 100 goats walking the streets with two people sitting on jackasses and herding them.”
“It is very absurd,” he added.
The Lebanese government has opened schools and public shelters for people who have been displaced, but Mario said many of them do not have enough food. He also said gas prices have increased, and people are afraid to drive.
“It really saddens me seeing the kids affected by it,” said Mario. “Hezbollah made this decision, and it was a unilateral decision.”
“I doubt that the Shia people support them,” he added, referring to Hezbollah. “They cannot say it out loud that they do not support them, but I doubt people are happy within less than two years, for the second time in a row, to have to leave their homes and try to find a place to stay.”
Lebanese government urged to develop LGBTQ-inclusive plan for displaced people
Article 534 of Lebanon’s Penal Code states “any sexual intercourse contrary to the order of nature is punishable” by up to a year in prison. Several judges in recent years have opted not to use the statute to prosecute LGBTQ people who have been charged under it.
Helem, a Lebanese LGBTQ and intersex rights group, on March 4 called upon the Lebanese government and international NGOs to develop a response to the Israeli airstrikes that is “comprehensive, fair, and inclusive of all groups, without exception or discrimination.
“The experience of the previous war demonstrated that state response plans were not sufficiently inclusive of displaced LGBTQ+ individuals,” said Helem. “Many faced compounded challenges, including the inability to access state collective shelters, exposure to harassment or violence, difficulty accessing health and psychosocial services, and fear of disclosing their gender identity or sexual orientation due to stigma and discrimination.”
“Any emergency plan that fails to take the most vulnerable groups into account exposes their lives and dignity to additional risks,” added the group.
Helem also made the following requests:
• Integrating a rights-based and nondiscrimination approach in all stages of planning and implementation, ensuring safe and equal access to assistance and services.
• Training staff working in shelters and emergency response on principles of protection from gender-based violence and discrimination, including issues related to gender identity and sexual orientation.
• Reassessment of the currently adopted shelter model, which relies exclusively on the concept of the “traditional family” aligned with a specific social structure. In practice, this leads to the systematic exclusion of non-traditional families and individuals who do not belong to conventional family units, including LGBTQ+ individuals, survivors of domestic violence, migrant workers, and people without supportive family networks.
• Involving civil society organizations specialized in gender issues and LGBTQ+ rights in the design, implementation, and monitoring of the emergency response plan.
• Establishing clear monitoring and accountability standards to ensure that violations or discriminatory practices do not occur during the implementation of the emergency plan.
“Disasters and conflicts do not justify the suspension of rights or the neglect of marginalized groups. On the contrary, the need for a humanitarian approach grounded in dignity and equality becomes even more urgent in times of crisis.”
“Helem places its expertise and experience at the disposal of relevant authorities and affirms its readiness to cooperate to ensure that the emergency plan is more just, effective, and inclusive,” said Helem. “Dignity is indivisible, and protection must include everyone without exception.”
Colombia
Claudia López wins primary in Colombian presidential race
Former Bogotá mayor’s wife lost reelection bid on Sunday

Former Bogotá Mayor Claudia López on Sunday won her primary in the race to succeed Colombian President Gustavo Petro.
López, a centrist who is running as an independent, defeated Leonardo Huerta in the “Consulta de las Soluciones” primary.
López was the Colombian capital’s mayor from 2020-2023. She was a member of the Colombian Senate from 2014-2018.
López is running to succeed Petro, the country’s first leftist president who cannot seek a second consecutive term under Colombia’s constitution. Other presidential candidates who won their respective parties’ primaries on Sunday include Sen. Iván Cepeda, a member of Petro’s Historic Pact party, and Sen. Paloma Valencia of the conservative Democratic Center, the country’s main opposition party that former President Álvaro Uribe leads.
Juan Daniel Oviedo, who finished second in the Democratic Center’s primary, is openly gay.
The first-round of Colombia’s presidential election will take place on May 31.
Polls indicate López is trailing Cepeda and Valencia, who are considered the two frontrunners.
A second round will take place is no candidate receives at least 50 percent of the vote on May 31. López would become Colombia’s first female and first lesbian president if she wins the election.
López’s wife loses Senate seat
Colombia’s congressional elections also took place on Sunday.
Former Congressman Mauricio Toro, a member of the center-left Green Alliance party, in 2018 became the first openly gay man elected to Colombian Congress when he won a seat in the House of Representatives.
He lost his reelection bid in 2022. Voters on Sunday elected Toro for a second term.
Congresswoman María del Mar Pizarro, a bisexual Historic Pact member, won re-election.
Caribe Afirmativo, a Colombian LGBTQ and intersex rights group, notes only two of the 33 openly LGBTQ congressional candidates won their respective races. Among those who lost is Sen. Angélica Lozano, a bisexual woman who in 2018 became the first openly LGBTQ person elected to the Colombian Senate.
Lozano is married to López.
Lozano in a message posted to her Instagram page expressed “heartfelt gratitude to everyone for their support and love.”
“I will end my work in Congress on a high note by ensuring (the) child support and service contractor protection bills will become a reality in June,” she said.
Uganda
Ugandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow
Clare Byarugaba founded PFLAG-Uganda
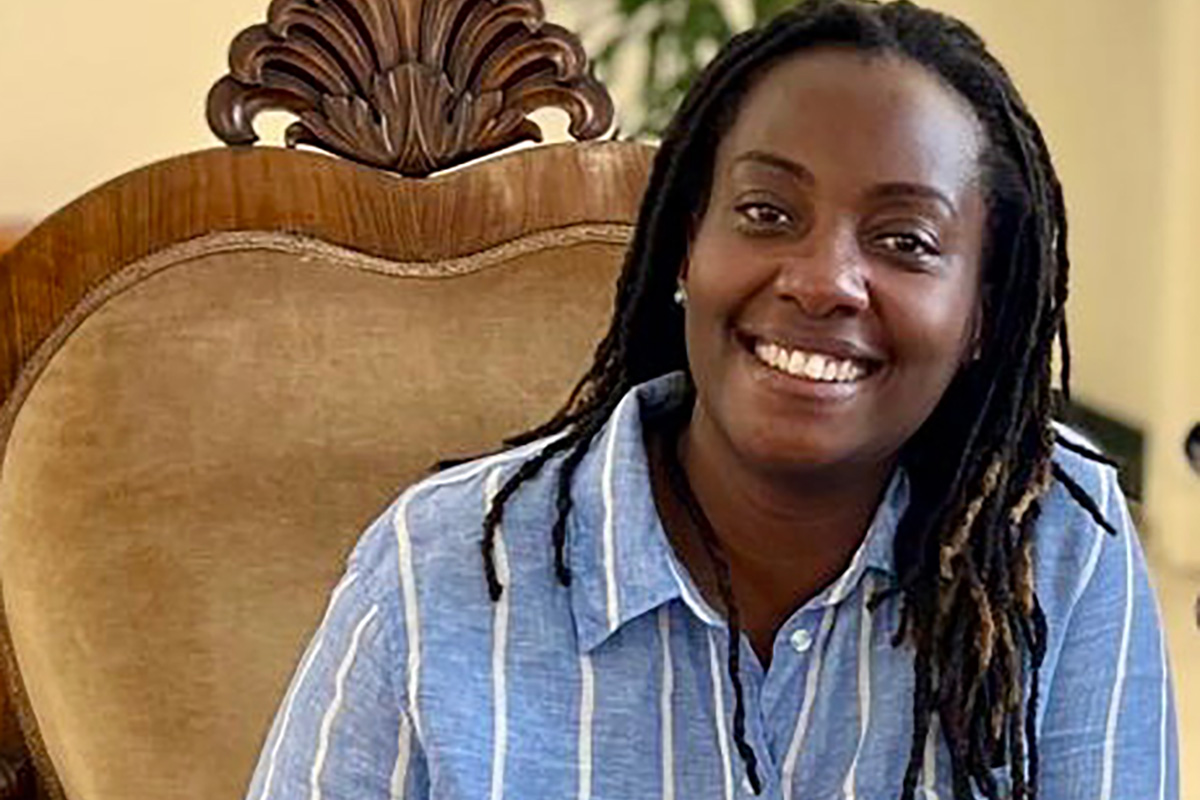

The Charles F. Kettering Foundation has named a prominent Ugandan LGBTQ activist as one of its 2026 fellows.
Clare Byarugaba, founder of PFLAG-Uganda, is one of the foundation’s five 2026 Global Fellows.
Byarugaba, among other things, has been a vocal critic of Uganda’s Anti-Homosexuality Act. Byarugaba in 2024 met with Pope Francis — who criticized criminalization laws during his papacy — at the Vatican.
The foundation on its website says it “is dedicated to bringing research and people together to make the promise of democracy real for everyone, everywhere.”
“Clare is the kind of hero who rushes toward the emergency to help,” said PFLAG CEO Brian K. Bond in a Feb. 27 statement to the Washington Blade. “She founded PFLAG-Uganda as the country pushed to criminalize homosexuality and those who support LGBTQ+ people. Yet, she never hesitated in her courage, telling us that families wanted to organize to keep their LGBTQ+ loved ones safe, and PFLAG was the way to do it. Clare Byarugaba not only deserves this honor, but she will use her compassion and experience to teach the world about LGBTQ+ advocacy as a Kettering Global Fellow.”
-

 National4 days ago
National4 days ago13 HIV/AIDS activists arrested on Capitol Hill
-

 Photos5 days ago
Photos5 days agoPHOTOS: Sydney Gay and Lesbian Mardi Gras Parade
-

 Florida3 days ago
Florida3 days agoFla. Senate passes ‘Anti-Diversity’ bill that could repeal local LGBTQ protections
-

 Uganda4 days ago
Uganda4 days agoUgandan activist named Charles F. Kettering Foundation fellow