National
Jimmy Carter, beloved humanitarian and human rights advocate, was supporter of LGBTQ rights
Historic, first-ever meeting with gay activists held at Carter White House in 1977
Former President Jimmy Carter, who died Sunday at the age of 100, is being remembered by both admirers and political observers as a progressive southern Democrat and former Georgia governor who pushed for an end to racial injustice in the U.S., and as a beloved humanitarian who worked hard as president and during his post-presidential years to improve the lives of people in need throughout the world.
Carter’s death comes over a year after the passing on Nov. 19, 2023, of former First Lady Rosalynn Carter, his wife and devoted partner of 77 years. Carter also had the distinction of becoming the oldest living former U.S. president after the death at the age of 94 of former President George H.W. Bush on Nov. 30, 2018.
The former president’s passing also follows his decision in February 2023 to receive hospice care at his family home in Plains, Ga., at the age of 98 after declining additional medical intervention to continue treatment of several ailments that required hospitalization over the previous several months.
Modest beginnings
Jimmy Carter was born Oct. 1, 1924, at a hospital in his hometown of Plains, Ga., where he was raised on his parents’ peanut farm. His decades of public service took place after he graduated from the United States Naval Academy in 1946 and he began his service as a submariner.
He left the Navy after the death of his father in 1953, taking over the Carter family business in what was then a segregated Georgia with strong lines between Blacks and Whites. He was an early supporter of the nascent civil rights movement and became an activist within the Democratic Party and a leading voice for the change needed to end racial segregation.
Carter was first elected to public office in 1963 as a state senator, for which he served until 1967. He successfully ran for governor in 1970 and served as Georgia governor until 1975, when he turned his attention to a possible run for U.S. president as a progressive southern Democrat.
Many political observers have said although he was relatively unknown outside of Georgia and within the leadership of the Democratic Party, Carter was able to parlay voter fatigue and the public’s response to the Nixon Watergate scandal and the growing opposition to the Vietnam War to establish himself as an outsider candidate removed from scandal and bad policies.
Appearing to answer the nation’s needs at that time, Carter’s slogan at the start of his presidential campaign was, “A Leader, For A Change.” He came out ahead of nine other Democrats, most of them better known than him, to win the 1976 Democratic nomination for president.
The thirty-ninth President of the United States, Carter served from 1977 to 1981 at a time when support for LGBTQ people was in its early stages, with many elected officials remaining cautious about the potential political risk for outwardly embracing “gay rights.”
Yet during his 1976 presidential campaign, Carter surprised some political observers when he stated at a press conference during a campaign trip to San Francisco in May of that year that he would sign the Equality Act, the gay civil rights bill introduced by then U.S. Rep. Bella Abzug (D-N.Y.) if it reached his desk as president.
“I will certainly sign it, because I don’t think it’s right to single out homosexuals for abuse or special harassment,” he said.
While Carter did not back away from that statement, gay activists were disappointed at the time of the Democratic National Convention in New York City in July 1976, when they said convention officials at the request of the Carter campaign refused to include a gay rights plank as part of the Democratic Party’s platform approved at the convention.
Some LGBT Democratic activists attending the convention said they agreed with the contention of Carter supporters that Carter should not be hampered by a controversial issue that could hurt his chances of defeating Republican President Gerald Ford in the November 1976 presidential election.
Carter narrowly defeated Ford in the election. Some political observers said Ford might have won except for the negative fallout from his decision to pardon former President Richard Nixon, who resigned from office in the midst of the Watergate scandal and allegations that Nixon engaged in illegal activity by playing some role in the break-in at the Democratic Party headquarters in D.C.’s Watergate office building that triggered the scandal.
In March of 1977, just over two months after Carter was inaugurated as president, the White House hosted an historic, first-of-its-kind meeting with fourteen prominent gay rights leaders from throughout the country. Carter did not attend the meeting and was staying at the presidential retreat at Camp David, Md., at the time of the meeting, which was organized by presidential assistant for public liaison Margaret “Midge” Costanza. But White House officials said Carter was aware of the meeting and supported efforts by Costanza and other White House staffers to interact with the gay leaders.
“The meeting was a happy milestone on the road to full equality under the law for gay women and men, and we are highly optimistic that it will soon lead to complete fulfilment of President Carter’s pledge to end all forms of Federal discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation,” said Jean O’Leary, then co-executive director of the National Gay Task Force, which helped select the gay activists who attended the meeting. Among those attending was D.C. pioneer gay rights advocate Frank Kameny.
But about one year later in 1978, some LGBT leaders joined famed gay San Francisco Supervisor Harvey Milk in criticizing Carter for being slow to speak out against California’s Proposition 6, also known as the Briggs Initiative, a ballot measure asking voters to approve a law to ban gay and lesbian individuals from working in California public schools as teachers or staff members.
In a June 28, 1978, letter to Carter, Milk called on the president to take a stand against Proposition 6 and speak out more forcefully in support of LGBT rights. “As the President of a nation which includes 15-20 million lesbians and gay men, your leadership is vital and necessary,” Milk wrote.
About four months later, in a Nov. 4, 1978, campaign speech in support of California Democratic candidates in Sacramento, three days before the Nov. 7 election, Carter spoke out against Proposition 6 and urged voters to defeat it. Others who spoke out against it earlier were former President Ford and then former California GOP Governor Ronald Reagan as well as California’s then Democratic Governor Edmund Jerry Brown.
Voters defeated the proposition by a margin of 58.4 percent to 41.5 percent, with opponents of the anti-gay measure thanking Carter for speaking out against it.
During his presidency Carter helped put in place two new federal cabinet-level agencies – the Department of Energy and the Department of Education. One of the highlights of his presidential years was his role in bringing about the historic Camp David Accords, the peace agreements between Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin and Egyptian President Anwar Sadat.
The initial agreement, signed in September 1978, which led to the first-ever peace treaty between Israel and Egypt one year later in 1979, came about after Carter invited the two Middle East leaders to meet together with him and to begin negotiations at the U.S. presidential retreat at Camp David, Md. Sadat and Begin were awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1978 for their contributions to the historic agreements that were brokered by President Carter.
Despite this and other important achievements, Carter faced multiple setbacks the following year in 1979 related to international developments that political observers say Carter and his advisors failed to address properly. Among them was the revolution in Iran that toppled the reign of Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi and installed the fundamentalist Islamic regime headed by Ayatollah Khomeini that led to a dramatic drop in Iran’s production and sale of oil. That quickly led to a dramatic rise in the cost of gasoline for American consumers along with a shortage of gas at fuel pumps leading to long lines as filling stations.
If that were not enough, Carter was hit with the take-over of the U.S. Embassy in Tehran on Nov. 4, 1979, by militant Iranian youths supported and encouraged by Khomeini who held as hostages 52 U.S. diplomats and American citizens with no sign that they would be released any time soon. As Carter’s poll ratings declined, then U.S. Senator Edward Kennedy (D-Mass.) announced his candidacy for the 1980 Democratic presidential nomination in a rare challenge to an incumbent president.
With all that as a backdrop, gay Democratic activists launched a campaign to elect far more openly gay and lesbian delegates to the 1980 Democratic National Convention than they had in 1976. A record number of just over 100 gay and lesbian delegates emerged from this effort, with many of them pledged to Kennedy. And this time around, the Democratic Party leaders backing Carter at the convention, as well as Carter himself, according to some reports, expressed support for including a “gay” plank in the party’s platform, which the convention adopted in an historic first.
But when it became clear that Kennedy and California Governor Jerry Brown, who also challenged Carter for the 1980 Democratic nomination, did not have enough delegates to wrest the nomination from Carter, gay activists expressed concern that the Carter campaign was backing away from taking a stronger position in support of gay rights.
Their main concern was that the response by the Carter campaign to a “gay” questionnaire the National Gay Task Force sent to all the Democratic and Republican presidential candidates seeking their party’s nomination in 1980 was significantly less specific than the response by Kennedy and Brown.
Among other things, the activists said the Carter campaign’s response, which was prepared by Carter Campaign Chairperson Robert Strauss, did not make a commitment for Carter to sign an executive order ending the longstanding discrimination against gays and lesbians in federal government agencies, including the military. The Carter campaign response also did not express support for the national gay rights bill, even though Carter had expressed support for it back in 1976.
Carter supporters, including many in the then gay and lesbian community, pointed out that Straus’s response to the questionnaire expressed overall support for the rights of the gay and lesbian community and a commitment to follow up on that support over the next four years. Gay Carter supporters also pointed out that Carter would be far more supportive than Ronald Regan, who had captured the 1980 Republican presidential nomination.
Some historians have said that the final straw in dooming Carter’s chances for a second term, in addition to his seeming inability to gain the release of the American hostages held in Iran, was the final televised debate between Carter and Reagan. With most political observers saying Reagan was an infinitely superior television candidate, those observations appeared to be confirmed when Carter’s poll numbers dropped significantly following the final debate.
Although Reagan captured 51.8 percent of the popular vote, with Carter receiving 41.0 percent and independent candidate John Anderson receiving 6.6 percent, Reagan won an Electoral College landslide, with 489 electoral votes compared to 49 for Carter. Reagon won in 44 states, with Carter winning in just 6 states and the District of Columbia.
Carter Center and post-presidential career
Both Carter supporters as well as critics and independent political observers agree that Jimmy Carter’s years after leaving the White House have been filled with years of work dedicated to his passion for the advancement of human rights, peace negotiations, advancing worldwide democracy, and advancing disease prevention and eradication in developing nations.
Most of that work was accomplished through The Carter Center, an Atlanta based nonprofit organization that Carter and wife Rosalynn founded in 1982. Twenty years after its founding, Jimmy Carter was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 2002. The Nobel Committee, among other things, stated it selected Carter for the Nobel Peace Prize “for his decades of untiring effort to find peaceful solutions to international conflicts, to advance democracy and human rights, and to promote economic and social development.”
In the years following his presidency Carter also continued to lend support as an ally to the LGBTQ community. During a book tour promoting his book, “A Full Life: Reflections at Ninety,” Carter stated in a July 2018 interview with Huff Post Live, that he supported same-sex marriage.
As a long-time self-described born-again Christian, Carter said in the interview, “I think Jesus would approve gay marriage,” adding, “I think Jesus would encourage any love affair if it was honest and sincere and was not damaging to anyone else, and I don’t see that gay marriage damages anyone else.”
His expression of support for same-sex marriage came four years after he responded to a question about his thoughts about LGBTQ rights and religion during an appearance at Michigan’s Grand Rapids Community College in 2014.
“I never knew of any word or action of Jesus Christ that discriminated against anyone,” he said. “Discrimination against anyone and depriving them of actual equal rights in the United States is a violation of the basic principles of the Constitution that all of us revere in this country,” Carter stated at the event.
Florida
DNC slams White House for slashing Fla. AIDS funding
State will have to cut medications for more than 16,000 people

The Trump-Vance administration and congressional Republicans’ “Big Beautiful Bill” could strip more than 10,000 Floridians of life-saving HIV medication.
The Florida Department of Health announced there would be large cuts to the AIDS Drug Assistance Program in the Sunshine State. The program switched from covering those making up to 400 percent of the Federal Poverty Level, which was anyone making $62,600 or less, in 2025, to only covering those making up to 130 percent of the FPL, or $20,345 a year in 2026.
Cuts to the AIDS Drug Assistance Program, which provides medication to low-income people living with HIV/AIDS, will prevent a dramatic $120 million funding shortfall as a result of the Big Beautiful Bill according to the Florida Department of Health.
The International Association of Providers of AIDS Care and Florida Surgeon General Joseph Ladapo warned that the situation could easily become a “crisis” without changing the current funding setup.
“It is a serious issue,” Ladapo told the Tampa Bay Times. “It’s a really, really serious issue.”
The Florida Department of Health currently has a “UPDATES TO ADAP” warning on the state’s AIDS Drug Assistance Program webpage, recommending Floridians who once relied on tax credits and subsidies to pay for their costly HIV/AIDS medication to find other avenues to get the crucial medications — including through linking addresses of Florida Association of Community Health Centers and listing Florida Non-Profit HIV/AIDS Organizations rather than have the government pay for it.
HIV disproportionately impacts low income people, people of color, and LGBTQ people
The Tampa Bay Times first published this story on Thursday, which began gaining attention in the Sunshine State, eventually leading the Democratic Party to, once again, condemn the Big Beautiful Bill pushed by congressional republicans.
“Cruelty is a feature and not a bug of the Trump administration. In the latest attack on the LGBTQ+ community, Donald Trump and Florida Republicans are ripping away life-saving HIV medication from over 10,000 Floridians because they refuse to extend enhanced ACA tax credits,” Democratic National Committee spokesperson Albert Fujii told the Washington Blade. “While Donald Trump and his allies continue to make clear that they don’t give a damn about millions of Americans and our community, Democrats will keep fighting to protect health care for LGBTQ+ Americans across the country.”
More than 4.7 million people in Florida receive health insurance through the federal marketplace, according to KKF, an independent source for health policy research and polling. That is the largest amount of people in any state to be receiving federal health care — despite it only being the third most populous state.
Florida also has one of the largest shares of people who use the AIDS Drug Assistance Program who are on the federal marketplace: about 31 percent as of 2023, according to the Tampa Bay Times.
“I can’t understand why there’s been no transparency,” David Poole also told the Times, who oversaw Florida’s AIDS program from 1993 to 2005. “There is something seriously wrong.”
The National Alliance of State and Territorial AIDS Directors estimates that more than 16,000 people will lose coverage
U.S. Supreme Court
Competing rallies draw hundreds to Supreme Court
Activists, politicians gather during oral arguments over trans youth participation in sports
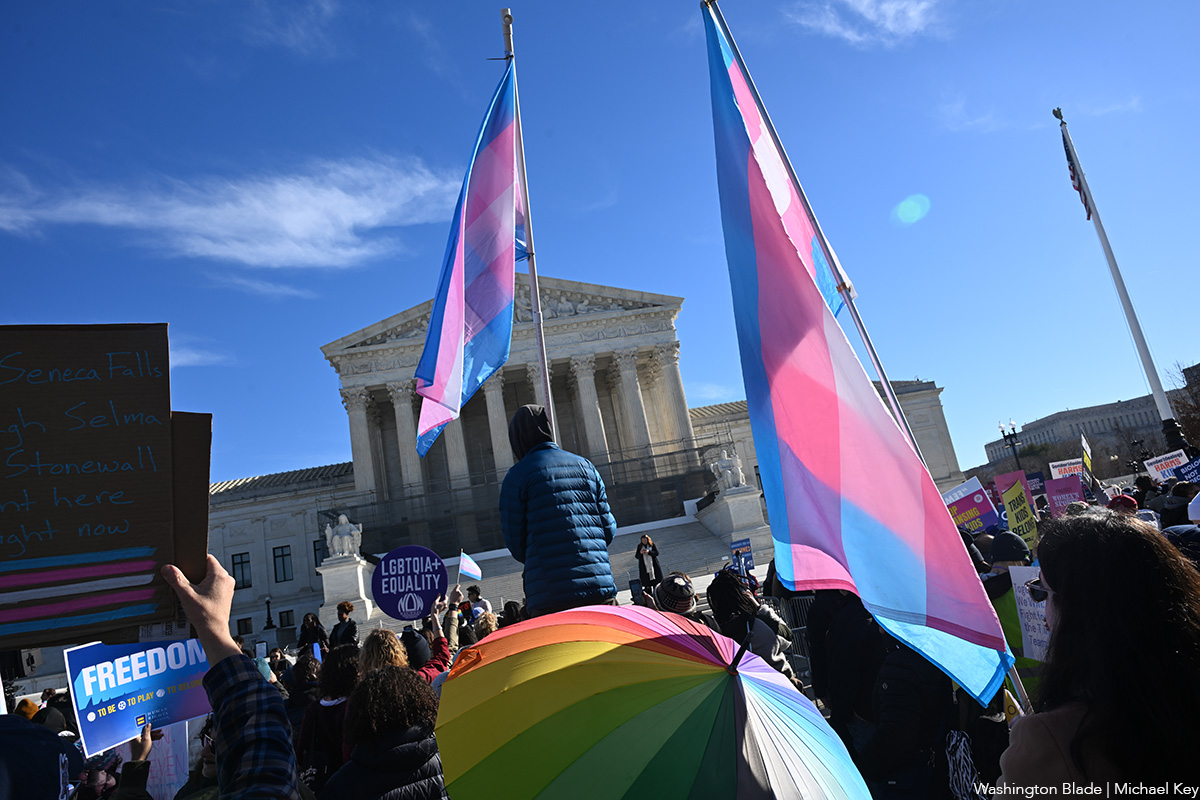
Hundreds of supporters and opponents of trans rights gathered outside of the United States Supreme Court during oral arguments for Little v. Hecox and West Virginia v. B.P.J. on Tuesday. Two competing rallies were held next to each other, with politicians and opposing movement leaders at each.
“Trans rights are human rights!” proclaimed U.S. Sen. Ed Markey (D-Mass.) to the crowd of LGBTQ rights supporters. “I am here today because trans kids deserve more than to be debated on cable news. They deserve joy. They deserve support. They deserve to grow up knowing that their country has their back.”
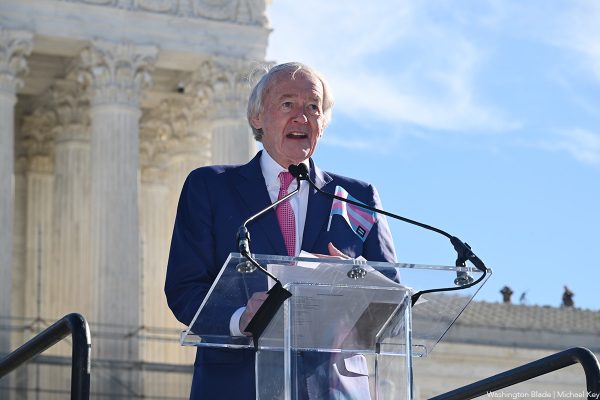

“And I am here today because we have been down this hateful road before,” Markey continued. “We have seen time and time again what happens when the courts are asked to uphold discrimination. History eventually corrects those mistakes, but only after the real harm is done to human beings.”
View on Threads
U.S. Education Secretary Linda McMahon spoke at the other podium set up a few feet away surrounded by signs, “Two Sexes. One Truth.” and “Reality Matters. Biology Matters.”
“In just four years, the Biden administration reversed decades of progress,” said McMahon. “twisting the law to urge that sex is not defined by objective biological reality, but by subjective notion of gender identity. We’ve seen the consequences of the Biden administration’s advocacy of transgender agendas.”
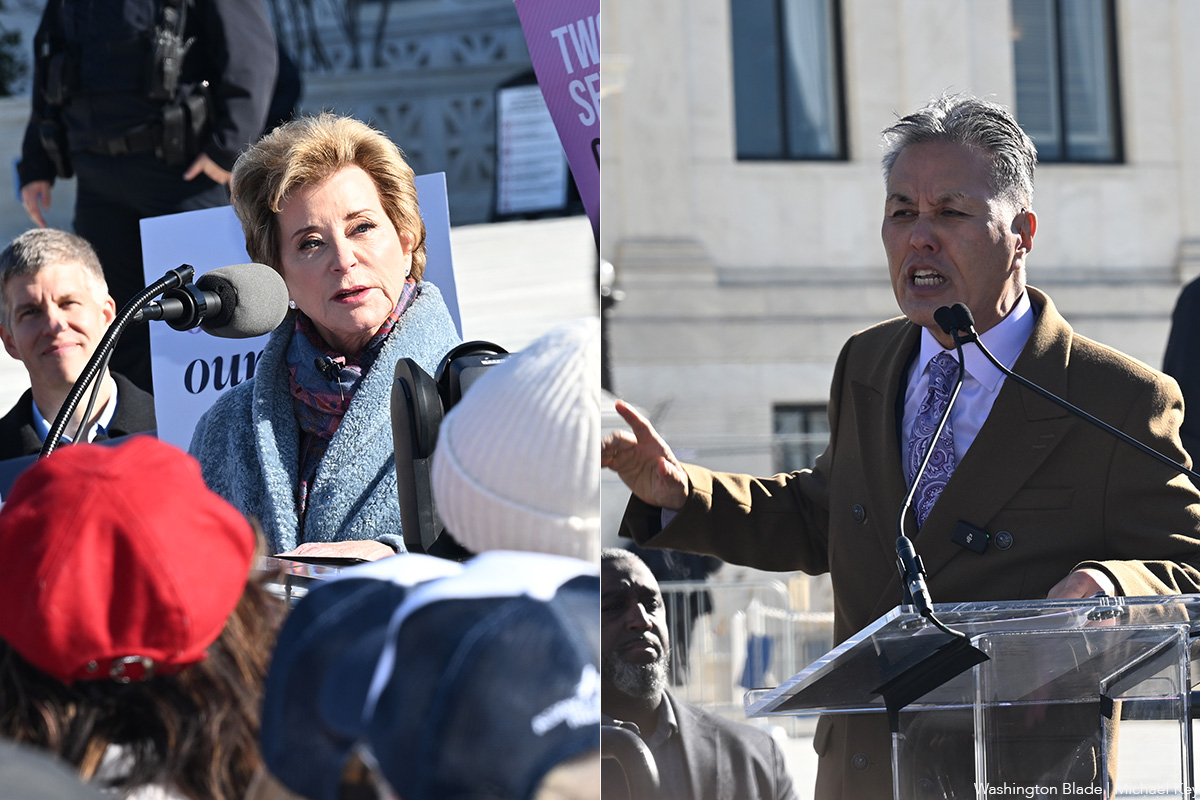

U.S. Rep. Mark Takano (D-Calif.), chair of the Congressional Equality Caucus, was introduced on the opposing podium during McMahon’s remarks.
“This court, whose building that we stand before this morning, did something quite remarkable six years ago.” Takano said. “It did the humanely decent thing, and legally correct thing. In the Bostock decision, the Supreme Court said that trans employees exist. It said that trans employees matter. It said that Title VII of the Civil Rights Act protects employees from discrimination based on sex, and that discrimination based on sex includes discrimination based on gender identity and sexual orientation. It recognizes that trans people have workplace rights and that their livelihoods cannot be denied to them, because of who they are as trans people.”
“Today, we ask this court to be consistent,” Takano continued. “If trans employees exist, surely trans teenagers exist. If trans teenagers exist, surely trans children exist. If trans employees have a right not to be discriminated against in the workplace, trans kids have a right to a free and equal education in school.”
Takano then turned and pointed his finger toward McMahon.
“Did you hear that, Secretary McMahon?” Takano addressed McMahon. “Trans kids have a right to a free and equal education! Restore the Office of Civil Rights! Did you hear me Secretary McMahon? You will not speak louder or speak over me or over these people.”
Both politicians continued their remarks from opposing podiums.
“I end with a message to trans youth who need to know that there are adults who reject the political weaponization of hate and bigotry,” Takano said. “To you, I say: you matter. You are not alone. Discrimination has no place in our schools. It has no place in our laws, and it has no place in America.”
U.S. Supreme Court
Supreme Court hears arguments in two critical cases on trans sports bans
Justices considered whether laws unconstitutional under Title IX.

The Supreme Court heard two cases today that could change how the Equal Protection Clause and Title IX are enforced.
The cases, Little v. Hecox and West Virginia v. B.P.J., ask the court to determine whether state laws blocking transgender girls from participating on girls’ teams at publicly funded schools violates the 14th Amendment’s Equal Protection Clause and Title IX. Once decided, the rulings could reshape how laws addressing sex discrimination are interpreted nationwide.
Chief Justice John Roberts raised questions about whether Bostock v. Clayton County — the landmark case holding that Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 protects employees from discrimination based on sexual orientation or gender identity — applies in the context of athletics. He questioned whether transgender girls should be considered girls under the law, noting that they were assigned male at birth.
“I think the basic focus of the discussion up until now, which is, as I see it anyway, whether or not we should view your position as a challenge to the distinction between boys and girls on the basis of sex or whether or not you are perfectly comfortable with the distinction between boys and girls, you just want an exception to the biological definition of girls.”
“How we approach the situation of looking at it not as boys versus girls but whether or not there should be an exception with respect to the definition of girls,” Roberts added, suggesting the implications could extend beyond athletics. “That would — if we adopted that, that would have to apply across the board and not simply to the area of athletics.”
Justice Clarence Thomas echoed Roberts’ concerns, questioning how sex-based classifications function under Title IX and what would happen if Idaho’s ban were struck down.
“Does a — the justification for a classification as you have in Title IX, male/female sports, let’s take, for example, an individual male who is not a good athlete, say, a lousy tennis player, and does not make the women’s — and wants to try out for the women’s tennis team, and he said there is no way I’m better than the women’s tennis players. How is that different from what you’re being required to do here?”
Justice Samuel Alito addressed what many in the courtroom seemed reluctant to state directly: the legal definition of sex.
“Under Title IX, what does the term ‘sex’ mean?” Alito asked Principal Deputy Solicitor General Hashim Mooppan, who was arguing in support of Idaho’s law. Mooppan maintained that sex should be defined at birth.
“We think it’s properly interpreted pursuant to its ordinary traditional definition of biological sex and think probably given the time it was enacted, reproductive biology is probably the best way of understanding that,” Mooppan said.
Justice Sonia Sotomayor pushed back, questioning how that definition did not amount to sex discrimination against Lindsay Hecox under Idaho law. If Hecox’s sex is legally defined as male, Sotomayor argued, the exclusion still creates discrimination.
“It’s still an exception,” Sotomayor said. “It’s a subclass of people who are covered by the law and others are not.”
Justice Elena Kagan highlighted the broader implications of the cases, asking whether a ruling for the states would impose a single definition of sex on the 23 states that currently have different laws and standards. The parties acknowledged that scientific research does not yet offer a clear consensus on sex.
“I think the one thing we definitely want to have is complete findings. So that’s why we really were urging to have a full record developed before there were a final judgment of scientific uncertainty,” said Kathleen Harnett, Hecox’s legal representative. “Maybe on a later record, that would come out differently — but I don’t think that—”
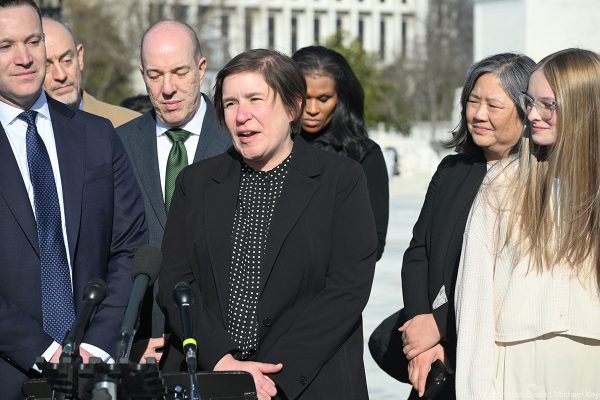

“Just play it out a little bit, if there were scientific uncertainty,” Kagan responded.
Justice Brett Kavanaugh focused on the impact such policies could have on cisgender girls, arguing that allowing transgender girls to compete could undermine Title IX’s original purpose.
“For the individual girl who does not make the team or doesn’t get on the stand for the medal or doesn’t make all league, there’s a — there’s a harm there,” Kavanaugh said. “I think we can’t sweep that aside.”
Justice Amy Coney Barrett questioned whether Idaho’s law discriminated based on transgender status or sex.
“Since trans boys can play on boys’ teams, how would we say this discriminates on the basis of transgender status when its effect really only runs towards trans girls and not trans boys?”
Harnett responded, “I think that might be relevant to a, for example, animus point, right, that we’re not a complete exclusion of transgender people. There was an exclusion of transgender women.”
Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson challenged the notion that explicitly excluding transgender people was not discrimination.
“I guess I’m struggling to understand how you can say that this law doesn’t discriminate on the basis of transgender status. The law expressly aims to ensure that transgender women can’t play on women’s sports teams… it treats transgender women different than — than cis-women, doesn’t it?”
Idaho Solicitor General Alan Hurst urged the court to uphold his state’s ban, arguing that allowing participation based on gender identity — regardless of medical intervention — would deny opportunities to girls protected under federal law.
Hurst emphasized that biological “sex is what matters in sports,” not gender identity, citing scientific evidence that people assigned male at birth are predisposed to athletic advantages.
Joshua Block, representing B.P.J., was asked whether a ruling in their favor would redefine sex under federal law.
“I don’t think the purpose of Title IX is to have an accurate definition of sex,” Block said. “I think the purpose is to make sure sex isn’t being used to deny opportunities.”
Becky Pepper-Jackson, identified as plaintiff B.P.J., the 15-year-old also spoke out.
“I play for my school for the same reason other kids on my track team do — to make friends, have fun, and challenge myself through practice and teamwork,” said Pepper-Jackson. “And all I’ve ever wanted was the same opportunities as my peers. But in 2021, politicians in my state passed a law banning me — the only transgender student athlete in the entire state — from playing as who I really am. This is unfair to me and every transgender kid who just wants the freedom to be themselves.”

Outside the court, advocates echoed those concerns as the justices deliberated.
“Becky simply wants to be with her teammates on the track and field team, to experience the camaraderie and many documented benefits of participating in team sports,” said Sasha Buchert, counsel and Nonbinary & Transgender Rights Project director at Lambda Legal. “It has been amply proven that participating in team sports equips youth with a myriad of skills — in leadership, teamwork, confidence, and health. On the other hand, denying a student the ability to participate is not only discriminatory but harmful to a student’s self-esteem, sending a message that they are not good enough and deserve to be excluded. That is the argument we made today and that we hope resonated with the justices of the Supreme Court.”
“This case is about the ability of transgender youth like Becky to participate in our schools and communities,” said Joshua Block, senior counsel for the ACLU’s LGBTQ & HIV Project. “School athletics are fundamentally educational programs, but West Virginia’s law completely excluded Becky from her school’s entire athletic program even when there is no connection to alleged concerns about fairness or safety. As the lower court recognized, forcing Becky to either give up sports or play on the boys’ team — in contradiction of who she is at school, at home, and across her life — is really no choice at all. We are glad to stand with her and her family to defend her rights, and the rights of every young person, to be included as a member of their school community, at the Supreme Court.”
The Supreme Court is expected to issue rulings in both cases by the end of June.
-

 U.S. Supreme Court4 days ago
U.S. Supreme Court4 days agoSupreme Court hears arguments in two critical cases on trans sports bans
-

 U.S. Supreme Court5 days ago
U.S. Supreme Court5 days agoAs Supreme Court weighs trans sports bans, advocate and former athlete speaks out
-

 Virginia4 days ago
Virginia4 days agoWoman arrested for anti-gay assault at Alexandria supermarket
-

 Commentary4 days ago
Commentary4 days agoHonoring 50 queer, trans women with inaugural ‘Carrying Change’ awards

















