Local
Local gay student blocked from making blood donation despite FDA easing policy
Red Cross acknowledges delays, study to examine further change
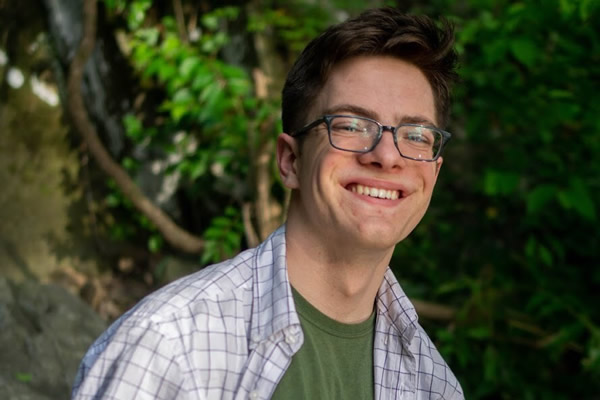


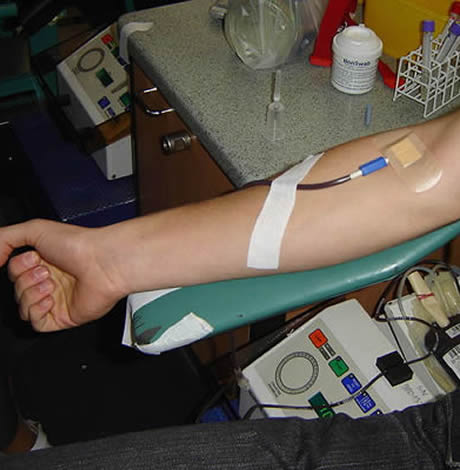
A gay D.C. native otherwise qualified to donate blood was denied that chance at a local hospital, demonstrating that obstacles remain after the FDA eased its ban on gay donations — even as the agency has set up a pilot study to assess lifting the blanket policy altogether.
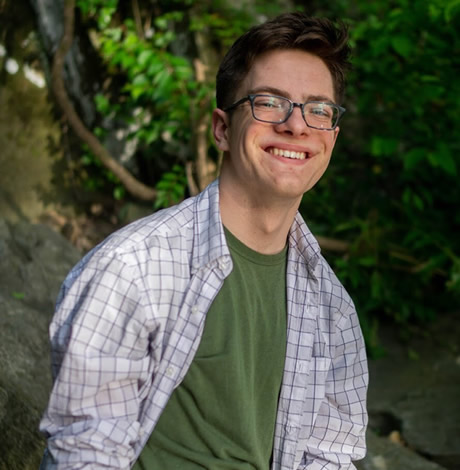
Aubrey Lay, a 19-year-old student at the College of William & Mary, told the Washington Blade after the FDA eased its policy last month he registered with his family at Children’s National Hospital, a D.C.-based pediatrics center, in hopes of making a contribution under the belief he’d meet the new requirements.
“As a gay man, I was very excited that the FDA had relaxed its guideline restrictions on MSM donating blood, however imperfect this change may be,” Lay said. “This meant that for the first time since graduating high school, I would be able to donate blood.”
Lay said he would have been ineligible to donate under the former rule requiring 12 months of abstinence for gay men, but believed he would have been eligible under the new rules requiring only three months. Although the hospital’s website had the old information online, Lay said he proceeded to his appointment on April 29 under the “wishful thinking” the hospital would accept him.
But Lay was ultimately blocked from making a donation.
“It turned out I was giving them the benefit of the doubt where I shouldn’t have,” Lay said. “I signed in and had my intake interview during which I explained my sexual history, and that I had last had sexual contact in early January, over the three-month limit. After answering all these questions, I got my finger pricked and iron levels checked, and height, weight, [blood pressure] taken. Only then was I told that I would not be able to donate because the hospital’s policy has not yet caught up to national standards.”
Lay said he was “shaken” by the experience, having wanted to make a blood donation to help out as the nation battles the coronavirus crisis.
As evidence going to the hospital was a risk he didn’t take lightly, Lay said it was the first time he’d left his house in a month because he and his family took the Virginia stay-at-home order “very seriously.”
“I certainly would not have risked my own health, and that of others, had I known I would be turned away,” Lay said.
Amid the blood shortage during the coronavirus pandemic, the FDA last month announced it would ease the ban on blood donations for various groups, including men who have sex with men.
The earlier ban, established in 2015, required gay men to be abstinent for 12 months before making a donation, but the new policy eased those restrictions, requiring a deferral period of three months.
Before 2015, the FDA had a lifetime ban on blood donations from men who have had sex with men. The policy was implemented in 1983 at the height of the AIDS epidemic based on fears donations from gay men would allow HIV to enter the blood supply.
Lay, upon being denied the ability to donate blood, said he found the office of the hospital’s president next to the blood donation room and sought an audience.
The president, Lay said, apologized for the confusion and connected him with the doctor in charge of the blood bank. The doctor, Lay said, told him the hospital’s computer systems were interlaced with the new policy and — in normal times without coronavirus — it would take a month to disentangle them and make them consistent with the new policy.
The website for the Children’s National Hospital has been updated and no longer indicates it follows the earlier 12-month policy, but is in the process of making a transition to conform to the new guidance by June 2020.
A Children’s National Hospital spokesperson confirmed the center is still in the process of updating its policy for gay donors and expects resolution next month.
“We have the deepest appreciation for all our blood donors and see every day how their donation saves lives,” the spokesperson said. “We take every step to adhere to all regulations around blood donation and are working to update our policies, donor questionnaire and computer systems to align to the new FDA regulations. The FDA just approved the donor questionnaire for sites to use and we are hoping to have all policies in place in June. We encourage anyone who would like to donate to make an appointment and double check on the eligibility before coming in.”
Lay’s story isn’t unique as other gay men have reported being unable to donate blood after the FDA eased its ban. Whether or not each of these men expected to meet the requirements under the new deferral period of three months is unclear.
Gay TV personality Andy Cohen says he was denied the chance to donate, even though his plasma would be rich in the antibody for COVID-19. Lukus Estok, a young gay man who recovered from COVID-19, also told his story about being denied the opportunity to make a donation at the New York Blood Center. His Facebook post went viral on social media and was featured in a Good Morning America article.
Mathew Lasky, a spokesperson for the LGBTQ media watchdog GLAAD, which has been leading calls for a change in blood policy, said more and more stories are emerging of LGBTQ people being blocked from making donations despite the recent change.
“GLAAD is continuing to pressure the FDA to put science above stigma, and to remove any time-based deferral on gay and bisexual men, and others in the LGBTQ community, donating blood,” Lasky said. “In the meantime, it’s critical for individual blood centers to begin adhering to the new FDA guidelines as not to continue needlessly discriminating against LGBTQ people, and to address the critical blood supply shortages we’re seeing during COVID-19.”
The American Red Cross, which had called for the FDA to shorten its deferral period from the 12 months to three months before the new policy was implemented, cautioned via a spokesperson the implementation of updated rules “will take time.”
“As the largest blood provider in the country, we are working to implement the updated FDA eligibility changes and will provide an update on timeline in the near future,” the spokesperson said. “It’s important to note that the implementation process includes potentially thousands of individuals and involves complex system updates that do take time. We are working to develop a reinstatement process to share with potential donors in the near future.”
UPDATE: A Red Cross spokesperson after publication of this article told the Blade a June 1 target date has been set for full implementation of the FDA policy change.
“The American Red Cross is working to implement the updated FDA eligibility changes on June 1,” the spokesperson said. “We just want to emphasize that this process includes potentially thousands of individuals and involves system updates that will take time to implement.”
Even as blood centers work to update their system to conform to the new policy, LGBTQ advocates have said the change is insufficient and the FDA should scrap its deferral requirements entirely for men who have sex with men and instead implement a policy based on individual risk assessment. Such a policy could enable, for example, monogamous gay men or gay men with safe sex practices to make blood donations.
Among those calling for this change is California Attorney General Xavier Becerra, who last month led a letter to the Department of Health & Human Services with 19 other attorneys general urging the Trump administration to abandon the deferral period, citing the success of other countries, such as Spain, Italy and Portugal, that have implemented gender-neutral policies.
Many voices have emerged calling for any and all obstacles to gay men making blood donations being lifted because testing could determine whether a blood donation has HIV. Experts, however, say some caution is necessary as a window exists between donation and testing in which the test wouldn’t be able to determine if a donation was free of the virus.
Scott Schoettes, counsel and the HIV Project Director at Lambda Legal, articulated that warning in a conference call last month with reporters.
“People believe that it catches all new cases of HIV or new cases of Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, other blood borne infections,” Schoettes said. “That is not the case. There is still a window period during which that testing would not uncover a newly acquired infection.”
But in a rare situation of hitting both the gas and brake at the same time amid a policy change, the FDA has indicated the agency also is in the early stages of a pilot program to determine whether or not the ban can be changed further in favor of a risk-based assessment.
Megan McSeveney, an FDA spokesperson, confirmed the agency is set to begin the study with “about 2,000 men who have sex with men and who would be willing to donate blood.”
“This study, being conducted at community health centers in key locations across the United States, could generate data that will help the FDA determine if a donor questionnaire based on individual risk assessment would be as effective as time-based deferrals in reducing the risk of HIV,” McSeveney said.
The Red Cross is participating in the efforts to ensure a new risk-based policy as opposed to a deferral period will keep the blood supply safe, a spokesperson for the non-profit said.
“We are very early in the study – we are currently finalizing the content of the new questions, and developing the specifics of the protocols, including site selection, which then will require government and ethical review board approval,” the spokesperson said. “The results of testing in combination with the responses to the questionnaire will be used to determine the value of the questions in interdicting new HIV infections.”
Based on the limited information of the study, there’s no indication a change will, in fact, follow eliminating the deferral period for gay men entirely in favor of a risk-based assessment.
Sarah Kate Ellis, CEO of GLAAD, said in a statement the pilot study was wholly necessary given medical experts who say any kind of deferral period is “stigma, not science.”
“During the current crisis, the FDA is wasting time and money on a pilot study when all the scientific research and medical authorities plainly state that gay and bi man should not be restricted from donating blood,” Ellis said. “All blood donations, regardless of sexual orientation, are screened to ensure healthy samples and now the American Medical Association, leading elected officials, and more than 600 medical professionals have all done the work for the FDA and unequivocally state that this ban needs to end.”
Lay, caught in the middle of reconsideration of the policy, said he awaits the day when the restrictions are changed so LGBTQ people can finally donate blood at a time when their help is needed.
“Because of this crisis, blood donation centers should not be turning people away at the door who are by all measures qualified donors, risking their health and the health of those around them by their very presence in these spaces,” Lay said. “It is so important that we make this discrepancy between policy and practice known so that we can push for more transparency in blood donation, and hopefully full implementation of the new policy, albeit imperfect.”
Cameroon
Gay Cameroonian immigrant will be freed from ICE detention — for now
Ludovic Mbock’s homeland criminalizes homosexuality

By ANTONIO PLANAS | An immigration judge on Friday issued a $4,000 bond for a Cameroonian immigrant and regional gaming champion held in federal immigration detention for the past three weeks.
The ruling will allow Ludovic Mbock, of Oxon Hill, to return to Maryland from a Georgia facility this weekend, his family and attorney said.
“Realistically, by tomorrow. Hopefully, by today,” said Mbock’s attorney, Edward Neufville. “We are one step closer to getting Ludovic justice.”
The rest of this article can be found on the Baltimore Banner’s website.
District of Columbia
Bowser appoints first nonbinary person to Cabinet-level position
Peter Stephan named Office of Disability Rights interim director

D.C. Mayor Muriel Bower has named longtime disability rights advocate Peter L. Stephan, who identifies as nonbinary, as interim director of the D.C. Office of Disability Rights.
The local transgender and nonbinary advocacy group Our Trans Capital and the LGBTQ group Capital Stonewall Democrats issued a joint statement calling Stephan’s appointment an historic development as the first-ever appointment of a nonbinary person to a Cabinet-level D.C. government position.
“This milestone appointment recognizes Stephan’s extensive expertise in disability rights advocacy and marks a historic advancement for transgender and nonbinary representation in District government leadership,” the statement says.
The statement notes that Stephan, an attorney, held the position of general counsel at the Office of Disability Rights immediately prior to the mayor’s decision to name him interim director.
The mayor’s office didn’t immediately respond to a question from the Washington Blade asking if Bowser plans to name Stephan as the permanent director of the Office of Disability Rights. John Fanning, a spokesperson for D.C. Council member Anita Bonds (D-At-Large), said the office’s director position requires confirmation by the Council.
Stephan couldn’t immediately be reached for comment.
“At a time when trans and nonbinary people ae under attack across the country, D.C. continues to lead by example,” said Stevie McCarty, president of Capital Stonewall Democrats. “This appointment reflects what we have always believed that our community is always strongest when every voice is represented in government,” he said.
“This is a historic step forward,” said Vida Rengel, founder of Our Trans Capital. “Interim Director Stephan’s career and accomplishments are a shining example of the positive impact that trans and nonbinary public servants can have on our communities,” according to Rangel.
District of Columbia
Capital Stonewall Democrats set to celebrate 50th anniversary
Mayor Bowser expected to attend March 20 event

D.C. Mayor Muriel Bowser, members of the D.C. Council, and local and national Democratic Party officials are expected to join more than 150 LGBTQ advocates and supporters on March 20 for the 50th anniversary celebration of the city’s Capital Stonewall Democrats.
A statement released by the organization says the event is scheduled to be held at the Pepco Edison Place Gallery building at 702 8th St., N.W. in D.C.
“The evening will honor the people who built Capital Stonewall Democrats across five decades – activists who fought for rights when the odds were against them, public servants who opened doors and refused to let them close, and a new generation of leaders ready to carry the work forward,” the statement says.
Founded in 1976 as the Gertrude Stein Democratic Club, the organization’s members voted in 2021 to change its name to the Capital Stonewall Democrats.
Among those planning to attend the anniversary event is longtime D.C. gay Democratic activist Paul Kuntzler, 84, who is one of the two co-founders of the then-Gertrude Stein Democratic Club. Kuntzler told the Washington Blade that he and co-founder Richard Maulsby were joined by about a dozen others in the living room of his Southwest D.C. home at the group’s founding meeting in January 1976.
He said that among the reasons for forming a local LGBTQ Democratic group at the time was to arrange for a then “gay” presence at the 1976 Democratic National Convention, at which Jimmy Carter won the Democratic nomination for U.S. president and later won election as president.
Maulsby, who served as the Stein Club president for its first three years and who now lives in Sarasota, Fla., said he would not be attending the March 20 anniversary event, but he fully supports the organization’s continuing work as an LGBTQ organization associated with the Democratic Party.
Steven McCarty, Capital Stonewall Democrats’ current president, said in the statement that the anniversary celebration will highlight the organization’s work since the time of its founding.
“Capital Stonewall Democrats has been fighting for LGBTQ+ political power in this city for 50 years, electing people, training organizers, holding this community together through some really hard moments,” he said. “And right now, with everything going on, that work has never mattered more. This gala is the first moment of our next chapter, and I want the community to be a part of it.”
The statement says among the special guests attending the event will be Democratic National Committee Vice Chair Malcolm Kenyatta, who became the first openly gay LGBTQ person of color to win election to the Pennsylvania General Assembly in 2018.
Other guests of honor, according to the statement, include Mayor Bowser; D.C. Council member Zachary Parker (D-Ward 5, the Council’s only gay member; D.C. Council member Anita Bonds (D-At-Large); Earl Fowlkes, founder of the International Federation of Black Prides; Vita Rangel, a transgender woman who serves as Deputy Director of the D.C. Mayor’s Office of Talent and Appointments; Heidi Ellis, director of the D.C. LGBTQ Budget Coalition; Rayceen Pendarvis, longtime D.C. LGBTQ civic activist; and Phillip Pannell, longtime D.C. LGBTQ Democratic activist and Ward 8 civic activist.
Information about ticket availability for the Capital Stonewall Democrats anniversary gala can be accessed here: capitalstonewalldemocrats.com/50th
-

 Health5 days ago
Health5 days agoToo afraid to leave home: ICE’s toll on Latino HIV care
-

 Colombia4 days ago
Colombia4 days agoClaudia López wins primary in Colombian presidential race
-

 The White House4 days ago
The White House4 days agoTrump will refuse to sign voting bill without anti-trans provisions
-

 Iran4 days ago
Iran4 days agoMan stuck in Lebanon as Iran war escalates