U.S. Supreme Court
Expert challenges prevailing analysis that SCOTUS will uphold trans healthcare ban
NCLR’s Shannon Minter more optimistic about U.S. v. Skrmetti

Less than a week after oral arguments were concluded in the landmark U.S. v. Skrmetti case, most pundits and legal experts seem to agree the U.S. Supreme Court is poised to uphold Tennessee’s law banning gender affirming health treatments for minors.
Shannon Minter, however, is not convinced.
In fact, as the legal director for the National Center for Lesbian Rights told the Blade during an interview on Tuesday, “neither I nor the lawyers I know who are following and have litigated these cases” buy into the “negative” analysis published by many mainstream press outlets after the parties addressed the justices at One First Street on Dec. 4.
“I was totally surprised,” Minter said, and “really disappointed,” in coverage of the oral arguments that appeared in places like SCOTUSblog, where Amy Howe wrote that “nearly all of the court’s conservative majority expressed skepticism about a challenge to Tennessee’s ban on puberty blockers and hormone therapy for transgender teenagers.”
The article was hardly an outlier. The New York Times reported it was “probable” that “there were at least five votes for rejecting the equal protection challenge to the law,” while Slate’s Mark Joseph Stern explained that Skrmetti will determine whether “constitutional limits on sex discrimination” can “survive this 6-3 conservative supermajority” and then concluded that “after two and a half hours of arguments, it appears the answer will be no.”
Conservative justices not in lockstep
From the interpretation of key exchanges between the justices and the parties last week to assessments of whether and to what extent certain conservatives might be inclined to join their liberal colleagues in this case and expectations for how precedent-setting decisions could shape its outcome, Minter offered a variety of reasons for why he is skeptical of the reasoning that undergirds much of the mainstream opinion on where the court is likely to land when a decision in Skrmetti is published, as expected, in June 2025.
Asked why his take on Wednesday’s oral arguments diverged so significantly from those offered by many reporters and legal analysts, Minter suggested that conservative Justice Samuel Alito might be responsible to some extent for “the negative perception [reflected] in the mainstream press” because he was “unremittingly negative and spoke a lot” and “took up most of the space.”
Last week aside, given his well established, deeply conservative ideological bent and record of skepticism toward LGBTQ rights, one might reasonably expect Alito to issue a decision that would uphold Tennessee’s trans healthcare ban. Likewise with respect to Justice Clarence Thomas who, compared to Alito, is hardly less conservative or more solicitous of opportunities to expand the LGBTQ community’s rights and freedoms.
Minter characterized both justices’ engagement with the Skrmetti litigants as “negative,” adding that another conservative on the bench, Brett Kavanaugh, was occasionally prickly but otherwise seemed eager to understand the nuances of the case and address questions like whether or how “a ruling in favor of the plaintiffs, here” might “predetermine what we would have to do in a sports case.”
By contrast, it is difficult to predict where the other conservatives on the high court might land on legal questions central to the case. Neil Gorsuch, for instance, was difficult to read even before he declined to ask a single question or otherwise speak when the court heard oral arguments last week.
Minter noted that “less than four years ago when the court issued its decision in Bostock v. Clayton County, it was Gorsuch whose majority opinion, cosigned by the conservative Chief Justice John Roberts and their liberal colleagues, recognized “that discrimination because a person is transgender is inherently based on sex, that it is a type of sex discrimination.”
“So the issue here” in the Skrmetti case “looks awfully similar,” Minter said, because the core legal questions concern the constitutionality of “a statute that targets transgender people” and confronts the court with the question of “whether or not [the law] discriminates based on sex.”
Acknowledging that one should not read too deeply into Gorsuch’s decision to play his hand “extremely close to the vest” during oral arguments, Minter said, “I would like to think that if he had a significant change of view” since authoring the court’s landmark opinion on anti-trans discrimination in 2020, the justice would have “wanted to ask some questions to explore that.”
For these reasons, “just from the very outset,” one might reasonably expect or at least “be hopeful that Justice Gorsuch will continue to [treat] these issues the same way that he did in Bostock,” Minter said.
He added that Roberts, likewise, was careful last week not to indicate which direction he was leaning and instead asked both parties to address concise but challenging questions. While Minter conceded that “It’s hard to draw any definitive conclusion,” he said the chief justice’s performance offered little reason to suspect that he has “shifted his fundamental understanding of these issues from one case to another.”
In a more “encouraging” showing last week, the court’s sixth conservative justice, Amy Coney Barrett, appeared to be “taking these issues very seriously” and “very genuinely grappling with whether or not this is a sex based law, and even with whether discrimination against transgender people, which is considered in its own right, [should] be subject to some sort of heightened scrutiny,” Minter said.
Another major reason for optimism, Minter said, was the “very belabored” discussion of Bostock on Wednesday that was kicked off by the court’s interest in revisiting recent caselaw and the petitioners’ masterful application of relevant precedent to legal questions at issue in Skrmetti.
Elizabeth Prelogar, the Biden-Harris administration’s U.S. solicitor general who represents the federal government and argues alongside the petitioners, did “such a beautiful job of saying that the analysis of Bostock itself was not new,” but rather “drew upon preexisting equal protection case law,” Minter said.
Importantly, he said Prelogar was careful to delineate how both the statutory proscriptions against workplace discrimination ordained by Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the rights guaranteed by the Equal Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment “rely on something called but-for causation, where all you have to show is that sex, in this case, was a but-for cause of the discrimination — meaning it doesn’t have to be the only cause; there can be other factors at play, but as long as it is a cause, it’s discrimination.”
“The reason Bostock was a surprise is just that, sadly, we’re so accustomed to the law not being applied equally or fairly to transgender people,” said Minter, who credited Gorsuch for applying “the law and the preexisting analysis honestly and fairly to transgender people” and deciding, “correctly,” that “there’s just no way to apply this framework that we’ve always applied and not come to the conclusion that this is sex discrimination.”
After the 2022 decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, which overturned decades-old abortion protections that were first established with Roe v. Wade in 1973, critics argued the conservative justices had cavalierly abandoned the principle of stare decisis, which holds that courts should abide or defer to previous precedent-setting decisions, where possible, especially in landmark decisions that govern how people live their lives.
Asked whether the Supreme Court might be less inclined to overturn decisions like Bostock that were issued more recently and authored by the justices who currently serve on the bench, Minter said “absolutely,” adding that it would be “extraordinary for them to not follow the analysis and reasoning in a decision they decided so recently.”
The stare decisis issue provides more reason for optimism about Skrmetti, Minter said. Overturning important precedent is “unsettling to the stability of the law and to the status and stature of the court,” and “it helps that Bostock was a 6-3 decision” rather than a narrower, more contentious case settled by a 5-4 majority.
The future of gender-affirming care
The path by which U.S. v. Skrmetti reached the highest court in the land is a case study of the devastating consequences, the second and third-order effects, of scapegoating a vulnerable community with a moral panic that is allowed to fester thanks to fear and bigotry.
After several years in which state legislatures collectively introduced hundreds of bills targeting the rights of trans young people and their families, including access to healthcare, the Movement Advancement Project reports that 37 percent of transgender youth (ages 13-17) now live in places that legally prohibit them from accessing best practice medication and surgical care, with dozens of states enforcing these bans.
Among them, of course, is Tennessee, where a complaint was filed last year and fast-tracked through the federal courts such that now, justices on the Supreme Court are debating whether unelected judges or democratically elected lawmakers should adjudicate complex questions that advocates (for queer and trans communities, for civil liberties, for healthcare providers) believe are best addressed by patients and families or caregivers in close coordination with trained specialists who operate under evidence-based guidelines for clinical practice.
Apart from litigation before the high court, another development that signals the appetite and the political will for bringing anti-trans policies and politics from statehouses to the national stage was the massive spend on anti-trans advertising to support Trump and other Republican campaigns during the 2024 election cycle, which Minter noted was “very painful and distressing” for trans people and their families.
After Nov. 5, debates about whether and the extent to which the GOP’s anti-trans messaging strategy may have delivered electoral victories for the president-elect, or for the congressional Republicans who maintained control of the U.S. House and reclaimed their majority in the U.S. Senate, have given way to concerns about the escalation of transphobic hate speech and the legislative and legal attacks against the community that began to ramp up well before the incoming Trump-Vance administration will be seated with the 119th Congress next month.
At this juncture, Minter said that trans young people and their families must wait to see not only how the Supreme Court decides U.S. v. Skrmetti and what the corresponding implications might be in terms of their access to healthcare, but also whether and how and how aggressively the attacks against them will take shape in January and beyond.
In the meantime, “there are some basic things people can do to protect themselves,” Minter said. For example, “this would be a good time to get your identity documents updated, if you haven’t done that yet. It’s a good time to make sure your prescriptions are current. if you live in a state that has banned trans healthcare for minors and you’re the parent of a transit child, you know, it’s good to explore out of state resources. It would be a good thing for transgender people to go ahead now and get copies of their medical records, or at least make sure you know how you can quickly do so in case you do need to make any adjustments to how you’re obtaining the care, if you need to find a new provider or explore out of state resources, depending on what may happen in your state.”
He added, “Now, if there’s some sort of national action,” like a federal ban on access to transgender medicine for minors, “then, of course, it’s not necessarily going to matter where you live, or what state you live in” but “NCLR and other legal groups are prepared to immediately challenge” any such action on the national level.
Here again, Minter, a transgender litigator who came out in his 30s and who throughout his career has argued highly consequential cases, with some yielding major advancements in LGBTQ civil rights, is optimistic. “The post election polling has shown that the public would not be supportive of that action,” he said, because Americans “would far prefer the federal government, the president, and Congress focus on issues that matter broadly to people, especially the economy.”
Earlier, when discussing an exchange between Barrett and the parties, which concerned the justice’s questions about America’s history of de jure (official, lawful) anti-trans discrimination, Minter remarked that”It’s a good thing” ACLU attorney Chase Strangio, who represents the plaintiffs alongside Prelogar, was there “to explain to the court that, yes, there certainly has been a long history of governmental discrimination against transgender people.”
Ticking through some examples Strangio had shared with the court, Minter noted American officials’ enforcement of bans on military service, bans on government employment, bans on marriage, bathroom bans, gendered dress codes based on birth sex, and policies under which trans parents or guardians were forced to forfeit custody of their children or dependents.
Barrett’s pursuit of this line of questioning, Minter said, was an optimistic sign. And perhaps there is even reason for hope that a conservative Christian Trump-appointed jurist’s interest in the country’s record of anti-trans discrimination could carry implications beyond how she decides the tremendously consequential case that is now before the court.
Either way, Barrett — along with the other justices and their clerks and the courtroom staff, together with attorneys, spectators, journalists, and other observers who were lucky enough to score a spot to see the action live from One First Street (or, at least, were able to tune in remotely) — saw Strangio make his case on Wednesday, becoming the first out transgender lawyer ever to argue before the high court.
U.S. Supreme Court
Competing rallies draw hundreds to Supreme Court
Activists, politicians gather during oral arguments over trans youth participation in sports
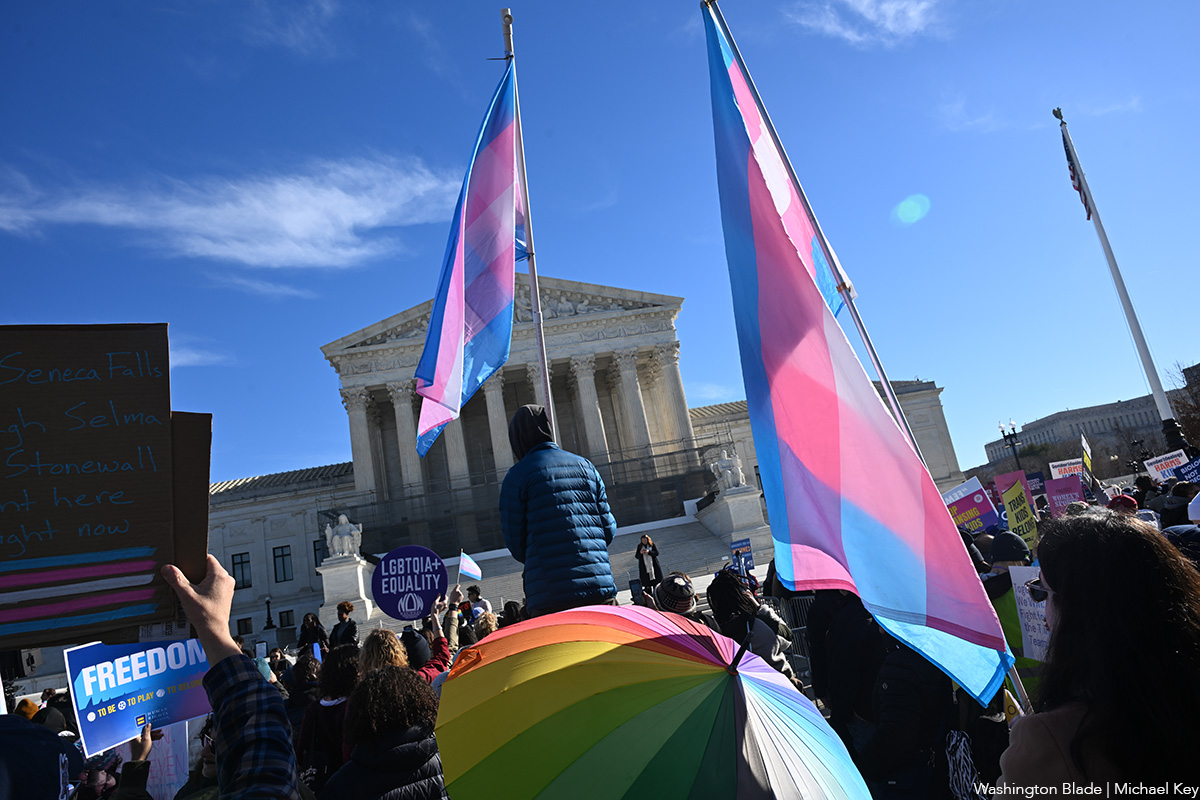
Hundreds of supporters and opponents of trans rights gathered outside of the United States Supreme Court during oral arguments for Little v. Hecox and West Virginia v. B.P.J. on Tuesday. Two competing rallies were held next to each other, with politicians and opposing movement leaders at each.
“Trans rights are human rights!” proclaimed U.S. Sen. Ed Markey (D-Mass.) to the crowd of LGBTQ rights supporters. “I am here today because trans kids deserve more than to be debated on cable news. They deserve joy. They deserve support. They deserve to grow up knowing that their country has their back.”
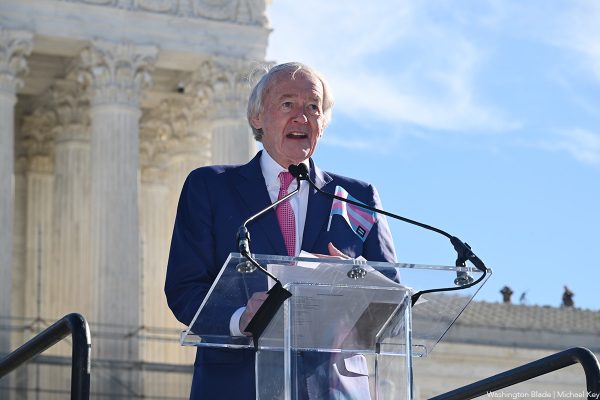

“And I am here today because we have been down this hateful road before,” Markey continued. “We have seen time and time again what happens when the courts are asked to uphold discrimination. History eventually corrects those mistakes, but only after the real harm is done to human beings.”
View on Threads
U.S. Education Secretary Linda McMahon spoke at the other podium set up a few feet away surrounded by signs, “Two Sexes. One Truth.” and “Reality Matters. Biology Matters.”
“In just four years, the Biden administration reversed decades of progress,” said McMahon. “twisting the law to urge that sex is not defined by objective biological reality, but by subjective notion of gender identity. We’ve seen the consequences of the Biden administration’s advocacy of transgender agendas.”
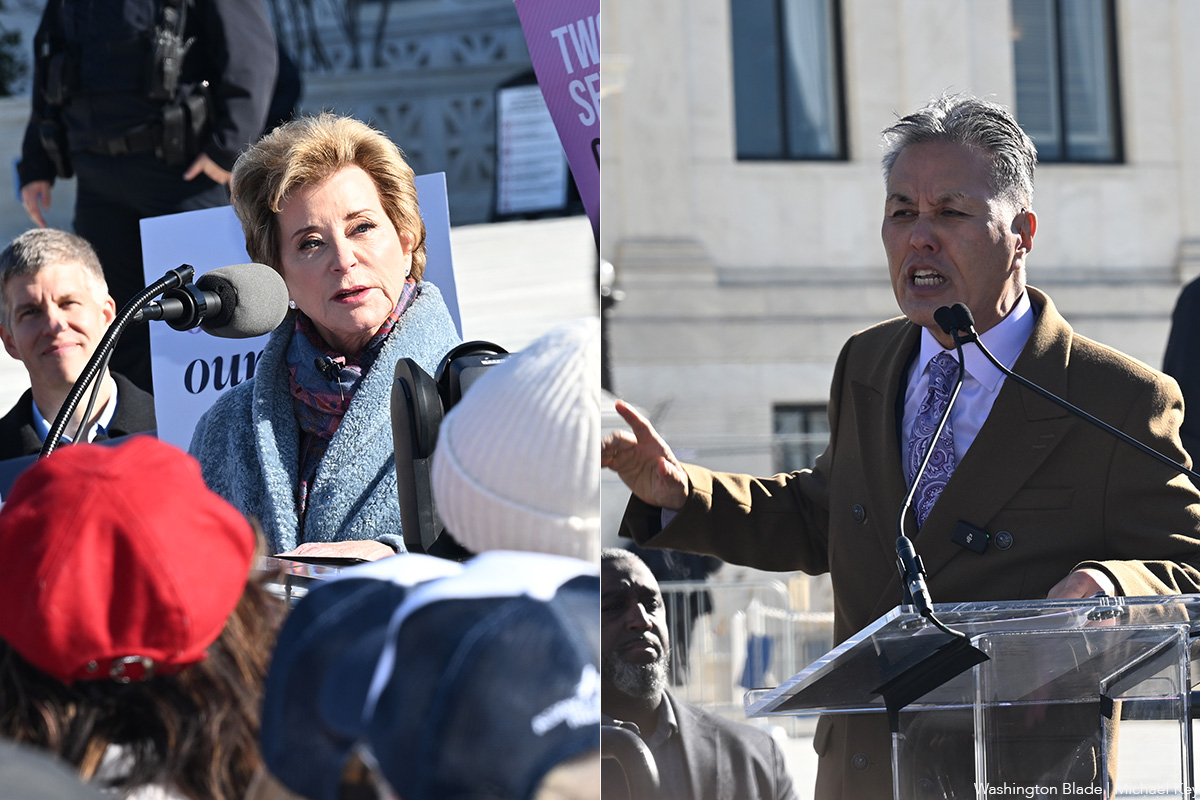

U.S. Rep. Mark Takano (D-Calif.), chair of the Congressional Equality Caucus, was introduced on the opposing podium during McMahon’s remarks.
“This court, whose building that we stand before this morning, did something quite remarkable six years ago.” Takano said. “It did the humanely decent thing, and legally correct thing. In the Bostock decision, the Supreme Court said that trans employees exist. It said that trans employees matter. It said that Title VII of the Civil Rights Act protects employees from discrimination based on sex, and that discrimination based on sex includes discrimination based on gender identity and sexual orientation. It recognizes that trans people have workplace rights and that their livelihoods cannot be denied to them, because of who they are as trans people.”
“Today, we ask this court to be consistent,” Takano continued. “If trans employees exist, surely trans teenagers exist. If trans teenagers exist, surely trans children exist. If trans employees have a right not to be discriminated against in the workplace, trans kids have a right to a free and equal education in school.”
Takano then turned and pointed his finger toward McMahon.
“Did you hear that, Secretary McMahon?” Takano addressed McMahon. “Trans kids have a right to a free and equal education! Restore the Office of Civil Rights! Did you hear me Secretary McMahon? You will not speak louder or speak over me or over these people.”
Both politicians continued their remarks from opposing podiums.
“I end with a message to trans youth who need to know that there are adults who reject the political weaponization of hate and bigotry,” Takano said. “To you, I say: you matter. You are not alone. Discrimination has no place in our schools. It has no place in our laws, and it has no place in America.”
U.S. Supreme Court
Supreme Court hears arguments in two critical cases on trans sports bans
Justices considered whether laws unconstitutional under Title IX.

The Supreme Court heard two cases today that could change how the Equal Protection Clause and Title IX are enforced.
The cases, Little v. Hecox and West Virginia v. B.P.J., ask the court to determine whether state laws blocking transgender girls from participating on girls’ teams at publicly funded schools violates the 14th Amendment’s Equal Protection Clause and Title IX. Once decided, the rulings could reshape how laws addressing sex discrimination are interpreted nationwide.
Chief Justice John Roberts raised questions about whether Bostock v. Clayton County — the landmark case holding that Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 protects employees from discrimination based on sexual orientation or gender identity — applies in the context of athletics. He questioned whether transgender girls should be considered girls under the law, noting that they were assigned male at birth.
“I think the basic focus of the discussion up until now, which is, as I see it anyway, whether or not we should view your position as a challenge to the distinction between boys and girls on the basis of sex or whether or not you are perfectly comfortable with the distinction between boys and girls, you just want an exception to the biological definition of girls.”
“How we approach the situation of looking at it not as boys versus girls but whether or not there should be an exception with respect to the definition of girls,” Roberts added, suggesting the implications could extend beyond athletics. “That would — if we adopted that, that would have to apply across the board and not simply to the area of athletics.”
Justice Clarence Thomas echoed Roberts’ concerns, questioning how sex-based classifications function under Title IX and what would happen if Idaho’s ban were struck down.
“Does a — the justification for a classification as you have in Title IX, male/female sports, let’s take, for example, an individual male who is not a good athlete, say, a lousy tennis player, and does not make the women’s — and wants to try out for the women’s tennis team, and he said there is no way I’m better than the women’s tennis players. How is that different from what you’re being required to do here?”
Justice Samuel Alito addressed what many in the courtroom seemed reluctant to state directly: the legal definition of sex.
“Under Title IX, what does the term ‘sex’ mean?” Alito asked Principal Deputy Solicitor General Hashim Mooppan, who was arguing in support of Idaho’s law. Mooppan maintained that sex should be defined at birth.
“We think it’s properly interpreted pursuant to its ordinary traditional definition of biological sex and think probably given the time it was enacted, reproductive biology is probably the best way of understanding that,” Mooppan said.
Justice Sonia Sotomayor pushed back, questioning how that definition did not amount to sex discrimination against Lindsay Hecox under Idaho law. If Hecox’s sex is legally defined as male, Sotomayor argued, the exclusion still creates discrimination.
“It’s still an exception,” Sotomayor said. “It’s a subclass of people who are covered by the law and others are not.”
Justice Elena Kagan highlighted the broader implications of the cases, asking whether a ruling for the states would impose a single definition of sex on the 23 states that currently have different laws and standards. The parties acknowledged that scientific research does not yet offer a clear consensus on sex.
“I think the one thing we definitely want to have is complete findings. So that’s why we really were urging to have a full record developed before there were a final judgment of scientific uncertainty,” said Kathleen Harnett, Hecox’s legal representative. “Maybe on a later record, that would come out differently — but I don’t think that—”

“Just play it out a little bit, if there were scientific uncertainty,” Kagan responded.
Justice Brett Kavanaugh focused on the impact such policies could have on cisgender girls, arguing that allowing transgender girls to compete could undermine Title IX’s original purpose.
“For the individual girl who does not make the team or doesn’t get on the stand for the medal or doesn’t make all league, there’s a — there’s a harm there,” Kavanaugh said. “I think we can’t sweep that aside.”
Justice Amy Coney Barrett questioned whether Idaho’s law discriminated based on transgender status or sex.
“Since trans boys can play on boys’ teams, how would we say this discriminates on the basis of transgender status when its effect really only runs towards trans girls and not trans boys?”
Harnett responded, “I think that might be relevant to a, for example, animus point, right, that we’re not a complete exclusion of transgender people. There was an exclusion of transgender women.”
Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson challenged the notion that explicitly excluding transgender people was not discrimination.
“I guess I’m struggling to understand how you can say that this law doesn’t discriminate on the basis of transgender status. The law expressly aims to ensure that transgender women can’t play on women’s sports teams… it treats transgender women different than — than cis-women, doesn’t it?”
Idaho Solicitor General Alan Hurst urged the court to uphold his state’s ban, arguing that allowing participation based on gender identity — regardless of medical intervention — would deny opportunities to girls protected under federal law.
Hurst emphasized that biological “sex is what matters in sports,” not gender identity, citing scientific evidence that people assigned male at birth are predisposed to athletic advantages.
Joshua Block, representing B.P.J., was asked whether a ruling in their favor would redefine sex under federal law.
“I don’t think the purpose of Title IX is to have an accurate definition of sex,” Block said. “I think the purpose is to make sure sex isn’t being used to deny opportunities.”
Becky Pepper-Jackson, identified as plaintiff B.P.J., the 15-year-old also spoke out.
“I play for my school for the same reason other kids on my track team do — to make friends, have fun, and challenge myself through practice and teamwork,” said Pepper-Jackson. “And all I’ve ever wanted was the same opportunities as my peers. But in 2021, politicians in my state passed a law banning me — the only transgender student athlete in the entire state — from playing as who I really am. This is unfair to me and every transgender kid who just wants the freedom to be themselves.”

Outside the court, advocates echoed those concerns as the justices deliberated.
“Becky simply wants to be with her teammates on the track and field team, to experience the camaraderie and many documented benefits of participating in team sports,” said Sasha Buchert, counsel and Nonbinary & Transgender Rights Project director at Lambda Legal. “It has been amply proven that participating in team sports equips youth with a myriad of skills — in leadership, teamwork, confidence, and health. On the other hand, denying a student the ability to participate is not only discriminatory but harmful to a student’s self-esteem, sending a message that they are not good enough and deserve to be excluded. That is the argument we made today and that we hope resonated with the justices of the Supreme Court.”
“This case is about the ability of transgender youth like Becky to participate in our schools and communities,” said Joshua Block, senior counsel for the ACLU’s LGBTQ & HIV Project. “School athletics are fundamentally educational programs, but West Virginia’s law completely excluded Becky from her school’s entire athletic program even when there is no connection to alleged concerns about fairness or safety. As the lower court recognized, forcing Becky to either give up sports or play on the boys’ team — in contradiction of who she is at school, at home, and across her life — is really no choice at all. We are glad to stand with her and her family to defend her rights, and the rights of every young person, to be included as a member of their school community, at the Supreme Court.”
The Supreme Court is expected to issue rulings in both cases by the end of June.
U.S. Supreme Court
As Supreme Court weighs trans sports bans, advocate and former athlete speaks out
PFLAG staffer Diego Sanchez competed at University of Georgia in 1970s

The U.S. Supreme Court will hear two cases Tuesday addressing the legality of banning transgender women and girls from participating in sports under the 14th Amendment.
Though the two cases differ slightly in their fact patterns, they ultimately pose the same constitutional question: whether laws that limit participation in women’s sports to only cisgender women and girls violate the Equal Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment.
In both cases — Little v. Hecox and West Virginia v. B.P.J. — trans girls filed lawsuits against their respective states, Idaho and West Virginia, arguing that the bans violate their right to equal protection under the law by subjecting them to different standards than cisgender girls.
Lindsay Hecox, now 24, filed her lawsuit in 2020 while attending Boise State University. That same year, Idaho enacted the “Fairness in Women’s Sports Act,” which barred trans women from participating in any sport in public schools, from kindergarten through college. Although Hecox underwent hormone therapy that significantly lowered her testosterone levels, she was still excluded under the law when she attempted to try out for the women’s track and cross-country teams.
The second case centers on B.P.J., a 15-year-old trans girl who has identified as female since third grade and has been on puberty blockers since the onset of puberty. In 2021, West Virginia enacted the “Save Women’s Sports Act,” which requires sports teams to be designated by “biological sex” rather than gender identity. B.P.J.’s mother filed suit on her behalf after her daughter was barred from participating on her school’s girls’ cross-country and track teams.
A key distinction between the two cases is that attorneys for B.P.J. have argued that because puberty blockers were part of her development, her body is more aligned with that of a cisgender girl than a cisgender boy. Despite these differences, both cases raise the same constitutional issue: whether it is lawful to bar someone from participation in sports based on sex assigned at birth.
The Washington Blade spoke with PFLAG Vice President of Policy and Government Affairs Diego Sanchez.
Sanchez is a trans elder with firsthand experience as a college athlete at the University of Georgia and later became the first openly trans legislative staff member on Capitol Hill.
His dual experience — as a former athlete and a longtime policy expert deeply familiar with constitutional law — gives him a unique perspective on the questions now before the Supreme Court. Sanchez will also be one of the featured speakers at a rally on the steps of the court as the justices hear arguments.
When asked how attitudes toward trans athletes differ from when he competed at the University of Georgia from 1976-1980 to today — when 27 states have passed laws restricting trans participation in sports — Sanchez said the contrast is stark.
“I had the good experience of being supported by my teammates and my coach,” Sanchez said. “The thing that’s so different today is that these [trans] kids are able to go home and get kisses and hugs from their parents, being lauded in the stands by their families, and then being told that who they are doesn’t necessarily fit with who they’re allowed to be in their expression at the moment, and that to me, seems a terrible injustice.”
Sanchez emphasized that sports offer lessons that extend far beyond competition.
“When you’re an athlete, you learn an awful lot of things about life,” he said. “You learn about leadership, but you also learn that your best effort becomes part of a team effort … how you feel as an individual contributor is affected by what ends up being part of how you live your life as an adult.”
After his time as an athlete, Sanchez began working in government, eventually serving as senior policy advisor to then-U.S. Rep. Barney Frank (D-Mass.) until Frank’s retirement in 2013. Sanchez said that one of the most important aspects of his role was simply being visible as a trans person in spaces where many lawmakers had never knowingly met one before.
“My job was to make sure that no one, no legislator, could say that they had never met a trans person,” Sanchez said.
Sanchez also addressed the broader implications the Supreme Court’s decision could have on how gender is treated within institutional systems.
“I don’t think it affects how people perceive their own gender or express their own gender, but I do think that it could create barriers if it doesn’t welcome the way that community and society actually are,” he said. “The most important thing for people to know … is to remember that every person is an individual, and that the right to contribute to society should be something that is supported by the government, not hindered.”
He added that the court’s role must be understood within the framework of checks and balances established by the Constitution.
“The risk, of course, here is always remembering that we have three branches of government, so that this action by the judiciary branch may or may not have implications on whether or how things can be perceived or executed at other branches,” Sanchez said. “I would hope that our government is interested in letting the future generations and current generations be the best that they can be as well.”
“Do people get to live their lives as they are, or is the government an obstruction or a support?”
When asked what message he would share with young trans athletes watching the Supreme Court take up these cases, Sanchez said community support remains critical, regardless of how the justices rule.
“Make sure that the environment that you put yourself in is something that honors who you know you are and supports you becoming the best person you can be, and that anything that takes away from that is purely dissonance,” he said.
“What we do with dissonance is what distinguishes us as whether we excel or doubt.”
That same sense of community, Sanchez said, is what rallies — like the one planned outside the Supreme Court — are meant to reinforce, even as decisions are made inside the building.
“Rallies, including tomorrow’s, are about people knowing they’re not alone, and hearing from other people who support who they are,” he said. “There is support across the country … I wish that I had had someone my age now that I could have looked to, but I am the role model, but I didn’t have any.”
Looking ahead to the possibility that the court could uphold bans on trans athletes, Sanchez said the immediate challenge will be ensuring that families and communities continue to affirm trans youth amid legal uncertainty.
“Having the endorsement of being supported who you are, it helps you so much,” he said. “You cannot put the issue of rights back into the genie’s bottle once people experience what freedom and welcoming is.”
For Sanchez, whose life has spanned decades of change in both sports and government, the cases before the Supreme Court represent a pivotal moment — not just legally, but culturally.
“Living your life, for me, does not require bravery,” he said. “It’s just taking one step and then another.”
-

 U.S. Supreme Court5 days ago
U.S. Supreme Court5 days agoSupreme Court hears arguments in two critical cases on trans sports bans
-

 Virginia5 days ago
Virginia5 days agoWoman arrested for anti-gay assault at Alexandria supermarket
-

 Commentary5 days ago
Commentary5 days agoHonoring 50 queer, trans women with inaugural ‘Carrying Change’ awards
-

 District of Columbia5 days ago
District of Columbia5 days agoRuby Corado sentenced to 33 months in prison

















